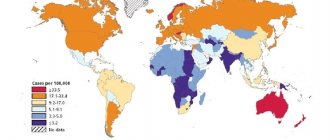
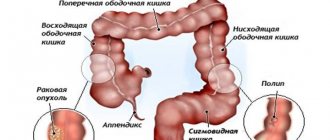
Colon cancer is a disease that involves the growth of a malignant tumor in the colon. According to statistics, this type of intestinal cancer ranks second after rectal cancer. If we consider the oncological situation as a whole, then this type of cancer accounts for about 5% of all cases of the disease.
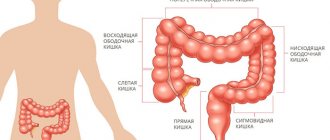
The disease affects both men and women equally. The disease is usually diagnosed between the ages of 50 and 70 years. The most common cancer is the sigmoid colon, and slightly less common is cancer of the ascending colon.
What is colon cancer?
This is a malignant tumor that is one of the top three among other cancers in terms of incidence and mortality throughout the world.
Colon cancer originates from the mucous membrane of the colon and can spread to all layers of the intestinal wall and affect nearby organs and structures. Colon cancer affects men more often. Most often, this disease is diagnosed between the ages of 50 and 75 years, but recently it has been detected more often than before in young patients.
Main types of tumors
- Adenomas (tubular, villous, tubulovillous).
- Polyps (hyperplastic, adenomatous, inflammatory).
- Hamartroma is a growth that appears when one of the elements of healthy tissue begins to develop disproportionately.
- Villous tumors of the colon are round tumors covered with small papillae.
- Leiomyoma, lymphoma and lymphangioma are similar types of tumors that develop from smooth muscle tissue, lymphatic tissue and lymphatic vessels, respectively.
- Hemangioma is a formation in blood vessels.
Causes and risk factors for development
Among the risk factors for developing colon cancer are: a diet high in fat, red meat and low fiber, alcohol consumption, smoking, low physical activity, diabetes, chronic inflammatory diseases of the colon (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), presence of a family history of colorectal cancer.
In 3-5% of patients, colon cancer is associated with the presence of hereditary syndromes (familial adenomatosis of the colon and MUTYH-associated polyposis, Lynch syndrome).
Colon cancer. Symptoms
Early forms of colon cancer do not cause any symptoms for a long time; in most cases, they are detected during colonoscopy in patients without any complaints. As the tumor grows, the patient develops and develops dyspeptic symptoms (decreased appetite, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, bloating or flatulence, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region), stool disorders, mucus and blood appear in the stool. In patients with damage to the left side of the intestine, intestinal obstruction often occurs. Patients also complain of constant weakness and increased fatigue, causeless weight loss, and progressive iron deficiency anemia is characteristic.
Often, patients consult a doctor only after the appearance of severe symptoms: traces of blood and mucus in the stool, prolonged constipation, changes in the appearance of stool, pain and a significant deterioration in the general condition.
Treatment options for benign tumors
Since any tumor is an already formed formation, conservative treatment methods are ineffective. Until recently, such growths could only be removed surgically. Nowadays, complete or partial resection (cutting out) is used mainly in the last stages, when the pathology is completely advanced. Until it has come into full force, various options for minimally invasive intervention are used. The formation is burned out with a laser or destroyed by radio waves, compressed, depriving access to blood, etc. The procedure lasts only a few minutes. Hospitalization is not required after it, no traces remain.
The sooner you see a doctor, the higher the chance that he will be able to help you. Therefore, if you have not seen a proctologist for a long time, it’s time to make an appointment. The doctors working in our clinic are masters of their craft. Make an appointment, and benign formations of the large intestine will no longer bother you.
Diagnosis of colon cancer
The gold standard for diagnosing colon diseases is colonoscopy. The study allows not only to visualize the tumor, determine the location and size, macroscopic type, assess the risk of complications (perforation, bleeding), but also obtain tissue samples for histological examination.
If colon cancer is detected at colonoscopy, a CT scan of the chest and abdomen with contrast is prescribed to exclude the presence of tumor metastases.
As additional research methods, the following can be performed: MRI of the abdominal cavity and pelvis using contrast; in difficult cases, PET-CT - positron emission tomography - is used.
Histological types of colon adenomas
There are 3 histological types of colon adenomas:
- Tubular;
- Tubular villous;
- Villous.
The separation criterion is the ratio of villous and tubular structures. Tubular adenoma of the colon - what is it? Microscopically, tubular adenoma is represented by proliferating adenomatous epithelium. The tumor consists of branching and significantly convoluted glandular tubes, longer than in the normal intestinal mucosa. In tubular adenoma, no more than 25% villous tissue is present. Tubular adenoma of the colon has a mucous membrane-covered base. It is represented by connective tissue, smooth muscle cells and blood vessels. Tubular adenomas have a stalk and a smooth lobulated surface. Less often they are located on a wide base. Creeping tubular adenomas, which protrude slightly above the surface of the mucous membrane, are very rare.
In tubular-villous adenomas, the number of villi increases, which can be detected both on the surface of the polyp and inside large glands. The glands lengthen, acquire an irregular shape, and fit tightly to each other. The degree of epithelial dysplasia increases. In tubular-villous adenoma, the percentage of villous tissue varies from 25 to 75%. The tumor consists of pronounced lobules and has small areas with villi or very small lobules.
Villous adenoma consists of thin finger-like outgrowths of the connective tissue of the lamina propria, which are covered with epithelium. In villous adenomas, a small number of glands and 75% of the villous component can be found. Macroscopically, villous adenomas have a wide base and a “shaggy” surface. There is a special histological type of colon adenoma - serrated adenoma. The tumor is close in structure to a hyperplastic polyp, but has the potential for malignancy.
Adenomatous epithelium belongs to the category of neoplastic. For this reason, each adenoma has signs of dysplasia of varying severity. Histologists distinguish 3 degrees of dysplasia of tubular adenoma of the colon:
- 1st degree – weak;
- 2 degrees – moderate;
- Grade 3 – severe.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with low grade dysplasia is a poorly differentiated tumor. It can transform into adenocarcinoma.
Stages and methods of treatment of colon cancer
Treatment options for colon cancer depend on the stage of the process. Thus, at stages 0 and 1, it is possible to perform a minimally invasive endoscopic operation during colonoscopy.
Stage 2-3 requires removal of the section of intestine with the tumor and all regional lymph nodes. The method of performing such an operation is determined by the doctor. An open, laparoscopic or robotic method can be used. To improve long-term treatment results, preoperative chemotherapy is sometimes used.
If a patient is diagnosed with stage 3 colon cancer, then after surgery such a patient is prescribed adjuvant chemotherapy - it reduces the risk of tumor recurrence.
In the case of stage 4, the treatment strategy is developed at a multidisciplinary council, taking into account the localization and spread of the primary tumor, metastases, and concomitant diseases. Both chemotherapy and surgery, or a combination of both, can be used.
Diagnosis of pathology
The first thing you need to do to identify the presence of benign tumors in the large intestine is to consult a proctologist. During the consultation, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history: asks about his lifestyle, hereditary and acquired diseases, and troubling symptoms. Conducts a finger examination. If necessary, prescribes:
- General blood analysis. Indicates the presence of anemia and low hemoglobin levels.
- Examination of feces for occult blood. If present, this may indicate damage to the intestinal walls.
- Other tests. Depends on the type of pathology, its form, manifestation, causes, etc.
As for instrumental examinations, the main ones among them are:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS).
- Digital examination of the rectum.
- Irrigoscopy.
- Sigmoidoscopy.
- Colonoscopy.
If a tumor is detected during diagnosis, and the doctor has doubts about its benign quality, an additional biopsy (sampling of materials for analysis) may be prescribed.
Operations performed for colon cancer
Right hemicolectomy – used for tumors of the ascending colon and cecum, hepatic flexure of the colon. The surgeon removes the final portion of the small intestine and the right half of the colon.
Left-sided hemicolectomy - required when the left parts of the colon are affected by tumors.
Resection of the transverse colon is rarely performed when the tumor is located in the middle third of the transverse colon. Most often in such situations they resort to extended right-sided hemicolectomy or extended left-sided hemicolectomy.
Resection of the sigmoid colon - removal of the sigmoid colon with a tumor.
If it is impossible to radically remove the tumor, then to prevent the development of complications, a palliative or symptomatic operation is performed (formation of a bypass intestinal stoma, colon stenting, formation of a bypass anastomosis, etc.), which helps improve the patient’s condition and makes it possible to safely begin chemotherapy.
Establishing diagnosis
Currently, experts give preference to instrumental high-precision diagnostics. The most commonly used are colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy, during which a diagnostic biopsy of the identified formation can be performed. To clarify the extent of the process, irrigoscopy (x-ray of the colon) is also used.
In addition to instrumental diagnostics, a number of laboratory tests are required: blood tests; stool tests (coprogram, etc.), as well as ultrasound, MRI (if necessary). After an accurate diagnosis is made, therapy begins.
Therapeutic measures after surgery
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where doctors monitor vital functions (blood pressure, oxygen saturation, kidney function), and also provide the necessary therapy. If the postoperative period is favorable, the patient is transferred to a hospital ward, where he receives further treatment. The doctor selects the diet for the patient in the postoperative period individually, depending on the volume and nature of the intervention. The main task after surgery is early rehabilitation of the patient. Subsequent treatment tactics after discharge are determined based on the results of histological examination at the oncology consultation
Colon cancer metastases
Metastases can be regional - to the lymph nodes that collect lymph from the intestine, and distant. The most common sites of distant metastases in colon cancer are the liver and lungs. Less commonly, metastases can affect the spleen, adrenal glands, bones, and retroperitoneal lymph nodes. The most difficult to treat are peritoneal metastases - peritoneal carcinomatosis.
It is important to remember that stage 4 is not a death sentence! Correctly developed treatment tactics can achieve 15-year survival in 11% of patients.
Recovery after surgery
The Ilyinskaya Hospital has implemented the concept of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS).
This set of measures is aimed at the fastest possible physical and psychological rehabilitation of the patient after even extensive surgical interventions, as well as social adaptation. The ideology is based on the results of many years of international clinical research, recognized and implemented in all developed countries. It includes: preoperative preparation - prehabilitation, a special technique for administering anesthesia during surgery in combination with minimally invasive operating techniques, early mobilization of the patient (you can sit up in bed, do breathing exercises, get to your feet soon after transfer to the ward), early alimony ( You can start eating and drinking soon after surgery). This helps to quickly restore intestinal function and avoid the development of complications from the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
All patients who have undergone surgery for colon cancer remain under the supervision of an oncologist and regularly undergo scheduled examinations to timely detect the progression of the disease and adjust the individual treatment plan.
Advantages of going to Ilyinskaya Hospital
The treatment strategy for patients with colon cancer at the Ilyinskaya Hospital is based on the concept of a multidisciplinary combined and integrated approach, combining the use of modern surgical technologies with the achievements of radiation, drug and immunotherapy. Each clinical case is reviewed at an oncology council (Tumor-board), which includes: a chemotherapist, an oncologist surgeon, a radiologist, a radiologist, an oncopsychologist, and a rehabilitation physician. This approach allows us to develop the most effective personalized treatment tactics for the patient, take into account all individual nuances and achieve maximum efficiency.
Our doctors
Prokhorov Yuri Anatolievich
Surgeon, head of the surgical service of CELT, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Lutsevich Oleg Emmanuilovich
Chief Surgeon of CELT, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Chief Specialist of the Moscow Department of Health in Endosurgery and Endoscopy, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Head of the Department of Faculty Surgery No. 1 of the State Budgetary Educational Institution BPO MGMSU, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Doctor of the Highest Category, Professor
43 years of experience
Make an appointment
Gordeev Sergey Alexandrovich
Surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
42 years of experience
Make an appointment