Diseases of the biliary system
Gallstone disease (hereinafter referred to as cholelithiasis) is a chronic disease of the gallbladder, which can be asymptomatic, exacerbating only with the development of inflammation and blockage of the bile ducts by stones.
GSD already occurs in 10% of the world's population3. Gallstones consist of substances that are poorly soluble in bile, in most cases cholesterol. There are various reasons for the formation of stones: genetic, demographic, dietary, and also due to various concomitant diseases or taking certain medications. The structure of once formed stone constantly changes, anhydrous cholesterol accumulates inside it4.
- Risk factors are age (40-69 years)3, heredity, predisposition, female gender.
- The development of this disease in women is associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy and childbirth, which contribute to the formation of stones5.
During menopause, due to a decrease in sex hormones, the contractility of the gallbladder weakens5.
The connection between cholelithiasis and the nature of nutrition has been proven. Excessive saturation of bile with cholesterol is promoted by foods high in animal fats (fatty meat, milk, cream, lard), simple carbohydrates (fast food, sweets, baked goods). Stone formation is provoked by frequent consumption of spicy seasonings and a deficiency in the diet of vitamins (especially vitamin E)5.
The tendency to stone formation occurs with increased reabsorption of bile acids. This occurs under conditions of slow movement of food through the intestines, which is facilitated by a lack of dietary fiber (vegetables, fruits)5. One of the main factors in the development of cholelithiasis is obesity. Moreover, the risk of stone formation is directly proportional to excess weight. If with a body mass index (BMI) from 25 to 30 the risk of cholelithiasis increases by 2 times, then with a BMI over 35 it increases by 20 times6.
Sudden weight loss also has a negative impact on stone formation. With a sharply limited unbalanced diet, the circulation of bile acids is disrupted, which leads to the formation of stones5.
There is information about the connection between lack of physical activity and the process of stone formation. Thus, in people who spent 40 hours a week watching TV, cholelithiasis was detected 2 times more often. The disease is much less common in people engaged in physical labor5.
Diagnostics
A careful collection of medical history and eating habits plays a major role in determining the cause of pain. During a physical examination, a gastroenterologist checks for cystic symptoms that indicate an inflammatory process. The diagnostic search involves a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination of the biliary system. The following methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder.
According to sonography, the size and contours of the gallbladder and the condition of the bile ducts are assessed. During the examination, stones and adhesions may be noticed. To study the contractile activity of the organ, a test with a choleretic breakfast is indicated. - ERCP.
The technique of reverse contrasting of the bile ducts is necessary for detailed visualization of their condition, finding small stones that were not visible during sonography. ERCP is performed using an endoscope, so it is both a diagnostic and therapeutic method. - Duodenal sounding.
Obtaining several portions of bile is necessary for its microscopic and bacteriological analysis. An increased number of leukocytes and mucus are found in the bile. During bacterial culture, a mixed bacterial flora is usually found. - X-ray techniques.
A plain radiography of the abdominal cavity is performed to identify complications - calcification of the gallbladder wall, free gas under the diaphragm. To clarify the diagnosis, cholecystography, MSCT of the abdominal organs, and dynamic scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary system are recommended. - Laboratory research.
In the hemogram for inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder, leukocytosis and increased ESR are detected. A biochemical blood test is performed to look for signs of cholestasis (increased alkaline phosphatase and cholesterol levels) and to assess the content of direct bilirubin.
The list of gallbladder diseases also includes less common pathologies:
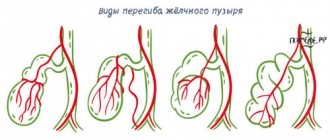
- Congenital anomalies of the biliary tract - changes in the size, shape of the biliary tract, size of the gallbladder. Pain in these cases can occur when the bladder is torsion or volvulus2.
- Congenital anomalies of the bile ducts - atresia (congenital absence), underdevelopment (hypoplasia). These anomalies usually appear in early childhood2.
- Bile duct cysts. They develop very slowly, so in about half of cases symptoms appear decades later2.
- Choledocholithiasis is the formation of stones in the common bile duct, usually occurring in old age. It may not manifest itself in any way for several years2.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
For mild pain, indicating a chronic process, it is permissible to limit yourself to non-drug methods. The patient is given a detailed diet plan, which involves the exclusion of animal fats, extractives, and alcohol. The diet depends on the preservation of the biliary function of the bladder. To increase the volume of bile, mineral waters are prescribed. In case of an acute pain attack, you should go to the hospital as soon as possible.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment is carried out for uncomplicated forms of gallbladder disease, without the risk of organ destruction. At the initial stage, antispasmodics and analgesics are used to relieve painful symptoms. Then etiopathogenetic therapy is selected, which may include several groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics
. For exacerbation of cholecystitis and cholangitis, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used. To accelerate the elimination of bacterial toxins and endotoxins, treatment is supplemented with infusion therapy. - Choleretic agents
. After stopping the acute process, drugs are prescribed that improve the flow of bile. They are divided into 2 groups: cholekinetics, which stimulate the contractile activity of the gallbladder, and choleretics, which increase the volume of the water component of bile. - UDHC
. The use of ursodeoxycholic acid is one of the methods of non-surgical treatment of cholelithiasis. With long-term use (up to two years), the active substance dissolves stones and helps normalize the biochemical composition of bile.
After the elimination of acute inflammation, physiotherapeutic techniques are prescribed. For chronic cholecystitis, it is advisable to use reflexology, SMT therapy, and electrophoresis. It is effective to use decoctions of medicinal plants that have hepatoprotective and choleretic properties. Spa treatment at balneological resorts is recommended.
Cholecystectomy. Gallbladder stones
Lithotripsy
For calculous cholecystitis, methods of non-invasive crushing of stones are widely used. In gastroenterology, extracorporeal shock wave and contact lithotripsy are more often performed. This treatment is characterized by the absence of tissue trauma and a short rehabilitation period. Lithotripsy is only required for stones up to 2 cm in size.
Hepatic colic and diet
A properly selected diet can not only cure hepatic colic, but also relieve the symptoms of cholelithiasis. The diet should be low-fat and easily digestible.
Patients should eliminate or limit the consumption of foods such as cheese, lard, mayonnaise and cream. In addition, frying should be avoided; it is better when you cook the dish in the oven or steam.
Patients who are obese should reduce their body weight, and those who additionally suffer from hypertriglyceridemia should reduce their levels of simple sugars and disaccharides.
Weight loss in obesity
What pain occurs in chronic cholecystitis?
All chronic diseases associated with the pathways for the outflow of bile are accompanied by lethargy, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdomen and in the heart area. People who suffer from these diseases spend a long time trying to find the cause of their illness, going through a huge number of doctors. Experts may make the wrong diagnosis for a long time, confusing cholecystitis or dyskinesia with gastritis, ulcers or rheumatism. This error can also occur in the opposite direction. The patient will be treated for diseases of the biliary tract, and the cause of all the pain was an ulcer or gastritis.
Elderly people who are faced with diseases such as cholecystitis note the absence of pain and attacks. This phenomenon occurs due to the fact that in old age, people’s sensitivity decreases, and as a result, pain sensitivity.
pain in the back and in the right hypochondrium due to cholecystitis
People suffering from chronic cholecystitis may experience unpleasant symptoms such as heartburn and nausea, as well as a bitter taste in the mouth and belching. There is a possibility of bad stool, diarrhea and constipation. The central nervous system, which cannot function normally, is also involved in this. The person becomes aggressive and irritated, cannot sleep well and get enough sleep. Nervousness and anger appear.
Organ function
The function of the gallbladder in the human body is to store bile, which comes continuously from the liver. Here the liver secretion settles, becomes more concentrated, and then, when food enters the digestive tract, it is reflexively released into the duodenum.
A person can live a full life without a bladder, then the question arises why a gallbladder is needed. The fact is that the liver constantly produces bile; the secretion enters the bladder through the ducts, where it lingers for several hours (until food arrives). Liver bile is golden yellow in color, its pH ranges from 7.3–8, and its relative density is 1.008–1.015.
In the gallbladder, bicarbonates are absorbed, due to which the pH level decreases to 6–7, and the density increases to 1.026–1.048, which means that such a secretion will better perform its tasks: stimulate the functioning of the intestines, pancreas, have a bacteriostatic effect, break down fats , promote the absorption of water-insoluble fatty acids, cholesterol, vitamins, neutralize pepsin and create conditions for the activation of pancreatic juice enzymes.
If the gallbladder is not functioning well, a cholecystectomy (removal) is performed. In this case, the liver secretion constantly enters the duodenum and, in the absence of food there, begins to affect the intestinal tissue. Since bile stimulates the secretion of pancreatic juice and gastric mucus, their production is also disrupted.
In the absence of a gallbladder, the digestion process slows down, and hence flatulence, dysbacteriosis, colitis, enteritis, and reflux.
What is the pain with cholecystitis?
During attacks of this disease, a woman experiences severe cutting pain in the area of the right hypochondrium or in the epigastric region. The pain spreads throughout the right half of the body, extending from the neck to the shoulder blade. The pain can also move to the entire abdomen and intensify with every breath. During an exacerbation, nausea and vomiting with bile often occur. During an exacerbation of this disease, the skin is yellow and pale, the tongue is coated, and the mouth is dry. The abdominal wall in the upper part is motionless and hurts when pressed.
By the way, cholecystitis causes back pain.
Here it must be said that the same symptoms as cholecystitis may also occur in another disease. Unpleasant and cutting sensations in the chest and right shoulder blade are observed with coronary heart disease. The most important thing is to find out the reason that provokes those same pains. Exacerbation of cholecystitis occurs when consuming large quantities of unhealthy, fatty foods and other “forbidden” foods. A relapse of exacerbation may occur due to stress, nervous burnout and situations that affect the psyche and mental state in general. People suffering from cholelithiasis or pericholecystitis may experience an attack of illness due to severe physical exertion. An exacerbation can even be triggered by driving a car on bad roads with potholes, riding a bicycle or riding horses.
pain in the back and in the right hypochondrium due to cholecystitis
Jaundice that appears after an attack can have several causes. It usually appears with cholelithiasis, but can also appear with hypermotor dyskinesia. In some cases, with such diseases, white-gray stool is possible. This phenomenon will occur within a couple of days.
A person has a mild form of gallstone disease, an exacerbation appears and goes away unexpectedly. After some time after the attack, usually the next day, the patient recovers.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of exacerbations and attacks of cholecystitis, you need to adhere to proper nutrition and diets. It is necessary to give up all bad habits, lead an active lifestyle, play sports and keep yourself in good shape. You need to pay attention to all kinds of infectious diseases and not let them get to you. A person suffering from such an illness needs to eliminate stress and conflict situations from his life as much as possible.
If a person has already been diagnosed with any disease, then he needs to be periodically examined by a gastroenterologist and engage in disease prevention. It must be remembered that all exacerbations of chronic diseases usually occur in autumn and spring.
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis
A disease such as inflammation of the gallbladder can bother a woman for a very long time with periodic exacerbations. These exacerbations can be made even more frequent and stronger if you violate the diet prescribed by your doctor and eat excessive amounts of junk food: smoked, fatty and fried foods.
The cause of the disease in question is improper flow of bile in the body. Chronic cholecystitis usually affects women in middle age, over 40 years of age. In this case, there is an effect on estrogens - female sex hormones, and on their paths for the outflow of bile.
hurts with cholecystitis
Symptoms of the disease:
- Lethargy and weakness of the whole body, fever, headache.
- Nausea, possible vomiting. Bloating and bad taste in the mouth.
- Severe pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, which spreads to all parts of the body, for example, to the left hypochondrium.