Colon diseases can be identified by three signs: bloating, stool disturbances, and painful sensations. Patients with diseases of the large intestine complain of bloating, which haunts them in the afternoon.
They note that the pain subsides only with the onset of night. If we talk about stool disorders, then this is an indispensable sign of colon pathology.
Some suffer from constipation, others suffer from diarrhea. Constipation occurs more often, but if diarrhea begins, it is characterized by a high frequency of bowel movements, a small amount of stool containing mucus and blood.
The nature of pain in pathologies of the colon
Weight loss is a sign of colon pathology.
Pain due to pathology of the colon has a unique localization. They are often felt on the side of the abdomen and near the anus.
Less common are unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region, as well as above the navel.
Even in the absence of pain, there will be pain when palpating the area in the iliac region on the right and left.
They become more intense if a person drinks milk or eats a lot of vegetables or coarse cereals. The main character of the pain is aching, accompanied by a feeling of fullness.
If the intestines are freed from gases and feces, the pain subsides. However, immediately before defecation, the pain may become more severe. Sometimes they are cramp-like in nature.
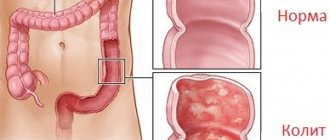
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis begins in the rectum.
Among diseases of the colon, ulcerative colitis is perhaps the only pathology leading to sudden weight loss.
With ulcerative colitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane develops. The rectum is most often affected, and this is where the disease begins.
And only then, in the absence of adequate treatment, it quickly spreads further through the large intestine. The disease is chronic, with exacerbations occurring quite often.
Analyzing the causes of ulcerative colitis, researchers came to the conclusion that a hereditary factor is involved. After all, the disease begins in the event of a genetic defect in the immune system.
The disease manifests itself in the appearance of ulceration, erosive surfaces, and foci of hemorrhage directly in the intestine itself. May be accompanied by the formation of polyps and other neoplasms.
Local signs of colitis include bleeding. In this case, patients detect blood in their stool almost constantly. Even outside of an exacerbation, blood may be present. Another important local symptom, which has already been discussed above, is bowel dysfunction.
Constipation, like diarrhea, definitely makes itself felt. However, there is no system. Some suffer from constipation, others from diarrhea, and still others from their alternation.
Anatomy and physiology
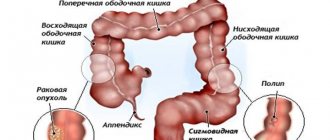
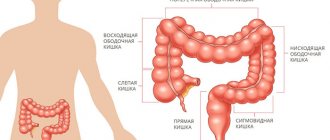
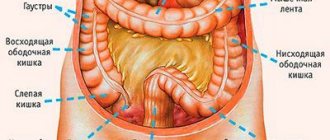
The large intestine is separated from the overlying small intestine by a muscular valve, the so-called. ileocecal sphincter or bauhinian valve. The large intestine is located in the lower part or floor of the abdominal cavity and includes the following sections:
- Caecum (lat. – caecum). It is 3-8 cm long and 4-7 cm wide. This section of the large intestine is equipped with a vermiform appendix, the appendix. The cecum with the appendix is projected onto the right middle and lower part of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Colon (lat. – colon). The longest section of the small intestine. The colon, about 4 cm in diameter, borders the entire lower floor of the abdominal cavity with loops of the small intestine and other organs. Hence the name. In the colon, its initial ascending part is distinguished. 12-20 cm long from the cecum to the right bend, the so-called. hepatic angle. The transverse colon is its middle part, 50 cm long, from the hepatic angle to the splenic angle, the left bend. The descending part, 22-23 cm long, runs from the splenic angle to the sigmoid colon. Due to the fact that the transverse part sags slightly, the configuration of the colon resembles the letter M.
- Sigmoid colon (lat. - colon sigmoideum). The same applies to the colon, and in the form of two loops 54-55 cm long and 4 cm in diameter is located between the descending part and the rectum. It is projected onto the anterior abdominal wall in its lower left part.
- Rectum (lat. - rectum). Located in the pelvic cavity. The length of the rectum is 14 cm. The width in the initial sections is 4 cm, then it expands into the ampulla of the rectum 7.5 cm, and ends with a narrow opening of the anus.
Compared to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract , the large intestine has its own characteristics. Unlike the pink small intestine, the large intestine has a grayish color. On the outside it is covered with a serous connective tissue membrane. Parts of the colon, and in some cases the cecum, are fixed to the walls of the abdominal cavity by the mesentery. This mobile anatomical formation is formed by two layers of peritoneum. Vessels and nerves pass through the mesentery to the intestines.
The middle muscular layer is represented by an inner circular or circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. Peristaltic (wave-like) contractions of these muscles ensure the movement of the food bolus through the intestinal tube.
But, unlike other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, the outer muscle layer here is continuous only at the junction of the cecum with the appendix , and in the rectum. And for the most part it is represented by three ribbons. These tapes seem to tighten the intestinal tube. As a result, protrusions and haustra are formed on its surface. The haustrae are separated from each other by transverse grooves. These grooves correspond to the semilunar folds of the mucous membrane.
There are no villi on the mucous membrane, like in the small intestine. It contains secretory glands that secrete digestive juice. Colonic juice is secreted at rest, but its amount is small.
Food contents enter the large intestine from the small intestine in small portions at the moment the ileocecal sphincter opens. In response to mechanical irritation, juice secretion increases many times over. It contains: amylase, lipase, and a number of other digestive enzymes. But in general, the content of enzymes in the juice of the large intestine is low, 20 times less than in the juice of the large intestine.
The amount of absorbed food components is also small. Here, those food components that are not absorbed in the small intestine are absorbed in small quantities. The main function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the bolus of food and form feces in a daily amount of 150 g or more.
When eating plant foods, more feces are formed than when eating foods of animal origin. Plant foods contain a large amount of indigestible fibers that absorb intestinal toxins. The final section of the gastrointestinal tract, the rectum, serves as a reservoir for feces. The act of defecation is controlled by muscle valves - the internal and external sphincter.
The functioning of the large intestine is largely influenced by the microflora it contains, represented by bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, and bacteroides.
The main functions of physiological intestinal microflora:
- The final breakdown of undigested food components.
- Inactivation of bile components and digestive juices that enter the large intestine from the overlying sections of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Neutralization of toxic products formed during the digestion of food.
- Synthesis of vitamin K and some B
- Destruction of pathogenic intestinal microflora.
- Participation in other nonspecific immune reactions.
Along with microflora, immune protection is provided by accumulations of lymphoid tissue located in the mucous membrane, lymphatic follicles.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease develops rapidly in the body.
The difference between Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis is the spread of the inflammatory process both to the intestine itself and to neighboring organs (esophagus, stomach).
Not the entire surface is affected, but individual areas. Inflamed areas take turns with healthy areas.
The inflammatory process may not affect the rectum at all. If it starts there, the intestine will undergo pathological narrowing, because not only the mucous membrane itself is affected, but also the submucosal layers.
This is where granuloma cells gather. As the disease progresses, the lymphatic vessels are affected.
Symptoms depend on the development of the disease. If the inflammatory process has affected the right side of the colon, then bloating will be noticeable, diarrhea and pain will appear. If the disease is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen, then intestinal obstruction is possible.
It can be complete or partial. In any case, the patient will feel sharp pain and nausea, which can quickly develop into vomiting. If the disease affects only the small intestine, then signs characteristic of all diseases of this organ will appear: weight loss, hypovitaminosis, metabolic disorders.
The situation is aggravated by the appearance of purulent fistulas in the anal area. When the duodenum and esophagus are affected, the symptoms are similar to those of a peptic ulcer.
Crohn's disease is a very serious disease. It leads not only to local negative manifestations. Unhappy general symptoms develop quite quickly. This is a feverish state, changes in the joints, eyes, liver. Skin rashes often appear.
Diagnosing Crohn's disease is difficult. It is better to be examined in a hospital setting, since a number of important tests can be carried out there as quickly as possible. When making such a diagnosis, they begin by excluding dairy products and compensating for protein intake through other foods.
Diagnostics
Difficulties in diagnosing diseases of the small intestine are explained by the peculiarities of its location. Analysis of the clinical picture, histological, endoscopic, and immunological methods are of decisive importance.
Almost all diseases of the colon are detected by fiber colonoscopy (flexible fiber colonoscopes with fiber optics are used). The examination also includes:
- study using contrast agents
- angiography
- fistulography
- lymphography
- parietography
- ultrasound
- research using radioactive isotopes.
Ischemic colitis
Atherosclerosis is the cause of ischemic colitis.
This disease is caused by a pathological narrowing of the vessels responsible for the blood supply to the colon.
The disease begins with the appearance of inflammation in areas that do not receive enough nutrients. Then ulceration begins in these places.
Eventually, the intestinal lumen narrows, leading to obstruction. The main causes of ischemic colitis are serious diseases that result in impaired blood supply:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- vein diseases
The listed pathologies lead to ischemic colitis after a long time. Therefore, the main age group of patients is elderly people.
You need to think about the possibility of developing ischemic colitis if after eating (15 minutes later) you feel pain in the left abdomen and there is blood in the stool. As the disease progresses, these two symptoms will become more pronounced.
The pain will intensify, and bleeding will become regular, even clots will appear in the stool.
Colitis after antibiotic therapy
Lincomycin causes the development of specific colitis.
Long-term treatment with antibiotics causes the development of specific colitis. Most often, the disease begins after taking lincomycin, tetracycline.
It was noted that the likelihood of the disease increases in those who took medications orally and combined them with other medications.
For example, with laxatives. Due to the entry into the intestines of substances dangerous to microorganisms, the beneficial microflora is massively destroyed and washed out (as is the case with laxatives).
In such conditions, clostridia begins to actively reproduce. This is a dangerous microbe, the secretions of which have a detrimental effect on the condition of the intestinal wall. Its toxic secretions lead to the destruction of the intestinal mucosa and can even cause perforation.
The hallmark of this disease is considered to be plaques that can be found everywhere on the mucous membrane. They are called membranes in another way, and the colitis itself is called pseudomembranous.
Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, 3 stages of the disease are distinguished: mild, moderate, severe.
- The mild form is manifested only by diarrhea. It continues as long as antibiotics enter the body. After completing the course of antibiotic therapy, the symptoms disappear.
- Moderate severity is characterized by the continuation of symptoms even after discontinuation of antibiotics. Frequent watery diarrhea is accompanied by pain before defecation. Signs of intoxication gradually increase. There is a feeling of weakness, nausea, which can develop into vomiting.
- Severe form. Signs characteristic of a moderately severe condition are aggravated. Heart problems appear: the pulse quickens, and the pressure can drop significantly.
In order not to bring the condition to a critical level, it is better to stop taking them if diarrhea occurs during antibiotic treatment and consult a doctor. This will prevent the development of the disease.
If it is necessary to continue treatment, drugs that kill clostridia are prescribed. For example, metronidazole, vancomycin. If the situation cannot be normalized, the patient is hospitalized.
Advantages of endoscopic examination in a paid clinic
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is carried out after appropriate preparation - following a special diet and complete cleansing of the intestines with the help of potent laxatives.
- In a European-style clinic, the patient will receive detailed recommendations on balancing the diet, which will help them calmly, without weakness or discomfort, undergo the stage of fasting and cleansing the intestines.
- Modern equipment allows a highly qualified specialist to conduct an examination with pinpoint precision without damaging the intestinal mucosa.
- The systematic process will take no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient will wake up in the room without experiencing any negative sensations.
- Patients who have already undergone intestinal endoscopy note that their expectations of something painful and terribly unpleasant were absolutely not justified.
Be attentive to your health! If sudden intestinal problems do not go away within 2-3 weeks, consult a specialist.
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, st. Kantemirovskaya 53, k1 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 51, k3 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |
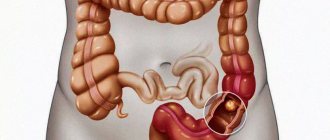
Intestinal tumors
Two types of neoplasms develop in the colon.
Benign and malignant neoplasms very often develop in the colon. At the same time, the championship belongs to the latter.
Many people suffer from colon cancer, and especially rectal cancer.
Moreover, it is the left part that is mainly affected (3/4 of all cases). The largest number of cases are among people over 50 years of age.
The older a person is, the higher the risk of developing this pathology. The following groups of people are considered to be at risk:
- whose diet is dominated by foods rich in animal fats;
- affected by colon polyps;
- those suffering from ulcerative colitis;
- with a family history;
- with a history of colon cancer.
It is almost impossible to detect cancer in its early stages. As a rule, people simply do not pay attention to constipation and minor abdominal pain. The only thing that is alarming is blood in the stool, and even then it can be classified as a manifestation of hemorrhoids.
If the tumor is on the right, the temperature rises, weight goes away, and diarrhea becomes too frequent. If the tumor is on the left, then you will suffer from constipation, the pain will be cramping in nature.
Treatment of pain in the intestines on the right and left lower abdomen
To determine the cause of severe pain in the intestines on the left and right side of the lower abdomen, the patient should visit a doctor. After the initial examination and consultation, the patient will be sent for testing. A general analysis of blood, urine and feces will show the internal indicators of the body and demonstrate the presence of any abnormalities in the systems of the human body.
For clearer results, the patient is referred for a bacteriological examination of stool, colonoscopy and endoscopic examination. After receiving the test results, the attending physician prescribes treatment for the patient. A medical expert prescribes medication, homeopathic or surgical intervention in advanced cases.
If necessary, to obtain information about the condition of the internal organs, the doctor refers the patient to undergo a computed tomography or ultrasound scan. These diagnostic tests are not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under sixteen years of age. Health care professionals do not recommend these procedures for certain groups of the population. The use of radiation and contrast fluid can negatively affect healthy organs.
To make an appointment for a consultation or examination at the private clinic “KDS Clinic”, leave a request on the website and managers will contact you as soon as possible.