Urine tests
- one of the most common laboratory tests that diagnose almost any disease. By studying the concentration of elements excreted in the urine, it is possible to monitor the slightest deviations in the functioning of the urinary, cardiovascular and immune systems.
General urine analysis
A general urine test is a sequential study of the physical characteristics of the biomaterial, its chemical composition and microscopic diagnosis of the existing sediment.
Urine color
The color of urine depends on its concentration and the amount of coloring elements. Normally, its color range is a palette from straw yellow to amber. Pale shades indicate regular use of diuretics, heavy drinking, or kidney failure. Dark colors (strong black tea) indicate hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver or cholelithiasis. Red shades, reminiscent of meat slop, indicate serious kidney damage or tumor processes in the body.
Urine clarity
In a healthy person, urine should remain clear for several hours after filling the test container. Slight turbidity may occur due to the presence of moderate amounts of epithelial cells or mucous secretions in the material. Severe cloudiness of urine is observed:
- In the presence of red blood cells (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, bladder cancer)
- In the presence of leukocytes (pyelonephritis, cystitis)
- With a high content of bacteria (pyelonephritis, cystitis)
- In the presence of protein (pyelonephritis, amyloidosis)
- With a large amount of epithelial tissue (pyelonephritis)
- When salts precipitate (phosphates, oxalates, urates)
- Flat epithelium appears in urine from the external genitalia and indicates urethritis in men and lack of hygienic procedures before collecting material in women
- Transitional epithelium is part of the mucous membrane of the urinary tract and indicates cystitis or lesions of the ureters
- The renal epithelium indicates acute nephritis, nephrosis, infections and poisoning
Sign up for a urine test
Make an appointment
Urine density
The density of urine is determined by the salts and organic substances dissolved in it - protein, sugar, bilirubin. Also, the density of urine is affected by the cells present in it in certain diseases. These are bacteria, leukocytes and erythrocytes. In cases of increased or decreased density of the biomaterial, a specialist may prescribe additional diagnostic measures to more fully study the functioning of the kidneys.
Urine smell
Unusual smelling urine can be a symptom of various diseases. With cystitis, the smell of ammonia vapor appears, with ketonuria - the smell of acetone. A fruity tint is characteristic of diabetes, and when infected with E. coli, the urine takes on the smell of feces.
Acidity of urine
One of the most important indicators of the acid-base balance in the body, with which you can determine the concentration and activity of hydrogen ions. An increase or decrease in the acidity of urine is most often associated with dietary habits, the use of medications, or the occurrence of infections. In the absence of timely correction of urine acidity to normal values, the development of pathological processes is possible - the formation of kidney stones, an increase in blood viscosity, the proliferation of pathogenic flora, the accumulation of waste and toxins as a result of a slowdown in metabolism.
Sugar in urine
Normally, the urine of a healthy person does not contain sugar. The presence of glucose in the urine indicates that the patient has diabetes mellitus, pituitary gland or kidney disease. In this case, the specialist may prescribe additional studies and tests.
Protein in urine
The appearance of protein in the urine is associated with inflammation in the bladder, ureters and urethra. Often protein in the urine can be observed during pregnancy, allergies, heart failure, epilepsy and leukemia. There are cases when the presence of protein is detected in healthy people after serious physical exertion, long walking, or severe hypothermia.
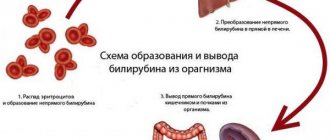
Bilirubin in urine
Bilirubin in the urine is detected in cases where the kidneys take on the function of excreting this organic substance when its level in the blood sharply increases. Possible causes are hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, liver failure, cholelithiasis. Normally, bilirubin is excreted from the body as part of bile without causing harm to health.
Hemoglobin in urine
The reason for the appearance of hemoglobin in the urine is considered to be the rapid breakdown of red blood cells, as a result of which this protein, which is involved in the transfer of oxygen, is released. The liver and spleen do not have time to break down a large amount of hemoglobin, so it is partially excreted by the kidneys, ending up in urine. This process can occur against the background of malaria, myocardial infarction, hemolytic disease, mushroom poisoning, kidney injuries and acute nephritis.
Sign up for a urine test
Make an appointment
Red blood cells in urine
Red blood cells in the urine are found in cases of serious pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract. These include oncological diseases of these organs, tuberculous processes of renal tissue, traumatic lesions, the presence of stones, as well as inflammation. Normally, small red blood cells should not be present in the urine. Sometimes they may appear in quantities of no more than 3 pieces.
Leukocytes in urine
White blood cells (leukocytes) perform a protective function in the body, neutralizing various toxins, bacteria and viruses. Their presence in urine is allowed in quantities of no more than 3 pieces. In the event of a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes in urine, the patient must undergo additional studies to exclude such serious diseases as kidney tuberculosis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, cystitis, and oncological diseases of the urinary system. Sometimes the presence of leukocytes in the urine is explained by non-compliance with personal hygiene rules during the collection of biomaterial or inflammatory processes of the external genital organs.
Epithelium in urine
Epithelial cells in urinary sediment can differ from each other and reflect various ailments:
Cylindrical bodies in urine
Cylinders are protein or cellular compounds formed in the renal tubules as a result of organ pathology. Based on what type of casts were found in the urine, the disease can be diagnosed. If cylindrical bodies are detected, it is necessary to stop using medications that can affect the kidneys and immediately consult a specialist.
Salts in urine
Increased levels of salts in the urine are a sign of poor nutrition and low fluid intake, severe physical activity, infection or disease. If the appearance of salts in urine is constant or their concentration is too high, then the patient is prescribed an additional examination (daily tests according to Zimnitsky) to monitor kidney function.
Bacteria in urine
The presence of bacteria in the urine or bacteriuria may indicate the presence of an infection in the urinary tract, or lack of personal hygiene during preparation for the test collection. To determine the type of bacteria and means of combating them, it is necessary to carry out bacteriological culture of urine. Most often, bacteriuria is accompanied by additional symptoms - frequent urination, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, changes in the color and smell of urine, increased body temperature when the inflammatory process spreads to the kidneys.
Mushrooms in urine
The causes of the appearance of fungi in the urine may be fungal infections of the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis) and external genital organs (vulvovaginitis, balanoposthitis), as well as long-term use of antibiotics or malfunctions of the immune system.
Causes of toxic hepatitis
There are several reasons that cause toxic liver damage:
- industrial poisons - organophosphorus pesticides, insecticides, trichlorethylene, metals and metalloids, arsenic, aldehydes, phenols, etc.;
- plant alkaloids - strychnine, quinine, aconite, cocaine, colchicine, hyoscine, etc.;
- toxins of poisonous mushrooms;
- alcoholic drinks;
- medicinal hepatotoxins - anticonvulsants, antituberculosis, psychotropic drugs, antibiotics, cytostatics and more.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of toxic hepatitis include:
- unfavorable environmental situation;
- frequent stress;
- poor nutrition;
- long-term uncontrolled use of medications;
- alcohol abuse;
- concomitant diseases of the hepatobiliary system (associated with impaired excretion of bile from the body).
Cost of seeing a doctor
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
Urinalysis
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 110101 | General urine analysis | urine (morning portion) | count | 1 k.d. | 345 rub. | 690 rub. | 0 |
| 110102 | 2 glass sample | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 575 rub. | 1150 rub. | 0 |
| 110103 | 3 glass sample | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 690 rub. | 1380 rub. | 0 |
| 110104 | Rehberg's test | urine + blood (serum) | count | 1 k.d. | 403 rub. | 805 rub. | 0 |
| 110105 | Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 920 rub. | 1840.00 | 0 |
| 110106 | Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 345 rub. | 690 rub. | 0 |
Advanced urine analysis study
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 090101 | Creatinine | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090102 | Urea | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090103 | Uric acid | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090104 | Phosphorus | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090105 | Magnesium | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090106 | Glucose | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090107 | Calcium | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090108 | Alpha amylase | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 345.00 rub. | 690.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090109 | Total protein | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 230.00 rub. | 460.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090110 | Na+/K+/Cl- | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 460.00 rub. | 920.00 rub. | 0 |
| 090112 | Microalbumin | urine | count | 1 k.d. | 575.00 rub. | 1150.00rub | 0 |
| 090121 | Deoxypyridinoline (DPID) | urine | count | 3-5 k.d. | 2300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
All our services and prices
1.General information
It has been known in medicine since time immemorial: everything that circulates in the body or leaves it can sometimes tell much more and better about the patient’s condition than the patient himself. All that remained was to learn to understand this “language” - the language of biological fluids, mucus and other substances.
Modern medical science is armed with powerful optical and electron microscopes, centrifuges, filters, spectrum analyzers; developed methodology for laboratory biochemical, bacteriological, virological research, computer databases and other technologies that could not even be imagined a hundred or two hundred years ago. However, some diagnostic criteria and principles do not change: physical characteristics such as color, consistency, smell, volume, and frequency still matter to the doctor.
A change in the color of urine (in particular, darkening), especially if it is accompanied by any discomfort or pain, cannot but alert you. Urine is one of the most important biological fluids, and, being a residual waste product of blood filtration in the kidneys, it serves as an informative indicator of the general condition of the body and the processes occurring in it.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Preparing for a urine test and rules for collecting urine
The biochemical composition of urine directly depends on the quantity and quality of fluid and food consumed, as well as physical and psycho-emotional stress. Therefore, on the eve of the procedure, it is recommended to avoid fatty and spicy foods, sweet or spicy delicacies. It is necessary to reduce physical activity.
Urine is collected in the morning in a clean and dry container. For research, it is advisable to take a “medium” portion. Before collecting biomaterial, it is recommended to carry out hygienic treatment of the external genitalia using a shower or wet wipes. During menstruation, it is advisable to refrain from taking the test, as its results during this period may be inaccurate. It is not recommended to collect material after sexual intercourse and defecation, or to use urine that has been in the refrigerator for more than 3 hours for research.
Treatment of toxic hepatitis
First of all, the treatment of toxic hepatitis involves the most complete elimination of contact with the toxic substance. Patients are prescribed strict bed rest. If toxins penetrate through the digestive tract, gastric lavage is performed before starting drug therapy. Further, in order to remove poison from the body, patients with toxic hepatitis may be advised to take adsorbents, drip infusion of electrolyte solutions, and in case of severe liver damage, blood purification (plasmapheresis or hemosorption).
To activate the process of eliminating toxic substances during the treatment of hepatitis, choleretic drugs can be used, and in case of mushroom poisoning, antidotes can be used. In order to maintain liver function, vitamin therapy is carried out using B vitamins and ascorbic acid.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
– one of the most popular laboratory tests in urology and nephrology. It allows you to accurately identify hidden inflammatory processes and pathologies of the genitourinary system, and is also an additional method for determining the level of leukocytes in the urine. To obtain a reliable result, the patient must, 24 hours before collecting the material, stop drinking alcohol, carbonated drinks, protein products, smoked foods, fatty and spicy foods. You should not donate urine according to Nechiporenko during menstruation. Taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs can also distort the data obtained. Before the procedure, it is necessary to toilet the external genitalia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of toxic hepatitis includes instrumental and laboratory methods that are also used in identifying other acute and chronic liver lesions. During the first medical consultation, a physical examination and history taking are performed. In most cases, this allows you to get a rough idea of the reasons that triggered the development of toxic hepatitis.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing liver damage:
- biochemical blood test - determination of the level of direct, indirect and total bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, AlT and AST and γ-GTP;
- coagulogram - prescribed to assess the state of the hemostatic system;
- general blood and urine tests;
- tests to exclude the presence of other forms of hepatitis.
Instrumental diagnostic techniques:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- liver scintigraphy;
- MRI;
- laparoscopic examination with targeted puncture biopsy of the liver.
Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky
Urine analysis according to Zimnitsky
is one of the ways to check the excretory function of the kidneys, which helps determine how correctly these organs are functioning and whether the patient is at risk of possible complications in the form of acute renal failure. This study is recommended in cases of certain diseases:
No special preparation is required for Zimnitsky's analysis. The patient does not need to limit himself in food and drink. Immediately before collecting biomaterial, it is recommended to exclude spicy dishes and foods that stain urine - beets, rhubarb - from the regular menu. For the study, you will have to stock up on a set of 8 clean jars, as well as a notepad for recording the volume of liquid consumed and the time for collecting the analysis in the next container. Every time before visiting the toilet, it is necessary to perform genital hygiene.
When examining urine, any detected deviations from established standards in the direction of exceeding them are considered to be pathology.
Improper functioning of the kidneys is also indicated by the presence of protein, epithelial cells, and bacteria in the urine. Don't panic and self-medicate. Only a specialist can correctly interpret the analysis results!
Sign up for a urine test
Make an appointment
Complications of toxic hepatitis
In case of mild poisoning, timely treatment of toxic hepatitis leads to complete relief from the disease. In more severe cases, massive liver damage can lead to serious complications.
Liver failure
– a complex of symptoms, including weight loss, swelling of the face and legs, jaundice, accumulation of ascitic fluid, subcutaneous hemorrhages, mental and neuromuscular disorders.
Cirrhosis of the liver
– replacement of hepatocytes with fibrous connective tissue.
Hepatic coma
– a progressive disruption of the organ and central nervous system, which can lead to death.
Literature:
- Chronic alcohol intoxication / A. Ya. Grinenko et al. - St. Petersburg: R. Aslanov Publishing House: Legal Center Press, 2007. - 537 p.
- First steps in clinical, laboratory and functional diagnostics of internal diseases: Textbook. manual on propaedeutics internal. diseases / A.B. Smolyaninov, L.N. Vereshkina, V.A. Reiza; Ed. V.A. Novitsky; Military medical acad. - St. Petersburg. : Military medical. acad., 2002. – 163 p.
- Toxicological chemistry [Electronic resource]: textbook. manual / Salnikova E. V., Kudryavtseva E. A.., Lebedev S. V., Skalnaya M. G. - Orenburg: Orenburg State University, 2012. - 228 p.