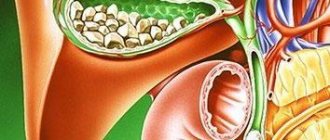
Not a single organ in a pregnant woman’s body remains “indifferent” to the new state of its owner.
A woman’s organs and systems are forced to work with double load, providing nutrients to both the mother and the unborn child. Any malfunction in the functioning of these systems and organs can have a negative impact on the fetus. A fairly common occurrence is a pathology such as gallstones during pregnancy, or cholelithiasis in a pregnant woman. What to do in this case?
How does pregnancy affect the gallbladder?
According to the observations of specialists, diseases of the biliary system are much more common in women than in representatives of the opposite sex, and doctors do not exclude the influence of hormones on these pathologies. During pregnancy, hormonal levels change, which can lead to increased symptoms.
- Due to hormonal changes (especially when progesterone levels decrease), smooth muscles throughout the body, including the gallbladder, relax.
- As a result, the secretion of bile slows down, which can cause cholestasis (stagnation of bile), and then stone formation.
- The expanding uterus puts pressure on the peritoneal organs, often causing their displacement, and in the case of a bladder, deformation or twisting of the bile ducts, which also affects the biliary system.
The compressive effect of the pregnant uterus on the gallbladder is manifested by pain in the abdomen, which is especially typical in the last trimester of pregnancy.
Manifestation of the disease in a pregnant woman
Symptoms of cholelithiasis can be confused with toxicosis
When the disease just begins, it rarely makes itself felt and is asymptomatic. Sometimes mild pain may occur in the right side. In this case, the disease is easier to diagnose and treat without surgery. But pregnant women have a different situation and most often they immediately feel unpleasant signs.
Sometimes the expectant mother confuses the symptoms of gallstone disease with toxicosis. But, as a rule, toxicosis lasts throughout the first trimester. If the unpleasant sensations continue to bother you, then you need to be examined by a doctor and have an ultrasound scan.
Symptoms to watch out for:
- Cutting and pain in the abdomen and on the right side under the ribs.
- Nausea and vomiting are the same signs that can easily be confused with toxicosis.
- Cloudy urine with a dark tint.
- There may be a feeling of heaviness in the right side.
- The skin takes on a yellowish tint.
- Feeling of heartburn.
- In some cases, the stool becomes discolored. This symptom is often found with hepatitis and because of this, the diseases can be confused.
- The whites of the eyes become yellowish.
- There may be a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Gases.
- Digestive disorders.
- Girdle pain.
Having noticed these symptoms, the expectant mother should consult a doctor for advice and under no circumstances self-medicate. After all, she risks not only her health, but also the life of the baby.
Can stones occur during pregnancy?
The formation of gallstones is not a spontaneous process and requires some time. Can gallstones develop during pregnancy? It may well be, although most often during the period of bearing a child, an existing cholelithiasis, which until then was asymptomatic, worsens.
At-risk groups
Is it possible to determine the likelihood of developing such an undesirable combination as gallstones and pregnancy? Yes, there are certain risk groups for gallstone disease, both among pregnant women and among other patients:
- first of all, these are women with a genetic predisposition, that is, if gallstone disease has been observed in several generations of the family or there have been cases of pregnancy with gallstones in the family;
- the risk is high in patients whose diet is dominated by foods with excess cholesterol levels, fatty, smoked, fried foods, as well as pickles and marinades;
- Overweight women and diabetics are no less at risk;
- Among working women, those most susceptible to stone formation are those who do not follow a diet, do not distribute food intake into approximately equal portions throughout the day, and allow long breaks in food.
All this should prompt the idea that the call for pregnant women to adhere to a healthy lifestyle is not at all the routine precaution of a gynecologist.
Mechanism of formation of gallstones
Symptoms of choledocholithiasis
The disease is asymptomatic as long as the stones are freely evacuated through the duodenum and intestines. Severe symptoms occur when the lumen of the common bile duct closes. It is similar to the signs of cholecystitis:
- intense pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the back. When the area of the papilla of Vater (the place where the ducts from the gallbladder and pancreas flow into the duodenum) is blocked, it becomes the surrounding papilla. Drawing, aching, dull, sometimes sharp;
- alternately increasing and decreasing yellowness of the mucous membranes and skin. The first yellowing occurs 10-12 hours after the onset of pain;
- light yellow or white stool;
- dark brown urine;
- Body temperature may rise.
The pain subsides when the stone passes into the duodenum and the bile flow is restored. When the next stone migrates, the whole picture will repeat itself. The condition gets worse if inflammation begins.
Symptoms
What symptoms indicate that a woman has begun to develop at least one gallstone during pregnancy?
- As a rule, the first of them are pain, paroxysmal biliary colic under the right rib with irradiation to the neck, shoulder blade, and right shoulder.
- Pain may occur during fetal movement.
- In addition to pain, nausea, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, and vomiting may be observed.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis during pregnancy based on clinical indicators is complicated by their similarity to the manifestations of toxicosis.
Characteristic pain should be a reason to consult a doctor and undergo an examination (usually an ultrasound).
Cholestasis during pregnancy - what is it?
10.11.2021
Gestational cholestasis is a condition that may appear towards the end of pregnancy . This usually results in jaundice and persistent itching. The disease goes away after childbirth , but often recurs in subsequent pregnancies. Requires symptomatic treatment and frequent monitoring of the fetus.
Cholestasis during pregnancy - what is it?
Cholestasis is a set of biochemical disorders and clinical symptoms that appear when the secretion of bile acids in the liver or the outflow of bile through the bile ducts is obstructed. Common causes of cholestasis are gallstone deposits or the presence of tumors in the abdominal cavity, such as pancreatic . In some pregnant women, cholestasis may occur spontaneously.
The main causes of gestational cholestasis are high levels of estrogen at the end of pregnancy and increased sensitivity of liver to this hormone . The disease usually appears in the third trimester. Very rarely, symptoms appear in early pregnancy . Genetic factors play an important role in cases of cholestasis during pregnancy . The appearance of cholestasis during the first pregnancy carries a high risk of occurrence in the second and subsequent pregnancies.
Cholestasis during pregnancy and consequences for the child
The first symptom is usually itchy skin. It can be very persistent and significantly reduces quality of life. Skin itching often worsens in the evening and at night. After a few weeks, other symptoms of gestational cholestasis appear, such as yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as darker urine and changes in stool color. Sometimes fatty diarrhea . These symptoms, although they may be concerning, usually do not pose a significant threat to the mother's health.
However, cholestasis can be dangerous for the child. The most common complication is premature birth , which entails, for example, the risk of hypoxia. Less common complications include decreased fetal heart rate and meconium aspiration syndrome. In the most severe cases, the fetus may die.
Cholestasis during pregnancy - diagnosis
Cholestasis in a pregnant woman should be suspected if skin itching appears between 25 and 32 weeks of pregnancy . Stagnation of bile is mainly indicated by biochemical disorders. Laboratory blood tests show elevated levels of bile acids and bilirubin, as well as elevated levels of liver , mainly ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). These indicators can be increased in many other diseases of the liver and biliary tract.
Correct interpretation of results is important. Cholestasis during pregnancy is confirmed by an increased concentration of conjugated bilirubin and an excess of the upper limit of alkaline phosphatase activity by at least two times. Differential diagnosis should include cholestasis due to viral hepatitis and cholelithiasis . These diseases should be especially considered if additional symptoms or jaundice appear in early pregnancy or the postpartum period.
Cholestasis during pregnancy - how to treat?
Ursodeoxycholic acid is the main drug used in the treatment of cholestasis in pregnancy. This drug is considered the most effective in combating itching. Cholestyramine and steroids, mainly dexamethasone, are also used. Steroid medications also speed up the maturation lungs , which is important in case of premature birth . Cholestasis of pregnancy requires frequent monitoring of the pregnancy , including fetal heart rate and movements. For severe cholestasis with elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood some doctors recommend induction of labor after lungs reach maturity. As a rule, such an attempt is made at 36 weeks of pregnancy .
Diet for cholestasis during pregnancy
Bile is involved in the digestion of fats. Impaired bile secretion also means poor absorption of fats, including essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins. The best sources of vitamins A and D are full-fat dairy products, fatty sea fish and liver . If symptoms of fatty food intolerance are severe, a low-fat diet
Vitamin A and D are naturally found in carrots, tomatoes, pumpkin and green peas. Leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, and parsley are natural sources of vitamins E and K. Although these vitamins are found in higher amounts in the diet, supplementation may be necessary. Vitamin K supplements are especially important as they are essential for proper blood . The use of any vitamins in the form of dietary supplements or medications must be agreed with your doctor .
Cholestasis during pregnancy - consequences
Even despite appropriate treatment, there is a several tens of percent risk of premature birth with complications such as perinatal hypoxia or perinatal death of the child. The risk increases with maternal bile acid concentrations. The occurrence of cholestasis during one pregnancy also carries a high probability of cholestasis in subsequent pregnancies, as well as when using oral contraceptives. These drugs are contraindicated in patients who have developed cholestasis during pregnancy . These patients also have a higher risk of developing gallstones in the future.
Published in Pregnancy and pregnancy management Premium Clinic
What to do if you have gallstones?
If gallstones are discovered, the pregnant woman will have to seriously reconsider her diet and, if necessary, be prepared to take medications. In acute cases that pose a threat to the life of a pregnant woman, surgical treatment may be required. Let's consider the types of therapy in more detail.
Diet
Pregnancy with gallstones may well end in a successful spontaneous birth without any complications if the woman follows dietary recommendations (treatment table No. 5) and does not provoke stagnation of bile and movement of stones.
- To do this, you will have to completely give up fatty, fried, smoked, spicy and canned foods, spices and seasonings and hot or fatty sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise), rich broths, jellies, coffee, cocoa and all products containing it.
- Preference should be given to unsaturated broths from fish, “lean” meat, vegetables, as well as low-fat dairy products, eggs (only 1 per day, soft-boiled or scrambled), fruits and vegetables in raw, boiled or baked form.
- Products, preparations and herbs (for teas and decoctions) that have a pronounced choleretic property are not allowed.
In addition, long breaks in food intake, which provoke stagnation of bile, vegetarianism, any kind of mono-diets for weight loss and other experiments are not allowed. All this should be postponed until the postpartum period.
Medicines
To relieve pain, it is allowed to take No-shpa or Papaverine; the treating gynecologist must choose the medicine.
Recently, one has increasingly heard about the possibility of dissolving stones with medications, however, all of them are contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and therefore are not applicable in our case. The woman’s task is to alleviate the symptoms and, under the supervision of a doctor, “hold out” the pregnancy to a successful completion. And start serious treatment after childbirth.
Surgery
If unbearable pain, general condition (fever, chills, fever, prolonged vomiting) and blood test results indicate the presence of a serious inflammatory process caused by blockage of the bile duct, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
It is advisable to remove gallstones during pregnancy using a minimally invasive laparoscopic method.
This technique allows you to minimize complications that arise during surgery and significantly reduce the postoperative rehabilitation period.
Medical Internet conferences
According to our study, the manifestation of PVD most often occurs in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, 1-13 weeks - 66.6% (20) cases, 14-27 weeks - 26.7% (8) cases, 28-40 weeks -6, 7% (2) of cases , which is associated with an increase in the sensitivity of receptors to progesterone in the wall of the bladder and a decrease in its contractile activity (hypomotor dyskinesia) along with the high lithogenicity of bile induced by endogenous estrogens. In addition, the lipid spectrum of the blood serum may change in pregnant women, since during pregnancy there is a partial “switching” of the main energy processes from carbohydrate sources to lipid sources. Thus, during pregnancy, women experience several mechanisms that contribute to the formation of gallstones.
The average age of pregnant women with PVD was 31.32±0.76 (19-37 years). In 60% (18) of cases, the age of women ranged from 30 to 37 years, 40% (12) of cases - from 19 to 29 years. In 16.7%(5) of cases, rural residents, urban - in 83.3%(25) of cases. The proportion of working patients is 80% (24) of cases, non-working 20% (6). All pregnant women in the study group were registered at the antenatal clinic until 12 weeks of pregnancy. Primigravidas accounted for 46.7% (14) of cases, multigravidas accounted for 53.3% (16) of cases. The first birth was expected in 53.3% (16) of cases and repeat births were expected in 46.7% (14).
Acute calculous cholecystitis occurred in pregnant women against the background of gastrointestinal diseases in 46.7% (14) of cases: cholelithiasis in 40% (12) of cases and gastric ulcer in 6.7% (2). A history of viral hepatitis B was noted in 6.7% (2) of cases, and hepatitis C was noted in 3.3% (1) of cases. A history of appendectomy was noted in 13.3% (4) of pregnant women. Excess body weight was observed in pregnant women in 60% (18) of cases.
Among the clinical symptoms in the combination of pregnancy with PVD, nausea was observed in 93.3% (28) of cases, prolonged pain in the right hypochondrium predominated in 90% (27) of cases and pain in the epigastric region - in 53.3% (16) of cases, vomiting – in 60% (18) of cases and in 40% (12) of cases – weakness. An increase in body temperature (37.0-37.5ºС) was observed in 26.7% (8) of cases. The appearance of complaints after an error in diet was noted in 46.7% (14) of cases. There were no symptoms of peritoneal irritation in the study group. A positive Murphy's sign was observed in 13.3% (4) of cases.
According to the results of laboratory research:
- leukocytosis - 26.7% (8) cases
- increased levels of AST and ALT – 13.3% (4) cases
- increased alkaline phosphatase levels – 13.3% (4) cases
- increased levels of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase – 6.7% (2) cases
- bilirubinemia - 3.3%; (1) cases
According to our study, the ultrasound picture of acute cholecystitis is characterized by a combination of three main signs, which is confirmed by a number of authors.
– increase in the size of the gallbladder in 33.3% (10) cases
– thickening of the gallbladder wall in 26.7% (8) cases
– positive ultrasound symptom of Murphy type in 16.7% (5) cases
A combination of all three symptoms was observed in 6.7% (2) of cases. In 53.3% (16) of cases, gallstones were found in pregnant women.
When pregnant women were admitted to the surgical hospital, the general condition was satisfactory in 93.3% (28) cases, and moderate in 6.7% (2) cases.
The course of pregnancy in patients with acute calculous cholecystitis was complicated by the threat of premature birth in 3.3% (1) cases and the onset of labor in 6.7% (2) cases, in 20% (6) cases - toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy and in 6.6 % (2) cases – spontaneous abortion that began in the first trimester of pregnancy.
All pregnant women received conservative therapy; in 60% (18) of cases, there was an improvement in their general condition on days 1–2. Laparoscopic and laparotomic cholecystectomy was performed in 16.7% (5) of cases due to the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy. With progressive pregnancy, pregnant women were discharged from the hospital in 83.3% (25) of cases, in 6.7% (2) of cases, after surgical treatment, the pregnancy was interrupted - spontaneous abortion in a short period of pregnancy, in 3.3% (1) of cases, the pregnant woman was transferred to the maternity ward with a threat of premature birth and in 6.7% (2) cases - transfer to the maternity ward with the onset of labor.