The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Reflux esophagitis
can rightfully be considered one of the most common diseases of the esophagus. According to data for 2010, 5 million people in Russia suffer from it. No more than 2 out of 10 people receive adequate therapy for their disease. It often occurs due to contact of the mucous membrane of the esophagus with the contents of the stomach. The latter is known to be highly acidic and affects the lower esophagus. As a result, a person experiences pain, heartburn and other symptoms of indigestion.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to track the real incidence of reflux esophagitis, because it often occurs with mild symptoms and people do not seek help from specialists. For patients with reflux esophagitis, constant heartburn that occurs after eating is a normal option. They relieve discomfort with an Almagel tablet or other usual remedy. Such carelessness can cost a person dearly, since reflux esophagitis is not the safest disorder. It often causes severe bleeding and even cancer.
The second category of patients can be called people with constant, severe symptoms of the disease requiring outpatient treatment. The most dangerous are reflux with complications (ulcers and bleeding). This form of the disease requires hospitalization.
GERD and reflux esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is often confused with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). These are two different conditions that differ primarily in their approach to therapy. Their main differences are presented in the table.
Differences between reflux esophagitis and GERD
| Comparative characteristics | GERD | Reflux esophagitis |
| Definition of the concept | When the disease occurs, gastric contents reflux into the esophagus. In this case, the mucous membrane lining it suffers, since it is not adapted to contact with acids. | |
| Are there any changes in the esophageal wall? | If the disease has an uncomplicated course, then the mucous membrane retains its normal structure. | The walls of the esophagus are always inflamed. |
| Establishing diagnosis | The doctor makes a diagnosis during the initial examination of the patient. | A diagnosis can be made only after performing FGS with endoscopic examination of the esophagus. |
| Features of therapy | Medicines are taken only as needed. | A person must regularly take medications that will prevent narrowing of the esophagus, bleeding, cancer and other complications. |
Thus, esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, which can be diagnosed during fibrogastroscopy. GERD can develop without esophagitis, but esophagitis is always combined with GERD.
Approximate price tags for treatment in major centers
| X-ray of the esophagus | Average cost of the procedure |
| Moscow | 2000 rub. |
| St. Petersburg | 1700 rub. |
| Ekaterinburg | 1050 rub. |
| Kyiv | 900 UAH |
| Dnepropetrovsk | 760 UAH |
| Minsk | 60 bel. rub |
| Almaty | 6000 tenge |
| Omsk | 717 rub. |
| Novosibirsk | 1033 rub. |
| Kharkiv | 780 UAH |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 1000 rub. |
| Samara | 1540 rub. |
| Chelyabinsk | 1005 rub. |
| Odessa | 865 UAH |
| Volgograd | 870 rub. |
| Permian | 800 rub. |
Causes of reflux esophagitis
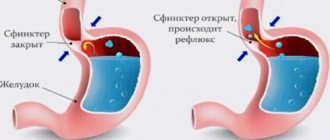
The lower esophageal sphincter is a natural valve between the esophagus and the stomach, which prevents its contents from coming back out. The food that the stomach has begun to digest moves lower and does not rise into the esophagus. Sometimes reflux of stomach contents occurs, but this does not happen often during the day and does not cause discomfort in a person, therefore it is considered a variant of the norm. The disease is said to occur when reflux of gastric contents occurs very often. At the same time, food masses contain a large amount of acid.
Reflux esophagitis has a number of different causes. In young children, it usually occurs due to an underdeveloped neuromuscular system, namely the cardiac part of the esophagus. This is why babies often burp.
Also, the cause of reflux esophagitis can be gastritis or peptic ulcer: because of them, the pressure inside the stomach increases, and the mobility of the gastrointestinal tract is significantly reduced. In addition to heartburn, the patient experiences cramps and hypertonicity. Stress, obesity, decreased salivation and poor nutrition can disrupt intestinal motility. Among the most dangerous foods are citrus fruits, chocolate, tomatoes, fatty and spicy foods, coffee and alcoholic drinks. Smoking and the use of certain medications, especially sedatives and hypnotics, prostaglandins, nitrates and nitrites, also harm the esophagus and stomach.
Before starting therapy, it is important to establish and eliminate the pathological factor that led to the development of reflux esophagitis. Otherwise, the disease will recur all the time.
| Cause of the disease | Mechanism of disease development | Conditions that can provoke reflux esophagitis and GERD |
| Increased pressure on the sphincter of the lower esophagus | High intra-abdominal pressure, which causes food to rise. |
|
| Weak lower esophageal sphincter | If the valve does not work, then the reflux of contents from the stomach into the esophagus occurs very often. |
|
| Increased acidity of gastric juice | If the gastric contents contain too much hydrochloric acid, then even single reflux of food into the esophagus can lead to the development of the disease. Sometimes gastric juice is more aggressive due to the fact that it contains too many enzymes. |
|
Factors influencing the occurrence of heartburn and discomfort
There are many reasons why the digestive system malfunctions. These include:
- chronic stress, depression;
- presence of bad habits (smoking, drinking large amounts of alcohol, overeating);
- excess body weight, including during pregnancy (especially in the last stages);
- unhealthy diet, where preference in food is given to fatty, spicy and smoked foods;
- excessive consumption of certain foods: coffee, strong tea, black bread, fresh baked goods, tomatoes and dishes containing tomatoes, chocolate, mint, carbonated drinks;
- increased stomach acidity;
- undergoing a course of treatment on certain medications that give a similar side effect;
- rest, which consists of lying down immediately after eating;
- postoperative consequences;
- Constant work that involves frequent bending;
- uncomfortable tight clothing (belts, corsets).
Doctors have been trying for many years to give an accurate definition of this disease. This is a difficult task, since heartburn also occurs in healthy people, without causing discomfort or adversely affecting the functioning of the body.
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis
It is very important to pay attention to the first symptoms of reflux esophagitis, which can be divided into two categories. The first category is the esophageal manifestations of reflux esophagitis, and the second category is the extra-esophageal clinic.
Esophageal symptoms are caused by damage to the mucous membrane of the organ. They appear as follows:
- Heartburn.
Heartburn becomes more intense after drinking alcohol, after physical activity, after overeating. Although in patients with reflux esophagitis, heartburn can occur at almost any time. The more the esophageal mucosa is affected, the stronger this symptom will be. Some diseases also affect the frequency of heartburn: inflammation of the gastric mucosa, ulcerative defects of the digestive system, etc.
- Pain.
Painful sensations are concentrated behind the chest, and sometimes rise higher. They are almost always combined with heartburn. You can cope with the pain if you take an antacid, for example, Rennie or Almagel. Pain has a relationship with food intake. This is its distinguishing feature from heart pain, which cannot be relieved with antacids.
- Belching of sour contents.
This symptom is indicated by most people suffering from reflux esophagitis. Often during belching, some food comes out.
- Swallowing disorder.
This symptom is observed in those patients who have suffered from esophagitis for a long time. The bolus of food passes through the esophagus with difficulty, this process is accompanied by pain.
In addition to the symptoms described above, patients may suffer from damage to the vocal cords, lungs, bronchi, and trachea. Acidic contents can enter the respiratory system and cause inflammation. As a result, a person can be treated for a long time for bronchitis, asthma, laryngitis and even pneumonia, and the exact cause of the disorder will never be established.
If reflux esophagitis is chronic, then additional symptoms of the disorder are:
- Voice change. He becomes hoarse.
- Cough, which, if the trachea is affected, will be dry. If inflammation of the bronchi or lungs occurs, the cough becomes wet.
- A sore throat.
- A runny nose that has plagued the patient for a long time.
The esophagus and other organs that suffer from the damaging effects of stomach acid will bleed. As a rule, bleeding is minor, but can lead to anemia. Its symptoms manifest themselves in increased weakness and weakness. You may develop a craving for unusual smells. Patients often experience deterioration in the condition of their nails, skin and hair.
Types of disease
According to the nature of the flow:
- spicy;
- chronic.
According to morphological characteristics:
- Catarrhal. The most common form, in the absence of therapy, transforms into other forms.
- Erosive. Erosion occurs on the walls of the esophagus. Appears due to infections, chemical burns or reflux.
- Hemorrhagic. Occurs due to infection.
- Pseudomembranous. A fibrinous film appears, which is not closely adhered to the mucosa. The reason is infection.
- Necrotic. Occurs due to weakened immunity.
- Phlegmonous. The cause is the entry of a foreign object, characterized by acute inflammation.
- Hydropic. Swelling of the mucous membranes of the esophagus.
Diagnosis of reflux esophagitis
A standard examination is not enough to make a diagnosis. Laboratory diagnostics provide virtually no information on the disease. With its help, it will only be possible to assess the general state of a person’s health, as well as identify some complications of the disease. When a person comes to see a doctor, he will prescribe only 3 tests: blood, urine and stool. Changes in reflux esophagitis will affect only the blood picture.
| Abnormalities in the blood picture with reflux esophagitis | What do these violations indicate? |
| An increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in women up to 15 mm/hour, and in men up to 10 mm/hour. A decrease in the level of red blood cells in women to 3.6*1012, and in men to 4.4*1012. A decrease in hemoglobin levels in women to 120 g/l, and in men to 130 g/l or less. | An increase in ESR indicates that there is inflammation in the body. A drop in hemoglobin and red blood cell levels indicates developing anemia, in which the number of oxygen-carrying cells decreases. |
A diagnosis can only be made using an examination method such as FGS - fibrogastroscopy.
Features of the FGS
During the procedure, a thin tube is inserted into the patient's mouth, which is equipped with a camera and a working instrument. Before the examination, you need to stop eating 3-4 hours before it starts. Do not drink water 40 minutes before the procedure.
The patient will need to take a towel and a disposable napkin with him. The person is placed on his left side. To reduce the discomfort that occurs when the tube is inserted, the patient is sprayed with an anesthetic solution on the root of the tongue. Then a mouthpiece is inserted into the patient's mouth; it will need to be clamped between the lips and teeth.
FGS cannot be called a pleasant procedure, but it takes no more than 7 minutes. At this time, the doctor examines the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus and stomach. If there is a need, tissue is removed using altered tissue. It is then studied under a microscope. The doctor will be able to detect atypical cells, bacteria, and thinned epithelial structures in it.
The doctor will be able to make an initial diagnosis immediately after FGS. If laboratory examination of tissues is required, data can be obtained after 7-14 days.
Evaluation of results
After the examination, the doctor will be able to make the following conclusion:
- Catarrhal reflux esophagitis.
This is the most “harmless” version of the disease. The mucous membrane is loose, full-blooded, and there are no serious damages. This type of esophagitis is not divided into stages.
- Erosive reflux esophagitis.
In this case, the esophagus will be covered with ulcers, or thinned areas of the epithelium will be found on it. This condition requires immediate treatment, as it threatens the development of bleeding and can lead to stenosis or complete obstruction of the organ. Ulcerative defects are dangerous due to their degeneration into cancerous tumors. The erosive form of the disease is divided into stages. The doctor must take the material for microscopic examination.
- Presence of bleeding
, which complicates erosive esophagitis. Often in such patients, laboratory diagnostics reveal anemia, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms (increased fatigue, distortion of taste, etc.). A person can undergo outpatient treatment, since there is no threat to his life. However, if cancer cells are found in the tissues taken for analysis, hospitalization is required.
- Fibrin plaque on the walls of the esophagus.
This sign indicates that the disease has been progressing in a person for a long time.
Sore throat after FGS
After FGS, the patient may experience a sore throat. It occurs in 90% of people. Even if the procedure was carried out perfectly, it is impossible to exclude the occurrence of discomfort. Pain develops due to the fact that the device injures the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The stronger they are, the longer the pain will haunt the person. Sometimes they are stored for 14 days after the procedure. The pain will go away when the mucous membrane of the esophagus is restored.
If the pain is intense, then you need to consult a doctor to make sure that the esophagus has not been severely injured. In the hospital, the patient may undergo fluorography or a chest x-ray. If free air is found in the organs, this indicates a rupture of the esophageal wall. In this case, the person requires immediate surgical intervention. However, one should not be afraid of FGS, since the described case is a rare exception, which is practically not recorded in modern medicine.
As a rule, sore throat after the procedure does not require any therapy. The mucous membrane of the organ will recover on its own. If the pain causes discomfort, then you can take a drug from the NSAID group, for example, Nimesulide or Meloxicam. They are not capable of harming the digestive system. However, in such cases, it is better to consult a doctor.
What is important to know
The relevance of the problem of GERD is also due to the fact that almost every second inhabitant of the planet periodically experiences symptoms of this disease, unaware of its presence in their body. What is the danger of this disease?
- first of all, in reducing the quality of life of the patients themselves;
- secondly, in severe complications such as the development of peptic ulcers , stenosis and perforation of the esophagus .
Studies of the disease have established a clear relationship that the gastroesophageal reflux factor can be traced in the genesis of some dental diseases, ENT diseases, as well as bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular diseases. But, despite the relevance of the problems associated with esophagitis, its danger is underestimated.
In this regard, it is important to find out how esophagitis manifests itself in its most common form.
Degrees and stages of disease development
If the patient is diagnosed with an erosive form of the disease, the doctor will have to indicate the degree and stage of its development in the diagnosis. You can understand what exactly the doctor meant using the table.
| Degree of disease development | Los Angeles classification of disease | Stage | Classification of the disease according to Savary-Miller |
| A | Thinning of the epithelium 1-5 mm long | 1 | Single erosions |
| B | Thinning more than 5 mm | 2 | Erosions are confluent, but do not cover the entire circumference of the esophagus |
| C | Erosion covers 3/4 of the organ | 3 | Erosion and inflammation cover the entire circumference of the esophagus |
| D | More than ¾ of the organ is affected | 4 | There are complications of the disease in the form of stenosis, ulcerative defects, etc. |
| 5 | There are symptoms of precancer in the lower part of the esophagus (Barrett's esophagus). | ||
The higher the stage of the disease, the higher the likelihood of developing complications.
Classification by degree of damage
In modern clinical practice, several classifications based on different criteria are used. The basic classification according to the degree of damage is as follows:
1. Non-erosive reflux esophagitis. On the inner wall of the esophagus, only redness of the mucous membrane is noted.
2. Erosive reflux esophagitis. Erosive lesions are noted.
Most experts consider this classification to be too primitive, since it reflects the degree of progression of the disease only in the most general terms.
As data obtained from endoscopic studies were collected, gastroenterologists from different countries developed their own classifications with expanded morphological criteria.
Classification by A.F. Chernousova
The scientist divided esophagitis into three forms:
1. Mild esophagitis. The lower third of the esophagus is moderately hyperemic and edematous, the folds of the mucous membrane are thickened, and the esophagus itself is slightly dilated.
2. Moderate esophagitis. More severe swelling and hyperemia in the lower third of the esophagus, its lumen is expanded (but at the same time narrowed at the site of inflammation), there are erosive lesions of the mucous membrane, accompanied by bleeding.
3. Severe esophagitis. Pronounced hyperemia and swelling of the lower third of the esophagus, a significantly expanded lumen of the esophagus (at the same time there is a spasm in the affected area), the mucous membrane is ulcerated, and bleeding foci of erosion are found under fibrinous deposits.
Classification by A.F. Chernousova was adopted back in 1973 and for more than 20 years was quite popular among domestic specialists.
Hetzel-Dent classification
According to this classification, there are four degrees of the disease:
- I degree: there is hyperemia (redness) and looseness of the mucous membrane in the absence of erosive lesions.
- II degree: no more than 10% of the mucosa is involved in the erosive process.
- III degree: erosion affects no more than 50% of the mucosa.
- IV degree: erosive lesions of most of the mucosa or deep peptic ulcer in any part of the esophagus.
This classification was used until the mid-90s. Then it was replaced by the Los Angeles classification, and the Hetzel-Dent criteria began to be gradually forgotten.
Los Angeles classification
In 1996, the Congress of the World Gastroenterological Organization was held in Los Angeles. At the congress, a new classification was adopted, which has become widespread in foreign clinical practice².
| Degree | Clinical manifestations |
| A | One or more mucosal tears not exceeding 5 mm in length, none of which extends between the apices of the mucosal folds |
| B | The length of one or more mucosal tears exceeds 5 mm, and none of them extends between the upper parts of two folds of mucous membranes |
| C | Mucosal tears extend between the apices of two or more mucosal folds but occupy less than 75% of the circumference of the esophagus |
| D | Mucosal tears extend between the apices of two or more mucosal folds, occupying more than 75% of the circumference of the esophagus |
Classification according to A.N. Okorokov
In domestic clinical practice, Okorokov’s classification has taken root, which also distinguishes four degrees of severity of the disease, but with more understandable criteria:
- I degree: edematous and hyperemic mucosa, abundant mucous discharge is noted.
- II degree: in addition to edema and hyperemia, isolated erosions are observed on the mucous membrane.
- III degree: swelling, hyperemia and bleeding of the mucous membrane, multiple erosions.
- IV degree: most of the esophagus is affected by erosion, the secreted mucus acquires a viscous consistency.
Savary-Miller classification
Mention should also be made of the Savary-Miller classification, adopted in 1994 and widely used both in foreign and domestic clinical practice. At its core, it represents a slightly modified version of the Hetzel-Dent classification:
- I degree: against the background of edema and hyperemia of the mucous membrane, linear erosions are observed, which occupy no more than 10% of the circumference of the lower third of the esophagus.
- II degree: erosions merge, occupying up to 50% of the circumference of the lower third of the esophagus.
- III degree: multiple erosive lesions that occupy more than half the circumference of the lower third of the esophagus.
- IV degree: deep ulcers, strictures (narrowings) of the esophagus in the affected area, cylindrical metaplasia of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of reflux esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is dangerous because it does not cause intense symptoms, which is why many people do not consult a doctor on time. The pathology progresses, leading to the development of dangerous complications. To prevent this situation, you need to start therapy in a timely manner.
Treatment of reflux esophagitis consists primarily of eliminating the disease that caused it (gastritis, neurosis, peptic ulcer or gastroduodenitis). Proper therapy will make the symptoms of reflux less pronounced, help reduce the harmful effects of gastric contents thrown into the esophagus, increase the resistance of the esophageal mucosa and quickly clear the stomach after eating.
General recommendations
A person with reflux esophagitis needs not only to take medications, but also to reconsider their lifestyle in general.
Therefore, doctors give all patients the following recommendations:
- Quitting cigarettes. Nicotine provokes an increase in the acidity of gastric juice, relaxes the walls of the esophagus, which leads to the progression of the disease.
- You should not lie down immediately after eating. For half an hour after eating, you need to remain in a sitting position, or walk a little at a slow pace. You should not run or lift weights. Any physical activity after eating is prohibited.
- Limits on heavy lifting after meals are 3 kg for women and 5 kg for men.
- 2-3 hours before bedtime you should stop drinking alcohol. You also need to eat no later than this time.
- To prevent the symptoms of the disease from worsening while lying down, it is recommended to use an additional pillow to keep the upper body elevated. This will reduce heartburn and chest pain.
- Clothing should not tighten the abdominal area. You should not tighten your belt, corset or girdle tightly after eating.
- It is important to direct efforts to get rid of concomitant diseases: gastritis, obesity, ulcers, etc. If this is not done, then it will not be possible to get rid of reflux esophagitis.
Diet
A very important component of the treatment of reflux esophagitis is diet. Patients should give up fatty and spicy foods, coffee, chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes, alcohol and smoking.
Many people believe that following a diet means eating tasteless foods and limiting themselves in everything. Actually this is not true. It is important to remove only certain foods from your diet. Using various culinary techniques, you can make your menu varied, tasty and very healthy.
The following products are prohibited:
- Drinks that contain caffeine: Coca-Cola, energy drinks, cocktails.
- Drinks with gases.
- Alcohol.
- Flour products that increase acid production in the stomach.
- Chocolate and sweets.
- Dairy products.
- Flaxseed and olive oil, animal fats. Vegetables and fruits that contain acids: radishes, pomegranates, citrus fruits, etc.
Food should not be fried using animal or vegetable fats. Such products contribute to the production of gastric juice in excess quantities. This entails the progression of the disease. Food should be boiled, steamed, or stewed in its own juice.
Recommendations for preparing healthy and tasty dishes:
- Wrap.
Using foil or parchment paper, you can cook almost any meat product without adding oil. Spices can be replaced with salt, dried herbs, and natural vegetables.
- Using the oven.
Baking is the optimal cooking method for people suffering from esophagitis. At the same time, no oil is added to the dishes, which reduces the fat content of meat products. You can fill the food with water. Not only meat, but also side dishes are prepared in one baking sheet, which allows you to reduce time spent in the kitchen. It is important to bake dishes no longer than 70 minutes. The optimal temperature is 200 °C.
- Cooking
in a steamer or slow cooker.
These modern devices can significantly increase the value of any dish and add juiciness to it. Steam treatment gives products a pleasant taste and does not destroy the vitamins they contain. You can add salt and herbs to your dishes. - Cooking over an open fire.
This method of processing food should be practiced during outdoor trips. Excess fat will be removed from the meat, while it will retain its juiciness and tenderness. It is important not to marinate foods in hot brines.
To get rid of reflux esophagitis, you need to reduce the consumption of oil and mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard and other hot sauces. They negatively affect the condition of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and increase the acidity of gastric juice.
Food should not be too hot or cold, as this will irritate the esophagus.
More details:
Diet for reflux esophagitis: triggers and healthy foods
Taking medications
Antacids. If the recommendations described above do not help, then special medications are prescribed that reduce stomach acidity - antacids. For peptic ulcers and erosions, it is recommended to take antisecretory drugs (proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers). This will reduce the pressure inside the stomach, make it resistant to food intake, normalize intestinal motility and eliminate the symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
Modern proton pump inhibitors are represented by 5 substances: omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole. To decide on the drug, you need to visit a gastroenterologist.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to study some features of proton pump inhibitors (data from 2014-2016).
| Individual characteristics of the patient | Which drug is better to choose? | Why this particular drug and not another? |
| It is necessary to take drugs that help reduce the AP enzyme (Enalapril, Lisinopril, Captopril, Ramipril, etc.). | Pantoprazole or rabeprazole | In people who have heart disease or high blood pressure, taking omeprazole and esomeprazole increases the likelihood of heart attack and stroke. These drugs neutralize the protective effect of drugs for the treatment of cardiac pathologies, as they help reduce the level of AP enzyme. |
| Pregnant woman after 13 weeks | Lansoprazole, pantoprazole | The American Medical Association has not found any toxic effects that these drugs could have on the woman or fetus. They are not prescribed before the 13th week of pregnancy, since at this time the formation of the basic systems of the future organism occurs. Omeprazole, esomeprazole and rabeprazole are not prescribed during pregnancy. |
| Patients with bronchial asthma | Omeprazole or esomeprazole | Reflux esophagitis and bronchial asthma are interrelated diseases. There is evidence that the listed medications have a positive effect on the condition of the respiratory system. |
| Patients with liver diseases (hepatitis cirrhosis, fatty hepatosis, etc.). | Any drugs, but preference is given to rabeprazole. | The minimum dose of rabeprazole is 10 mg, which is 2 times less than the dosage of other drugs. Scientists believe that this particular drug damages the diseased organ less than others. |
| It is necessary to quickly and permanently reduce the acidity of gastric juice | Lansoprazole, pantoprazole or rabeprazole. | The effect of taking omeprazole and esomeprazole develops only 3-4 days after the start of treatment. Other drugs begin to act from the first day of taking them. |
Histamine blockers. If for some reason patients cannot take proton pump inhibitors, then they are prescribed histamine H2 blockers. They are less effective, so they are taken in large doses. They are used only in extreme cases. These are drugs such as: Famotidine, Ranitidine, Nizatidine and Roxatidine.
Prokinetics. It is not enough to simply reduce the acidity of gastric juice; it is important to reduce the number of its contents reflux into the esophagus. This can be achieved through the use of prokinetics. These drugs improve the contractility of the gastrointestinal tract and help normalize the process of food movement through them.
Such medicines are represented by the following brands:
- Domperidone
(Motilak, Motonium, Motilium). These are the drugs of choice for inflammation of the esophageal wall. They allow you to normalize the functioning of the sphincter, stomach and intestines.
- Cisapride
(Coordinax, Peristil). These drugs affect the lower esophageal sphincter and the stomach. Their tone increases and the frequency of reflux decreases.
- Metoclopramide
(Raglan, Perinorm, Cerucal). If reflux into the esophagus occurs very often, and other drugs do not reduce their number, then Metoclopramide is prescribed. However, it has a number of side effects, including increased fatigue, muscle tics and weakness.
Esophageal protectors are means to protect the esophageal mucosa from external influences, including the effects of acid or alkaline reflux in GERD. Currently, we are talking about a new pharmacological group, the representative of which is a bioadhesive formula based on hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate to protect the mucous membrane. The only representative at the moment is the drug Alfazox.
Any medicine must be prescribed by a doctor. All of them have indications and contraindications for use. These must be taken into account before starting treatment.
To get rid of pain in the esophagus, you need to take antacids. They are also indicated for heartburn. Antacids do not cure esophagitis, but they perfectly relieve its main symptoms. They have a minimal set of contraindications, so they can be used without a doctor's prescription.
The most famous antacid is Almagel. He arrived earlier than the others. Modern drugs are significantly superior to it in effectiveness. Such drugs include: Gaviscon, Maalox, Rennie, Megalac.
They begin to act faster and remain active longer than Almagel. In addition, such drugs better reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
Some people take a baking soda solution to relieve heartburn. However, this traditional medicine recipe only harms the diseased esophagus and stomach. Baking soda relieves irritation, but then causes the acid to be released several times more, and reflux becomes more frequent. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend giving up soda to get rid of heartburn.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko - GERD, reflux esophagitis and HEARTBURN - causes, symptoms and effective TREATMENT:
Operation
Most often, the disease can be managed using conservative methods. Surgery is rarely performed if a person develops severe complications.
You need to go to see a surgeon in the following cases:
- Bleeding began from the esophagus.
- Food does not move through the esophagus due to its persistent narrowing.
- The sphincter has undergone irreversible changes.
- Precancer was diagnosed.
- Cancer was diagnosed.
Sometimes it is enough to simply remove the pathological tumor, and sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire tube or part of the esophagus. However, the indications for surgery must be serious.
Therapeutic measures
Treating reflux esophagitis in any form consists, first of all, in eliminating the root cause that led to its formation. These pathologies include gastritis and neurosis, as well as gastroduodenitis. If the correct treatment is identified, reflux esophagitis can manifest itself as mild symptoms, and with the help of therapy it will be possible to reduce the harmful effects of the gastric components that enter the esophagus.
Proper treatment will increase the resistance of the esophageal mucosa, leading to prompt cleansing of the stomach after eating food.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a proper diet, which excludes the consumption of chocolate, tomatoes, citrus fruits, caffeine and nicotine. Additionally, the doctor prescribes medications aimed at reducing stomach acidity. These drugs include antacids.
In the presence of peptic ulcers and erosions, antisecretory drugs are prescribed. Due to this, gastric pressure is significantly improved, which leads to overall stability of the stomach and food intake. Gastric motility is also normalized and all symptoms are eliminated.
In order to prevent the worsening of symptoms that occur in a horizontal position, additional pillows are required to elevate the upper body. This method helps reduce heartburn and pain that appears in the sternum.
Answers to popular questions
- How to identify reflux esophagitis in a child?
Reflux occurs 3 times more often in children than in adults. The esophagus of babies has mechanisms to protect against the development of esophagitis, so this condition rarely develops in childhood. Its main symptoms are: causeless crying of the baby, increased anxiety after eating, increased body temperature, chest pain. The disease can be managed without medications. After each feeding, you need to hold the baby upright. If this does not help, then you need to use adapted formulas that have a thick consistency to feed the baby, for example, Nutrilon, Frisovo, Enfamila.
- How long does it take to be treated for reflux esophagitis?
Throughout your life you will need to follow recommendations regarding lifestyle and nutrition. The duration of taking the drugs is determined individually. As a rule, proton pump inhibitors are taken in a monthly course. They will need to be repeated 2 times a year.
- What is biliary reflux esophagitis?
If a person has diseases of the biliary tract and gallbladder, and also has weakness of the sphincters, this can lead to the reflux of duodenal contents into the esophagus. In this case, the organ will suffer from the destructive effects of bile. This disease is often combined with severe gastritis and peptic ulcers. Therapy is carried out according to a similar scheme. At the same time, it is important to additionally focus efforts on treating the biliary system.
- Can reflux esophagitis cause an esophageal ulcer or organ cancer?
If the disease exists for a long time without treatment, then the risk of developing these complications is extremely high.
Author of the article:
Gorshenina Elena Ivanovna |
Gastroenterologist Education: Diploma in General Medicine received from the Russian State Medical University named after. N. I. Pirogova (2005). Postgraduate course in the specialty "Gastroenterology" - educational and scientific medical ]Our authors[/anchor]
Forecast
Reflux pathology responds quite well to treatment, but often after stopping therapy, relapses of the disease occur, especially if you do not change your lifestyle and habits.
- In patients with mild to moderate disease, lifestyle changes and H2 blockers are effective in most cases.
- In the presence of a severe form of the disease, proton pump inhibitors are prescribed.
- If the pathology is characterized by a recurrent course, a longer course of therapy or surgery may be required to prevent the development of complications.
Prevention
To prevent relapse of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that provoke it:
- The first requirement is to normalize nutrition.
- The second step is to monitor your own weight. Obesity is a direct path to the onset of reflux esophagitis.
- The third stage is to pump up your abs.
- The fourth rule is to quit smoking.
- The fifth stage is to equip the sleeping place correctly. The head should be higher than the stomach.
- The sixth requirement is to eat in a timely manner. Make a clear meal schedule.
- The seventh postulate is normalization of sleep.