- What is viral hepatitis C
- Prevalence of viral hepatitis C
- How do you get infected with the hepatitis C virus?
- Hepatitis C virus testing
- What is special about the hepatitis C virus?
- How does hepatitis C occur?
- When do signs and symptoms of hepatitis C appear?
- What period after infection must pass for laboratory markers of viral hepatitis C to appear in tests?
- Can viral hepatitis C be cured?
- Where to start treatment?
- Which doctors treat hepatitis C?
- When to start treatment?
- Is it possible not to treat viral hepatitis C?
- Modern methods of treating viral hepatitis C
- Hepatitis S/C (Video - interview with B.L. Lurie)
What is viral hepatitis C, how does it manifest, why is it dangerous?
How is the virus transmitted and can hepatitis C be cured? Which doctors treat and where to start treatment? Hepatitis C
(
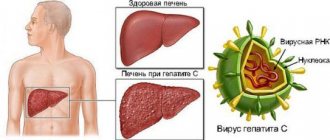
Hepatitis C Virus
) is an inflammatory liver disease caused by the HCV virus (Hepatitis C Virus). The disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Chronic viral hepatitis C, for many years, occurs without symptoms, which makes the disease especially dangerous. The HCV virus uses healthy liver cells to replicate, causing the cells to be destroyed and replaced with fibrous tissue. Without treatment for hepatitis C, the likelihood of developing the worst consequences, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, increases dramatically. That is why it is so important to promptly identify the disease and begin therapy. Modern antiviral drugs can cure hepatitis C completely.
Symptoms of hepatitis C
The disease is most often asymptomatic, but some nonspecific manifestations are possible:
- fatigue, increased fatigue;
- nausea, loss of appetite.
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- joint pain;
- sleep disorders;
- skin itching.
up
How do you get infected with the hepatitis C virus?
The virus is transmitted through blood. You can become infected with the virus through tattooing, piercing, visiting a manicure salon, medical manipulations with blood, including blood transfusions, administering blood products, operations, or at a dentist appointment. Infection is also possible through shared use of toothbrushes, razors, and manicure accessories. Read more…
Sexual transmission is rare, as is transmission of the virus from the mother during pregnancy. Breastfeeding is not prohibited if you have hepatitis C, but you should be careful if blood appears on your nipples.
It is impossible to become infected with the hepatitis C virus through household contacts. The virus is not transmitted by airborne droplets, shaking hands, hugging or using shared utensils. Patients with viral hepatitis C do not need isolation and do not pose a danger to others. In Russia, however, they are exempt from military conscription.
up
Hepatitis D
The infection is caused by the hepatitis D virus (HDV virus).
Quite a specific disease.
It cannot exist independently, and, as a rule, comes in combination with the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
The hepatitis D virus is transmitted during sexual intercourse or through the exchange of needles among intravenous drug users.
Relatively common transmission from an ill pregnant woman to the fetus.
It is possible to become infected through blood transfusions or dialysis, but this is very rare in developed countries.
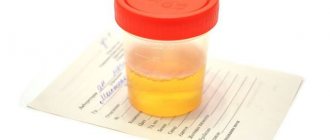
Hepatitis C virus testing
To determine the hepatitis C virus in the blood, it is necessary to take an Anti-HCV antibody test, which shows whether there has ever been contact with the virus. The cost of analysis is 550 rubles
.
- Anti-HCV - negative - no contact
- Anti-HCV - positive - there was contact
The presence of antibodies does not mean the presence of the virus in the blood, and if the Anti-HCV result is positive, a PCR analysis of HCV-RNA is done
, based on the results of which we determine whether the hepatitis C virus is present in the blood.
The cost of the analysis is 750 rubles
.
Sign up for a free consultation to schedule an examination. ANONYMOUSLY.
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
up
Diagnostics
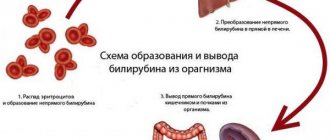
The most important diagnostic method is considered to be a general and biochemical blood test. The virus is recognized by a high ESR and numerous leukocytes in the general analysis, as well as by high levels of bilirubin, ALT and AST in the blood.
These indicators indicate possible disturbances in liver function, but do not allow a specific diagnosis to be made. RNA PCR testing for the presence of antibodies to the virus will help to reliably detect hepatitis C, but the cost of such an analysis is quite high.
Additionally, the doctor prescribes an MRI or CT scan, liver ultrasound, and tissue biopsy. Recently, special rapid tests for detecting the virus in the blood have appeared on sale, which can be used at home.
What is special about the hepatitis C virus?
After the virus enters the human body, it enters the liver through the bloodstream, infects liver cells and multiplies there.
The hepatitis C virus is characterized by genetic variability and the ability to mutate. There are 6 main genotypes of the virus and more than 40 subtypes. This is why the virus often manages to “deceive” the immune system, which leads to the development of chronic viral hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is one of the main reasons leading to liver transplantation, which is why it is better not to delay its treatment.
up
Causes of infection and routes of transmission
The source of the disease is a virus carrier or a sick person. There are two ways of transmission of infection: sexual and parenteral. The virus enters the body through damage to the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals.
These paths may appear in the following cases:
- damage to the skin or mucous membranes with instruments containing the virus in a hairdressing salon, beauty salon (tattoo or manicure), dentistry;
- during surgical intervention using instruments that have undergone poor-quality sterilization treatment;
- during transfusion of contaminated donor blood or its components to the recipient;
- reusable use of disposable syringes (common among injection drug users);
- frequent change of sexual partners without the use of barrier methods of contraception (condoms).
Remember! Infection cannot occur through contact or household contact. In addition, it is impossible for the newborn to get the virus through breast milk, but the child can become infected with a dangerous disease during childbirth.
..
How does hepatitis C occur?
There are two forms of hepatitis C virus: acute and chronic. The acute form is most often asymptomatic and is diagnosed only by chance when markers of acute hepatitis C are detected in the blood - anti-HCV-IgM, which remains in the blood for no more than 6 months after infection with the virus.
After suffering from acute viral hepatitis C, there are three possible scenarios:
- About 20% of patients experience complete recovery;
- In 20% of patients, inactive chronic viral hepatitis C develops with the absence of laboratory markers of the inflammatory process in the liver;
- The remaining 60% have chronic hepatitis with clinical and laboratory manifestations of liver damage.
The transition of the disease to a chronic form occurs unnoticed. Liver damage increases over the years and the patient develops liver fibrosis with subsequent liver dysfunction. The disease progresses slowly over years. In patients with active hepatitis, the risk of developing cirrhosis within 20 years reaches 20%, of which 5% develop liver cancer.
up
Forecast
The earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis for future life. In women, complete recovery is possible in 50-60% of cases, but viruses of types 2 and 3 are more difficult to treat. The effectiveness of treatment also depends on the weight and age of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathologies, lifestyle and bad habits.
Lifespan
Life expectancy also depends on changing habits
Even if it is not possible to completely get rid of the virus, proper and timely treatment will extend a full life for another 20-30 years.
The younger the infected person, the longer he will live before hepatitis C develops into cirrhosis. The greatest danger is the chronic form of the disease, which more often ends in cancer and death of the patient.
Consequences
Lack of treatment is fraught with constant progression of the virus, but here too much depends on the patient’s body. Someone can live with hepatitis for up to 40 years, while others die after 3-4 years. In any case, the most dangerous and more likely consequences of hepatitis include cirrhosis, liver failure and coma, and liver cancer.
Where to start treatment?
From the examination.
A standard examination provides complete information about the virus, its genotype and viral load, as well as a detailed picture of the condition of the liver. For this purpose, biochemical blood tests are carried out to determine the structural and functional state of the liver cells, ultrasound, and assessment of the degree of fibrosis (using the Fibroscan, FibroMax, Fibrotest methods).
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
An important and necessary part of the examination is to exclude contraindications for prescribing therapy, since the instructions for antiviral drugs prohibit their use for a number of concomitant pathologies.
up
Prevention
It is not always possible to avoid infection, but you can minimize the risk by following a few simple rules.
Prevention measures:
- giving up bad habits and drug use;
- strict adherence to hygiene;
- receiving medical and dental services only in trusted places;
- refusal of casual sex.
Paying attention to your health is the key to a long and quality life.
Modern methods of treating viral hepatitis C
The international standard for the treatment of viral hepatitis C is combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin. Doses of drugs and duration of treatment are selected by the doctor individually depending on many factors (see Treatment of viral hepatitis C).
Recently, new drugs with direct antiviral action have appeared, significantly increasing the possibility of complete recovery. Therapy with new drugs is prescribed according to individual regimens.
up
First signs
At an early stage, hepatitis C can only be detected by chance, during a routine routine examination. However, there are some symptoms that should alert the patient and force him to see a doctor.
Early signs of hepatitis C:
- asthenia;
- constant weakness, lethargy;
- fever;
- a sharp decrease in performance, fatigue;
- anorexia;
- headache;
- occasional nausea;
- sleep disorders;
- liver enlargement.
Spider veins may appear on the skin or an enlarged abdomen (dropsy). Sometimes, patients complain of pain in muscles and joints, a feeling of stiffness and impaired mobility.
In general, these symptoms can easily be confused with poisoning or minor disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Most patients try to relieve an unpleasant condition with the help of sorbents, hepatoprotectors and antispasmodics, missing the time necessary for active treatment.
Summary of key recommendations
1. Alcohol screening and counseling to reduce moderate and heavy alcohol consumption
For all persons with HCV infection, it is recommended that alcohol consumption be assessed and, if moderate to high levels of consumption are identified, behavioral interventions to reduce alcohol consumption be offered.
2. Examination of patients to determine the stage of liver fibrosis or cirrhosis
In resource-limited settings, the aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio (APRI) test or FIB-4 test is used instead of other expensive noninvasive tests such as elastography or FibroTest.
Recommendations for the treatment of hepatitis C
3. Examination to determine indications for treatment
All adults and children with chronic HCV infection should be assessed to determine whether antiviral therapy is indicated.
4. Treatment
WHO recommends treatment for all persons aged 12 years and older with known HCV infection, regardless of stage of disease. When treating people over 18 years of age with chronic HCV infection, WHO recommends pangenotypic regimens using DAAs. WHO recommends the following treatment regimens for adolescents with chronic hepatitis C aged 12-17 years and weighing at least 36 kg:
- sofosbuvir/ledipasvir for 12 weeks for genotypes 1, 4, 5 and 6;
- sofosbuvir/ribavirin for 12 weeks for genotype 2;
- sofosbuvir/ribavirin for 24 weeks for genotype 3.
For children under 12 years of age with chronic hepatitis C, WHO recommends:
- delay treatment until the child is 12 years old;
- no longer prescribe courses of interferon-based treatment. New highly effective oral pan-genotypic DAA regimens for children under 12 years of age are expected to become available in late 2022 or early 2022. This will expand access to treatment and make it possible to start treatment for this vulnerable group of patients earlier in the course of the disease.
Symptoms
The incubation period of hepatitis C (from the moment of infection until the appearance of the first clinical signs) has a fairly large time gap - from 2 weeks to 6 months. But with primary hepatitis infection, symptoms do not appear for many years. The person does not even suspect that he is a carrier of the virus and a potential threat to others. In most cases, the disease is determined accidentally, for example, during a routine examination, and is already chronic.
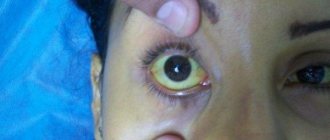
Important! Further progression of hepatitis C is rarely accompanied by direct signs, such as yellowing of the whites of the eyeball, enlarged liver, fever, chills.
The disease is more characterized by secondary symptoms:
- Aches, moderate joint pain;
- Constant low-grade body temperature, sometimes turning into fever;
- Fatigue, drowsiness, depression;
- Nausea, burning in the abdominal cavity;
- Loss of body weight for no apparent reason.
Similar symptoms are present in the etiology of many diseases, characteristic of both men and women. That is why diagnosis in the early stages can be extremely difficult.