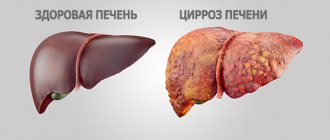
Normal liver structure
The liver is a vital exocrine gland that is dark red in color and performs hundreds of different functions, including:
- Metabolism. In the liver, proteins are broken down into amino acids, the most important compound is synthesized - glycogen, into which excess glucose is processed, and fat metabolism also occurs (the liver is sometimes called a “fat depot”). In addition, it metabolizes vitamins and hormones.
- Detoxification. The liver neutralizes various toxins and bacteria, after which their breakdown products are excreted by the kidneys.
- Synthesis. This gland synthesizes bile, consisting of bile acids, pigments and cholesterol. Bile is involved in the digestion of fats, the absorption of vitamins, and stimulates intestinal motility.
The liver has a complex structure.
Normally, the liver parenchyma is fine-grained, homogeneous in structure, penetrated by a network of vessels and capillaries, as well as bile ducts. The anatomical location of the liver (right hypochondrium) allows you to effectively practice ultrasound and collect the necessary data that allows you to draw conclusions about normal functioning or pathological abnormalities.
The basis of the liver is formed by serous and fibrous membranes. Inside there are lobules, between which bile canaliculi are located and capillaries are laid. Large channels are formed from them, thanks to which blood circulates and the outflow of produced enzymes and acids occurs.
As a result of the diagnostics, increased echogenicity of the liver is often detected - this means that a pathological process has been started in the organ. The most common diseases: hepatitis, liver failure, cancer. All of these diseases are the result of a person’s inattention to their health.
Answers to the most frequently asked questions in case of liver diseases or pathologies
Liver screening is performed for patients with hepatitis B and C, cirrhosis of the liver, and residents of those regions that have high rates of liver cancer. Screening for autoimmune liver disease is necessary to detect autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. It is a blood draw from a vein, on the basis of which the presence of antibodies is detected:
- To the mitochondria.
- To smooth muscles.
- To microsomes of the kidneys and liver.
- To the parietal cells of the stomach.
Echogenicity - what is it?
Echogenicity is a special term used in echography to refer to the ability of organs and tissues with different acoustic densities to reflect sound waves. They are converted into a picture that appears on the screen during the study.
Note: Each organ of the human body has a certain echogenicity.
Knowing these data, the doctor can make a conclusion about its increase or decrease in a particular person. Deviation from generally accepted parameters means that negative factors provoked diffuse changes in the structures and functioning of internal organs: kidneys, pancreas, intestines, spleen, stomach and liver.
This research method makes it possible to visualize organs, identify the disease and monitor its dynamics. Reflection is possible when a section with high acoustic resistance appears along the wave path.
In addition, reflection of ultrasonic waves is possible when they reach the boundary separating tissues with different acoustic resistance. The greater this difference, the stronger the response signal. Visually, on the screen of an ultrasound machine, the condition and echogenicity of the liver may look like this:
- A light area indicates a pathology in which the echogenicity of the liver parenchyma is increased. Most often, this means the formation of some kind of compaction with a low fluid content - a calculus (stone), fat deposits, scar, tumor or abscess.
- Gray area (of varying intensity) – indicates moderate echogenicity, i.e. normal state of the organ.
- Very dark and black areas are a pathology with reduced echogenicity.
Coarse-grained structure of liver tissue
The liver must be protected!
In the absence of timely treatment, a coarse-grained echostructure of the organ may be observed. On an echogram, the liver appears dull, weak and friable. Numerous tubercles are visible on its surface.
The circulatory system does not appear. Hepatitis of various origins, alcohol and drug addiction, and severe obesity lead to such changes in the parenchyma of the gland.
This condition of the liver is considered dangerous, as the organ begins to lose its ability to regenerate. In addition, necrosis (death) of liver tissue cells may begin.
Reasons for increased echogenicity of the liver
Any deviations in echogenicity are important signals indicating problems with the liver, which should not be ignored, since everything in the body is interconnected. Impaired functioning of one organ can lead to disruption of the functioning of other individual organs and subsequently to an unfavorable outcome in general.
| Pathology | Peculiarities |
| Chronic hepatitis | Homogeneous structure, the echogenicity of the liver is moderately increased. |
| Cirrhosis | At an early stage of the disease, the liver is enlarged. In later stages, on the contrary, dystrophy appears with a decrease in size. Heterogeneous structure, reminiscent of a mosaic. |
| Dystrophy and steatosis (fatty infiltration) | The gland increases in size and increased echogenicity is detected, due to the reflection of acoustic waves from fat cells replacing healthy parenchyma. |
| Chronic cholangitis | Inflammation of the bile ducts is accompanied by a high degree of echogenicity (hyperechogenicity), since sound waves are actively reflected from the dilated walls of the ducts. |
| Alveococcosis, opisthorchiasis (helminthic infestation) | The image will be blurry, the echogenicity will be diffusely enhanced, with areas of healthy and damaged tissue of a light color. |
| Cyst | Cystic formations usually contain an accumulation of pus, which is observed on the monitor as a slightly increased echogenicity. |
| Neoplasms | A benign hemangioma or adenoma has a homogeneous structure, with a smooth or uneven contour border and increased density. |
| Liver abscess | The initial stage of the incipient inflammatory process is represented by a small segment of reduced echogenicity, but as the abscess develops, heterogeneous echodensity is observed - either low or too high. |
Other diseases that contribute to increased tissue density include:
- Heart diseases.
- Diabetes.
- Focal or diffuse form of fatty hepatosis.
- Obesity.
- Drug poisoning.
- Inflammation of the pancreas and other organs located near the liver.
Anechoicity - a black spot on the health map
Areas that are unable to reflect ultrasound waves are called anechoic, or echo-negative. They are displayed on the monitor of the ultrasound machine in black. Liquids also lack echogenicity, so they are depicted in the same way.
Often detected anechoic areas indicate the presence of cystic formations. Small cysts (up to 5 cm in diameter) regress after a few months. Large formations are tolerant to special therapy.
In patients over 50 years of age, such a “finding” during an ultrasound usually indicates a malignant formation. Its untimely treatment is life-threatening. Immediate treatment is necessary for complications of a tumor in the kidneys: pyelonephritis, urolithiasis or arterial hypertension.
Echo-negative formation is a sign of normality. This is the cyclically formed ovarian gland - the corpus luteum. It is impenetrable to ultrasound, so it is displayed on the monitor in a dark color. After menstruation, the formation can be defined as the corpus luteum. If menstruation is delayed, then it indirectly indicates the onset of pregnancy.
Symptoms of pathology
Detection of increased echogenicity of the liver usually occurs in the presence of health complaints. Symptoms of the disease may be the following:
- deterioration of immunity - manifests itself in frequent colds, fatigue, general malaise;
- increase in liver size;
- change in the color of the palms (they become reddish);
- gynecomastia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- weight gain;
- the appearance of swelling;
- yellowish color of the skin and eyeballs;
- itchy skin;
- brown coating on the tongue;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- diarrhea.
Redness of the palms as one of the symptoms of impaired liver function
The following changes are observed in biochemical analysis:
- blood parameters such as bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase increase;
- lipid balance is disturbed;
- the level of total protein decreases, the ratio of protein fractions is disrupted;
- Glucose levels increase.
The liver is a very “patient” and “silent” organ. For a long time it may not bother a person in any way, while the pathological process has already started. Don't wait for unpleasant symptoms to appear. Regular visits to the doctor, a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will help to significantly reduce the risk of liver disease.
Indications
The method can be used both at the stage of screening studies and at the stage of final diagnosis. The purpose of liver ultrasound is to assess the condition of the liver and organ blood flow, identify diffuse and focal pathological changes, determine the severity of the disease and the extent of the pathological process, conduct differential diagnosis, and select conservative treatment tactics or surgical intervention. In addition, liver ultrasound is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment during and after therapy, as well as to monitor the course of the disease in remission.
Ultrasound of the liver is prescribed for pain in the right hypochondrium, traumatic injuries to the abdominal area, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, the appearance of laboratory signs of liver dysfunction, drug and alcohol abuse, and long-term use of medications that have a negative effect on the condition of the organ. Ultrasound of the liver is also performed if there is a suspicion of a liver abscess, a primary oncological process in the tissue of the liver parenchyma, or metastatic damage to the organ in tumors of other localizations.
To monitor the course of the disease, timely detect complications and relapses, liver ultrasound is regularly performed for already diagnosed diffuse lesions of the organ, previously suffered hepatitis and cancer in remission. Liver ultrasound is a highly sensitive diagnostic procedure that allows you to detect cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, liver abscesses, traumatic hematomas, metastases, primary liver cancer, Budd-Chiari syndrome, calcifications and some other pathological processes. There are no contraindications to the study.
Peculiarities
Increased echogenicity of the liver is not a disease, but a kind of symptom indicating the presence of problems with the gland. The reasons for their occurrence may be different. It is believed that a violation of the echogenicity of the liver can manifest itself in a child over 10 years of age or in an adult.
Interpretation of liver ultrasound results also depends on the condition of neighboring organs and, above all, the pancreas. It is closely interconnected with the liver, so any deviations and disturbances in its functions immediately affect the state of the liver parenchyma.
If an ultrasound scan reveals diffuse echogenicity of the liver and pancreas, this indicates that the tissues of the organs have a heterogeneous structure. Such changes in the pancreas may indicate the following pathologies:
- pancreatitis (acute or chronic);
- formation of tumor formations;
- the appearance of areas of necrosis;
- development of lipomatosis (replacement of pancreatic cells with adipose tissue).
Ultrasound examination helps to make an accurate diagnosis
If the echogenicity of the pancreas is higher than that of the liver, the results of the entire study may be interpreted incorrectly. Additional research methods may be needed to clarify the diagnosis.
Determination of gland size according to Kurlov
Internal fabrics vary in density. During percussion - tapping in the projection area of a certain part of the body, sound phenomena appear. Kurlov’s technique is based on this.
The study can be direct - tapping with the fingers of one hand, and mediocre - with the 3rd finger of the right hand, tapping is carried out on the middle phalanx of the same finger, but of the left hand.
What are the normal values for an adult?
In an adult, the gland is normally located in the epigastric zone in the area of the right hypochondrium, covered by the diaphragm. The gland has four lobes - right and left, quadrate and caudate. The left lobe is partially located in the epigastric region.
The average weight of the gland is 1500 g. However, the total mass of the organ tends to change upward (more often) or less (less often) under the influence of pathological factors. The most common causes include cirrhosis of an alcoholic nature and viral hepatitis.
Kurlov's norms for an adult are presented in the table:
| Line | Length (in millimeters) |
| Right midclavicular | 80-100 |
| Anterior median | 70-90 |
| Left costal arch | 60-80 |
Diagnostics
Signs of diffuse liver changes
To identify changes in the structure of the liver and detect compactions, they resort to ultrasound. It is carried out according to the following scheme: the person is placed on his back and scans are performed during normal breathing and inhalation.
If the liver is located high and small in size, the patient lies on his left side and throws his head back. At the first stage, the scan is carried out from the upper part of the abdominal cavity towards the navel, due to which the contours and structure of the parenchyma are determined.
The surface of the edge and lobe of the liver - right and left - is examined by moving the sensor along the costal arch. At the second stage, the condition of the bile ducts and the circulatory network - venous and arterial - is studied. During the study, the shape of the liver and its contours are determined, which are clearly visible in a healthy organ.
Interpretation of ultrasound results reveals the existence of pathologies in the liver tissue. But there is a possibility of a distorted result, depending on the condition of neighboring organs. So the echogenicity of the affected pancreas is higher than the liver, which can affect the change in parameters. Additional tests must be used to diagnose the disease.
Echogenicity is determined by color
When, based on the results of the examination, the doctor sees increased echogenicity of the hepatic parenchyma and a diffusely heterogeneous structure is observed, additional diagnostic methods will be proposed. This will allow us to find out what caused the anomaly.
Held:
- Collection of patient history and complaints. If the information collected coincides with the signs of disease development, and the results of an ultrasound of the liver show increased echogenicity, this means that a diagnosis can be made.
- Visual inspection. The abdominal cavity is palpated, the doctor looks at the condition of the skin and eyes. An enlarged liver may indicate a pathological process.
- Blood chemistry. Needed to clarify data about processes occurring inside the liver, or to detect markers of hepatitis or HIV.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging. They confirm that the echogenicity of the liver is increased, and also provide a more detailed picture of the pathological condition.
- Biopsy. A separate area where local heterogeneity of echogenicity is observed is subjected to additional analysis to identify or exclude neoplasms.
The final diagnosis is made based on a combination of data from a medical examination, general tests, patient complaints, and liver ultrasound.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the contrast agent is possible. Computer diagnostics must not be used in the following cases:
- pregnancy;
- severe liver failure;
- individual hypersensitivity to the components of the contrast agent;
- technetium intolerance;
- the age of the patient under study is up to 15 years;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- acute glomerulonephritis;
- fever;
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- myeloma;
- kidney failure.
If these pathologies and conditions exist, alternative diagnostic methods are used - magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, positron emission tomography. Each of them has its own characteristics, positive qualities and safety of use, but CT is a universal way to examine not only organs, but also arteries, veins, lymphatic vessels, hepatic and bile ducts.
Treatment
If the echogenicity of the liver is increased, then treatment should be carried out comprehensively and solve the following problems:
- Elimination of the root cause - medications are used to treat the underlying disease.
- Inflammatory processes are relieved with antibiotics, and if hepatitis develops, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- Normalization of liver functions - hepatoprotective therapy is carried out, within the framework of which natural remedies are taken to heal and improve the condition of the gland. Hepatoprotectors (Karsil, Gepabene, Heptral, Essentiale Forte) protect gland cells and promote their restoration.
- To relieve pain symptoms, painkillers and drugs that improve the flow of bile are prescribed.
- Normalization of the patient’s general well-being - the emphasis is on cleansing and strengthening the body, in order to increase its protective functions and performance.
The main group of drugs for the treatment of the liver
The doctor selects the treatment regimen individually, taking into account the type of pathology, the severity of symptoms, the presence of concomitant diseases and other nuances. For concomitant diseases of the biliary system and pancreas, choleretic agents are used to eliminate congestion, as well as digestive enzymes that normalize the processes of breakdown and digestion of incoming food, which reduces the load on the liver.
At the same time, antioxidants, multivitamin complexes, antispasmodics, drugs to improve the motor functions of the gallbladder and intestines, and agents to support the immune system are prescribed. For severe swelling and fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites), diuretics are prescribed. Painkillers and choleretic preparations help relieve pain.
Important! If the treatment was successful and the degree of echogenicity is within the normal range, this does not mean that the liver is absolutely healthy. Most likely, structural changes in its parenchyma will remain for life, and the liver will require maintenance therapy.
Folk remedies
- Tansy has a choleretic effect and has a beneficial effect on organ cells. Recommended for restoring basic liver functions. The decoction is indicated for use in cases of alcoholism, cirrhosis, hepatitis, and in the treatment of infant jaundice . Pour dried flowers (2 tablespoons) into a liter of water and cook over low heat for 25 minutes. Leave the strained broth for 1 hour. Take 1/2 cup three times a day every 6 hours.
- Liver cleansing . Preparation lasts 5 days, for this you need to include only cereals, vegetables and fruits in your diet. After unloading, you need to do an enema. After 2-3 hours, the liver warms up: to do this, apply a hot heating pad to the liver area under the rib. It is advisable to carry out the procedure in the evening before bedtime.
- Herbal cleansing. Pour 1 tablespoon of immortelle flowers and corn silk into a saucepan, pour boiling water (1 cup) and bring to a boil. Infuse the resulting decoction for an hour, strain and drink warm on an empty stomach. An hour after taking the product, warm the liver with a heating pad.
Any traditional medicine can be used only after consultation with your doctor. Otherwise, complications are likely.
© 2022 – 2022, . All rights reserved.
Diet for increased echogenicity of the liver
Experts are of the opinion that with increased echogenicity of the liver, nutrition should be dietary. Food can be stewed, boiled, baked and steamed. Eating fried, fatty and salty foods is strictly prohibited, because such foods are “hard” on the liver and the manifestations of the disease may intensify.
Spicy, smoked, salty foods, sour fruits, heavy foods (legumes, mushrooms, duck, lamb, fatty fish) will lead to an increase in the symptoms of the disease. It is recommended to give up sweet carbonated drinks, black coffee and tea, cocoa, and chocolate.
You should drink at least 1.5 - 2 liters of liquid per day - this is still mineral water, compotes, juices, fruit and herbal teas, fruit drinks and other vitamin drinks. Alcohol is completely excluded.
Meals are needed in small portions, 5-6 times a day. The last meal is optimal 2 hours before bedtime. Patients are recommended to consume fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, lean fish and dietary meat. Fasting days are arranged 1 – 2 times a week.
Diet for Liver Health
Following these recommendations will help not only the liver, but also the pancreas. The diet can also reduce the risk of complications and is suitable as a preventive measure.
Proper preparation for the study and its conduct
- CT with the introduction of a contrast agent (orally or in the form of an intravenous injection) is performed on an empty stomach: the last meal should be at least 6 hours before the procedure. Examination without contrast injection does not require special preparation.
- A CT scan of the liver is performed in a specially equipped room. The sequence of the procedure is as follows:
- the patient lies down on the table and is prohibited from moving during the CT scan;
- in some cases, the patient’s limbs are secured with straps;
- at certain moments the patient, at the request of the specialist, holds his breath.
- The examination time is 5 minutes.
- After it is completed, the patient needs to drink a large amount of fluid, which will help remove the contrast agent from the body.
- Computed tomography itself is a painless procedure, but in some cases it can be complicated by an allergy to the contrast. It manifests itself as a skin rash, nausea and dizziness, fever and swelling.
If at least one of these symptoms appears, you must inform your doctor.
Prevention
Following rules that help maintain liver health can also help in treating an already damaged organ:
- Stick to proper nutrition.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Annual examinations to identify hidden pathologies.
- Exercise caution when communicating with infected patients.
- Take medications only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Compliance with safety precautions when staying in a gas-filled room and when working with toxic materials.
- All procedures involving the use of a needle (injections, tattoos, piercings) should only be performed in specialized organizations.
The echogenicity of the liver is an important indicator of the health of this organ. If increased echogenicity is detected, you should definitely consult your doctor and get recommendations for additional diagnostic tests. It is highly likely that you will need drug therapy and diet.
Therapeutic measures
After identifying the disease that has caused changes in the structure of the liver, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment regimen. Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the causes of the development of pathology.
With minor changes in the structure of the liver tissue, as a rule, a special diet is selected that excludes junk food and alcohol, and medications are also prescribed that restore the organ system.
For more serious changes, treatment is supplemented by taking antibacterial agents, antibiotics and special vitamin complexes. A course of treatment with antiviral agents is possible.
Unfortunately, with serious forms of liver tissue damage, therapeutic measures are often ineffective.