Intussusception - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of intussusception involves disintussusception—the release of the strangulated intestine. According to Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 203 “On approval of criteria for assessing the quality of medical care,” treatment of intussusception should be carried out no later than an hour after diagnosis.[7] The fact is that the pathological process in the wall of the strangulated intestine is very dangerous. Therefore, it is important to carry out disinvagination as early as possible and as quickly as possible.
There are two main principles for the treatment of intussusception: surgical (operative) and conservative.
In case of severe general condition of the child, it is necessary to carry out preoperative preparation:
- restore water and electrolyte balance;
- reduce hyperthermia;
- improve microcirculation;
- introduce antibacterial drugs as early as possible.
Conservative therapy
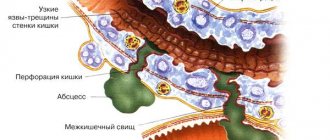
Treatment of intussusception for a long time was exclusively surgical, since the level of diagnosis was low. At the moment, in the absence of convincing data for peritonitis and necrosis of the strangulated intestine, conservative treatment is carried out using a special manipulation - air disinvagination.[8] This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and does not cause pain to the child. Its essence lies in inserting a special tube - a rectal probe with an air injection system connected to it and a pressure gauge (rectoscope with a Richardson balloon connected). Under a certain pressure, air is pumped into the intestines, and with the help of gas pressure, the invariant is straightened.
This method is considered the gold standard for conservative treatment of intussusception. Its effectiveness has been confirmed by many multicenter studies.[11][12][13][14][15]
There is also a method of hydrodisinvagination, based on the effect of hydrostatic pressure on the intussusception. It involves the use of an enema with the injection of a warm saline solution or a barium suspension under the control of an X-ray machine that conducts continuous filming.
It is worth noting that the method with a barium suspension, according to the authors, has one advantage: barium is a fairly dense and heavy substance, which can provide a better chance for conservative disinvagination. However, at present this suspension is not used, as it can lead to a serious complication: if a breakthrough of the intestinal wall occurs during disinvagination, the barium suspension will enter the abdominal cavity, from where it will be extremely difficult to remove it, which will give rise to the development of severe peritonitis.
Hydrodisvagination itself is indicated in the Federal Clinical Guidelines as an additional treatment method, but it is less preferred.[8]
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of intussusception is performed much less frequently. There are clearly defined indications for its implementation:
- the presence of peritonitis and a verified diagnosis of “Intussusception”;
- more than 24-48 hours from the onset of the disease;
- lack of effectiveness from three attempts at conservative disinvagination (pneumodesinvagination).
If the appropriate equipment is available and the surgeon is sufficiently qualified, intussusception is eliminated through laparoscopic access. If it is not possible to perform laparoscopic disinvagination, they resort to an open technique, which is inferior only in terms of postoperative rehabilitation.
The duration of rehabilitation is extremely individual and depends on many factors. It is generally accepted that after laparoscopic release of the strangulated intestine, rehabilitation is easier and faster due to reduced pain.
Intestinal obstruction and its types
Intestinal obstruction - as a congenital pathology
Nutrients travel a long way in the body in order to provide all cells with energy and building material. At the same time, the final digestive processes occur in the intestines, including the absorption of food substrates and excretion of feces.
The total length of the human intestine is 4 meters. The appearance of an obstructed area in any part of the intestine can lead to serious consequences.
The intestine has a muscular lining. Wave-like muscle contraction ensures the movement of food and feces into the lumen of the organ. Violation of this intestinal function may be one of the causes of obstruction.
Stagnation of feces only aggravates the condition, since this results in increased absorption of water and hardening of the stool. However, much more often, obstruction is formed due to more serious pathologies.
Intestinal obstruction can be complete or incomplete. With incomplete obstruction, the patient's intestines still produce gas.
Symptoms
Bowel obstruction may be caused by a tumor
The symptoms of intestinal obstruction will depend on the location and duration of the obstruction. For example, vomiting is an early sign of small intestinal obstruction.
The same symptom may appear with prolonged obstruction of the large intestine. Partial obstruction can cause diarrhea.
Recovery after intestinal surgery
After surgery for a bowel obstruction, your stomach and intestines will need time to return to normal activity and heal. You may not be allowed to eat right away. Your diet will be gradual, from liquids to soft and bulkier foods.
You may need pain medication for the first week after the procedure. Some medications, such as opioids, can interfere with healing, causing severe constipation and are therefore used with caution. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause bleeding in the stomach or intestines. Typically, pain medications are carefully administered and monitored after surgery for bowel obstruction, and intravenous fentanyl, panadol, or methadone are some common methods of pain management.
As you change your diet, you may also need an x-ray of your abdomen to confirm that you are being treated and that there is no blockage left. During this time, you will need intravenous fluids to maintain hydration and nutrition. As your diet changes, you should begin to have small bowel movements, and you can expect normal bowel movements once you start eating solid foods.
Full recovery may take several weeks to several months. It is not easy to predict how long you will need to recover as it depends on how well you tolerate fluids and solids rather than the type of surgery. However, the surgery involves removing a large section of the colon and may take some time to recover from.
Treatment of small intestinal obstruction
As we have already said, treatment of obstruction begins at the stage of examining the patient. Infusions of rehydrating solutions are carried out, the loss of electrolytes is replenished, and the contents accumulated in the adductor section of the intestine are aspirated using a nasogastric tube. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed. The main stage of treatment for intestinal obstruction is surgery, which should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis. It is possible to delay the operation for 2-3 hours to stabilize the patient’s condition. Surgical intervention involves laparotomy - opening the abdominal cavity with subsequent revision and elimination of the causes that caused the development of obstruction:
- The adhesions are cut.
- Hernias are sutured.
- Remove stones or intestinal parasites.
During the operation, the viability of the intestine must be assessed. If there are signs of necrosis, resection of the affected area is performed.
The greatest difficulty is intestinal obstruction caused by malignant neoplasms. In this case, the operation is more extensive. If possible, the tumor is removed within healthy tissue. If this is not possible, palliative operations are performed, for example, bypass anastomoses are performed.
In case of extensive neoplasms or carcinomatosis of the peritoneum, anastomoses have a short-term effect and the obstruction recurs. In such cases, a stoma is indicated - the section of the intestine located above the obstruction is brought out onto the abdominal wall. The intestinal contents will be discharged into a special bag, a colostomy bag. This is a psychologically very difficult operation for patients, but only it can save their lives.
In these cases, if possible, antitumor treatment is carried out, and if the results are stable, reconstructive interventions are performed.
Types of surgery for bowel obstruction include:
- Surgical resection : Removal of the obstruction is necessary when a mass such as a tumor is present.
- Removing adhesions : If you have scar tissue compressing the outside of your intestines, it is often necessary to cut them off, although the scar tissue may return.
- Stent placement : A stent, which is a tube that holds the intestine open, may be placed inside the intestine to allow food and stool to pass through and prevent blockages. This may be necessary when bowel obstruction recurs or when the bowel is severely damaged.
- Colostomy/ileostomy : If your intestines are damaged or inflamed, you may need a permanent or temporary ileostomy or colostomy, which is an artificial opening in the abdomen to remove waste or stool. Sometimes these are temporary structures needed to prevent a severe gastrointestinal infection from spreading throughout the body. However, it is possible that the ends of the intestine cannot be reconnected and these openings may be required for a long time.
- Revascularization . Ischemic colitis may require revascularization, which is the repair of blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the intestines.
Prevention
Preventive measures are not complicated. You need to know them, then health problems can be avoided.
For infants, first of all, timely and competent introduction of complementary foods. The quantity and quality of food should be correlated with the needs of the child at a certain month of life.
There is no need to overfeed him. New food should be introduced only after the body has adapted to the previous one. Vegetable and fruit purees should be given with caution and careful observation.
In cases of intestinal infections, there is no need to self-medicate . It is urgent to show the child to a doctor. If your baby often experiences discomfort and pain in the abdomen, there is a reason to immediately conduct a study to rule out the appearance of adhesions and tumors.
Adults with regular intestinal problems should also undergo an examination to determine or exclude these causes.
Both adults and children should promptly get rid of worms if they appear. This is especially true for children attending preschool institutions (the risk of infection in children's groups is much higher). The appearance of worms is not a harmless phenomenon; a large number of parasites can also provoke intestinal volvulus.
Preventive measures are also necessary after surgical interventions in the intestinal area, including after the elimination of intussusception. During this period, the likelihood of paresis occurring is high. Therefore, postoperative measures include measures of drug support.
Diagnosis of the disease
Intestinal obstruction: diverticulosis
Diagnosis of intestinal obstruction includes a physical examination of the patient, laboratory and instrumental studies.
First of all, the doctor learns about the patient’s complaints and conducts a general examination. Already at this stage, characteristic signs of pathology are revealed. In addition, the doctor needs to find out the medical history and also find out whether the patient has had surgical interventions in recent years.
The physical examination will include palpation, percussion, and auscultation using a phonendoscope. The first two methods help detect bloating and signs of pain. When listening, organ motility disorders are often revealed.
If at this stage the doctor does not identify accurate signs of intestinal obstruction, laboratory and instrumental tests will be prescribed.
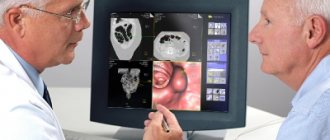
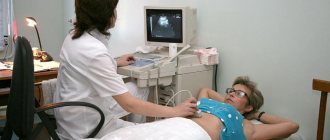
The main instrumental method is scanning the abdominal cavity. In this case, the doctor receives an image of the intestines, on which it is easy to notice signs of obstruction. Scanning also helps to clarify the area of obstruction and the severity of the pathology.
The following scanning methods are used:
Causes of the disease
In infants, the exact causes are difficult to determine. But often the problem is preceded by inflammation of the mucous membrane. Also, sometimes the condition is provoked by a cold suffered by the child.
Many experts associate the occurrence of intussusception in children under one year of age with the introduction of complementary foods. Sometimes this is done illiterately: roughage is given in large quantities.
But even with proper feeding, the problem cannot be ruled out. Fiber from plant foods (and often complementary feeding begins with the introduction of vegetable purees) increases motility, which can also lead to intussusception.
In children older than one year , the disease can occur as a result of the formation of a tumor in the rectum - no matter malignant or benign. The process can also be triggered by the presence of polyps or progressive lymphoma, Henoch-Schönlein disease or Meckel's diverticulum. Sometimes associated with rough food or too much food. The presence of a large number of worms.
In adults, the causes of intussusception may be:
- Muscle spasm or paresis. Spikes. Occurs with myocardial infarction, taking potent medications, urinary stones, diseases of the nervous system, intestinal surgery
- Mechanical obstruction.
- With strong external pressure on the intestinal area, if a foreign object hits.
- Strangulation obstruction. There are three types of such obstruction: volvulus, nodulation and pinching. This is the most severe type of obstruction.