Every day our body encounters many bacteria, viruses, fungi, each of which is potentially dangerous to humans. But the happiness is that we don’t even notice most of them and are not aware of the danger threatening us. And the whole point is that our immune system actively fights any pathogenic organisms without allowing them to even begin to act against us. What is “immunity”, what factors affect it and how can we influence immunity? We will look at all this in order.
Immunity and intestines: the relationship is obvious!
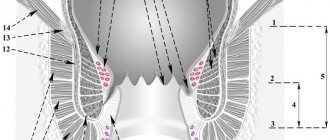
I’ll tell you even more: immunity lives in the intestines! Almost 80% of all immune cells carry out their patrol here. It just so happens that perhaps the most powerful organ has one serious vulnerability - it is constantly in contact with the external environment. First of all, through the foods we eat at breakfast, lunch and dinner. At any moment, pathogenic microbes and other hostile agents can enter it, so a powerful “firewall” for the intestines is simply necessary. Another thing is normal microflora! Our immunity has the most friendly relationship with her, they understand each other perfectly. Bacteria “prescribed” in the intestine play an important role in the direct regulation of immune responses to invading aggressors. In addition, they participate in the processes of absorption and synthesis of vitamins, in the absorption of minerals necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system.
Turboslim Active fibers, 60 g, Evalar
491 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Probiotics and prebiotics: what's the difference?
So, intestinal microflora and immunity are closely interrelated. An imbalance between friendly and pathogenic bacteria leads to an increase in the number of immune cells responsible for the development of inflammation, including chronic inflammation. And not only in the intestines, but also in other organs, which creates the preconditions for the development of diseases and acceleration of the aging process. prebiotics are most often used to correct microbiome disorders.
.
Probiotics for the intestines are preparations with live bacteria, representatives of normal microflora. But prebiotics do not contain bacteria themselves, but they contain biologically active components that improve the vital activity of beneficial microorganisms and create the most comfortable conditions for them.
Large wheat fiber with calamus, 150 g, Health Compass
99 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
How does immunity work?
Immunity is a well-defined system of organs that, when interacting with each other and influencing other systems of the body, are able to form, train and control the cells of our body specifically to combat atypical cells and pathogenic microorganisms. The immune organs include :
- Bone marrow;
- thymus (thymus gland);
- accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the digestive, respiratory, and genitourinary systems;
- The lymph nodes;
- spleen.
They all work to protect us, while performing many different complex physiological processes and chemical reactions, but the result is amazingly capable cells that recognize danger and cells aimed at destroying it - the so-called suppressors that regulate excessive aggressiveness, and mediators are biologically active substances. Together they organize a coordinated process to protect our body.
Everyone, of course, is primarily interested in how to effectively and quickly strengthen the immune system, but in order to find out, we need to figure out which immune organs we can influence and which we cannot. And, looking ahead, let's say that immunity is formed in the intestines.
The bone marrow and thymus are the central organs of immunity and they, so to speak, control the process. And we are practically unable to influence the improvement of the process of their work, well, except for adequate physical activity for the comfort of the bone marrow and careful attention to the balance of hormones (do regular examinations with an endocrinologist) . But the spleen, lymph nodes and lymphoid tissue are peripheral in our immune defense, but no less important. In this case, the intestines are especially interesting for us, since we can influence its work positively and significantly, and accordingly, increase the overall immunity of the body.
The effectiveness of the protective function of lymphoid tissue in the gastrointestinal tract depends on the intestinal microbiota. Back at the beginning of the 21st century. scientists realized that microbiota is an important part of the immune system and can contain 1014-1015 bacterial cells, with the largest number living in the gastrointestinal tract - 75-78%. The symbiosis of all these bacteria that are beneficial to us is called “intestinal microbiota.”
The intestinal microbiota is responsible for metabolism, the formation of a protective layer of the intestinal mucosa, suppression of the development of pathogenic microorganisms, participates in detoxification of the body, colonizes the intestines, entering into competition with pathogenic flora.
What can negatively or positively affect general immunity and the intestinal microflora, as an important part of the immune system?
Probiotics
Many people know how important bifidobacteria are for the immune system. However, modern probiotics also include other microorganisms: strains of lactobacilli, lactococci, enterococci, streptococci, propionibacteria and even E. coli. And each of them has its own unique biological properties. Probiotics help solve a number of problems. For example, the possibilities of their use are being actively studied:
- to reduce the risk of respiratory system infections;
- for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and for their prevention;
- in schemes for eliminating (eradicating) the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which contributes to the development of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer;
- in complex therapy of allergies;
- in the fight against obesity, diabetes;
- to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases;
- in the treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system (for example, chronic cystitis).
And this, of course, is not all the possibilities for using probiotics.
Psyllium (psyllium husk), 100 g, polezzno
334 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Prebiotics
Preparations in this group, as we already know, do not contain live bacteria, but they contain components that improve the functioning of beneficial bacteria and stimulate the growth of microflora. But prebiotics may have a number of other beneficial properties that significantly expand the possibilities of their use. A classic example is plant dietary fiber. Thus, psyllium (psyllium seed husk) helps maintain the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract, regulates bowel movements, has a beneficial effect on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and exhibits detoxifying properties. Corn dextrin helps slow the absorption of glucose and prevent its accumulation in fat depots, maintain normal cholesterol levels, improve skin condition, and accelerate the removal of toxins and metabolic products from the body.
Prebiotics can include many components, including those that are familiar to us for completely different properties: soy and milk peptides, antioxidants (vitamins A, C, E, carotenoids, glutathione, coenzyme Q10), unsaturated fatty acids, lysozyme, vegetable extracts (seaweed, carrot, rice, pumpkin, garlic). And this is not a complete list!
Multiflora, 30 capsules, Evalar
646 ₽
Dietary supplement NOT A MEDICINE
Building a defense
Have you noticed that some people can sit quietly in a draft, walk in the cold in a light jacket, swim in a cold river, communicate with friends who have a cold, and still not get sick? While others take care of themselves with all their might, wear gauze masks during epidemics, wrap themselves in warm sweaters and woolen socks, and still do not recover from colds? What is this connected with? It's all about immunity!
Our immunity is the body's main defense mechanism against viruses and bacteria.
The development of the immune system in the process of evolution determined the very possibility of human existence. Immunity can be innate and adaptive (acquired).
Innate immunity is the body’s ability to recognize and neutralize various bacteria and viruses based on common characteristics. As the name implies, this is a basic property of the body that it receives at birth. Adaptive immunity recognizes more specific, individual pathogens; it is formed in the process of encountering them, after illnesses or vaccinations.
Signs of immune failure
- frequent acute respiratory infections
- frequent exacerbations of chronic infectious diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, pyelonephritis, adnexitis, etc.)
- frequent recurrences of herpetic rashes
- pustular skin lesions
- joint and muscle pain
- prolonged increase in temperature or lack of temperature response in acute infectious diseases
- swollen lymph nodes
- poor wound healing
- malignant neoplasms
- weakness
- chronic fatigue syndrome
The immune system is formed in a person in the womb, and a lot depends on heredity. But lifestyle also plays a very significant role in the functioning of the immune system. And if we can’t do anything about heredity, then we can strengthen the immune system by following certain rules!
How to strengthen your immune system?
Hardening
Hardening is, in essence, training the immune system. The main principle of hardening: moderation, gradualness and regularity.
Start small: walk more, ventilate the apartment more often, walk around the house barefoot, wipe yourself with a sponge or towel moistened with cool water, wash your face with cool water. Then you can move on to more serious procedures: dousing with cold water, contrast shower. Contrast showers, by the way, are very useful for training the cardiovascular system, improving skin condition, and preventing cellulite. Just remember to be careful and gradual! If you already have problems with the cardiovascular system, consult your cardiologist first.
The regularity of hardening procedures and the absence of long breaks between them are very important.
You can start hardening procedures only if you are completely healthy. Ideally, after consulting a doctor.
Nutrition
To strengthen the body, you need a balanced diet rich in vitamins and microelements. In order for you to receive all the necessary substances and microelements, your diet should be as varied as possible. Every day, all main food groups should be present in the diet: dairy, starchy, vegetables, fruits, sources of complex carbohydrates, protein and fats. Complex carbohydrates are found in cereals, pasta, potatoes, bran bread and unleavened whole grain breads. They take a long time to digest, unlike simple carbohydrates, which are found in sugar, cookies, cakes and other sweets. A person also needs indigestible carbohydrates - fiber or dietary fiber. They create a feeling of fullness, and, in addition, are useful for digestion. Such carbohydrates are found in oatmeal and wholemeal bread.
In addition, our body needs fats, since they help absorb vitamins A and E. If there is not enough fat in the body, the skin looks worse, the liver suffers, and sex hormones cease to be produced. Fats are saturated and unsaturated. The latter are better absorbed and, accordingly, they are more useful. They are good to get from fatty fish, avocados, almonds, and olive oil. Of course, the consumption of foods containing hidden unhealthy fats, such as mayonnaise, sausage, and cakes, should be limited.
Sources of protein are fish, meat, dairy products, eggs, legumes, nuts, mushrooms.
Eat as many vegetables and fruits as possible, preferably in thermally unprocessed form for greater preservation of vitamins.
Vitamins and probiotics
Numerous studies show that in Russia, and in other countries too, the vast majority of people suffer from hypovitaminosis - a lack of vitamins. As is known, vitamins are not formed in the human body, with the exception of vitamin D and vitamins synthesized by intestinal bacteria, and therefore must be constantly present in food. But even with the most rational diet (and let’s be honest, most of us have a far from perfectly balanced diet), the human diet today is “understaffed” with vitamins by 20–30%. The absorption of vitamins from “artificial” preparations is often higher than from regular food.
Accordingly, it is necessary to take multivitamin preparations regularly. During periods of illness, stress, depression, increased workload, pregnancy, smoking, alcohol abuse, and taking antibiotics, the need for vitamins increases. The duration of taking multivitamins is determined by your doctor and is usually 1–3 months; it is advisable to repeat the course 2–4 times a year. Vitamins are better absorbed if the daily dose is divided into several doses; it is better to prescribe the main dose in the first half of the day, since in the evening and at night the metabolism in the body slows down. Since a person has always received vitamins from food, it is better to take vitamin preparations with meals, so they are absorbed more fully.
In addition to vitamins, probiotics are important to strengthen the immune system. Probiotics are medications or biologically active food additives that contain live microorganisms that are representatives of the normal human microflora. They are designed to restore the disturbed balance of microorganisms inhabiting various human mucous membranes, and therefore are used for the treatment and prevention of immunodeficiency, dysbacteriosis and related diseases.
Probiotics stimulate the immune system at all levels, which has been proven in numerous clinical studies. Probiotics and vitamins should not be prescribed to yourself; it is better if a doctor does it.
Regime and physical activity
For the normal functioning of the entire body and a person’s well-being, a regimen is very important.
Try to get up and go to bed at the same time and get enough sleep. Rest more, walk in the fresh air. It is necessary to play sports and do exercises.
Regular physical activity has a beneficial effect on the immune system. During active physical activity, the overall tone of the body increases, mood improves, which contributes to greater activity and a surge of energy, the blood is enriched with oxygen, sleep and appetite improve. Physical activity helps relieve stress; the body produces endorphins (“happiness hormones”).
And be sure to walk in the fresh air. Weather permitting, try to spend at least an hour a day outside. Ideally, during daylight hours, because the sun is necessary not only for the production of vitamin D, but without sunlight the level of serotonin (another “happiness hormone”) in the blood, which is responsible for our good mood, decreases. In autumn and winter, the problem of lack of sunlight is especially relevant - we get up in the dark and leave work after sunset. Take advantage of every opportunity to catch daylight: walk during your lunch break, be sure to plan walks on the weekend.
Rejection of bad habits
Bad habits - smoking, alcohol, drug and drug abuse - greatly weaken the body's immune system, impair the functioning of many organs, destroy blood vessels, the brain, lungs, and increase the risk of developing diseases. In fact, if you constantly poison yourself with smoking, alcohol, etc., it is difficult to expect good condition from your body. Alcohol and nicotine suppress the immune system, as a result of which it ceases to perform its protective functions. By the way, many medications can weaken the immune system, so, firstly, you should not thoughtlessly take pills without a doctor’s prescription, and secondly, if you are taking medications, strengthen measures to strengthen the immune system.
Positive life attitude
People have a close relationship between the physical and emotional components. If life does not bring joy and pleasure to a person, then biological mechanisms of self-destruction are triggered. Be positive, enjoy every day - there is always a reason for this. The ability to positively perceive any reality is, without exaggeration, the key to health and longevity.
We hope that our tips will help you become healthier, and the upcoming autumn-winter season will bring you only joy, not illness!