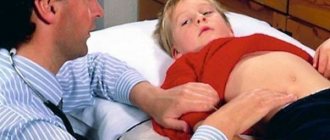
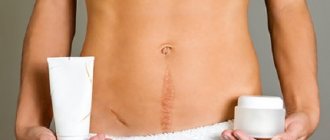
Inflammation of the appendix of the human cecum is called appendicitis. It is one of the most common pathological processes that develop in humans; in most cases, immediate surgical intervention is necessary.
Acute appendicitis has for a long time held the palm among the most common pathologies of the abdominal cavity, so anyone can encounter such an unpleasant pathology, and, of course, he will need to know all aspects of the operation, including how long the operation for appendicitis lasts .
Causes of inflammation of appendicitis
According to some ideas, one of the causes of inflammation is mechanical blockage (obstruction) of the lumen of the appendix and, as a consequence, activation of the intestinal flora.
The causes of mechanical blockage in most cases are “coprolites”, that is, fecal stones. Less commonly, this occurs due to the development of a tumor or the presence of a foreign body. There is also a connection between the presence of problems with stool and the development of appendicitis, since coprolites can develop against the background of fecal retention in the intestines.
Poor nutrition can provoke the onset of inflammation.
In addition to mechanical causes, there are also infectious causes. It is believed that diseases such as typhoid fever, tuberculosis, infections caused by parasites and amoebiasis can independently cause appendicitis
Features of rehabilitation
Surgical removal of the appendix is the only way to cure appendicitis. Despite its apparent simplicity, this is a full-fledged operation that traumatizes the body and requires a full recovery period.
According to modern data, the appendix has lost its original functions and is a vestige. This is a small (7-10 cm) dead-end section of the cecum; its inflammation is called appendicitis.
There are two types of operations to excise it:
- abdominal - with an incision in the peritoneum;
- laparoscopic - with several small incisions through which instruments are inserted.
Rehabilitation after removal of appendicitis using laparoscopy is easier due to the smaller size of the sutures and damage to the skin.
With any type of operational activity, the following occurs:
- receiving anesthesia;
- cuts and sutures on the intestines and blood vessels;
- skin damage;
- general body stress.
The recovery period, which includes:
- Postoperative nursing care. The patient should begin to move and get up at the recommended time, and receive drug therapy to avoid infection. To reduce severe pain, anesthetics are prescribed - first in injections, after discharge - in tablets.
- A special diet helps relieve stress on the injured intestines, improve digestion and normalize stool.
- Normalized physical activity protects against excessive effort, but stimulates blood circulation and accelerates metabolism.
The duration of rehabilitation after appendicitis in adults depends on the type of operation, characteristics of the body and much more.
Important . The recovery period is an essential part of the treatment of appendicitis; the success of this stage depends more on the patient than on the doctor.
Diagnosis of inflammation of appendicitis
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- X-ray, which allows you to detect coprolites, intestinal obstruction, but the only drawback is its low effectiveness in the early stages.
- Irrigoscopy is carried out by introducing contrast agents (mainly a suspension of barium sulfate).
- Computed tomography reveals blockage of the cecum or any changes in its lumen.
- Ultrasound examination is used most often in the diagnosis and detection of appendicitis; such a study shows the presence of fluid in the pelvis, as well as in the right iliac fossa, which indicates the development of local peritonitis. The ultrasound result may indicate the presence or absence of coprolites.
- There are also laboratory methods, they involve analyzing the results of a blood test. In acute appendicitis, a change in white blood cell counts is observed as a response of the body's immune system to inflammation, ESR.
Historical reference
Laparoscopy is most often used for diagnostic examination of the abdominal cavity.
Laparoscopy has been developed over many decades, so it is difficult to single out one person as the pioneer of the approach.
In 1902, German veterinarian Georg Kelling from Dresden performed the first laparoscopic surgery on a dog, and already in 1910, Swedish surgeon Hans Christian used this technique on humans.
Over the next few decades, the procedure was refined and spread throughout the medical community. The introduction of a camera with a computer chip was a key event in the development of laparoscopy, since the procedure in a new format could be used for diagnostic examination of the abdominal organs.
Types of pathology
Acute appendicitis - this type of inflammation appears when the lumen of the appendix decreases, accompanied by necrotic processes with the participation of bacteria located in the lumen. This type is subject to prompt intervention by a surgeon, within two days.
The chronic form is not a common case in clinical practice, occurring after appendectomy on the wall of the appendix.
What is laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a method of surgical and diagnostic intervention.
Laparoscopy is a method of minimally invasive surgical and diagnostic intervention. To perform such operations, surgeons use special equipment:
- A laparoscope is a tube with a set of lenses.
- Optical cable with light source.
- A video camera with a chip connected to the laparoscope.
- Monitor.
- Trocar.
For laparoscopic operations, surgeons make a small incision (no more than 2 cm), into which a laparoscope with a camera and other equipment is inserted.
The image from the camera is transmitted to the monitor, so the surgeon can control his manipulations in real time and observe small anatomical structures in high resolution.
How long does appendicitis surgery take?
Before any operation, each patient needs to know and understand all aspects of the upcoming operation, including its duration. Any practicing doctor, answering the question about the duration of the operation, will tell you such a time frame as: from 40 minutes to an hour, and it will be partly correct, but such an answer cannot be taken as an unshakable rule since many factors can arise before and during the operation , such as a person's anatomical feature, which may influence the duration of an appendectomy.
Physical exercise
The postoperative period is characterized by low mobility, violations of the integrity of blood vessels lead to increased blood clotting and the formation of blood clots. Most doctors believe that dosed exercises help relieve many rehabilitation problems.
Physical therapy (physical therapy) is part of recovery methods. Together with physiotherapy, it improves metabolic processes, stimulates blood circulation, tones muscles and blood vessels.
Exercises are prescribed while on bed rest. Shown:
- bending the legs at the knees;
- turns of the feet and hands;
- breathing exercises;
- other exercises that do not affect the abdominals.
Usually after 3 days the patient can get up. To help the abdominal muscles, many patients are recommended to wear a bandage. The stomach should be protected from excessive tension when coughing and other tremors.
In the future, the increase in physical activity occurs gradually. For the initial 2-3 months, the best way to recover is walking. It is better to walk in parks, where there are good, smooth paths and fresh air.
An important part of rehabilitation is strengthening the immune system. The doctor may prescribe special means to increase it.
Attention ! Lifting heavy objects weighing more than 3 kg is prohibited. You should not perform work that requires excessive effort and tension in the abdominal muscles.
For rehabilitation after removal of appendicitis, swimming in the pool is indicated. It helps, without overstraining the body, to increase the overall tone of all muscles.
For your information. You can start having sex 2-3 weeks after surgery, if your health allows.
How is surgery performed?
The most popular type of access, which is used in clinical practice during surgery, is the Volkovich-Dyakonov access, in which the surgeon’s scalpel passes along the McBurney line. The skin, subcutaneous fat, and superficial fascia of the abdomen are sequentially dissected, behind which the external oblique muscle becomes visible. By dissecting it, the surgeon is able to expand the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles. Then there are options for removing the cecal appendage: antegrade and retrograde.
The retrograde method is used very rarely when difficulties arise in removing the appendix into the wound, which may arise as a result of adhesions in the abdominal cavity. The appendage under the clamp is cut off and then plunged into the cecum with a suture. Gradually bandage the mesentery of the removed process
The antegrade method is more classical; it performs the same manipulations, only in the reverse order. That is, the mesentery is first ligated, a clamp is applied to the base of the cecal appendage, and only then the surgeon removes it.
After cutting off the appendix, it is mandatory to drain the cavity by suctioning out the liquid with a pump. If there are complications such as peritonitis or insufficient confidence in the success of the operation, drainage is placed.
| Laparoscopy | The operation is performed through insignificant, small-diameter holes (0.3-2 cm). A laparoscope is used | Advantages: unlike traditional surgery, a smaller hole is created during the operation, the patient’s rehabilitation time is short, the laparoscope provides the surgeon with more convenience and options when performing the operation. Disadvantages: the laparoscope does not provide a complete picture of the depth of the pathology and limits the surgeon’s movements. |
| Laparotomy | Surgical access is carried out by dissecting the anterior abdominal wall by the surgeon | Advantages: the surgeon gets convenient access to operated area Disadvantages: significant blood loss occurs; after such operations, “Keloid” scars may appear, which look like a tumor growth of connective tissue; when the anterior wall of the abdomen is dissected, nerve fibers may be damaged, and as a result, the sensitivity of this area will be impaired. |
| Transgastric method of operation | The surgeon's instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision made in the stomach | Advantages: avoids possible damage to the anterior abdominal wall and peritoneum; this method also provides more accelerated postoperative rehabilitation Disadvantages: Due to the complexity of the operation, high cost of instruments and technologies, it is used in very rare cases |
| Transvaginal method of surgery | Performed only on female patients, trocars are inserted through punctures (holes) in the posterior vaginal fornix. Used in cases of surgery on women of reproductive age | Advantages: no scar after surgery Disadvantages: inability to have sexual intercourse for 6 months after surgery |
| Transumbilical method of surgery | Trocars are inserted into the abdominal cavity through the umbilical region with the possibility of placing the surgeon's working instruments in the same plane with the appendix | Advantages: there are no traces of the operation (scars or scars), the patient quickly undergoes postoperative rehabilitation Disadvantages: possible surgical injuries, very rarely used |
Postoperative period
In cases of uncomplicated forms of appendicitis and a favorable course of the operation, the patient can be immediately taken to the surgical department, in other cases - to the postoperative ward or intensive care unit.
During the rehabilitation period, wound care and early activation of the patient are of great importance, allowing the intestines to “turn on” in time and avoid complications. Dressings are carried out every other day, if there are drainages - daily.
On the first day after the intervention, the patient may experience pain and increased body temperature. Pain is a natural phenomenon, because both the inflammation itself and the need for incisions imply tissue damage. Usually the pain is localized to the site of the surgical wound, it is quite tolerable, and the patient is prescribed analgesics if necessary.
Antibacterial therapy is indicated for complicated forms of appendicitis. Fever may be a consequence of surgery and a natural reaction during the recovery period, but it must be carefully monitored, since an increase in temperature to significant levels is a sign of serious complications. The temperature should not exceed 37.5 degrees during the normal course of the postoperative period.
Many patients prefer to lie in bed, citing weakness and pain. This is wrong, because the sooner the patient gets up and starts moving, the faster intestinal function will be restored and the lower the risk of dangerous complications, in particular thrombosis. In the very first days after the operation, you need to gather your courage and at least walk around the ward.
A very important role in interventions on the abdominal organs is given to diet and nutrition. On the one hand, the patient must get the calories he needs, on the other hand, he must not harm the intestines with an abundance of food, which during this period can cause adverse consequences.
You can start eating after the appearance of intestinal peristalsis, as evidenced by the first independent stool. The patient should be informed what can be eaten after surgery and what is better to avoid.
Patients who have suffered acute appendicitis are assigned to table No. 5. It is safe to consume compotes and tea, lean meats, light soups and cereals, and white bread. Fermented milk products, stewed vegetables, and fruits that do not contribute to gas formation are useful.
During the recovery period, you should not eat fatty meats and fish, legumes, fried and smoked foods; you should exclude spices, alcohol, coffee, baked goods and sweets, and carbonated drinks.
On average, after surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for about a week in uncomplicated forms of the disease, otherwise longer. After laparoscopic appendectomy, discharge is possible already on the third day after the operation. You can return to work after a month with open operations, with laparoscopy - after 10-14 days. A sick leave certificate is issued depending on the treatment performed and the presence or absence of complications for a month or more.
Contraindications
There are situations when the use of general anesthesia is impossible due to certain circumstances:
- The examination revealed acute mental illnesses, as well as neuralgic diseases.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: periods of slow heart rate or the occurrence of tachycardia when the rhythm reaches 140 beats/min.
- The patient has atrial fibrillation.
- There are disturbances that prevent normal blood supply to the brain.
- Myocardial infarction.
- The heart muscle is unstable.
- Swelling in the legs, shortness of breath, weakness, heart failure.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Pneumonia.
- Bronchitis in acute form.
- Alcohol and drug status of the patient.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Kidney or liver failure.
- The body exhibits symptoms of severe intoxication.
As a rule, the removal procedure for appendicitis is immediate and urgent. This means that there is no time to eliminate factors prohibiting general anesthesia. Therefore, they decide to use a regional method of pain relief.