Gastric papules are an erosive disease. The symptoms of the disease are varied and may not appear at the first appearance of processes on the organ. The causes of occurrence affect the type of formation of papules, because of this, an individual treatment regimen is recommended. The basic preventive treatment method is proper nutrition, avoidance of junk food and alcohol.
Reasons for appearance
The development of pathology can be provoked by the uncontrolled use of medications that can change the internal environment of the organ. Mesotherapy also affects the appearance of shoots. In addition, the following negative factors lead to the manifestation of papules:
- stomach injuries;
- regular smoking;
- chronic liver pathologies;
- bile in the mouth;
- increased acidity in the stomach;
- exhaustion of the body;
- being under stress;
- burns of mucous structures;
- diseases of the vascular system.
Diet and prevention
A strict diet is the main stage in the treatment of intraoral formations. It is important to teach yourself to eat right. You should eat small portions 5-6 times a day. The following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- alcoholic, low-alcohol drinks;
- citrus;
- fried, spicy foods;
- products containing coarse fiber.
The menu should include:
- oatmeal;
- semolina;
- jelly;
- steamed cutlets;
- baked vegetables, fish;
- dairy products.
Experience has shown that most erosive pathologies and gastric ulcers appear and worsen during periods of severe stress or after being depressed.
Therefore, it is important to avoid such situations and not give in to the manifestation of negative emotions. And as a preventive measure, proper healthy nutrition plays an important role. The article has been verified by the editors
Symptoms
There may be no manifestation of a papule in the antrum of the stomach. Most often, this pathology is asymptomatic or with minor symptoms. In the chronic form of the disease, the course of the disease is similar to gastric ulcer. Pay attention to symptoms such as:
Heaviness under the right rib may be a sign of pathology.
- belching with a sour smell;
- heartburn;
- heaviness under the right rib;
- disorders of the system that milks bile from the body;
- anemia;
- weakness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- decreased hemoglobin.
Stomach polyps
Stomach polyps
(eng.
stomach polyp
) - benign stomach tumors of epithelial origin, protruding into the lumen of the stomach, lesions (protrusions) of the mucous membrane on a stalk or on a wide, clearly limited base.
| Polyps of the fundic glands of the stomach* |
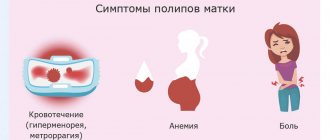
As a rule, stomach polyps do not manifest themselves in any way and the patient learns about them during an endoscopic examination of the stomach. But, as the polyp enlarges, bleeding ulcers may develop on its surface. Rarely, a polyp can block the pyloric canal and prevent food from passing from the stomach to the duodenum. Gastric polyposis can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain or tenderness when pressing the stomach
- nausea
- blood in stool
- anemia
The Kyoto Global Consensus on Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, in its commentary to Statement 17, notes that hyperplastic gastric polyps and Helicobacter pylori
are closely related (Sugano K. et al., see also Russian translation).
Classifications of gastric polyps
| Histological preparations of gastric polyps |
| Polyp ∅6 mm of the fundic glands of the body of the stomach of a 46-year-old woman, presumably also suffering from GERD** |
| Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach of the foveal type*** |
| Adenomatous polyp of the stomach*** |
There is no generally accepted classification of polyps. Depending on the number of polyps, single or multiple are distinguished. When the number of polyps is more than 20, they speak of gastric polyposis. Below are some classifications: Modern classification of polypoid formations of the stomach (Pirogov S.S., Sokolov V.V.):
- Polyps from the fundic glands
- Hyperplastic polyps:
- true hyperplastic polyps
- polypoid hyperplasia in the cardia (reflux origin)
- intestinal type
- foveolar type
- pyloric type
- fundal type
- inflammatory fibrous polyp
- juvenile polyposis
- Cronkite-Canada syndrome
- Gardner's syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Cowden's disease
- heterotopic pancreas
- xanthomas
The endoscopic classification proposed by S. Yamada in 1966 distinguishes 4 types of polyps (Maev I.V. et al.):
Type I - flat, raised, with unclear edges Type II - protruding, semicircular, with fairly clear boundaries Type III - clearly protruding, rounded. with retracted base type IV - pedunculated
According to the international histological classification, all gastric polyps are divided into true (adenomas) and tumor-like formations. Among all gastric polyps, adenomas occur in 14-15% of cases. Tumor-like lesions include hyperplastic and fibrous polyps, which according to their histological structure are not tumors and make up the majority of gastric polyps (more than 85%) and are built from glands lined with pitted epithelium (Margaryan L.A.).
Polyps and stomach cancer
In the structure of precancerous diseases of the stomach, the proportion of polyps is minimal - only 1%.
Adenomas undergo malignant transformation in 6-75% of cases and in 29-59% of cases they are found in patients with stomach cancer. The most dangerous in this regard are adenomas with a diameter of more than 2 cm. A hyperplastic polyp is not a precancer. Malignancy of hyperplastic polyps occurs very rarely (1.3%). In 18–25% of patients, cancer is found next to polyps (Margaryan L.A.). An alarming symptom is the appearance of ulceration at the top of the polyp. A biopsy from an identified polyp is mandatory, since it is impossible to differentiate its structure by appearance. Hyperplastic polyps can be observed (control gastroscopy 1-2 times a year), endoscopic removal of adenomatous polyps is mandatory, followed by a thorough histological examination of the removed polyp. In the presence of large polyps, especially those with a wide base, which cannot be removed using endoscopic techniques, surgical treatment is indicated (Firsova L.D. et al.).
Localization of polyps of the upper digestive tract in children
The frequency of detection of polyps in the upper digestive tract in children, according to various sources, varies from 0.5 to almost 3%. Most often in childhood, polyps of the cardio-esophageal junction (esophageal-gastric junction, cardia of the stomach or cardia) occur. Currently, they predominate in the structure of polypoid formations of the upper digestive tract in children. Mostly in children, polyps are found in the cardiac region of the stomach. Less commonly, polyps are found in the antrum of the stomach. Then, with decreasing frequency, they are found in the esophagus, body of the stomach, postbulbar parts of the duodenum and jejunum. Unlike children, in adults the priority is the corporoantral localization of polyps. Localization of polyps in different parts of the upper digestive tract of children, according to various authors (Erdes S.I., Sergeeva T.N.):
| Shcherbakov P.L. (1997) | Saralov S.N., Volkov A.I. et al. (2002) |
| Cardio-esophageal junction – 41.3% | Cardio-esophageal transition – 55.4% |
| Antrum of the stomach – 31.7% | Antrum of the stomach – 32% |
| Middle and lower thirds of the esophagus – 15% | Esophagus – 7.8% |
| Body of stomach – 6.5% | Body of stomach – 7.8% |
| Postbulbar sections of the duodenum – 3.6% | Postbulbar sections of the duodenum – 3.6% |
| Jejunum – 1.9% |
Literature for healthcare professionals regarding gastric polyps
- Firsova L.D., Masharova A.A., Bordin D.S., Yanova O.B. Diseases of the stomach and duodenum. Ch. Polyps of the stomach and duodenum // – M: Planida. – 2011. – 52 S.
- Yesenin D.Yu. Study of long-term results of endoscopic treatment of residual polyps. Abstract of dissertation. PhD, 01/14/17 – surgery. RMAPO, Moscow, 2011.
- Margaryan L.A. Comprehensive endoscopic diagnosis of gastric polyps. Abstract of dissertation. PhD, 14.00.27 - surgery. RMAPO, Moscow, 2009.
- Kaibysheva V.O., Ivashkin V.T., Baranskaya E.K., Shifrin O.S., Pyurveeva K.V., Leonovich A.E., Sklyanskaya O.A., Sheptulin A.A. Peutz–Jeghers syndrome: review of the literature and description of our own clinical observation // RZHGGK. 2011. No. 2. P. 54–61.
- Knyazeva B.G., Romanova T.P. Gastric polyps in elderly people suffering from peptic ulcer // XV Ros. Gastroenterology Week October 12-14. RZHGGK. 2009. No. 5. P. 30.
- Erdes S.I., Sergeeva T.N. Polyps of the cardioesophageal junction in children // Pediatrics. – 2006. – No. 6. – p. 101–109.
- Novikova A.S., Kolesnikova I.Yu. Clinical and morphological features of gastric polyps // Materials of the XXIII United Russian Gastroweek. RZHGGK. 2022. T.XXVII. No. 5. adj. 50. C. 22.
- Ioffe I.V., Trotsenko S.N. Analysis of the dependence of microcirculatory parameters in the gastric mucosa on the acid-forming function in patients with gastric polyps. Kharkiv School of Surgery, 2016, 3(78):165-168.
- Novikova A.S., Kolesnikova I.Yu. Features of acid production in patients with gastric polyps. Evidence-based gastroenterology. 2020;9(1):14-18.
- Kolesnikova I.Yu., Novikova A.S. Gastric polyps and atrophic gastritis. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2021;31(2):27–33.
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Polyps”, containing publications for healthcare professionals on this topic.
Video for medical university students
Still from a video lecture for medical university students: Abdieva G.Kh. Surgical diseases of the stomach and duodenum
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Video” section there are subsections “For doctors”, containing video recordings of reports, lectures, webinars in various areas of gastroenterology for healthcare professionals and “For medical students and residents”, containing recordings of lectures and educational materials.
Gastric polyps in ICD-10
Gastric polyps, depending on the type, belong to different classes and different headings of ICD-10:
- Non-adenomatous polyps - to Class XI. “Diseases of the digestive organs (K00-K93)”, section: “K31.7 Polyp of the stomach and duodenum”
- Adenomatous - to Class II. “Neoplastic neoplasms (C00-D48)”, heading: “D13 Benign neoplasm of other and ill-defined digestive organs”, “D13.1 Stomach”
Notes
Photo licenses (see Wikimedia Commons). *GNU Free Documentation License, V.1.2, by Samir. **CC BY 2.0 by Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA. ***GNU Free Documentation License, V.1.2, by KGH. Back to section
Types of papules
Depending on the cause of appearance and accompanying symptoms, the following types of papules are distinguished:
- By quantity: single, which are located in different parts of the digestive organ in small groups.
- multiple, with many formations in one place of the organ.
- acute form, which is characterized by the appearance of defects on the walls of the organ and a reduced level of protein in the body;
- full papules located in the upper folds;
- umbilical with an elongated center;
Causes and diagnosis
Erosion of the mucous membrane can be characterized as “corrosion” of the upper layer of the organ. This pathology can be caused by many factors:
- presence of chronic liver diseases;
- vascular pathologies;
- diabetes;
- burns of the mucous membrane by chemical vapors or liquids;
- intoxication of the body;
- surgical intervention in the organ;
- frequent eating of too spicy and/or hot foods;
- poor quality of chewing food;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- entry of bile into the organ cavity;
- increased acidity of gastric juice with parallel resistance of the mucous membrane;
- long-term use of NSAIDs, antibiotics, heart medications;
- prolonged exposure to stress.
Doctors say that stomach papules do not degenerate into malignant formations, but can appear in parallel with these tumors, and also occur with inflammation in the intestines, liver failure, pneumonia and some cardiovascular diseases.
Diagnosis of gastric erosion is carried out using endoscopic examination. Gastrofagoduodenoscopy, taking a piece of tissue from the pathogenic area for further examination, as well as stool analysis for the presence of blood impurities - this option gives a complete picture of the patient’s condition and makes it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Experts note that the presence of papules and ulcers on the walls of the organ and duodenum are the cause of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract and occupy second place after gastric ulcers.
Treatment of papules
For diagnostic purposes, the patient undergoes an endoscopic examination.
First, doctors perform an endoscopy and prescribe H2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors. If pathological bacteria are found in the body that can destroy the microflora of the stomach and cause papules, the parallel use of other anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. For rapid healing of the gastric mucosa, cytoprotectors are prescribed. And also with the help of intensive radiation therapy they improve blood circulation in the organ.
It is recommended to avoid stressful situations that can lead to disruption of the functioning of the stomach and digestive tract.
Nutrition during treatment
Proper nutrition is considered mandatory in the prevention of stomach diseases. Steam dishes, excluding fatty and fried foods. I recommend eating 4-6 times a day, but in small portions. The following products are considered important components of the diet:
- oatmeal;
- jelly;
- semolina porridge;
- low-fat cheeses;
- milk;
- sour cream:
- kefir;
- steam cutlets.
The following foods should be excluded from your diet:
Sauces should be removed from the patient’s menu.
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- fried foods;
- spicy foods;
- sauces;
- citrus juices;
- strong coffee or tea.
How to treat
Papules in the stomach are also called gastroduodenal erosions. Gastroenterologists note that this disease is detected in 20% of patients undergoing endoscopic examination. Such damage to the mucous membrane of an organ is dangerous because a person may experience asymptomatic internal bleeding, which entails the development of anemia.
Hemorrhagic papules can cause severe bleeding. They are manifested by vomiting and loose stools with copious amounts of blood. In this case, the person needs emergency hospitalization and emergency assistance from specialists.
In order to exclude such manifestations, it is necessary to carry out timely diagnosis of erosive lesions. Therapy for pathology is complex and is aimed not only at removing symptoms and abnormal processes on the wall of the organ, but also at eliminating the source of the disease.
Treatment of papules in the stomach is controlled by regular diagnostics - abdominal endoscopy. If the disease is caused by Helicobacter bacteria, then antibiotics are used. In other cases, treat by blocking H2 receptors, also called histamine receptors. Cytoprotectors are used for rapid healing of erosions on the gastric mucosa. The patient may also be prescribed laser treatment for pathological areas, but this procedure is performed exclusively in a hospital.
Therapy for gastroduodenal erosions is carried out in conjunction with a strict diet. Otherwise, it will be impossible to achieve the desired result.
Prevention and prognosis
The issue of this disease is dealt with by gastroenterologists, who claim that papules occur in 20% of patients. The danger is manifested in the risk of internal bleeding. The phenomenon is asymptomatic and can often cause anemia. The disease can be treated if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner and undergoes a gastrointestinal tract examination.
To prevent the development of pathology in the stomach, doctors recommend constantly following the basics of a healthy diet and not overusing fried and smoked foods. Regular examination of the digestive system is also an important component of health. Pay attention to the appearance of the first signs of papules on the organ and go for a consultation with a gastroenterologist. Early stages of the disease are easy to treat.
What are papules in the stomach and their symptoms
The opinions of gastroenterologists regarding the fact that erosion is the primary stage of gastric ulcer are divided. Some are inclined to believe that this is true, while others argue that erosion is an independent painful form. Papules on the mucous membrane of the organ resemble round or irregular shaped ulcers and have a yellow or red tint. Such a lesion can be localized in any part of the gastrointestinal tract and affects exclusively the superficial layer of the organ, without penetrating into the tissue of the muscle plate.
Papules can be single or multiple. Symptoms of the appearance of erosive defects are:
- severe pain, which is characterized by its constancy;
- weakness, lack of appetite;
- belching, heartburn, attacks of nausea;
- in the chronic stage, gastric bleeding may occur;
- anemia;
- bloody stools.
With lesions of this type, pain is often observed at night.
Treatment of papules in the stomach is not an easy task, since in most cases they appear against the background of other diseases and therapy, which has a local effect, only temporarily heals the lesions.