Acute erosive gastritis in the acute stage: treatment
To identify the causes of complaints with which the patient consulted a doctor, we use a wide range of diagnostic methods and tools.
For this purpose, expert-class medical equipment is used (digital ultrasound machine, Japanese-made fibrogastroendoscope, etc.) and laboratory tests of blood, urine, and feces. This provides the doctor with the most detailed picture of the disease and allows one to exclude other pathologies that have similar clinical manifestations.
Drug treatment of erosive gastritis is prescribed taking into account the results of the examination, and is an individual program developed for each patient separately.
Additional methods and means of treating gastritis
When treating gastritis, it often becomes necessary to involve specialists from other fields of medicine. This is due to the fact that diseases of the gastrointestinal tract rarely go away without leaving a trace for the body as a whole, which requires treatment of complications. In addition, the disease can be triggered by factors unrelated to the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, erosive gastritis in the acute stage is often accompanied by gastric bleeding, leading to anemia, which makes it necessary to involve a hematologist in the treatment. And the cause of damage to the gastric mucosa can be allergic reactions or endocrine disorders - the area of influence of an immunologist-allergist and endocrinologist.
Medicines for gastritis and ulcers
27.02.2018
heartburn from time to time . Irritation of the mucous membranes of the stomach leads to ulcers and gastritis . How to deal with this? First, change your diet and eating habits. Secondly, work with your doctor to choose a medicine.
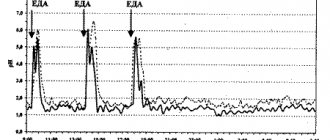
Ranitidine is an antiulcer agent. It is used for peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, reflux esophagitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus ), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum), chronic attack of gastric dyspepsia, accompanied by epigastric and chest pain, in conditions in which it is desirable reducing gastric secretion to prevent recurrent bleeding in people suffering from peptic ulcers .
Ranitidine is prescribed 150 mg 2 times a day, in the morning before meals and in the evening before bed. During the course of treatment for gastric and duodenal ulcers reflux esophagitis it is recommended to use the drug in single doses of 300 mg before bedtime. The course lasts 6–8 weeks. Maintenance therapy for the above indications - 150 ml at bedtime. For reflux esophagitis, renitidine is prescribed 150 mg 2 times a day and 300 mg at bedtime (course - 8 weeks). For Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, the initial dose of the drug is 150 mg 3 times a day, it can be increased to 600–900 mg (the dose is divided into three doses). For patients with chronic attacks of gastric dyspepsia, renitidine is prescribed 150 mg 2 times a day (course of treatment - 6 weeks). If there is a risk of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract caused by stress in seriously ill patients, and to prevent recurrent bleeding caused by peptic ulcers, it is recommended to take 150 mg 2 times a day.
When using the drug, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a malignant disease of the stomach . Ranitidine should be prescribed with caution to pregnant women and nursing mothers, as the drug crosses the placental barrier and passes into breast milk. For patients with renal failure, as well as children under 14 years of age, it is recommended to reduce the doses used. There are no absolute contraindications for the use of ranitidine.
Side effects are rare and do not require discontinuation of therapy . These include headache, dizziness , skin rash; convulsions, development of hepatitis, and thrombocytopenia are extremely rare.
Note to motorists: the presence of ranitidine metabolites in the urine gives a positive result in ICA tests for methamphetamine.
Famotidine is another effective antiulcer drug. It is prescribed for gastric and duodenal ulcers, reflux esophagitis syndrome and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Famotidine is also used to prevent the development of ulcers and as a remedy that eliminates the unpleasant consequences caused by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, 40 mg of medication is prescribed at night before bedtime or 20 mg 2 times a day (morning and evening). The duration of treatment is from 4 to 8 weeks. For preventive purposes, famotidine is taken once a day for 6 months. Dosage - 20 mg. Patients who suffer from reflux esophagitis are recommended to take the drug for 12 weeks, 20 mg 1-2 times a day.
The drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its components of the drug, during pregnancy and lactation.
When taking famotidine, numerous side effects are possible: lack of appetite, dry mouth , taste disturbances, nausea , vomiting, bloating , diarrhea or constipation headache , fatigue, tinnitus, transient mental disorders, muscle pain, joint pain , skin itching, bronchospasm, fever, acne , dry skin; in some cases - the development of cholestatic jaundice, increased levels of transaminases in the blood , rarely - arrhythmias.
For gastric ulcers , omeprazole, esomeprazole, atropine, and bismuth tripotassium dicitrate are also prescribed.
Published in Medicines Premium Clinic
Results of an application to the First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg
The priority task of our clinic’s specialists is not only to cure erosive gastritis, but also to eliminate the causes of this disease and any identified complications. This allows you to regain excellent health and quality of life that was disrupted by the disease. Using the latest advances in the field of gastroenterology allows us to guarantee the highest possible treatment results and return you to health.
“The First Family Clinic in St. Petersburg provides effective and comfortable treatment for erosive gastritis in our multidisciplinary centers. Our specialists are waiting for you in the Petrogradsky district at 16 Kamennoostrovsky Ave. (Petrogradskaya, Chkalovskaya, Gorkovskaya metro stations) and in the Primorsky district (at 36/2 Kolomyazhsky Ave. (Pionerskaya metro station) and "Specific").
To make an appointment, as well as to receive detailed information regarding the services of our clinic, call +7 (812) 300-5-300, order a call back or use the online appointment form with a doctor.
How to distinguish gastritis from gastric ulcer: main symptoms and signs
The symptoms that characterize gastritis and stomach ulcers are largely similar. However, the effectiveness of treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. It should be noted that only a medical specialist can distinguish gastritis from a peptic ulcer, and it is not so easy even for him to do this. The symptoms, as already noted, are very similar, so in some cases doctors can only assume a complication of gastritis due to the appearance of an ulcer. The final diagnosis of the patient can only be made by an experienced and qualified gastroenterologist based on the results of studies and tests. Most likely, the patient will have to undergo an X-ray of the stomach and FGDS. It is important to remember that these are not toys for boys, and diagnosing a serious condition such as a stomach ulcer should be taken very seriously.
Some patients prefer to independently determine whether they have diseases such as gastritis and stomach ulcers. For example, they try to determine the location, the source of pain. If we are talking about gastritis, then all the unpleasant sensations, as a rule, are concentrated in the epigastric area. If we are talking about a stomach ulcer, the pain is characterized as diffuse and quite sharp. Often it begins to radiate to the back or to the precordial or even iliac region. In general, the localization of pain depends solely on where exactly the so-called ulcerative defect is located.
Doctors emphasize that the so-called hunger pains that many patients experience are characteristic of both ulcers and gastritis. But it is important to pay attention to the dynamics of the appearance of such unpleasant sensations. For example, if pain begins to be felt several hours after eating, then we are most likely talking about gastritis. With a stomach ulcer, pain usually appears an hour after eating. It is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Patients experiencing such sensations prefer to neutralize them with the help of medications. Moreover, such drugs are mostly available. They are offered at the same affordable price as, for example, clutches as part of a special promotion such as the sale of women's leather bags.
There are a number of significant differences in the course of peptic ulcer disease and gastritis. With ulcers, periods of exacerbation of the disease are not uncommon - they usually occur in autumn or spring. As for gastritis, this disease does not depend on the seasonal factor - pain torments the patient both in summer and winter. The key role is played not by the time of year, but by the diet and principle of nutrition. Those who suffer from stomach ulcers often complain of pain that occurs mainly at night. Patients can eliminate discomfort only after eating. Gastritis does not interfere with nighttime rest; a person suffering from this disease usually experiences pain throughout the day.
In order to diagnose gastritis or peptic ulcer, the patient needs to take a blood test. With gastritis, the main indicators most often remain normal, but the presence of an ulcer is indicated by a low level of hemoglobin. Gastroenterologists pay attention to this. If we are talking about a stomach ulcer, then the symptoms of the disease are more pronounced than with gastritis. And if a patient notices increased heartburn or pain, or lack of effect from taking usual medications, then he should definitely consult a doctor.