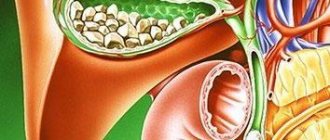
Cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts, occurring in acute or chronic form. In most cases, it occurs due to the penetration of a bacterial or parasitic infection from the intestines, gall bladder or through the circulatory system. In this case, the patient’s skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow, pain appears in the hypochondrium on the right side, and the temperature rises greatly.
The risk of this disease increases with age; most often the disease occurs in women between 50 and 60 years of age. The available statistics are due to the fact that by advanced age, people accumulate a number of past or untreated diseases (for example, gastritis, cholelithiasis, duodenitis, hepatitis, etc.), which can cause complications in the form of cholangitis.
In the international classification of diseases created by WHO (World Health Organization) to standardize medical diagnoses, various forms of cholangitis appear under several headings. The main disease code according to ICD-10 is K83.0.
Classification
The course of the disease is:
- Acute (occurs unexpectedly).
- Chronic (appears after an acute condition, either as an independent disease or as a result of complications of diseases of the digestive system).
Acute cholangitis is divided into:
- Purulent. With this pathogenesis, the liver and gallbladder are also susceptible to inflammation, since purulent cholangitis is characterized by the filling of the bile ducts with pus.
- Catarrhal. It manifests itself as swelling of the bile ducts, often ending in the formation of scars and narrowing of the ducts.
- Necrotic. It occurs as a result of pancreatic enzymes entering the bile ducts, which is accompanied by tissue death.
- Diphtheritic. The formation of ulcers and necrosis in the bile ducts leads to rotting of the walls and connective tissues of the ducts. In this case, the disease can affect neighboring organs.
Chronic cholangitis is divided into:
- Sclerosing, or, as it is also called, sclerosing cholangitis. The connective tissue in the bile ducts becomes much larger than the normal amount, resulting in narrowing of the lumen and deformation. Such growth leads to stagnation of bile and the manifestation of other related diseases.
Today, primary sclerosing cholangitis is a liver disease of unknown etiology, i.e. the causes and conditions for the appearance of new tissues are not obvious. In this regard, leading hepatology organizations around the world have established a generally accepted format and are constantly updating clinical guidelines that outline the latest methods for diagnosing and treating the disease.
PSC (primary sclerosing cholangitis) is classified as an autoimmune liver disease, including primary biliary cholangitis (liver cirrhosis) and hepatitis. Often the patient experiences cross-syndromes of these diseases.
The secondary form of SC (sclerosing cholangitis) is caused by inflammatory processes of large and small pathways located outside and inside the liver. Most often, this condition occurs as a complication of choledocholithiasis or cholangiocarcinoma, due to injury or infection of adjacent organs.
- Recurrent. The symptoms of this condition are called “Charcot’s triad”. This means that the patient has a whole combination of symptoms of multiple sclerosis, fever, jaundice, as well as pain in the upper abdomen.
- Latent. The most difficult to diagnose option, in which symptoms appear barely noticeable or are absent at all. The only signs of the disease can be itchy skin, weakness and gradual enlargement of the liver. Listen to your body and if you experience similar reactions, immediately contact qualified specialists.
- Septic lingering. A severe form of the disease, manifested, among other things, by an enlargement of the spleen, liver, and inflammation of the kidneys.
- Abscessing. This inflammation is characterized by the formation of abscesses followed by necrosis.
Complications
Approximately half of the diagnosed cases of cholangitis are uncomplicated forms that are completely treatable. 40% of diseases are accompanied by various complications, and another 10% are accompanied by multiple organ failure. Common complications of the pathology include: hepatitis, biliary cirrhosis, cholecystopancreatitis, peritonitis, liver failure and abscess, sepsis, infectious-toxic shock.
Early detection and proper treatment of pathology can prevent the development of complications. People who are concerned about the gallbladder and other abdominal organs need to undergo regular preventive examinations.
Stages and symptoms of cholangitis in adults
| Stage | Symptoms |
| I | - severe chills due to a sharp increase in body temperature, occurring once every 1-3 days; - weakness; - low blood pressure; - vomit; - pain in the upper abdomen on the right. |
| II | The above symptoms plus: - increased size and pain of the liver; - yellow skin tone (jaundice); - increase in the size of the spleen. |
| III | The worsening of the condition is characterized by: - renal failure; - increased urea and creatine in the blood; - disturbances in the functioning of the heart (arrhythmia, tachycardia, muffled groans); - development of pancreatitis. |
| IV | At the last stage of the disease there is: - more severe hepatic-renal failure; - coma. |
In the table presented, the signs of inflammation of the bile ducts are summarized and can simultaneously be suitable for different variants of the course of the disease, therefore, if you find similar manifestations in yourself, we recommend that you consult a doctor for a full diagnosis of the disease.
Diet during the acute period of cholangitis
In case of acute cholangitis, the patient is transferred to the treatment table number 5A. For chronic inflammation, you need to stick to table No. 5.
Diet No. 5. assumes compliance with the following recommendations:
- You need to eat 5 times a day, in small portions.
- Avoid eating before going to bed. Only a light snack is possible.
- Hot and spicy dishes, garlic, horseradish, and radish are prohibited. .
- The daily calorie content is 3500 kcal, where proteins account for 100 g, fats 100 g, carbohydrates 400 g.
- The menu should include products such as: buckwheat, cottage cheese, oatmeal, low-fat meat and fish.
- After you feel better, you can add vegetable and milk soups, baked and fresh vegetables, and dried bread to the menu.
Read more: Diet No. 5: food table, menu, diet principles
Diet No. 5A requires compliance with the following rules:
- You can eat any cereal, but they need to be boiled.
- Meat and fish are steamed.
- Frying as a method of cooking is prohibited.
- You should not include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Rye bread is prohibited.
- It is recommended to spend fasting days on cottage cheese and apples.
- To avoid constipation, a person should eat beets, vegetable juices, and dried fruits.
Causes of the disease
When identifying the etiology of cholangitis, the main ways of spreading the infection are identified: lymphogenous (with inflammation of the small intestine, gallbladder or pancreas), hematogenous (in other words, with blood) and migration from the duodenum.
List of bacterial infections - causative agents of inflammation:
- staphylococcus;
- Proteus;
- pale spirochete;
- typhoid bacillus;
- enterococcus;
- coli.
In the case of a parasitic infection, helminths (worms) settle in the bile ducts, the long stay of which contributes to the formation of harmful bacteria.
Cholangitis can also develop against the background of the following ailments:
- stagnation of bile;
- kinks of the bile ducts;
- toxoplasmosis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- choledocholithiasis;
- Crohn's disease;
- biliary tract cancer;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- cysts in the common bile duct;
- vasculitis;
- thyroiditis, etc.
The reason for the development of the disease in question can also be surgical intervention in adjacent organs, as a result of which the bile canaliculi were affected and damaged.
Surgical intervention
In case of ineffective drug treatment or bile outflow disorders, surgery is indicated:
- Abdominal surgery – resection (removal) of affected (purulent, dead) areas.
- Endoscopic technique. Drainage (insertion of a catheter to drain contents) of the biliary tract is performed, stenosis (narrowing) is eliminated, and stones are removed without resorting to abdominal surgery. This method allows you to avoid bleeding, reduce the risk of surgical injury, and speed up the rehabilitation (recovery) period after the manipulation.
Diagnosis of cholangitis
If symptoms indicating problems in the bile ducts are identified, the gastroenterologist prescribes a series of tests for the patient.
Stage I. Laboratory research
Includes analysis of patient biomaterials:
- Blood sampling for ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), leukocytes and neutrophils (from a finger).
- General urine analysis.
- Biochemical blood test (from a vein).
- Immunological analysis of blood serum. It is performed if primary sclerosing cholangitis is suspected.
Stage II. Instrumental examination
This type of study will allow you to classify the disease and, in accordance with the data obtained, begin treatment.
The analysis is carried out using devices:
- MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) is the main method for checking the bile ducts. It is based on the introduction of a special substance into the blood, which “highlights” the ducts during MRI scanning.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the abdominal cavity.
- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) is used for diagnosis as the main type of examination in the absence of an MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) apparatus. Unlike the first method, in this embodiment, the contrast agent is directly introduced into the duct system using a special device - a fibrogastroduodenoscope.
- PTC (percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography). The name of the method speaks for itself. A needle with a dye is inserted into the patient through the skin and liver. Then an x-ray is taken.
Based on the examinations performed, the attending physician begins to formulate a pathological diagnosis of cholangitis over time, taking into account the relationship with underlying diseases. As a result, the patient receives a detailed report.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
During the period of remission, physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed:
- UHF (high frequency electromagnetic field);
- Paraffin therapy (heat treatment using heated paraffin);
- Diathermy (use alternating current);
- Sodium chloride baths (mineral waters);
- Electrophoresis (exposure to electrical impulses);
- Inductothermy (use of high frequency magnetic field);
- Mud applications (heated therapeutic mud is used);
- Microwave therapy (exposure to an electromagnetic field, fluctuations in the microwave range);
- Ozokerite therapy (thermal treatment using medical heated ozokerite - an oil substance with a waxy consistency).
Treatment of cholangitis in adults
Depending on the extent and causes of the disease, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
| Basics of conservative treatment | Surgical operations |
|
|
Note! Advanced stages of the inflammatory process under consideration cannot be treated conservatively, because the ducts of the system are severely deformed.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis of the disease depends on many factors, ranging from the patient’s age to previous diseases and characteristics of the body.
Clearly, inflammation of the biliary tract is a serious disease that requires complete diagnosis and treatment. It is worth remembering that an incompletely cured disease will develop into a chronic form, in which the outcome is often unsatisfactory, since recovery is extremely difficult to achieve.
It is strongly not recommended to self-medicate, even with mild catarrhal form. Experienced doctors will be able to prescribe effective treatment and achieve a positive result in a short time.
The best remedy against cholangitis is prevention, because preventing the disease is easier than eliminating its consequences.
The following actions are recommended for those who have not encountered this problem or do not want to provoke relapses:
- Healthy food;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- walk in the fresh air more often;
- engage in physical education;
- periodically undergo examination by a gastroenterologist;
- promptly treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys.
Drug treatment
As mentioned above, drugs are widely used that reduce pain, eliminate infection and promote rapid recovery of the body.
The most popular drugs are:
- Meverin. The product has an antispasmodic effect. Used for symptomatic treatment of pain syndrome. The product is strong, so it is enough to use one capsule every 12 hours. To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to use it 20 minutes before eating. Contraindications: children under 15 years of age, pregnancy, hypersensitivity. Side effects: none noted.
- Drotaverine. The drug has an antispasmodic effect. It allows you to relieve pain and improve the patient's condition. It is necessary to use the product 1-2 tablets, 2-3 times a day. It all depends on the intensity of the pain syndrome. The duration of treatment is individual. People with hypersensitivity, pregnant women, and patients with liver and kidney failure should not take the medication. Side effects: tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, headache.
- Ademeteonine. The drug has hepatoprotective (protects liver tissue) activity. It allows you to protect the liver from negative effects on it. You need to take the drug 400-800 mg per day. Maintenance therapy – 2-3 tablets per day. The duration of treatment is determined individually. Contraindications: hypersensitivity. Side effects: pain behind the sternum, in the abdomen.
- Albendazole. The drug is used to remove parasites from the body. 400 mg per day is enough to actively eliminate the problem. In general, the dose is prescribed individually. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, hypersensitivity and children under 2 years of age. Adverse reactions: dizziness, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, impaired renal function.
- Rifampicin. In the last decade, it has been widely used to relieve itching in patients with cholangitis. It is able to increase the activity of liver microsomal enzymes. Thus, the sulfoxidation of di- and monohydroxy bile acids is accelerated. It is recommended to take 10 mg per kilogram of weight. The course of treatment is long and lasts for several months. It all depends on the condition of the patient himself. Use during pregnancy, childhood and breastfeeding is not recommended.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid. It can significantly reduce itching and reduce the amount of toxic bile acids formed. 15-20 mg per kilogram of weight is prescribed daily. The maximum dosage should not exceed 1200 mg per day. Contraindications include pregnancy, hypersensitivity and breastfeeding. Adverse reactions in the form of nausea, vomiting, and increased symptoms are possible.
- Cholestyramine. This drug has an affinity for bile acids. It is able to bind them in the form of a strong complex in the intestines. The medication is excreted along with feces, which significantly reduces skin itching. Every day it is enough to use one teaspoon of the drug 3 times a day. It is advisable to do this 40 minutes before eating, or the same time after eating it. The course of treatment may vary depending on the person's condition. The minimum is one month. The drug is used in reduced doses. It can cause poor absorption of vitamins and calcium. Pregnant women should not take it. A similar requirement is made for people with increased hypersensitivity. Adverse reactions: nausea, vomiting, intestinal disorders.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to suppress infection. These include Metronidazole, Tetracycline and Levomecitin. You can take them for no more than 2 weeks in an individual dosage.
- Tetracycline. This drug has a bacteriostatic effect. It should be used at a dose of 200-250 mg 2-3 times a day. For children, 20-25 mg/kg is enough. The duration of treatment is determined individually. Contraindications: hypersensitivity, pregnancy, lactation, impaired liver and kidney function. Side effects: skin pigmentation, inflammation of the mucous membranes, dysbacteriosis, allergic reactions. Usually the drug is well tolerated.
- Metronidazole. This is an antimicrobial drug. Take it one tablet 2-3 times a day. In special cases, the dosage is increased to 4-5 tablets. You should not make adjustments yourself; the product has a number of side effects. Thus, nausea, vomiting, weakness, a metallic taste in the mouth, and dizziness are possible. If symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. Contraindications: pregnancy, childhood, hypersensitivity and breastfeeding.
- Levomecitin. The medication actively destroys bacteria. It should be used at a dose of 250-500 mg 3-4 times a day. The daily dose should not exceed 2 grams. The nature of the treatment and dosage are prescribed by the attending physician. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation, psoriasis, eczema, hypersensitivity. Side effects: anemia, nausea, vomiting, fever, allergic reactions.
It is also worth immediately noting that if you have such a disease, you should not resort to the help of traditional medicine. After all, while a person chooses the optimal treatment for himself, the pathology will begin to progress.