It turns out that paraproctitis, an inflammation of the tissue surrounding the lower rectum, most often occurs in children under the age of 6 months.
Unfortunately, this is precisely the age when the child cannot yet say or even show what is bothering him. At the same time, paraproctitis (the concept is derived from the words para - next, proctos - rectum) is a rather dangerous disease even for adults. With paraproctitis, a purulent focus forms near the rectum, which can cause severe intoxication, fever in the child, and if left untreated, even break out. If an abscess located next to the rectum breaks into the intestinal cavity, a fistula is formed, which may require long-term treatment. If the abscess breaks into the pelvic cavity, then the inflammation can spread all the way to the abdominal cavity with the development of peritonitis.
What is the treatment for paraproctitis?
Treatment of paraproctitis involves making an incision in the skin near the anus to remove pus from the infected cavity and reduce the pressure inside it. Quite often this can be done on an outpatient basis using local anesthesia. Treatment of large or deep abscesses may require hospitalization in a specialized hospital that can provide adequate pain relief during surgery. Hospitalization is indicated for patients with a tendency to serious infectious complications (patients with diabetes mellitus and decreased immunity). Conservative (non-surgical) treatment with antibiotics alone is not as effective as drainage (removing pus). This is due to the fact that antibiotics cannot penetrate the abscess cavity and act on the purulent contents located there.
Symptoms:
- acute pain in the anus;
- swelling and hardness in the anus and/or buttocks;
- deformation of the anus;
- fever, chills;
- headache;
- restlessness or lethargy, loss of appetite;
- the pain increases with bowel movements and when touched.
In some forms of paraproctitis, urinary disturbances, a blurred clinical picture, and even the absence of primary symptoms are possible. When the abscess ruptures, pus is released.
Diagnostic methods
External manifestations of the inflammatory process during paraproctitis are hidden under the skin, so only a specialist can recognize them. The child's blood and urine are immediately taken for analysis: leukocytosis is detected in the blood.
If pus is released, a small amount is sent for bacteriological examination: the pathogen is identified and its sensitivity to antibiotics is assessed. To clarify the size and localization of the inflammatory focus, X-ray, ultrasound and endoscopic examination are performed.
What is the treatment for rectal fistula?
Treatment of rectal fistula is only surgical. Despite the fact that many options for surgical treatment of rectal fistulas have been developed, the likelihood of complications remains quite high. Therefore, it is preferable that the operation be performed by a coloproctologist (colorectal surgeon). Simultaneous treatment of fistula and paraproctitis is possible, although usually the fistula develops in the period from 4 to 6 weeks after drainage of the abscess, in some cases it can occur months and years later. The main principle of surgical treatment of rectal fistulas is the opening of the fistula tract. This is often accompanied by excision of a small portion of the anal sphincter, i.e. muscle that controls stool retention. Connecting the internal and external openings, opening the fistula tract and transforming it into an open state allows for rapid healing of the resulting wound in the direction from the bottom to the edges. Often, surgical treatment of rectal fistulas can be performed on an outpatient basis. However, treatment of deep or widespread fistulas may require hospitalization.
Why you should contact us
We have been working since 2002 - our services are trusted and consistently in high demand among patients. We provide written guarantees. We provide high-quality therapy - paraproctitis in children is treated by highly qualified doctors, professors and academicians, candidates and doctors of medical sciences. If necessary, we quickly gather consultations - the clinic employs 850 multidisciplinary specialists.
We have our own laboratory, so we do tests quickly on site. Equipped with innovative equipment - it allows you to carry out procedures delicately, painlessly, safely, accurately and quickly.
We have a convenient work schedule - we accept appointments every day, including holidays and weekends. It’s convenient to get to us - our 4 clinics are located in different areas of the city.
To make high-quality children's proctology more accessible, there is a discount system for patients and discount promotions are held. For more information, call us at the number provided 24 hours a day.
How long does the healing process take?
In the first week after surgical treatment of a fistula, the patient may experience moderate pain, which can be controlled with painkillers. The period of forced disability is minimal. After surgical treatment of a fistula or paraproctitis, a period of follow-up treatment at home is necessary using sitz baths 3-4 times a day. It is recommended to add dietary fiber or laxatives to the diet. To prevent contamination of underwear, you can use gauze bandages or pads. Normal stool has no effect on wound healing.
What it is
Paraproctitis is an inflammatory process of the tissue around the rectum. Among children, the disease is most common in infants under six months of age (almost 70% of all cases). In 20% of cases, paraproctitis is diagnosed in children aged from six months to a year, and only in the remaining cases, that is, extremely rarely, in older children.
Fact. According to statistics, the tissue around the rectum becomes inflamed more often in boys than in girls, which is associated with the structure of the organs of the genitourinary system.
To understand where the inflammatory process appears and how it proceeds, it is necessary to take into account the structural features of the rectum and organs in the pelvic cavity. The rectum contains several spaces around itself - ileo-rectal, pelvic-rectal, retrorectal, submucosal. The inflammatory process can begin in one of them or in several at once.
Types of paraproctitis
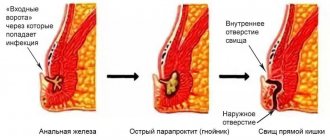
When the tissue - the fatty tissue located around the rectum - becomes infected, it separates from the healthy tissue, which is the beginning of the development of an abscess. If treatment is started during this period, the inflammatory process can be stopped; if not, the formed abscess or abscess opens, and a fistula tract appears. It leads either to the subcutaneous tissue or to the surface of the skin. Then paraproctitis becomes chronic.
There are several forms of pathology, depending on the location of the abscess:
- subcutaneous;
- submucosal;
- retrorectal;
- ischiorectal;
- pelvic-rectal.
What are the reasons for the development of paraproctitis in children?
In principle, they do not differ from the causes of this disease in adults. Paraproctitis occurs when bacteria enter the tissue that surrounds the rectum through the anal glands (glands located in the final part of the rectum), damaged rectal mucosa or damaged skin. However, in newborns and young children, the skin next to the rectum and the mucous membrane itself lining the intestine from the inside are much more vulnerable and can be easily injured - which, for example, can happen with constipation. In addition, in a small child, one should not forget about such a factor as maceration of the skin (violation of its integrity), which occurs, among other things, with diaper rash, frequent loose stools, constant wearing of diapers and simply violation of hygiene rules. For example, when the rectal area is contaminated with feces, the child is rarely washed, or the use of aggressive cosmetics for washing.
Over the course of a year, several dozen children are operated on for paraproctitis in Yekaterinburg. Moreover, their number is growing every year. During 2012 alone, 84 children were operated on in the purulent surgery department of the Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 9 (children over 6 months old are operated on here) and in the neonatal surgery department of the Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1. For comparison, in 2008, 51 patients with this disease were treated in both departments.
Why do young children suffer from paraproctitis?
In infants and adults, the disease is provoked by the same factors. Initially, the infection affects the rectal sinuses (crypts) or glands. Then the acute inflammatory process spreads to the cells of the anal area. Next, the damaged tissue begins to peel off from the healthy tissue, which contributes to the formation of an abscess (abscess).
In the absence of timely treatment, the abscess can spontaneously open either outward or into the subcutaneous tissue, resulting in the formation of a fistula.
Paraproctitis in a child
Factors contributing to the appearance of paraproctitis in newborns:
- In adults, the disease is caused by E. coli, in children - by staphylococci.
- Irregular structure of the anal glands.
- Frequent stools, which is typical for newborns.
- Obstipation is a common phenomenon in children under one year of age.
- Imperfect immune system.
- Presence of anal fissures.
- Transmission of respiratory diseases.
It is worth emphasizing that any infectious agents present in the baby’s body, for example, the presence of tonsillitis or sinusitis, can also provoke the disease. However, the most common cause of pathology is intestinal bacteria.
Provoking factors
Newborn babies have very delicate skin, and their mucous membranes are thin and easily wounded.
Therefore, if diapers are used incorrectly, with constipation, diarrhea and injuries, this disease can occur. Very minor abrasions and abrasions often become infected, and the inflammatory process cannot be avoided.
Even passing parts of dense feces or frequent and strong straining can cause paraproctitis; the disease is most often diagnosed in infants from birth to six months of age.
It's really very dangerous
If a spontaneous breakthrough of the lesion occurs, incomplete fistulas may form in the rectal or perineal region. It happens that the fistula can pass through the sphincter.
For infants, acute pelvic-rectal paraproctitis can develop into the initial form of sepsis, which is characterized by:
- there is sharp pain on palpation;
- the temperature rises to 40⁰ C;
- the baby does not respond to toys and words, he is lethargic and inactive;
- there are problems in the functioning of the heart;
- Frequent vomiting begins, which indicates the onset of general toxicosis.
The most dangerous complication of paraproctitis in young children is its anaerobic form, which is quite rare.
With this disease, there is a sharp deterioration in the general condition of the baby. The inflammatory process develops very quickly. This can lead to significant damage to the walls of the rectum.
Reviews
Svetlana immediately noticed the first symptoms of a deterioration in the child’s condition: he became capricious, slept all the time, but often woke up and cried. The scream was especially loud when he went to the toilet. Once again, while changing the diaper, I noticed that the skin around the anus was red and some kind of lump was visible. On the same day we went to the doctor, it turned out to be paraproctitis. At first I was shocked to learn that surgery was needed. Fortunately, we asked for help in time, so everything went well.
Antonina When my son was 3 months old, we were diagnosed with paraproctitis. I went to the doctor because I didn’t know what to do with the high fever. We were immediately taken to the hospital and examined. The doctor explained that the best option was surgery and excision of the abscess. I agreed. The period after the operation was difficult, constant dressings, crying, but I am glad that I did not delay treatment. Now my son is absolutely healthy.
Olga At the age of two and a half weeks, we were diagnosed with acute purulent paraproctitis. The doctor warned about the danger of delay, so the very next day we had an operation to excise the abscess. The baby woke up from anesthesia half an hour after the end of the operation, he was a little lethargic and capricious, but I was preparing for the worst. Three days later we were discharged home, and for several more weeks we underwent the necessary procedures. Overall, I think the operation was successful and the results were worth it.
Irina I know firsthand what childhood paraproctitis is. My son had his first operation to remove an abscess when he was 4 months old; he barely recovered from it and spent more than a week in the hospital. There were constant dressings, antibiotics were administered through a catheter. Six months later there was a relapse and I had to go through everything again. Immediately after the operation, we took an immunogram and underwent a comprehensive examination. We started strengthening the immune system and fighting the detected staphylococcus and dysbacteriosis. I hope we won't face any further infection.
Forecasts
Paraproctitis is not a deadly disease, but some of its consequences can pose a threat to the life of a child. With early diagnosis, the disease can be completely cured.
If the pathological process was detected late and complications arose, the duration of the course of therapy may increase several times. Surgical procedures help eliminate the consequences of paraproctitis. The prognosis for this disease is favorable in most cases.
Unfavorable prognosis is possible if the following factors are present:
- acquisition of a chronic form of paraproctitis;
- breakthrough of an abscess into the pelvic organs.
How is intestinal dolichosigma treated in a child? Find out the answer right now.
Treatment of acute forms of the disease
Treatment of children with acute paraproctitis is carried out only in a medical institution.
The early stage of the disease is characterized by the use of conservative therapy, which includes the following procedures:
- antibiotics are prescribed;
- microenemas are made with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula);
- methods of physiotherapeutic treatment are applied;
- It is recommended to take baths with warm water;
- strict adherence to hygiene and regime.
If a subcutaneous type of paraproctitis is diagnosed, then the general condition of the baby changes slightly.
There is a slight increase in temperature. The child begins to be capricious for no reason. There is swelling on the skin near the anus. Palpation allows you to feel a dense tumor in the form of a ball; when pressed, it is painful.
If there is an abscess or several, the best and most effective is surgical intervention. To do this, use an enema to free the intestines from feces.
The operation is performed using a special anesthesia; local anesthesia is added to the general one. At the next stage of the operation, a percutaneous puncture of the area where the abscess is located is performed.
The resulting pus is taken for analysis, and the wound is washed with an antibiotic. This helps get rid of further infection of the intestinal walls.
Important in treatment is the identification of the purulent tract, with the help of which pus from the perisphincteric space enters distant areas. This stage helps to make the right choice when performing an operation.
In this case, purulent masses from the intermuscular area can penetrate into another part of the cellular space. To determine the position of the stroke, ultrasound or probing is used.
Etiology and mechanisms of development
In childhood, paraproctitis has some features that distinguish the disease from the pathological process occurring in the adult body.
In the first case , monomicrobial flora is sown, in the second - mixed microbial flora .
The inflammatory process develops gradually.
To begin its formation, there must be trauma to the mucous membranes or stagnation of feces. The formation of obstruction of the duct becomes the cause of a retention growth, after opening of which the infection enters the perianal region.
The mechanism of development of the disease occurs in the following stages:
- Opening the retention growth.
- Spread of purulent masses throughout neighboring organs and systems.
- Formation of acute paraproctitis.
Complications and prevention
Among the possible complications of paraproctitis, the most common consequences are:
- involuntary opening of the abscess;
- the destructive effect of pus on the rectum;
- damage to the pelvic tissue;
- melting of the walls of the urethra and rectum;
- breakthrough of an abscess in the abdominal cavity;
- development of pancreatitis.
In especially severe cases, if left untreated for a long time, death can occur.
Prevention of paraproctitis in children includes compliance with the following simple rules by parents:
- keep an eye on your baby's stool;
- do not ignore constipation, contact a specialist;
- wash your child after each bowel movement;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- use high-quality diapers;
- eliminate diaper rash in a timely manner;
- Have regular routine check-ups with your pediatrician.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with palpation of the affected area. If the doctor suspects the presence of paraproctitis, the child is sent for instrumental examination to confirm the diagnosis. Some diagnostic methods are accompanied by painful sensations, so the attending physician himself chooses how to examine the little patient.
Why does a child have a stomach ache near the navel?
Typically diagnosis includes:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood chemistry;
- rectal probing;
- rectal ultrasound;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray.