The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Determining the causes of nonspecific pain is a serious task for neurologists, surgeons, obstetricians, gynecologists, traumatologists, orthopedists and specialists in other medical fields. Diseases accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen are difficult to diagnose and can pose a serious danger to the patient's health.
Causes of pain in the right side of the lower abdomen
Despite the obviousness of the sensations, this is a difficult problem in diagnosing acute and chronic diseases in the pelvic area.
The pain is manifested by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen (including on the right side) and can be combined with pain in the projections of the body located in:
- suprapubic, inguinal area;
- male genital organ;
- clitoris, vagina, uterus;
- urethra;
- back, lower back;
- buttocks, intestines.
The complexity of the problem is that a chronic pain impulse under the influence of various reasons can be formed in the central nervous system in the absence of a focus in the internal organs. Therefore, even the most modern medical studies often do not detect pathological changes.
However, let’s leave it to doctors to solve the complex problems of diagnosing nonspecific pain. Instead, we will focus on the obvious causes of pain to the extent that it is useful for the use of knowledge by a wide range of readers in order to prevent the causes of pain and timely access to a medical institution.
Common causes of pain in the lower abdomen are associated with irritation of sensory receptors:
- internal organs of the small pelvis of the right half of the body;
- the right hip joint, as well as the bones, vessels and lymph nodes of the right leg.
Organs partially or completely located in the pelvic area, including departments:
- digestion (part of the small intestine, liver, its ducts, pancreas, large intestine, including the appendix and anal area);
- urinary system, paired organs (kidneys, ureters), unpaired (bladder, urethra);
- female reproductive system (uterus, ovaries, oviducts, birth canal, vulva, clitoris);
- male reproductive system (testicles enclosed in the scrotum, spermatic cords, male genital organ).
Outside the human abdominal cavity, pain in the right side of the lower abdomen can be caused by diseases:
- right hip joint, including those involving bone, cartilage tissue, blood vessels, nerve fibers, ligaments and muscles in the pathogenesis;
- bones of the lower back, sacrum, coccyx, right femur, including those involving nerves, vessels, ligaments and muscles surrounding the bone tissue in the pathogenesis.
Pain radiating or reflected to the right side and lower abdomen from organs that are not anatomically related to the pelvic organs are not considered in this article.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Mild pain in the right side associated with hypothermia or physical activity does not require drug treatment. Mostly they go away on their own after 1-3 days. If the pain syndrome bothers you for a long time or the intensity of the pain increases quickly, you should immediately seek medical help. For excruciating pain, the doctor uses analgesics at the prehospital stage.
Conservative therapy
To relieve pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, narcotic analgesics, and antispasmodics are used in practical medicine. For quick pain relief, blockades are made with local anesthetics. These measures provide a temporary effect, so subsequently, to eliminate pain in the right side, etiotropic therapy is prescribed that affects the underlying disease. The following groups of medications are used in surgery and gastroenterology:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammation is controlled not only by classic NSAIDs, but also by 5-aminosalicylic acid derivatives and corticosteroid hormones. - Probiotics.
Medicines are needed to restore microflora and normal intestinal function, which helps reduce pain and eliminate dyspeptic disorders. - Infusion solutions.
Necessary for correcting dehydration of the body, removing toxic breakdown products from the blood, maintaining normal hemodynamic parameters. - Antibiotics.
The drugs are prescribed for generalized forms of salmonellosis, for the prevention of purulent complications of inflammatory diseases of the digestive organs. - Cytostatics.
Taken for severe forms of Crohn's disease when hormonal therapy is ineffective. They are also included in chemotherapy regimens used for malignant neoplasia of the colon.
To improve the patient's condition, symptomatic therapy is carried out. Antidiarrheal or laxative drugs, drugs with pancreatic enzymes, and prokinetics are selected. In order to correct metabolic processes, vitamin and mineral complexes containing iron are indicated. During the recovery period of chronic diseases, courses of physiotherapy, drinking mineral waters, and sanatorium-resort treatment are recommended.
Surgery
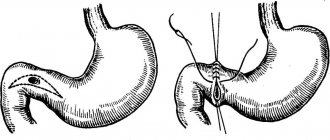
Urgent surgical intervention is performed for acute appendicitis (laparoscopic or classic appendectomy), strangulated hernia (revision of abdominal organs and hernioplasty). When fistulas and abscesses form in those suffering from Crohn's disease, their opening and sanitation is indicated. If total damage to all layers of the intestinal wall develops, the operation of choice is resection of the intestinal section.
If an ectopic pregnancy is interrupted, urgent surgical care is required. The type of operation is selected taking into account the severity of complications and the woman’s desire to have children in the future. An organ-sparing tubotomy or radical tubectomy is performed. When an ovarian cyst ruptures, a wedge resection or oophorectomy is performed. Some forms of endometriosis require elective surgical treatment.
Diagnosis of pain in the right side of the lower abdomen
Such pain, always nonspecific, accompanies numerous diseases and physiological abnormalities. They are usually combined with other symptoms that indicate the underlying cause of the disease.
- Intestinal diseases
- Kidney and bladder diseases
- Diseases of the genital organs in men
- Gynecology and cycle disorders
- Diseases of blood vessels and lymph
Intestinal diseases
The most obvious pain in the lower right side, or more precisely, in the iliac region, in the groin and in the navel area, is the pain of appendicitis. Details (see here).
The main diseases that can be combined with pain in the right side of the lower abdomen:
- Intestinal diverticulosis is a protrusion of the intestinal walls. The symptoms resemble those of appendicitis. Therefore, during surgery on the appendix, an inspection of the intestine is usually performed to exclude this pathology. The contents of the intestine accumulate in the diverticulum pocket, irritating the nerve endings and causing pain in the right lower abdomen. In severe cases, the pathology is combined with intoxication. In addition to pain, weakness, fever, constipation or diarrhea, and vomiting are detected.
- Intestinal blockage. When intestinal volvulus occurs, the pathogenesis is characterized by rapid development. This occurs due to the cessation of blood flow and disruption of the innervation of the intestinal walls. With mechanical blockage of the intestine (foreign bodies), peristalsis stops and severe pain is observed, radiating to the right side of the groin. It can be combined with vomiting after eating, with the absence of peristaltic sounds and with the expansion of the lumen of the intestinal loops.
- Duodenitis. Inflammation of the duodenum and small intestine is accompanied by pain, radiating, among other things, to the right side. Pain is projected onto the lower abdomen when the intestinal loops located closer to the right side of the body are predominantly affected. The pain is combined with signs of indigestion.
- Inguinal hernia. Pathology is classified as a surgical disease. A hernia is a combination of two factors: rupture of the internal layers of the abdominal wall and prolapse of the omentum and intestinal loops into the subcutaneous space. The integrity of the skin during hernias is not compromised. A hernia manifests itself as a sac-like protrusion of skin in the groin. If upon palpation it is possible to push the contents of the hernial sac inward, this is a reducible hernia. If it is impossible to reduce, it is a strangulated hernia. A strangulated hernia is dangerous. The intestinal loops, omentum with vessels and nerve fibers swell and swell. Their volume exceeds the diameter of the hernial ring. The pain intensifies with physical activity. Diagnosis is not difficult. Treatment is surgery to suturing the hernial ring.
- Liver diseases. The early stages of hepatitis are not characterized by a painful reaction. Pain develops in the later stages of inflammation. In severe cases, excruciating pain appears in the right lower abdomen; pathogenesis is accompanied by total damage to the organ (cirrhosis of the liver) and biliary tract (cholecystitis). The pain may go down to the groin area on the right side.
- Lesions of the rectum are manifested by pain radiating to the groin.
- Adhesions of the serous membranes of internal organs. In case of damage to the nerve fibers in the lower abdomen on the right, pain appears in the indicated area. The causes of adhesions are postoperative complications, congenital or acquired pathologies without previous surgical intervention.
Kidney and bladder diseases
Pain syndrome in different parts of the body, including the right (with right-sided lesions) in the lower abdomen.
Pain due to impaired urine production
Pain occurs when the kidneys lose their ability to produce urine, filter and absorb purified blood back into the bloodstream. Pain syndrome accompanies inflammation of the parenchyma, renal glomeruli, pelvis and cavities, as well as degenerative, dystrophic and oncological diseases of the kidneys. The pain develops over a short time and often cannot be relieved even with strong painkillers.
Pain due to urinary obstruction
Pain develops when an obstruction forms along the urethra and when it is impossible to remove urine outside the body. Pathological processes are more severe in men due to the narrow and long urethra. However, diseases in the ureters are more often detected in women due to the greater likelihood of inflammation of the female genital organs.
Painful urge to urinate is characteristic of the following diseases:
- Acute dilatation of the bladder. The reason is blockage of the urethral canal with urinary stones or an inflamed prostate (in men). It manifests itself as an ineffective urge to urinate.
- Blockage and inflammation of the ureter. Paired ureters connect the kidneys to the bladder. Pain in the groin on the right should be expected when urine stops in the distal (lower) part of the right ureter. The pain appears suddenly and intensifies very quickly with stagnation of urine. Various methods are used for treatment, including crushing stones with ultrasound and their surgical removal.
- Inflammation of the urethra – urethritis. Both men and women get sick. In men, the disease occurs with more serious consequences. Initially, the pathology manifests itself as a burning sensation and pain when urinating. Pain on the right in the groin area occurs when the right inguinal lymph node is involved in the inflammatory process.
Diseases of the genital organs in men
Pain is caused by inflammatory processes, injuries or infections of the genital organs. General symptoms of pain syndrome are nagging pain in the scrotum, radiating to the groin.
When the right lymph node is involved in the pathogenesis, the pain shifts to the corresponding area of the body:
- Orchitis – inflammation of the testicles;
- Inflammation of the male penis, including balanitis - inflammation of the glans, and posthitis - inflammation of the foreskin;
- Vesiculitis is a lesion of the seminal vesicles. The testes are paired organs that are located above the prostate;
- Epididymitis – inflammation of the testicular appendages;
- Cavernitis is inflammation of the cavernous bodies of the male penis;
- Prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland;
- Colliculitis is inflammation of the seminal tubercle.
Cycle disorders in women and gynecological diseases
Women have a more complex structure of the genital organs and a special physiology than men. This determines the frequent manifestation of pain in the pelvic area in the lower abdomen, including on the right. Cycle disorders are also almost always accompanied by pain.
Pain due to cycle disorders
Pain is not always associated with obvious pathologies. Painful cycles are typical for girls and young nulliparous women. In some cases, pain is a consequence of infections and colds of the pelvic organs.
- Menstrual pain – algomenorrhea. There is an increased flow of blood to the pelvic organs, followed by stagnation and accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity. Pain in the absence of signs of inflammation is primary algomenorrhea. Menstrual pain can be a consequence of gynecological inflammation and genital infections (secondary algomenorrhea). If bleeding is irregular and accompanied by pain, this condition is called algodismenorrhea. Pain in the lower abdomen often radiates to the groin and thigh, is accompanied by dizziness and blurred vision, and intensifies during sexual intercourse. When there are layers of gynecological pathologies, pain is accompanied by pathological vaginal discharge.
Obstetric pathologies
In some cases, pain is the cause of serious problems that threaten pregnancy and the woman’s health:
- Pain during pregnancy. Physiological pain that occurs for a short time due to intense hormonal changes, increased blood flow to the uterus, fetal growth and stretching of the ligaments that hold the uterus in the abdominal cavity. Such pain is usually not intense and occurs periodically. But pathological obstetric pain can be a sign of spontaneous abortion or ectopic pregnancy.
- Pain during spontaneous abortion. Pathology develops in the early stages of pregnancy. There are several stages of spontaneous abortion: threatened abortion and actual abortion (complete, partial). The pain is combined with vaginal bleeding of varying intensity. Cramping pain in the lower abdomen can radiate to the right when the corresponding pain receptors are irritated. With large blood losses and infection of the birth canal with pathogenic microflora, a state of intoxication develops that threatens the life of the mother and fetus.
- Pain during premature labor. Occurs in late pregnancy during the period from 28 to 37 weeks of gestation. The pain is combined with manifestations of toxicosis in a pregnant woman. To avoid complications, you should urgently contact a medical institution to provide qualified obstetric care.
- Pain during ectopic pregnancy. This is a condition when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity. When the embryo develops outside the uterus, compression of the vessels and walls of the fallopian tubes occurs, and there is a threat of rupture of the walls of the fallopian tubes and vessels on which the fertilized egg is attached. Emergency surgery is required.
Pain due to gynecological diseases
Characteristic of young women during or after previous sexually transmitted infections or hypothermia.
In old age, diseases occur due to hormonal imbalances:
- Salpingitis. In the context of our article, this is inflammation of the right fallopian (uterine) tube. There are mechanical causes of inflammation (injuries after the consequences of abortion, childbirth and other medical procedures) and microbial causes (genital infections). Pain in the lower abdomen on the right is usually accompanied by an increase in temperature. The pain increases with urination, physical activity and sexual intercourse.
- Adnexitis is inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. The disease usually occurs in girls and young women, sometimes it is unilateral (right-sided and left-sided adnexitis). This disease is also called “salpingoophoritis”.
- An ovarian cyst is a protrusion of an ovary. A vesicle is formed on the ovary, filled with transparent or translucent contents, as a result the ovary enlarges. The causes of cyst formation are hormonal disorders. Ovarian cysts manifest themselves as unilateral pain in the lower abdomen. Some types of cysts disappear on their own. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
- Apoplexy of the ovary. Rupture of an ovarian cyst is apoplexy, accompanied by internal bleeding. Occurs when a very large cyst forms, with excessive stretching of the ovarian walls, after physical exertion. It manifests itself as pain reminiscent of appendicitis. Sometimes the pain radiates to the anus, to the right side of the lower abdomen or to the thigh. Apoplexy usually occurs during the period of ovulation. Urgent surgery is indicated.
- Endometriosis. A gynecological disease of a non-inflammatory nature, which is characterized by increased proliferation of the mucous membranes of the uterus. The pathology is accompanied by changes in hormonal levels and increased bleeding. Endometriosis can develop in the genital area or outside of it, such as in the intestines. The disease manifests itself as pelvic pain in the lower abdomen on the right side, accompanied by prolongation of menstrual bleeding and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Endometritis. Inflammation of the superficial layers of the walls of the uterus. In some cases, deep layers are involved in the pathological process - endomyometritis. The main reasons are sexually transmitted infections, hypothermia, hormonal disorders. In severe cases, endometritis can result in purulent inflammation and accumulation of exudate in the uterus (pyometra). Endometritis manifests itself as pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes on the right. Additional symptoms are fever, signs of intoxication, vaginal discharge.
Diseases of blood vessels and lymph nodes
Blood vessels and the lymphatic system permeate the human body and nourish, among other things, the abdominal organs and legs.
Pain due to diseases of the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are formed at the junction of blood vessels. The most well-known to the average reader are the submandibular lymph nodes, which enlarge and respond with pain due to inflammation in the throat and mouth.
Accordingly, the inguinal lymph nodes enlarge with inflammation of the pelvic organs. There is right-sided inguinal lymphadenitis. The lymphatic system performs protective functions in the body. Pathogens recognized by lymphocytes are attacked, neutralized and removed from the body. During a massive attack, lymphocytes cannot cope with their functions, and inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs.
- Lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph node, in this case the inguinal one. It can develop on one or both sides, for example on the right side. Right-sided inflammation of the node is accompanied by its enlargement, manifests itself in the form of a painful, strictly limited swelling, and is often accompanied by pain on the right side of the lower abdomen. Sometimes this is accompanied by intoxication and increased body temperature.
Pain due to venous diseases
Pain syndrome accompanies pathological dilation of the veins in the pelvis. As a result, the outflow of blood from the tissues of the abdominal wall and pelvic organs is disrupted.
- Varicose veins of the small pelvis are typical for young women and girls. The main reason is stagnation of blood in the pelvic vessels, which develops during hormonal changes in the body, including puberty and pregnancy. In the first stages, the disease may be asymptomatic or with periodic pain before or after menstruation. Subsequently, persistent pain develops, usually in the lower abdomen, maybe on the right. Differential diagnosis is based on the use of instrumental visualization methods of pelvic blood vessels.
Pain due to lesions of the femoral artery
(aneurysm, femoral artery thrombosis, vasculitis - inflammation). The femoral artery supplies blood to the anterior abdominal wall, the genital area and groin, and the muscles of the lower extremities:
- An aneurysm is a separation of the inner walls of an artery and the formation of a sac-like protrusion on it. Below the site of the aneurysm, signs of blood supply deficiency develop, and above - blood stagnation. Characterized by severe pain, including in the groin area on the right.
- Vascular thrombosis. Similar phenomena occur following stenosis - narrowing or thrombosis of the lumen of an artery or its branches at the site of formation of cholesterol plaques.
Pain due to diseases of the hip joint
The pain often radiates to the groin area.
The main diseases of the hip joint, in which unilateral pain is possible:
- Coxarthrosis is arthrosis of the hip joint (right side of the body). This is a disease of a degenerative-dystrophic nature, which affects people mainly in the older age group. The disease is very common, since the hip joint bears the main load when a person moves. Inflammation is a secondary process and develops when a microbial factor is involved in the pathogenesis. One of the symptoms of coxarthrosis is pain radiating to the groin, which is necessarily combined with lameness and reduced joint mobility. The causes of coxarthrosis are stress on the joint, vascular diseases, autoimmune diseases and processes, metabolic disorders, injuries and congenital pathologies. In later stages, treatment is only surgical; the joint must be replaced with an implant.
- Aseptic necrosis of the right hip joint. It manifests itself as necrosis of the bone and cartilage tissue of the joint. The pain radiates to the groin from the affected surface. Differential diagnosis of the disease is based on the results of an x-ray examination.
- Perthes disease. It is characterized by a decrease in blood supply to the tissue area around the head of the femur and necrosis of the head of the hip joint. Boys under 15 years of age are most often affected. Pain in the joint is reflected in the lower abdomen. Joint deformation and lameness may develop.
- Inflammatory diseases of the hip joint on the right side. This group includes rheumatoid, purulent, gouty and infectious diseases. Common symptoms for all pathologies are inflammatory swelling in the joint area, increased local temperature, pain in the joints (initially in small ones), if the hip joint is affected, radiating to the groin area on the right side.
- Pain due to diseases of the lower back, radiating to the groin on the right side (see here).
Types of pain
Pain is a protective reaction of the body that occurs in response to various types of irritation of nerve endings in almost all parts of the body. Pain in the right side of the lower abdomen is part of the pathogenesis of diseases. Correct characterization of the types of pain is important during the early diagnosis of diseases of the pelvic organs, bones, joints and blood vessels.
Based on the description of pain, it is difficult to make a final conclusion about the pathological focus. But it is very important to indicate to the doctor the nature of the pain and its localization for objective examination using abdominal ultrasound, MRI and CT.
Dull aching pain in the right side
It is defined as a feeling of distension of the abdominal wall from the inside with a blunt object. Dull pain of low intensity, debilitating, aching and boring is a reflection of the involvement in the pathogenesis of a large number of small sensitive receptors responsible for the pain of internal organs. Pain emanating from the area of the right side, from below, is dull - a common sign of appendicitis, intestinal diverticulum, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, and tumors.
A dangerous sign is the abrupt spontaneous cessation of dull pain. This may mean necrotic processes in internal organs and disturbances in the conduction of pain impulses. Dull pain is sometimes combined with yellowness of the mucous membranes, nausea, general malaise and increased irritability.
Nagging pain in the right side
It is defined as a feeling of internal organs being pulled towards the abdominal wall or, conversely, being pulled away from it. May worsen with physical activity. The patient takes forced positions. As in the first case, pain is a reflection of the involvement of small superficial receptors of the abdominal wall in the pathogenesis. Develops in athletes with sprains in the groin. Pain can be the result of pathologies of the abdominal cavity (adhesions, hepatitis, inflammation of the kidneys, appendicitis, inflammation of the adrenal gland, duodenum) and pathologies of the pelvic organs (uterus, ovaries).
Specific nagging pains are detected in women at all stages of pregnancy and during menstruation. Rarely, nagging pain in the right side may accompany the movement of a small stone in the ureter or osteochondrosis of the lumbar region.
Sharp pain in the right side
Defined as acute, sudden and strong. The sensation is reminiscent of running a dull knife along the inside of the abdominal wall. Pain usually forms in a small pathological focus, less often in a large one. The most likely causes: gynecology, diseases of the urinary system and intestines, pinched nerves.
Cramps in the right side can be a manifestation of inflammation of the ovary, apoplexy, ovarian torsion, pinched nerve in the lumbar skeleton, intestinal volvulus, acute dilatation of the bladder, movement of a large stone in the right ureter and intestinal overflow with gases. It may intensify with straining, bending, or trying to turn the body. Combined with headache, fainting, blurred vision.
Stitching pain in right side
It is defined as tingling of the abdominal wall in the right side from the inside with a blunt thin object. It usually occurs periodically and forms in a small pathological focus during inflammation of the gallbladder, appendicitis, or when a stone moves in the left kidney. The stabbing pain can intensify when you sigh, when bending and turning, during physical activity, or when coughing.
The mechanism of pain syndrome formation
Parenchymal and hollow organs are capable of pain in different ways. The first include dense structures filled with cells and covered with a capsule. The second are tubular formations. On the right side of the abdomen there is only one parenchymal organ - the ovary in women.
All the rest are covered from the inside with a mucous membrane, equipped with muscle fibers in a circular and longitudinal direction and provide motility (transport function of contents). The difference lies in the absence of pain receptors on the mucous membrane and the possibility of a pain reaction only to spastic contraction or significant overstretching.
The ovaries give pain when the parenchyma increases the size of the organ with swelling, inflammation, tumor growth and stretches the capsule. And, conversely, in the case of a sharp decrease due to cyst rupture.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account additional mechanisms: sprain, adhesions, tumor germination into the nerve ganglia, irritation of the peritoneal layers by leaked secretions, inflammatory exudate. Based on the nature of the pain, one can guess what kind of process is occurring in the body if the lower abdomen on the right hurts.
The size of the removed ovary is increased due to hemorrhage and cyst formation
Other symptoms of pain in the right side
Pain is not specific and is far from the only symptom of diseases of the internal organs, joints and bones of the lower girdle of the human body. The most common symptoms accompanying the pain are a burning sensation, fever and nausea leading to vomiting. Correct interpretation of the signs of disease accompanying pain is possible only by a specialist.
Temperature. A decrease in temperature is evidence of the decline of vital functions. An increase in temperature, fever is an adaptive reaction of the body to the action of an infectious or non-infectious, internal or external pathogen. Increased temperature and pain in the right half of the body in the lower abdomen are often combined with gynecological diseases, inflammation of the kidneys and liver. One of the important indicators of fever is its type.
- A constantly high temperature of one or two degrees Celsius above normal is a sign of common inflammatory diseases.
- Fluctuations in temperature during the day by more than two degrees are frequent companions of purulent processes in the internal organs.
- Exhausting temperature (prolonged hyperthermia with differences of over two degrees) is evidence of septic processes in the internal organs.
- The absence of a pattern in temperature changes is a sign of rheumatic processes in the lower back.
Nausea, vomiting. These symptoms, combined with pain in the lower abdomen on the right, occur with completely different diseases, including lesions of the digestive, genitourinary, nervous systems and gynecological diseases. All these pathologies are characterized by the presence of symptoms of intoxication and/or stimulation of pain receptors.
Burning. It is noted for diseases of the pelvic organs, including inflammatory processes in the genitourinary area. A burning sensation occurs when urinating, during sexual intercourse, and is a sign of irritation of the mucous membranes of the urethra and external genitalia. A burning sensation can be an independent symptom and/or combined with pain in the lower abdomen.
Why Central Clinical Hospital RAS
Even for a regular preventive examination, it is better to go to a highly qualified, experienced gynecologist. And when health problems arise, this becomes especially relevant. The hospital's excellent equipment with equipment from leading global manufacturers allows the cause of the disease to be quickly and accurately determined. It has its own clinical diagnostic laboratory - you don’t have to wait long for tests, and most of them are ready on the day of your visit.
But the most important thing is that doctors who are in love with their profession work here. Many of them have an academic degree - these are C.M.N., professors, doctors of the highest category. Gynecology is one of the most important medical areas of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. All specialists constantly improve their skills and use the latest achievements of researchers in various fields. In complex and controversial cases, the question of prescribing the necessary treatment is decided by the council.
A warm, friendly atmosphere, affordable prices, convenient registration by phone or online are pleasant additional advantages. In addition, you can always be sure that at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences you are welcome and ready to help in the most difficult situation.