Diaphragmatic hernia: a disease that can be “ciphered”
What do we know about hiatal hernia?
To understand what a diaphragmatic hernia is, let's go back to the school anatomy course.
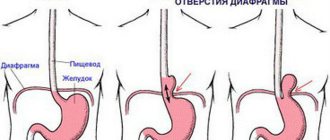
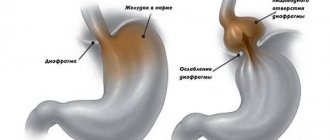
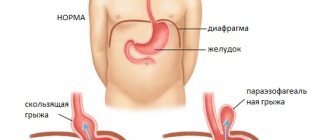
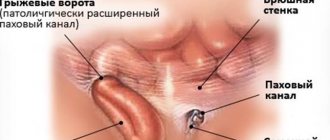
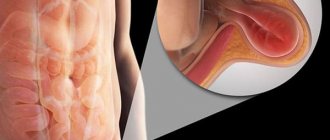
The diaphragm is the “fence” between the cavities, thoracic and abdominal. This is a special muscle that takes part in the breathing process. There are a number of openings in the muscle, including the esophageal opening. The very presence of the hole and the flexibility of the diaphragm are partly responsible for the occurrence of a hernia. If the section of the esophagus located below the diaphragm (partially with the stomach, less often with intestinal loops) shifts to the section located above the muscle, the patient is said to have a diaphragmatic hernia.
Causes of pathology
A hiatal hernia (HHH) can be congenital (with a shortened esophagus) or acquired.
The causes of the acquired condition are not fully known. It is assumed that the elastic tissue of the diaphragm is predisposing to the appearance of a hernia, especially if there is a family history of the disease.
The likely cause may be injury. However, the diagnosis is also made to patients who have never injured the diaphragm area.
Among the provoking factors are pregnancy, obesity and excess weight as such, chronic cough, heavy lifting, poor diet, constipation.
Symptoms of the disease
The patient may not notice a small hernia at all - it does not manifest itself in any way and does not affect the quality of life.
Most patients report the following symptoms:
- Heartburn
- Belching
- Abdominal pain (stomach area)
- Discomfort behind the sternum
- Shortness of breath and rapid heart rate
- Feeling of fullness in the epigastric region
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Symptoms may appear during abdominal exercises, sudden bending, or wearing tight clothes that are tightly tied at the waist.
Non-food manifestations include:
- Cough with no other proven cause
- Sore throat, nasal congestion
- Damage to tooth enamel
- Anemia.
Often the doctor has to exercise deductive abilities, finding a connection between a lingering cough of unknown etiology or low hemoglobin in a blood test and a hiatal hernia that no longer manifests itself.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of “diaphragmatic hernia of the diaphragm of the stomach” is made on the basis of an examination prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Basic methods are esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), x-ray of the esophagus and stomach with a contrast agent.
An endoscopic examination can both rule out diseases of the digestive system and determine the presence of a hiatal hernia, stomach diseases, such as ulcers or reflux esophagitis (GERD), since GERD is a common complication of the hiatal hernia.
An X-ray of the esophagus confirms the suspicion of a hernia and determines its size. For sliding (ascial) hernias, the degree is determined - from 1st to 3rd.
Recipes
Quick recipes for meat and fish dishes are based on chopped raw materials. In this form, they are better absorbed for hernia and other gastrointestinal pathologies.
Milk jelly
To prepare 1 liter of drink, take:
- fresh milk;
- 3 tablespoons potato starch;
- 3 tablespoons sugar.
If you wish, you can take a pinch of vanilla. Pour 3 cups of milk into the pan, bring to a boil, add sugar. The starch is diluted in the remaining milk and gradually poured into the pan. The contents are constantly stirred. The milk jelly is brought to readiness over low heat. 1-2 minutes after boiling, remove the dish from the heat.
Minced cod cutlets
Ingredients:
- 300 g minced meat;
- egg;
- 50 ml milk;
- 100 g bread;
- greenery;
- salt.
The oven is heated to 180-200 degrees. The bread is soaked in milk and squeezed out. The ingredients are mixed. Form small cutlets from the minced meat with wet hands and place them on a greased baking sheet. Cooking time – 20-25 minutes. For a side dish, prepare mashed potatoes or vegetable salad.
Why is a hiatal hernia dangerous?
Typically, a diaphragmatic hernia causes gastroesophageal reflux disease, which results in the reflux of acidic stomach contents into the esophagus.
GERD must be kept under control, as the disease can have unpleasant consequences. Among them are erosive esophagitis, narrowing of the esophagus due to the formation of scar tissue and, finally, the so-called Barrett's Esophagus - a threatening precancerous condition, which is characterized by the degeneration of esophageal cells.
What are the methods of anterior abdominal wall plastic surgery?
Plastic methods can be tension or non-tension.
Tension is a type of plastic surgery performed using the patient’s own tissues. This method received this name because, in order to eliminate a hernia defect, the tissues must be “tightened” and sewn together. The resulting tension in the tissues can cause pain after surgery and result in a possible relapse. At the present stage of development of medicine, this method of closing hernias defects is significantly inferior to non-tension methods.
Tension-free plastic surgery involves the use of modern mesh prostheses to strengthen the anterior abdominal wall. The prosthesis is a polypropylene network, which, due to its flexibility, strength and high degree of tissue “germination”, has shown its reliability and safety when used in hernia repair. Mesh prostheses come in different sizes, from small ones with a diameter of 5 cm for umbilical hernias, to large ones of 50 x 50 cm for giant incisional hernias. Modern three-dimensional mesh systems make it possible not only to strengthen the hernia defect in the form of a “patch”, but to completely fill it, significantly reducing the risk of relapse. In some situations, a special mesh is installed, the surface of which is coated with a special composition that allows it to safely contact the abdominal organs and avoid the formation of adhesions between them.
The open hernia repair operation consists of several stages:
- Isolation of the hernial sac. A skin incision is made above the hernial protrusion, the hernial sac is freed from the surrounding subcutaneous fatty tissue. The “hernial orifice” is distinguished.
- The hernial sac is opened, the condition of the contents of the hernial sac is assessed, and if there are no complications, the contents are immersed in the abdominal cavity.
- The hernial sac is excised, stitched and plunged into the abdominal cavity.
- The integrity of the anterior abdominal wall is restored (plasty is performed).
Hiatal hernia: treatment, drugs responsible for its success
Lifestyle change
A hernia of 1st and 2nd degree is most often treated conservatively, without surgery, subject to a certain diet (table number 5) and lifestyle.
- Avoid spicy, fatty, sour, fried foods.
- Make it a rule to eat small portions, avoiding long breaks between meals.
- Quit smoking and don't drink alcohol or soda
- Do not eat later than an hour and a half before going to bed
- Elevate the head of the bed to prevent stomach contents from refluxing during sleep.
You should also reduce heavy physical work and stressful situations as much as possible.
Drug therapy
Drugs that help improve the condition of hiatal hernia include antacids that neutralize gastric acid: Almagel and phosphalugel, Gaviscon, Maalox. They eliminate heartburn and belching.
Stomach pain and flatulence are well relieved by antispasmodics: enterospasmil and meteospasmil.
Proton pump blockers: omez, nexium, nolpaza, dexilant reduce gastric secretion, protecting the stomach and esophagus from the aggressive effects of acid if the disease is complicated by high acidity.
Surgery
If conservative treatment does not help, in cases of such serious complications as strangulation, and with a high degree of hiatal hernia, the patient is offered surgery.
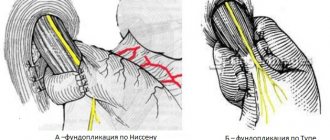
Our current progressive surgical treatment method is fundoplication performed laparoscopically. The operation completely eliminates the symptoms of diaphragmatic hernia in 80-90% of cases.
Important for the patient
Conservative and surgical treatment of gastric hernia should be performed in special medical institutions that have a high level of diagnostic and surgical support. It is necessary to understand that the operation is performed according to clear indications: when there is a direct threat of esophageal cancer, pain, strangulated hernia, and functional disorders are not amenable to conventional treatment.
In our clinic we offer a whole range of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Surgical repair of a gastric hernia is performed laparoscopically, which can immediately reduce the risk of postoperative complications. The length of stay in the hospital after surgery is several days.
List of used literature
- Chikinev Yu.V., Drobyazgin E.A. POST-TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMAL HERNIA (DIAGNOSTICS AND TREATMENT). Acta Biomedica Scientifica. 2017; 2(6): 163-166.
- Voitsekhovsky V.V., Anikin S.V., Goborov N.D., Yanovoy V.V., Bregadze Yu.E., Glushchenko V.V., Khatkeev V.I. A case of diagnosis of post-traumatic diaphragmatic hernia occurring under a mask pleurisy. Bulletin of physiology and pathology of respiration. 2022.
- Grishin, I. N. Hiatal hernia and reflux gastroesophageal disease: monograph. / I.N. Grishin, A.V. Vorobey, N.N. Chur. - M.: Higher School, 2015. - 224 p.
- Long-term results of endosurgical treatment of paraesophaneal hiatal hernias, E. I. Senderovich, E. E. Grishina, B. M. Garifullin, E. F. Gimaev, N. M. Kazakov, R. K. Ibragimov.
Frequently asked questions about hiatal hernia
What are the signs of a diaphragmatic hernia?
The disease may not manifest itself in any way, have a number of characteristic signs: belching, heartburn, stomach pain, or be disguised as cough, shortness of breath, palpitations. Therefore, the diagnosis is established not by a set of symptoms, but on the basis of an X-ray examination or fibrogastroscopy.
What can hurt with a diaphragm hernia?
The patient may experience chest pain, discomfort in the stomach, or, in the case of GERD, a sore throat.
How is a hiatal hernia treated?
A mild degree involves conservative treatment using the drugs described above and lifestyle correction: changing diet, eliminating bad habits. If these measures do not lead to relief of the patient’s condition, surgical intervention is indicated.
Recovery after surgery
After the operation is completed, the patient is transferred to the inpatient department, where doctors monitor his condition. If the patient feels well, he or she may be discharged the next morning. The rehabilitation period after removal of a gastric hernia is 3-4 weeks. The patient’s main task at this time is to follow the doctor’s recommendations for a quick recovery and return to their normal lifestyle. In order for the body to quickly recover after surgery, you need to follow the following rules:
- Stick to bed rest.
- Do not lift heavy objects, put off physical activity for a while.
- Go on a diet - your diet should include low-fat, fresh food in pureed or liquid form.
- Take medications - analgesics, proton pump blockers.
If symptoms such as bleeding, pain, or suppuration of wounds appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. After laparoscopic repair with fundoplication, recurrence of the disease is unlikely.