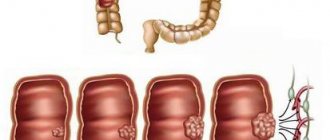
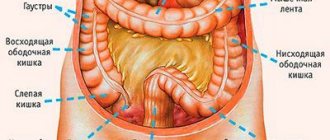
Colon cancer (colorectal cancer, CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors. Unfortunately, it is often diagnosed in late stages (3-4), since the tumor does not manifest itself for a long time.
Stage 3 intestinal cancer is characterized by the presence of metastases to regional lymph nodes. In this case, the degree of spread of the tumor can be any, from damage to the intestinal wall, including its muscle layer, to leaving the intestine and spreading to surrounding organs and tissues.
- Complaints and clinical picture
- Diagnosis of intestinal cancer stage 3
- Treatment of colorectal cancer
- Chemotherapy for stage 3 colon cancer
- Prognosis for colorectal cancer
- Prevention of colorectal cancer
Life expectancy at stage 1
Since the answer to the question of how long people live with colon cancer depends on the physical size of the primary tumor and the qualitative detection of metastases, it is important to undergo a special examination in time when a colon cancer clinic appears: constant abdominal pain and problems with stool, the appearance of blood or pus in the stool.
When the disease is detected at the first stage, the prognosis for colon cancer is as favorable as possible. The 5-year survival rate is as high as 92%, according to the National Cancer Institute.
This means that when treatment is carried out according to the standard protocol, more than 92% of sick people will tolerate it well, achieve remission and successfully live for more than five years after that. Surgeries for colon cancer are mainly performed at this stage.
Life expectancy at stage 2
Prognosis for stage 2 intestinal oncology directly depends on the extent of damage to the intestinal wall by the malignant tumor. At stage 2a, the disease affects the entire intestinal wall, but does not extend beyond it. In this case, the oncological focus can be clearly separated from the surrounding tissues, which increases the effectiveness of surgical treatment.
At stage 2b, the tumor spreads to neighboring organs - the liver, bladder, and uterus in women. A relatively favorable prognosis and high life expectancy for intestinal cancer are associated with the complete absence of metastases in other parts of the body or the spread of cancer through the lymphatic system.
At the same time, women have a more favorable prognosis when various parts of the intestine are affected - this is due to the characteristics of the growth of the tumor focus against the background of the influence of female sex hormones. When studying statistical figures, it is worth remembering that they essentially reflect the situation five years ago. Surgical techniques are constantly being improved, making it possible to eliminate pathological foci more thoroughly, and sometimes to perform minimally invasive surgical interventions. Accordingly, updated, more favorable and relevant statistical data will accumulate over time.
Understanding how long bowel cancer patients live and which treatment method should be chosen is based on the results of a preliminary medical examination. It is important to determine the stage of the disease as correctly as possible and not to miss its spread in the abdominal cavity, metastasis to other organs, or involvement of lymph nodes in the pathological process.
How many years a patient with intestinal oncology has left to live is determined by the professionalism of the operating doctor and the completeness of the operation. In the case of complete removal of the oncological focus, the postoperative recovery period is easier, and in the future a minimal course of chemotherapy for colon cancer is required.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the 5-year survival rate for this stage of colorectal cancer is as high as 87% for stage 2a and 63% for stage 2b.
Select a clinic and treatment
Diagnosis of cervical cancer
One of the most important methods for early detection of any female disease is regular gynecological examination. Since the clinical manifestations of precancerous and background diseases are not clearly expressed, differential diagnosis of cervical cancer will help to detect changes, including:
- cytological screening
- visual examination of the genitals
- colposcopy
- bacterioscopic/bacteriological examination
- targeted biopsy of the cervix
- biopsy of tissue from suspicious areas of the cervix
- curettage (scraping) of the cervical canal
- screening for sexually transmitted infections
Cytological screening
- This is a study of smears that helps to identify the beginning of the pathological process.
Colposcopy
– the main diagnostic method. If necessary, it is supplemented with manipulations (biopsy, cytology of smears, treatment of the cervix with acetic acid to detect flat condylomas, curettage of the cervical (cervical) canal, etc.).
Precancerous lesions in the cervix can be treated with cryosurgery, cauterization, or laser surgery. If oncology is suspected, a biopsy is performed during the above procedures to determine the extent of organ damage and the stage of cancer.
Cervical biopsy
is a surgical procedure in which a small amount of epithelium is removed from the cervix. This tissue sampling method is usually used after a gynecologist has discovered an abnormality during a routine examination. A biopsy may show the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) or precancerous cells or cervical cancer.
When monitoring the cervical epithelium, diagnostic methods such as:
- optical coherence tomography
- Ultrasound
- fluorescence spectroscopy
- irrigoscopy
- X-ray of the lungs
- rectoscopy
- MRI
- urography
- cystoscopy
- PET CT
- use of SCC tumor marker
- CT
Life expectancy at stage 3
The prognosis and clinical features of stage 3 colon cancer depend on the size and location of the tumor in the colon wall in combination with the number and location of lymph nodes involved. At stage 3a, the tumor reaches a small size and is located mainly in the intestinal lumen; it does not affect adjacent organs. Despite this, with a thorough examination, the doctor reveals the spread of the process to the regional lymph nodes.
The next stage, 3b, is characterized by a larger tumor size and its more aggressive spread along the wall of the intestines and abdominal organs. How many years patients with stage 3b colon cancer live is further influenced by the development of complications of the disease.
The most common complications that affect how many years patients with colon cancer at this stage will live include:
- Acute intestinal obstruction, which often develops when the tumor is located in the initial parts of the intestine
- Infectious complications, phlegmon and abscesses of retroperitoneal tissue
- Symptoms of damage to organs adjacent to the tumor
Stage 3c differs from previous stages in the spread of the pathological process to a large number of lymph nodes. At the same time, the tumor itself can be compact, not extend beyond the intestine and not lead to the development of typical complications. The inability to completely remove all cancer lesions at stage 3c reduces the 5-year survival rate to 53%. In this case, surgical treatment will necessarily be followed by a second stage - polychemotherapy. Modern pharmacological developments make it possible to improve expectations regarding how long a patient with intestinal cancer will live. Also in such clinical cases, radiation therapy for colon cancer can be performed.
The prognosis for intestinal oncology at stage 3a is relatively favorable - 89% of patients overcome the 5-year mark after an accurate diagnosis and the start of modern treatment. At stage 3b, the 5-year survival rate reaches 69%.
Select a clinic and treatment
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is quite common, ranking second among all gynecological cancers after uterine cancer.
At the bottom of the uterus is the cervix, which connects it to the vagina (birth canal). The first changes in this part of the uterus, which can later develop into cancer, often occur at the age of 20–30 years. This type of cancer is considered to be slowly progressive. 45-50 years is the average age of women diagnosed with cervical cancer. Treatment started on time can prevent the development of the disease.
9 out of 10 cases of cervical cancer are squamous cell
.
It develops from squamous cells in the part of the cervix closest to the vagina. Another type of cervical cancer is adenocarcinoma
, which develops in the glandular cells of the part closest to the uterus.
You should know that cervical cancer is preceded by benign and precancerous processes.
Benign changes include:
- simple ectopia;
- endocervicosis;
- leukoplakia;
- endometriosis;
- cicatricial deformation of the cervix, etc.
Precancerous - cervical dysplasia of varying severity.
Life expectancy at stage 4
An important distinguishing feature of stage 4 colon cancer is the detection of metastases in distant areas of the body. In the early stages, metastases form in the liver, through which blood passes from the abdominal and pelvic organs. Less commonly, lesions appear in the lungs, genitals, bones, pancreas and adrenal glands. The number and location of metastases significantly influence how long patients with stage 4 intestinal cancer live. In particular, in case of lung damage, additional methods are used - an intensified course of polychemotherapy or embolization of metastases with chemotherapy. Based on the response to treatment, reduction in size of metastases or their complete disappearance on CT/MRI, the doctor can determine how much time a patient with stage 4 colon cancer has left to live.
Often, a short life expectancy with the disease is due to late diagnosis of cancer or incorrect selection of individual treatment. Despite the disappointing statistics, prognosis for stage 4 colon cancer is extremely individual.
The following factors are of greatest importance in treating stage 4 colon cancer and determining prognosis:
- Age, patients under 60 years of age have a higher chance of recovery
- Gender, with a more favorable prognosis in men
- The presence of concomitant diseases, the most important in this regard are liver and kidney dysfunctions, the state of the cardiovascular system
- A history of oncology; upon initial diagnosis, the prognosis for stage 4 colon cancer is more favorable
- Sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy
To predict how long a patient with stage 4 colon cancer has left to live, it is important to evaluate not only medical factors and the possibility of specialized treatment, but also the patient’s psycho-emotional state. Of course, it is important to perform surgery in a timely manner, as well as chemotherapy to combat metastases. However, competent psychological support helps a person find the strength to fight the disease and believe that remission is achievable.
It matters not only how long patients with stage 4 intestinal cancer live, but also the quality and fullness of life.
It will be useful:
- Attending individual and group supportive psychotherapy sessions
- Selection of a competent physical activity regimen by the attending physician
- Communication with patients in communities dedicated to the disease, meeting those who have recovered from the disease
According to the National Cancer Institute, the 5-year survival rate for patients with stage 4 colorectal cancer reaches 11%.
Select a clinic and treatment
Risk factors
Most cases of cervical cancer are caused by long-term infection with one of the human papillomaviruses (HPV). HPV infection is very common, and most people with HPV infection do not develop cancer. There are more than 100 types of HPV, and only certain types are associated with cancer.
The following factors play a role in the occurrence of cervical cancer:
- smoking
- having multiple sexual partners
- weakened immune system (patient after organ transplant, HIV-positive, etc.)
- past or current chlamydial infection, as well as if there were/are other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- overweight
- three or more full-term pregnancies
- long-term use (five or more years) of oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
- Presence of first full-term pregnancy before age 17
- early sexual life
- low social status
- family predisposition to cancer and, in particular, cervical cancer
Clinics and prices for colon cancer treatment abroad
The cost of examination and treatment in foreign clinics depends, first of all, on the country and the level of the clinic. The cost of the medical program is also affected by the patient’s age, the presence of concomitant diseases, the stage of cancer and the type of tumor. Leading colon cancer treatment clinics abroad:
- Helios Clinic Berlin-Buch, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectology
- University Hospital Dusseldorf, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectology
- University Hospital of the University of Munich. Ludwig Maximilian, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- University Clinic named after. Goethe Frankfurt am Main, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Pulmonology, Allergology, Endocrinology and Diabetology
Average prices for examination and treatment:
- Diagnosis of colon cancer – 2,500 euros
- Laparoscopic resection of affected parts of the colon – 18,900 euros
- Resection of affected parts of the colon using the da Vinci robot – 28,450 euros
- Treatment of colon cancer with chemotherapy – 7,030 euros
- Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for colon cancer – 51,500 euros
- Oncological rehabilitation – 1,196 euros per day
Price list
*Note:
Prices are indicated for foreign citizens. Citizens of the Republic of Belarus can receive medical services without charging a fee. Read more...
*Prices in Bel. rub. *You can view all types of services and exact prices on the page
| Procedure name | Price in Belarusian rubles |
| Wide local excision of vulvar tumor | 466 |
| Wide local excision of vaginal tumor | 708 |
| Unilateral adnexectomy | 578 |
| Bilateral adnexectomy | 1 025 |
| Bilateral adnexectomy, omentectomy | 1 156 |
| Bilateral adnexectomy, resection of the greater omentum, surgical staging | 1 268 |
| Subcutaneous vulvectomy | 727 |
| Separate diagnostic curettage | 186 |
| Hysterectomy without appendages | 1 454 |
| Panhysterectomy | 1 752 |
| Panhysterectomy, omentectomy | 2 181 |
| Panhysterectomy, pelvic peritonectomy, omentectomy | 4 362 |
| Wertheim operation (panhysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy) | 3 206 |
| Wertheim operation with omentectomy | 3 486 |
| Wertheim operation (panhysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy) with retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy | 4 362 |
| Vulvectomy with femoroinguinal lymphadenectomy through separate incisions | 3 095 |
| Vulvectomy with femoroinguinal-iliac lymphadenectomy through separate incisions | 3 542 |
| Monoblock vulvectomy with bilateral femoral-inguinal lymphadenectomy with vulvar plastic surgery using a combined method | 4 921 |
| Vulvectomy with femoroinguinal lymphadenectomy through separate incisions and vulvar plastic surgery with bilateral island infero-gluteal flaps | 4 921 |
| Vulvectomy with femoroinguinal lymphadenectomy through separate incisions and vulvar plastic surgery with a TRAM flap | 4 940 |
| Operation Sturmdorf | 1 025 |
| Knife biopsy of the cervix | 130 |
Booking Health helps you get treatment abroad
If you want to find out prices for treatment of colon cancer in Germany, treatment of colon cancer in Israel or other countries, contact the medical tourism operator Booking Health. Fill out the “Send a request” form on the company’s website, and a medical consultant will contact you on the same day.
Booking Health specialists will also help you with such important points:
- Choosing the right clinic based on the annual qualification profile
- Direct communication directly with the attending physician
- Preliminary preparation of a treatment program without repeating previously conducted examinations
- Ensuring favorable prices for clinic services, without surcharges and coefficients for foreign patients (savings up to 50%)
- Make an appointment for the desired date
- Control of the medical program at all stages
- Assistance in purchasing and shipping medications
- Communication with the clinic after completion of treatment
- Control of invoices and return of unspent funds
- Organization of additional examinations
- Service of the highest level: booking hotels, plane tickets, transfers
- Translator and personal medical coordinator services