During pregnancy, a woman often feels alarming signals in the form of hiccups from the baby. This often worries girls, although there is little reason to panic.
Medicine has only assumptions about why a child hiccups in the stomach during pregnancy. Often this phenomenon is not a reason to sound the alarm, because babies are born healthy and alive.
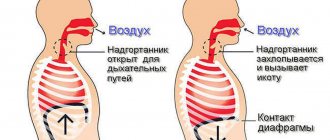
The vagus nerve, which connects all the internal organs of a person, is periodically pinched by the diaphragm. When this happens, there is a risk of negative reactions from the body.
At this time, the self-defense mechanism is triggered, and a signal is sent to the human brain to release the nerve.
The hiccups themselves occur when the diaphragm pushes air upward through the lungs.
It is worth considering the main reasons for the occurrence of this phenomenon in the womb:
- Ingestion of amniotic fluid. There is an assumption that the baby may accidentally swallow amniotic fluid, which is subsequently excreted through the woman’s urine. If a child takes in more water than needed, fetal hiccups begin, during which he removes excess fluid. According to observations, the baby wants to swallow the favorite taste of the product along with the water. For example, after a meal, when the mother has eaten the baby’s favorite dish, he also tries to feel its taste, then hiccups occur. To prevent this from happening, stop eating at night and then your sleep will be normalized.
- Preparing for an independent breathing cycle. It is believed that the last week before childbirth is marked by careful preparation of the child for independent breathing. Doctors believe that a full-term baby who has experienced hiccups in the mother’s belly is more adapted to breastfeeding and active breathing.
- Hypoxia. This reason is considered the most dangerous and occurs when the umbilical cord wraps around the fetal neck and the child does not have enough air. The connection between hypoxia and hiccups has not been officially proven. If you feel hiccups constantly for several days, you should consult a doctor.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the gynecologist prescribes a special procedure - cardiotocography. It detects uterine activity and fetal heart rate.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe a Doppler ultrasound to find out if there is increased blood flow between the placenta and the fetus.
Brief intrauterine hiccups, not accompanied by additional symptoms, are considered normal.
General information
The phenomenon of the maternal sphere (including the semantic experience of pregnancy) is determined by the specifics of experiencing the symptoms of pregnancy and plays a significant role in the external activity and mental state of a pregnant woman.
During this period, women react emotionally to all their sensations and any changes in the fetus. This is largely due to the restructuring of a woman’s self-awareness, which already includes the image of the unborn child as a separate human entity (the stage of accepting a new life within oneself). Most often, this stage during pregnancy occurs during the period when the fetus begins to move (week 16-18) and the mother herself begins to interpret its behavior: “woke up,” “worried,” “playing,” etc. As the fetus develops (33 weeks - 35 weeks), many women begin to worry about the fetus hiccupping in the stomach. Less commonly, hiccups are observed in the fetus during early pregnancy (from 24-25 weeks). The child hiccups especially often during the 32nd week of pregnancy, and also, according to surveys of pregnant women, often hiccups at the 37th week of pregnancy. It is impossible to clearly define the timing of the appearance of hiccups in the fetus, but most often this phenomenon occurs at the end of the second trimester, although most women begin to feel it later (in the third trimester). The same phenomena include fetal yawning, which occurs in earlier stages of pregnancy.
However, many pregnant women do not feel the “hiccup phenomenon” of the fetus in the stomach during pregnancy and often worry about this, and some women even doubt whether a child can hiccup in the womb? As studies show, this is due to the fact that a pregnant woman does not feel all the movements of the fetus, and many of them simply have a low sensitivity threshold and do not feel hiccups.
Sometimes pregnant women are not concerned about the fact of hiccups themselves, but why the baby in the stomach often hiccups or hiccups every day or constantly for 20-30 minutes 2-3 times a day, since many people associate this process with pathology. Women with an anxious type of pregnancy experience are especially worried, in whom the behavior of the fetus (moving, hiccups, yawning) is accompanied by anxiety, doubts and even fear.
How does hiccups manifest?
First of all, it must be said that hiccups are an unconditioned reflex caused by contraction of the diaphragmatic septum. Hiccups in the fetus manifest themselves individually: its duration can vary from 2-3 minutes to half an hour. The frequency of its occurrence also varies: for some – several times a day, for others – once a week. Accordingly, pregnant women have different emotions in relation to this phenomenon: some are worried, others are happy, and many are worried: is it dangerous and is help needed or not? We should also not forget that a pregnant woman’s feelings about the behavior of the fetus are quite subjective and there is no need to compare them with the feelings of other pregnant women and attach extreme importance to them.
Today, scientists believe that despite the uncertainty of the origin of such phenomena, the ability of a developing fetus to hiccup, swallow, yawn, and stretch is one of the factors (indicators) of physiologically normal intrauterine development and indicates its achievement of a certain level of psychophysical development. It has been proven that this is normal and is not a risk factor for fetal development, and the child does not experience any discomfort during the hiccup period.
FAQ
Why does the fetus hiccup at 26 weeks of pregnancy?
+
It is not known exactly what causes hiccups. It is believed that it occurs due to the ingestion of amniotic fluid and the development of hypoxia in the fetus. You can distinguish one condition from another using ultrasound.
What influences the development of hiccups?
+
The appearance of hiccups can be influenced by the mother's diet, as well as factors that provoke fetal hypoxia. These include smoking, staying in stuffy rooms, lying on your back for long periods of time, and excessive physical activity.
How to distinguish hiccups from other movements?
+
You can tell that your baby is hiccupping in the womb by its characteristic rhythmic kicks. They are similar to what adults experience during hiccups - the chest rises and falls rhythmically.
What to do if your child constantly hiccups?
+
If a child hiccups for a long time and constantly, you need to undergo an unscheduled ultrasound and Doppler examination of the umbilical cord blood flow to determine the cause of this phenomenon and exclude fetal hypoxia.
Causes
There is still no clear understanding among specialists of the reasons why a child hiccups in the stomach of a pregnant woman. There are several assumptions about why a child hiccups in the womb, however, there is no reliable and unambiguous confirmation of them. Assumptions about why a baby hiccups in the womb include:
- The fetus swallows a lot of amniotic fluid while in the womb and gets rid of it with the help of hiccups.
- Hiccups are caused by the formation of the nervous system in the fetus.
- Preparing the fetus for the process of independent breathing and training the diaphragm.
- Practicing swallowing movements.
- Hiccups are caused by the awkward position of the fetus. The basis of hiccups is a lack of oxygen ( fetal hypoxia ).
However, in cases of hypoxia, characteristic symptoms must be present - rapid fetal heartbeat, cardiac arrhythmia , prolonged increased fetal mobility, pressure surges, changes in the shape of the abdomen/reduction, weight loss in a pregnant woman.
What is hiccups
Hiccups are understood as a breathing disorder when a person begins to involuntarily take short breaths. The diaphragm, intercostal muscles and epiglottis are involved in this reaction. Contraction of the intercostal muscles leads to vibrations of the diaphragm and shortening of inspiration, and the closure of the epiglottis causes the sound characteristic of this condition.
It is not known for certain why hiccups occur, but there are several assumptions about this:
| Possible reason | Description |
| Evolution | It is believed that hiccups occur due to air entering the stomach. This happens when a person eats too quickly or talks with his mouth full. In infants, hiccups occur when the baby swallows air while sucking or the mother overfeeds him. |
| Diseases | Constant hiccups may indicate the development of a variety of pathologies. For example, it occurs in pathologies of the nervous system - pinched nerves, Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, inflammation of the brain and meninges. |
| External influences | This reaction can develop due to toxic damage to the nerves. It occurs with diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, and while taking certain medications (for example, antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, epidural anesthesia). |
Pathological hiccups do not go away for a long time and require mandatory medical intervention to determine and eliminate the cause that caused it.
Prevention
If the baby often hiccups and this causes psychological discomfort in the woman, to reduce these manifestations and prevent it, it is recommended:
- Change your position (take a knee-elbow position for a few minutes or lie on the other side).
- Increase the oxygen saturation of the mother and fetus (active frequent walks in the fresh air, breathing exercises, oxygen cocktail, meditation).
- Calm down, relax, do not focus your attention on the question: why does the child often hiccup in the womb, just talk to the child and stroke the belly.
What to do if hiccups occur in the womb of a child
As in adults, intrauterine hiccups quickly go away on their own and do not require any treatment. However, certain factors can trigger prolonged attacks that may not go away on their own. These include:
- Smoking by the pregnant woman or her family members indoors.
- Staying in a static position for a long time.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Staying in a stuffy room for a long time.
What can you do to stop your baby from hiccupping?
- Pat the belly and talk to the baby.
- Change position.
- Take a short walk.
- Do a light warm-up.
You should not take sedatives or other medications. Usually, hiccups go away on their own after these simple manipulations. However, if they do not help, it is worth getting tested for fetal hypoxia.
Important!
Hiccups can also occur due to the diet of a pregnant woman. If a woman eats a lot of sweets, the amniotic fluid also changes the taste. The baby likes it, which is why he begins to swallow more and more liquid.
List of sources
- Brusilovsky A.I. Life before birth. - M.: “Knowledge”, 1991.
- Gundarov I.A., Boyko N.N. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2006, 6, pp. 18-20.
- Bashmakova N.V. The role of predicting intranatal risk factors / I.V. Bashmakova, E.N. Kravchenko, V.G. Lopushansky // Obstetrics and gynecology. – 2008. – No. 3. – P. 57–61.
- Brutman V.I., Filippova G.G., Khamitova I.Yu. Dynamics of the psychological state of women during pregnancy and after childbirth. // Question psychol. 2002. No. 1 – P. 59 – 68.
- Bratus I.V. Emotional support by the mother of the process of interaction with the child / I.V. Bratus // Abstract. to the report at III All-Russian conference on psychotherapy, (1-3 Dec. 2010). – M., 2010.
Is this normal?
Hiccups are convulsive, jerky contractions of the diaphragm, often a symptom of overeating, hypothermia and other conditions.
Usually, several months before giving birth, the expectant mother feels not only the baby’s movements, but also other strange and incomprehensible tremors. Some women immediately realize what is happening. But there are also those for whom this moment begins to greatly disturb and put them into a state of panic. As a rule, this occurs starting from the 28th week of pregnancy. Particularly sensitive pregnant women may begin to feel them earlier, since the fetus begins to hiccup in the second trimester.
Signs of hiccups:
- uniform shocks with equal intensity;
- pass through the same time intervals;
- mom feels vibrations in her stomach;
- there is no feeling of discomfort in the expectant mother;
- visible pulsation from below in the abdomen.
Fetal hiccups are considered normal. This indicates that his nervous system is developing well and, in general, is developing correctly.
Children hiccup in different ways. For some, this process takes only a few minutes, for others it takes an hour or more. Everything is individual. With normal fetal development, hiccups can occur from 1 to 7 times during the day.
If the rhythmic tremors do not stop for a long period of time, then you need to “sound the alarm.” After all, this may indicate oxygen starvation of the fetus. It is necessary to contact a gynecologist to undergo the necessary examinations.
Changes in fetal activity
Changes in fetal activity may be associated with external influences. For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel - the inferior vena cava, and the flow of blood to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction - active movements. The same changes in the baby's activity can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother - if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, or sits with her legs crossed, the child, with her activity, forces the mother to change her position. A similar situation arises if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or, conversely, a decrease in fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology.
If after 28 weeks of pregnancy the baby does not make itself known for 3-4 hours, perhaps he is just sleeping. In this case, the expectant mother needs to eat something sweet and lie on her left side for half an hour. If these simple manipulations do not lead to results, you should repeat them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself known, this is a reason to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements may also indicate unwellness of the fetus, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia.
Determination of fetal condition
To determine the condition of the fetus, the doctor conducts a number of examinations:
Auscultation (listening)
The simplest thing is auscultation (listening) using a special wooden tube (obstetric stethoscope) or a special device that detects the fetal heartbeat; the doctor listens to the baby’s heartbeat. Normally it is about 120-160 beats per minute. A decrease in heart rate of less than 120 or an increase of more than 160 indicates intrauterine suffering in the child.
Ultrasound examination and Doppler testing
When performing an ultrasound, the doctor visually assesses the size of the fetus, the correspondence of fetal development to the gestational age, because with oxygen starvation the growth rate of the fetus slows down and its size lags behind the norm for each stage of pregnancy. The structure of the placenta and the presence of signs of aging in it also matter, as a result of which the function of transferring blood, oxygen and nutrients to the fetus usually deteriorates. During an ultrasound, the amount and type of amniotic fluid is assessed, which can also change with intrauterine fetal suffering. Doppler ultrasound of the blood vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord is a method for studying the speed of blood flow in these vessels. When the speed of blood flow in any vessel decreases, we can talk about fetal nutritional disorders of varying degrees of severity.
Cardiotocography (CTG)
This is an important method for assessing the condition of the fetus. CTG is performed during pregnancy of 33 weeks or more, since only in this period of intrauterine development of the baby is full regulation of the activity of the fetal cardiovascular system established by the centers of the spinal cord and brain. The fetal heartbeat is recorded for at least 40 minutes, and if necessary, the study can be extended to one and a half hours. The device detects and records the baby's heart rate. For example, when the oxygen concentration in the fetal blood decreases, the supply of oxygen to the cells of the nervous system decreases, which in turn affects the heart rate, especially when the child is awake. The obstetrician-gynecologist evaluates the heartbeat recording curve, episodes of decrease and sharp increase in the fetal heart rate and, based on these data, makes a conclusion about how comfortable the baby feels in the mother’s stomach.
If, during additional methods of assessing the condition of the fetus, initial disturbances in the supply of oxygen to the baby are detected, drug treatment is carried out aimed at increasing the access of blood and oxygen through the placenta and mandatory control examinations during the therapy. If the changes are profound and the baby experiences a severe deficiency of oxygen and nutrients, his condition suffers, an emergency delivery of such a patient is carried out.
Fetal movements are not only an indicator of its condition, it is a way for the baby to communicate with his parents. The movement of the baby in the mother's tummy is an unforgettable sensation that a woman can experience only in this short, but such a happy period of her life.
At what time does fetal movement begin?
The future baby begins to make its first movements early - already at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy . It is at this time that the first muscles and rudiments of the nervous system of the fetus are formed. Naturally, at this time the movements of the embryo are still very primitive - these are muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
about 10 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus begins to move more actively in the uterus, and, encountering an obstacle on its way (the walls of the uterus), change the trajectory of movements. However, the baby is still very small and the impacts on the wall of the uterus are very weak; the expectant mother cannot yet feel them. At 11-12 weeks of intrauterine life, the little man already knows how to clench his fists, grimace, wince; by 16 weeks of pregnancy he begins to react to loud, sharp sounds with increased motor activity, at 17 weeks the first facial expressions appear, and at 18 weeks he covers his face with his hands and plays. with the umbilical cord, squeezes and unclenches the fingers.
Gradually, with increasing gestational age, movements become more coordinated and more like conscious ones. As the baby grows up, the pregnant woman begins to feel his movements.
When does fetal movement begin during the first and subsequent pregnancies?
It is generally accepted that during the first pregnancy, the expectant mother feels the first movements of the fetus at 20 weeks of pregnancy, and for repeated pregnancies - at 18 weeks. This is not entirely true. A mother who is expecting her first child, indeed, most often begins to feel fetal movements a little later than a multiparous woman. This is due to the fact that “experienced” mothers know how the baby’s movements feel at first and what they should feel. Some primigravidas perceive the first movements of the fetus as increased intestinal motility, “gas”. Many women describe the first movements of the fetus as a feeling of fluid transfusion in the stomach, “butterflies fluttering” or “fish swimming”.
The first movements are usually rare and irregular. The time of the first sensations of fetal movements naturally depends on the individual sensitivity of the woman. Some expectant mothers feel the first movements already at 15-16 weeks, and some only after 20. Slender women, as a rule, begin to feel movements earlier than plump ones. Women who lead an active lifestyle and work a lot usually feel fetal movements later.
By 20 weeks, due to the formation of the spinal cord and brain, as well as the accumulation of a certain amount of muscle mass in the fetus, movements become more regular and noticeable.
From 24 weeks of pregnancy, the movements of the fetus already resemble the movements of a newborn - the expectant mother feels how the fetus changes position, moves its arms and legs. The motor activity of the fetus increases gradually and its peak occurs in the period from the 24th to the 32nd week of pregnancy. At this time, the activity of the baby’s movements becomes one of the indicators of his normal development. After 24 weeks, the baby begins to “communicate” with his mother through movements, respond to the sounds of voices, music, and the mother’s emotional state. As the gestation period increases beyond 32 weeks, the motor activity of the fetus gradually decreases due to the fact that the baby grows up and simply does not have enough space for active movements. This becomes especially noticeable at the time of childbirth. By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, the number of fetal movements may decrease slightly, but their intensity and strength remain the same or increase.