A person’s complaints of severe pain in the left hypochondrium often indicate inflammation of the pancreas. The examination of the patient begins with an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. A diagnostic method based on measuring the intensity of reflection of sound waves from the surface of organ tissues makes it possible to identify the smallest deviations in the functioning of the digestive system.
When assessing an echogram and morphological parameters of tissues, it is difficult for a doctor to make a mistake. The images that the sonographer creates during the examination are different in color. Light colors indicate the presence of seals in the organ, dark and black colors indicate liquid formations. A healthy pancreas, due to its homogeneous watery structure, is displayed in dark colors. The opposite picture indicates pathological changes and organ disease.
If you have been diagnosed with increased echogenicity of the pancreas, then carefully study the information below.
Where is the organ located and what parts does it consist of?
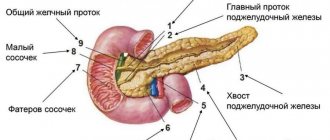
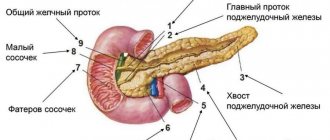
The gland is located in the area behind the peritoneum, to the left and slightly behind the stomach. It is protected by ribs and consists of a head, tail and body, so scanning of the sections occurs from different points. At the heart of the organ are small lobules that produce digestive enzymes and pancreatic islets that release humoral substances into the blood. Pancreatic juice, which serves as an enzyme, enters the duodenum and takes part in the digestion process.
Preparatory activities
The scan should be done on an empty stomach. To do this, the patient must fulfill several requirements:
• 24 hours before the procedure, exclude “heavy foods” from the diet.
• Dinner should be no later than 18:00.
• To relieve bloating and reduce gas formation, you can take Espumisan.
You need to bring a diaper and a towel to the ultrasound scan. During the examination, the patient lies on the couch. The ideal option would be to perform an ultrasound in the morning. In some cases, the patient will need to drink water before the procedure.
Why deviations are dangerous
Negligence towards pancreatitis can increase the risk of new foci of inflammation. The combination of diseases affects the overall health of a person. A critical manifestation of complications is disability.
If treatment of the disease is not started at its early stage, pancreatic enzymes enter the blood and create conditions for infection of other organs. Several diseases find a corresponding response:
- Liver and kidney failure.
- Bleeding in the stomach and intestines, erosions, ulcers.
- DIC syndrome (blood clotting disorder).
- Purulent-necrotic parapancreatitis.
- Mechanical jaundice.
- Liver hepatosis.
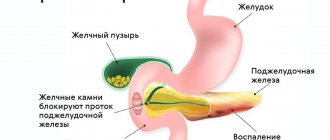
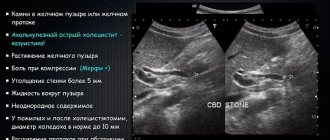
- Cholangitis, cholecystitis.
- Abdominal abscess.
Necrosis of the gland parenchyma develops tumors and cysts. Malignant tumors often appear in older men. Unusual thinness, loss of appetite, abdominal pain are the main symptoms of the disease. Only adequate timely therapy can reduce the chances of such complications occurring.
Video: Complication of chronic pancreatitis
How is the research going?
First, the patient lies on his back, then he turns on his left side. In this position, the tail of the gland is scanned. After this, he turns on his right side. To examine the condition of the head and body of the gland, the doctor asks the patient to take a semi-sitting position.
As landmarks for detecting the pancreas, the sonologist uses the aorta with the inferior vena cava, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, etc. There is a special program to determine the size of the organ. Even if all the indicators do not deviate from the norm, the doctor provides a detailed breakdown of the data in the conclusion.
The density of pancreatic tissue (echogenicity) depends on the age and body weight of the patient. Over the years, it decreases and acquires signs of hyperechogenicity. Normally, the structure of the gland is homogeneous. Proper preparation facilitates good viewing of all parts of the organ during the examination.
Consolidation of the pancreatic parenchyma
Methods for studying the parenchyma of the pancreas include questioning and examination of the patient, laboratory, instrumental and radiological methods. Compaction of the parenchyma can be a consequence of various diseases of the pancreas.
Symptoms include pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium, disorders of the digestive system that cause a person to feel discomfort, general weakness, and severe weight loss. The appearance of compaction of the parenchyma of an organ has a certain influence on the diet and nature of nutrition, the presence of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, and cystic fibrosis.
Pathological changes
- An abscess (abscess) of the pancreas looks like a pocket or bag filled with sequesters and heterogeneous fluid. As the patient's body position changes, the level of fullness changes.
- Acute or chronic pancreatitis, causing changes in the structure of a diffuse or focal nature. At the same time, the tissue density is reduced, the contours of the organ are not clear. The size of the gland and its ducts is higher than normal. Based on these changes, the doctor diagnoses pancreatitis.
- The appearance of necrotic foci and cysts further provokes the complete melting of pancreatic tissue (pancreatic necrosis). This appears as poorly structured hypoechoic areas.
- One of the consequences of pancreatic necrosis is the formation of many purulent abscesses, which, merging, form large areas of pus and sequestration.
- False cystic formations on the screen look like anechoic cavities filled with fluid.
- Tumors on ultrasound look like round or oval formations of low density and heterogeneous structure, abundantly covered with a network of blood vessels. If cancer is suspected, all parts of the gland must be examined very carefully. If the focus of a malignant tumor is in the head, then the sign will be jaundice. Ultrasound data also allows you to diagnose the type of cancer.
When to see a doctor
Any even minor symptoms should force a person to seek advice from a specialist. Often tumors in the early stages, like many diseases, are asymptomatic.
The following symptoms should make you think about your health:
- tachycardia;
- discomfort in the hypochondrium on the left side;
- a feeling of nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting;
- low pressure;
- difficulties with bowel movements;
- decreased appetite;
- feeling that the stomach is full, but not a single piece of food has entered it.
If you have at least 1-2 symptoms, you should definitely visit a therapist. He will prescribe an examination and visit to a gastroenterologist.
Tissue Harmonic Mode
Tissue harmonic imaging (THI) overcomes several limitations of B-mode. By obtaining harmonic overtones instead of radiated frequencies, reverberation artifacts are reduced. Image quality is improved by better delineating between fluid and solid structures, increasing spatial and contrast resolution, making millimeter-sized structures detectable. Thus, THI ultrasound may have better resolution than CT and MRI in the absence of excessive obesity or large amounts of intestinal gas, which may temporarily mask the pancreas. There are only a few downsides to THI: reduced frame rate, reduced penetration, and only marginally improved near-sound field image quality. This modality is commonly used with CEUS.
DO YOU CARE CORRECTLY FOR YOUR ULTRASOUND DEVICE?
Download your care guide now
Download PDF
The main symptoms of the inflammatory process
The symptoms of pancreatitis most often manifest themselves when diffusely heterogeneous changes in the structure of the organ are clearly defined and echogenicity is increased. The main manifestations include:
- heaviness in the epigastric (epigastric) region, nausea, vomiting;
- severe pain syndrome;
- subfebrile (37-38℃) body temperature;
- dyspepsia (painful and difficult digestion);
- intense gas formation;
- constipation (constipation), alternating with diarrhea (diarrhea);
- dry mouth, heartburn.
External symptoms include yellowness of the eyeballs, pallor, loss of body weight, and bloating.
Clinical signs - deviations in test results:
- Complete blood count: decreased hemoglobin and red blood cells, increased ESR, leukocytosis (significant increase in white blood cells).
- Blood biochemistry: high levels of enzymes (amylase, phospholipase, lipase), increased bilirubin, glucose, urea, decreased amount of total protein and protein fractions.
- Coprogram (stool analysis): steatorrhea - excess fat, the presence of undigested food fragments, increased elastase levels.
- Urinalysis: amylasuria (increased amylase), proteinuria (presence of protein), dark color.
When analyzing insulin, elevated levels of the hormone are recorded.
Treatment methods
Only after a complete examination and diagnosis can appropriate drug or alternative therapy be selected. Treatment must be carried out under the strict supervision of a gastroenterologist, who will coordinate, regulate the dosage and course of taking medications.
Most often, these types of pathologies are treated with the following methods:
- Acute pancreatitis involves taking medications that reduce acid production and the active production of pancreatic enzymes.
- Therapy for lipomatosis requires adherence to a strict diet, which includes the consumption of foods high in animal fats.
- The presence of calcifications requires dietary nutrition; in complex cases, surgical intervention is indispensable.
- Reactive pancreatitis is treated with appropriate medications and diet.
- To eliminate pain, painkillers are prescribed.
When treating all the pathologies described above, you should definitely stop drinking alcohol and smoking. A week after the start of therapy, the patient is recommended to undergo a repeat ultrasound to monitor the dynamics.
What is echogenicity
The content of the article
An inverted black and white image is what the sonographer sees during the examination. All human organs reflect ultrasound in their own way. The color depends on the density of the organ: the denser it is, the whiter the picture. For example, liquid is depicted in black. The ability of organ tissue to reflect ultrasound is called echogenicity.
Medications
Drug treatment for increased echogenicity is selected depending on the type of pathology. If a malignant neoplasm is detected in the pancreas, the patient undergoes surgery and chemotherapy in a hospital setting.
To stop the development of lipomatosis, it is enough to adjust your diet by adding dietary dishes to it. And in case of exacerbation of pancreatitis, drug treatment is additionally selected in addition to the diet.
To overcome the disease and prevent complications, drugs enriched with enzymes are recommended that help reduce the level of acidity in the stomach and agents that help reduce the fermentation activity of the organ.
The following medications give the best effect:
- Rutacid. This drug, presented in tablet form, helps reduce the level of acidity in the stomach.
Its main component is hydrotalcite. If a patient has problems with the pancreas and liver, then this drug is prescribed to reduce the amount of acid that passes from the stomach to other organs. You need to take the medicine 4 times a day, 2 tablets. It is better to take it after a meal, the interval should be at least 1 hour. The tablets should be chewed well and then washed down with water. The average duration of treatment is 1 month. This drug should not be prescribed to children under 12 years of age, to patients sensitive to the drug, or to those with renal failure. If the dose and course are exceeded, symptoms such as belching, diarrhea, and allergies may occur. Sold freely, average cost 220 rubles. - Nexium. The drug is presented in tablet form, containing exomeprazole. It is this substance that reduces the level of acid in the stomach, suppressing excessive secretion production. Take 1-2 tablets once a day, the duration depends on the severity of the disease, the standard course is 4 weeks. Before taking the tablet, you can dissolve it in water to make it easier to drink. The drug is not prescribed to children, women during pregnancy and lactation, or those with special sensitivity to the components.
- Aprotinin. This is an injection solution with the active ingredient of the same name, which helps suppress excessive fermentation. Prescribed to patients with acute pancreatitis, when tissue necrosis has already begun. The drug is administered 5 ml per day every hour, on the first day, and then up to 3 times a day, the duration of therapy is 3-5 days. The drug is not recommended for poor blood clotting, acute reactions to components, or the first trimester of pregnancy. Among the adverse events, an allergic reaction is most often observed. Price in Russian pharmacies from 500 rubles.
To relieve pain, you can take No-shpa, Diclofenac, Drotaverine.
Traditional methods
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas can also be treated using traditional medicine.
The following recipes give good results; with their help you can normalize the functions of the organ:
- Tincture of pink radiola. Before each meal, half an hour before, drink 1/2 tsp. The course is at least a month.
- Iris and wormwood. Take both ingredients in equal quantities, add 500 ml of water, and prepare a decoction. Leave for a couple of hours. Take 1/2 tbsp. before eating.
- Propolis tincture. 1 tbsp. l. tincture pour 2 tbsp. vodka, leave for 2-3 weeks. Take 50 drops once a day, adding them to milk or chamomile decoction.
- Potato juice. 1/2 tbsp. Drink freshly squeezed juice 30 minutes before meals for 2 weeks. Afterwards take a 10-day break and repeat the course.
- Herbal collection. In equal quantities, take dill seeds, St. John's wort, coriander, mint, elecampane root, and dried herbs. Mix, select 1 tbsp. l., pour 250 ml of boiling water, let it brew. Take 1/2 tbsp. 5 times a day.
Other methods
For treatment to have a quick effect, it is important to adhere to a diet.
Food must be boiled or steamed. It should only be eaten warm. No smoked meats, fatty, spicy, salty. You should not eat mushrooms or food with spices. Alcohol is strictly prohibited.
The diet should consist of:
- lean meats and fish;
- vegetables, stewed or boiled;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- fruit jelly.
You need to eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions.
Prevention
To prevent another exacerbation and increased echogenicity, the following preventive measures should be observed:
- completely eliminate smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- eat right and on time;
- eat at least 4 times a day, small portions;
- minimize the consumption of canned, fatty, spicy and smoked foods;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- play sports, preferably swimming.
Classification
The classification is based on the degree of echogenicity. Each category has a certain connotation. An experienced doctor, by the nature of the image, quickly identifies areas in which pathological processes occur.
Echogenicity has several degrees:
- low is displayed as a black or dark gray spot,
- middle, a light zone appears on the monitor,
- high shade of the area is lighter than normal.
According to the degree of distribution of changes, two types of increased echogenicity are distinguished:
- local,
- diffuse.