Date of publication: 04/01/2016
until March 31
We are giving away 1000 rubles for all services for a visit in March More details All promotions
Pancreatitis
- a disease that affects not only adults, but also children.
Pancreatitis in a child
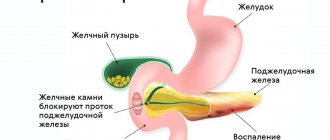
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas produces digestive enzymes. If for some reason these enzymes do not enter the esophagus, but remain in the gland, digestion of the mucous and glandular tissue begins, which causes pain and leads to destruction of the gland.
More information about pancreatitis
The child’s body responds more sensitively to any changes, and the processes in it proceed more actively. Therefore, almost any allergic or infectious disease in childhood affects the pancreas.
At the same time, acute pancreatitis is rare in children, since many factors contributing to its development are absent. In children, reactive and chronic forms of the disease are more common.
About the disease
Pancreatitis is a common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), which is accompanied by local inflammation of the pancreatic tissue and its ducts.
The organ in question plays a key role in the digestion process, ensuring the release of large amounts of enzymes into the intestines. The pancreas is also involved in controlling blood glucose levels through the secretion of insulin. Pancreatitis leads to disruption of these functions, which can cause a serious deterioration in the child’s condition. The disease occurs acutely or chronically. In children, it is important to recognize the pathology as quickly as possible in order to prescribe adequate treatment in a timely manner. Otherwise, the disease progresses and leads to organic damage to the gland tissue and an increased risk of developing serious complications - diabetes mellitus, severe digestive disorders, collapsed reactions (fainting and loss of consciousness).
Causes of development of pancreatic pathologies in the fetus
Congenital anomalies of the pancreas are genetic in nature. Often mutations occur due to the adverse effects of various factors on the expectant father or expectant mother at a certain time before conception, as well as in the first weeks of pregnancy.
Unfavorable conditions include:
- radiation exposure, x-rays;
- state of alcohol intoxication, the influence of large amounts of nicotine at the time of conception;
- taking certain medications;
- viruses and infections.
Symptoms of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a disease that in 90% of cases is accompanied by a violation of the secretion of digestive enzymes by the gland. The result of such a lesion is a deterioration in the functioning of the child’s gastrointestinal tract with the appearance of characteristic symptoms. The most common signs of pancreatitis in children are:
- pain in the abdomen - the discomfort is girdling in nature and radiates to the back;
- flatulence;
- violation of bowel movements such as diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38°C.
In infants and newborns, the symptoms of pancreatitis are less severe than in children of the older age group.
Sometimes parents may not even notice any special changes in the baby’s behavior. In adolescents, the symptoms of the disease differ in brightness and intensity. This is due to the influence of a significant number of provoking factors. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the form and duration of the pathological process, as well as the degree of damage to the pancreas. With chronic inflammation, the pain can be of a protracted, aching nature. At the same time, the child loses body weight, the condition of the skin, nails, and hair worsens.
If any of these signs are detected, parents should seek help from a doctor. Early diagnosis of pancreatitis with the prescription of adequate treatment helps to quickly stabilize the baby’s digestive function and minimize the risk of complications.
Major diseases of the pancreas
Most pathologies of the pancreas begin to develop with pancreatitis. It can have 2 forms - acute and chronic. In turn, acute pancreatitis is of 3 types:
- Edema – accompanied by severe swelling of the gland, which disappears within 5-10 days.
- Sterile pancreatic necrosis - some of the gland cells die, which is not associated with infection.
- Infected pancreatic necrosis - in this case, cells die due to infection. This is the most dangerous condition, leading to death in 80% of cases.
Chronic pancreatitis develops over a long period of time and is not accompanied by acute pain. This disease most often occurs in the age group of 35-50 years. The pain can be either constant or paroxysmal (around the abdomen). This symptom is the most characteristic.
Causes of pancreatitis
The pathogenetic basis of pancreatitis of any origin is local inflammation of the gland tissue.
The key mechanism of this pathological process is the release of excessive amounts of active enzymes, which begin to damage the organ's own structures. Hyperactivation of the secretory function of the gland can be either primary or secondary (develops as a result of pathology of other organs and systems). In newborns and infants, pancreatitis most often occurs as a result of congenital anomalies in the development of the organ and its ducts. Due to the lack of adequate outflow, enzymes accumulate inside the gland and trigger the process of lysis (chemical destruction) of its own tissues.
In school-age children and teenagers, activation of the secretion of bioactive enzymes can be triggered by the following factors:
- eating large amounts of fried and fatty foods - the child’s digestive tract is not suitable for digesting “heavy” foods;
- viral or bacterial lesions of the gastrointestinal tract with penetration of the pathogen into the pancreas;
- narrowing of pancreatic ductuses against the background of neoplastic processes in the abdominal cavity.
The risk of developing pancreatitis also increases with irregular nutrition, consumption of large amounts of fast food, and carbonated drinks. Damage to the pancreas sometimes occurs due to the use of aggressive medications or the entry of toxins into the baby’s gastrointestinal tract.
Impaired organ mobility
- Aberrant variant
. Develops against the background of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. It is expressed in the visualization of an additional pancreas that has grown into the wall of the stomach or intestines. The pathology itself is not dangerous, but it contributes to the development of complications.
An additional organ enters the cavity of the stomach or intestines, which causes inflammation or the development of tumors. The aberrant variant occurs in Edwards syndrome, which is characterized by various intrauterine defects. On ultrasound, the accessory gland has a hypoechoic structure and an additional anechoic duct.
Considering that the pathology is detected in the late stages of pregnancy, the baby is prepared for surgery in the coming days after birth or the functioning of the organ is monitored.
- Ring-shaped option.
The anomaly is associated with the development of the pancreas. The organ develops from two pancreatic kidneys located at the ends of the intestinal tube at 3 weeks from the moment of conception.
Over time, the buds begin to grow, and a system of ducts and branches is formed. The intestinal tube also develops and rotates, and both kidneys, starting from the 7th week from the last gestation, begin to move towards each other, enveloping the rotating intestinal tube, and merge into the head of the pancreas. A loop of the duodenum forms around it, and by the 10th week the pancreas completes its formation.
Under the influence of unfavorable conditions (alcohol, ionizing radiation), atrophy of the segment of the duodenum and stenosis of the organ occurs, as a result of which decompensation occurs, and one of the pancreatic rudiment fusions with the wall of the duodenum.
The annular pancreatic process compresses the duodenum, which is why in 33% of cases newborns with an annular pancreas have stenosis and intestinal atresia.
The pathology occurs quite often - in 5 cases per 1000 newborns. About 0.1% of spontaneous miscarriages in the study had a ring-shaped pancreatic bud. However, in half of the cases, a person learns about the pathology at the age of 30-50 years during an exacerbation of the disease or during an autopsy in the event of sudden death.
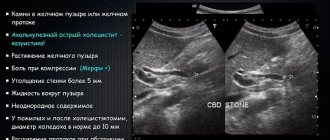
It is quite difficult to identify an annular pancreas on ultrasound. This usually occurs after the 20th week, when the organ is well visualized. The pathology is accompanied by intestinal atresia or stenosis, and an experienced doctor using a 4D sensor is able to see the abnormal shape of the organ. There are cases when a doctor may mistakenly mistake a non-standard form for a malignant tumor that has grown into the intestinal wall, so such a diagnosis should be treated with caution.
Despite the complexity, the pathology does not require termination of pregnancy. However, doctors must be prepared for the appearance of a baby with an annular pancreas. The child will be monitored, and in case of serious malfunctions in the functioning of the body, he will undergo surgery by making bypass loops of intestine around the area of the duodenum narrowed by the ring of the pancreas.
- Gland splitting.
This is an anomaly of the pancreatic ductal system, in which the organ splits and an additional duct is added, which takes on the main excretory function. Bile and digestive secretions are excreted through it, but the width of the duct is not intended for this. The drainage of the pancreas is disrupted, the pressure inside the duct increases, the duct is blocked and the pancreas becomes inflamed.
About 11% of people in the world are born with this pathology. Its main cause is considered to be a violation of the fusion of the germ layers, as a result of which the ducts do not unite, but remain as in the embryonic period. This happens between 30 days and 12 weeks from the moment of conception. In 70% of cases, complete bifurcation of the pancreatic ducts is visualized. All pancreatic juice exits through the accessory duct, and bile through the major duct.
In 25% of cases, the pathology causes congenital pancreatitis. In 6% of cases, the splitting of the ducts is incomplete, and in some areas the ducts are connected, but exit into the duodenum isolated from each other.
On ultrasound, bifurcation of the pancreas is expressed in heterogeneous echogenicity; the additional duct has a denser structure and increased echogenicity. If there is inflammation of the pancreas due to blockage of the duct, echogenicity decreases due to tissue edema. Often the pancreas has an increased size and a heterogeneous echostructure. However, pathology is not an indication for abortion, because in most cases doubling does not lead to disability if the fetus does not have identified chromosomal abnormalities.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
Gastroenterologists and pediatricians at SM-Doctor are specialists with experience of 10 years or more. Thanks to the extensive experience and modern equipment that our clinic is equipped with, doctors can quickly identify pancreatitis even in the early stages of development. All this creates optimal conditions for prescribing adequate treatment and, consequently, restoring the child’s condition in the shortest possible time. The doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis of pancreatitis at the first consultation. Anamnesis of the disease and features of the clinical picture help him with this. To verify the diagnosis, the following additional studies are prescribed:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemical blood test - special attention is paid to the level of alpha-amylase;
- ultrasound scanning (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs;
- stool test for elastase-1;
- CT, MRI of the abdominal cavity (if necessary in complex clinical cases).
If there is a suspicion of concomitant dysfunction of other internal organs and systems, the gastrologist refers the child for consultation to related specialists (infectious disease specialist, neurologist, nephrologist).
Treatment of pancreatitis
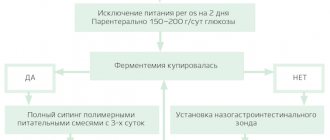
The key aspect of the treatment of pancreatitis is to ensure the maximum possible functional rest of the gland in the acute phase of inflammation.
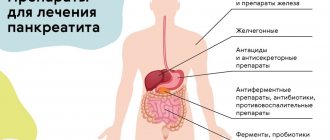
A significant decrease in the secretory function of the organ, created artificially, contributes to the natural attenuation of the activity of the pathological process. For this purpose, doctors prescribe bed rest and fractional consumption of still water (in the first days) with a gradual expansion of the diet through the use of pureed foods. To relieve the clinical picture with the help of medications, the following groups of drugs are used:
- analgesics and antispasmodics - to eliminate pain;
- antisecretory drugs;
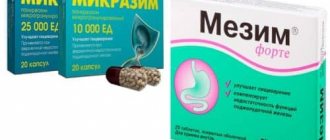
- enzymes - to stabilize digestive function;
- protease inhibitors.
Anomalies of pancreas development may sometimes require surgical treatment.
When a bacterial cause of the disease is identified, the doctor additionally uses antibiotics to destroy the pathogen. Prevention of the disease involves following a rational diet that is appropriate for the baby’s age, and timely treatment of other gastrointestinal diseases.
“SM-Doctor” is a modern clinic specializing in providing a full package of services for the diagnosis and treatment of all kinds of gastrointestinal diseases of children from 0 to 18 years old. Thanks to high-tech equipment and the extensive experience of our doctors, we guarantee a rapid improvement in the well-being of each patient. Contact qualified specialists at a convenient time!