Colon adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumor that develops from the glandular epithelium. In the structure of all oncological neoplasms of the large intestine, it ranks first, accounting for up to 95% of cancers of this localization.
- Causes of development of colon adenocarcinoma
- Classification of colon adenocarcinoma
- Symptoms of adenocaricnoma of the colon
- Examination for adenocarcinomas of the large intestine
- Diagnosis of colon adenocarcinomas
- Treatment of colon adenocarcinoma
- Metastasis of adenocarcinoma
- Complications of colon adenocarcinoma
- Forecast
What's happened
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumor developing from secretory glandular epithelial cells. It is localized on various internal organs, on the internal membranes of hollow organs, as well as human skin.
A distinctive feature of adenocarcinoma is the ability to produce secretions.
Such tumors can have a variety of sizes and shapes, which are directly dependent on the cellular and tissue functions, cellular and tissue structure of the organ that was affected.
Classification
Adenocarcinoma is usually classified according to the location (organ) of the lesion, according to its morphological characteristics, and according to its histological characteristics.
By location of the lesion (organ)
Adenocarcinoma very often affects organs such as:
- Lungs,
- Mammary gland,
- pancreas,
- prostate gland,
- Esophagus,
- Intestines.
According to histological characteristics
There are three types of adenocarcinoma:
G1 (Highly differentiated)
This type of adenocarcinoma is characterized by low-grade malignancy. The morphology of such adenocarcinoma: normal and not quite normal cells that can multiply quickly.
G2 (Moderately differentiated)
The composition of this adenocarcinoma is malignant cells that are very different from healthy ones and can multiply quickly. The nature of these cancers is more aggressive.
G3 (Low differentiated)
Cells of this type of adenocarcinoma are characterized by a high degree of malignancy. They are characterized by complete loss of signs of normal cells. They reproduce actively, unpredictably and haphazardly.
According to morphological characteristics
Based on this criterion, adenocarcinoma is divided into the following subtypes:
Acinar
This adenocarcinoma is a tumor of the prostate gland, is diagnosed more often than others and has a long asymptomatic course. During the study, tissue differentiation is clearly visible: cancer cells of various sizes with nuclei and cytoplasm.
Small-acinar
This is a type of cancer found in the peripheral (most often) prostate gland or transition zone of the prostate. It consists of small acini with structural disturbances in several places.
Mucinous
Adenocarcinoma with different types of cells, characterized by the presence of a cavity containing mucin. In this type of tumor, mucus is produced in large quantities and comes to the surface.
Dark cell
Cancer, inside the cells of which there are polymorphic nuclei with a predominant dark color. The structure is formed from these cells and cytoplasm. It has a glandular appearance. Typically, this subtype of adenocarcinoma progresses quickly, but it all depends on the differentiation of the neoplasm.
Serous
Cancer is formed from differentiated polymorphic and cellular structures. The nature of this tumor is quite aggressive.
Clear cell
Such adenocarcinoma has a cystic-tubular structure and may have a glandular structure. This cancer also develops rapidly, and metastases can often occur.
Tubular
The structure of such adenocarcinoma is cylinders, tubes and cubes (tubular structures). They are localized in fibrous connective tissue.
Follicular
The structure of such adenocarcinoma is colloidal particles. The size of the tumor is inversely proportional to the progression of the lesion: the larger the tumor, the slower the progression and vice versa. Metastases in this subtype of cancer spread through the bloodstream to various parts of the body.
Papillary (papillary)
The structure of this subtype of cancer is similar to papillae or papillomas. This type of adenocarcinoma has a good prognosis in most cases if treated on time.
Invasive
Characterized by the penetration of cancer cells into nearby organs and tissues. If suddenly such a carcinoma enters the blood and lymph, then the spread to parts of the body becomes hematogenous.
Stages
There are several stages of adenocarcinoma development.
Zero stage
Otherwise known as in situ. Malignant cells are present in the body. However, they do not go beyond the epithelial layer.
First stage
Cancer cells extend beyond the epithelium, spreading to other layers, but do not go beyond the boundaries of one organ.
Second stage
It is characterized by the growth of cancer and the presence of metastases in the area of the lymph nodes.
Third stage
Adenocarcinoma spreads to neighboring organs, metastasizing to some groups of lymph nodes.
Fourth stage
A cancerous tumor creates metastases to lymph nodes and organs located remotely from it.
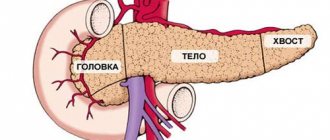
A little about the intestines and the cells that cause the disease
The human intestine is divided into 2 sections: thin and thick. The connection with the stomach begins with the subtle. There are:
- duodenum;
- skinny;
- ileum.
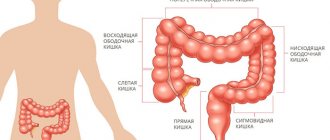
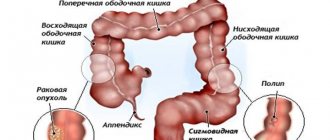
Here the maximum number of enzymes is located, the breakdown and absorption of nutrients is carried out. Everything needed is absorbed into the blood. The large intestine ensures the accumulation and reabsorption of water, the formation of a mass of toxins, and their removal from the body. He shares:
- to the cecum with a vermiform appendix (appendix);
- colon with four parts (ascending, transverse colon, descending, sigmoid and rectus).
The final segment is the rectal ampulla, anal canal and anus. Glandular cells are located on the mucous membrane of all parts. They are wedged between the epithelium and are absent at the tips of the villi. In total, they constitute up to 9.5% of the cellular composition of the small intestinal mucosa, the concentration increases as it approaches the thick section. They differ from their neighbors in their ability to produce mucus, which is necessary to protect the wall from passing feces.
When mucus accumulates, the cells at the apical end expand and take on a goblet-shaped appearance.
After secretion is released into the intestines, they again become prismatic. Malignant degeneration is characterized at first by slow growth into the intestine (endophytic growth) or outward (exophytic), then by a rapid transition to metastasis through the vessels to the nearest lymph nodes, lungs, liver and other organs.
The most severe course is observed at a young age. This is explained by anatomical changes in blood vessels in people over 40 years of age: the lumen decreases, the activity of transferring metastases is less pronounced. And up to 30 years of age, the intestine has a pronounced vascular and lymphatic network, which provides a high risk of metastasis.
Causes of adenocarcinoma
- Stagnation, inflammation of secretion in an organ or cavity;
- Poor nutrition;
- Obesity;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Influence of chemicals;
- Heredity;
- Diseases that were previously suffered by a person.
Let's look at the reasons directly related to certain organs that cause adenocarcinoma.
Pancreas
Adenocarcinoma probably forms there due to smoking or pancreatitis.
Osteosarcoma
Stomach
Cancer can occur due to the presence of Helibacter and due to epithelial changes in the mucous membrane of the organ, as well as due to Menetrier's disease (overdevelopment of the gastric mucosa), polyps, and chronic ulcers.
Prostate
The tumor occurs due to heredity, hormonal changes associated with age, the XMRV virus, chronic cadmium intoxication, and nutrient imbalance.
Symptoms of adenocaricnoma of the colon
Colon adenocarcinoma does not manifest itself for a long time. The first symptoms may appear when the tumor reaches a large size and affects other organs. In some cases, there are indirect signs of the presence of malignant neoplasms:
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Loss of appetite.
- Prostration.
- Anemia, which develops against the background of hidden bleeding from the tumor.
Symptoms are also determined by the location of adenocarcinoma. If the tumor is located in the right part of the colon, then, as a rule, the first symptoms observed are dyspepsia associated with disruption of the functioning of neighboring organs (stomach, pancreas, liver and gall bladder). Hidden bleeding is possible, against the background of which anemia and weakness develop. Since in this place the intestine has a wide lumen and liquid contents, obturation (blockage of the lumen) develops only in the last stages and then not in all cases. If the tumor is large, it can be felt through the abdominal wall.
The left part of the colon has a smaller diameter, and the intestinal contents have a denser consistency, so tumors of this location are more often manifested by intestinal obstruction. Stagnation of intestinal contents leads to increased processes of putrefaction and fermentation, which causes bloating and colicky pain. Constipation is replaced by diarrhea with foul-smelling stools. In some cases, blood may be found in the stool.
Symptoms
At the latent stage of the disease, there are no symptoms.
The first symptoms appear due to tumor growth:
- Pain in the area where the tumor is located;
- Presence of blood clots;
- The appearance of constipation;
- Growth of lymph nodes;
- Weight loss;
- Decreased hemoglobin;
- Fatigue;
- Low ability to work;
- Bad dream.
At the stage of intensive growth of cancer cells and the appearance of metastases, the severity of symptoms increases.
Let's look at the symptoms of the formation of adenocarcinoma in various organs.
Intestines
- Painful stomach;
- Unpleasant sensations after eating;
- Poor intestinal permeability;
- Loose stools alternating with constipation;
- Blood and mucus in the stool.
Esophagus
- Pain when swallowing;
- Dysgaphia;
- Active salivation.
Nasal cavity
- Swelling of the tonsils;
- Persistent inflammation of the tonsils;
- Pain in the larynx, pharynx, nose;
- Unpleasant sensations when swallowing;
- Ear pain;
- Speech impairment;
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Liver
- Pain in the area of the right rib and hypochondrium;
- The eyes and skin are yellowish.
Examination for adenocarcinomas of the large intestine
The gold standard for detecting early-stage colon adenocarcinoma is a total colonoscopy. Euroonco specialists recommend doing it to all people over 50 years old once a decade. This will prevent existing benign polyps from becoming malignant. This method causes some discomfort to patients, so it is often performed under intravenous anesthesia. The cost of such an examination is quite high, and it also requires special preparation.
Patients are not always ready for this procedure, so there is a simpler and more affordable option, although less accurate - testing stool for occult blood. If the test result is positive, the patient is referred for a total colonoscopy.
Diagnostics
Laboratory research
Thanks to them, it can be assumed that a person has oncology if his leukocyte formula is changed, ESR is increased, and there are few red blood cells in the blood. A stool test may show traces of blood (which, of course, is also a symptom of a number of other diseases).
X-ray
This study helps determine the size, shape, and location of the tumor. The procedure is carried out using contrast agents. Often this is barium.
Endoscopy
This procedure uses an endoscope. An examination of the internal organs is done in order to diagnose the disease or its absence. During this procedure, a biopsy is also taken to examine the tissue under a microscope.
Positive emission tomography and computed tomography
Thanks to these methods, it is possible to determine the size, shape, location of adenocarcinoma, and find where the metastases are located.
Ultrasound
This method is considered the most informative for studying adenocarcinoma of the kidneys and bladder. Ultrasound examination allows you to localize the source of the disease, determine how badly the walls of the organ are affected, and assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Treatment
Surgical intervention
Treatment is mainly carried out through surgical intervention.
To maintain a weakened body, specialists prescribe a course of physiotherapeutic medications.
Tomotherapy
One of the newest methods of treating adenocarcinoma is tomotherapy. Thanks to the use of a special 3D scanner, which provides a three-dimensional image of the affected area, it is possible to plan highly precise interventions. The risk of this operation will be minimal.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a method that makes it possible to cure this type of cancer. To use this therapy, you need to look at what stage the cancer is at and how it is spreading in the body.
If damaged lymph nodes are found after surgery, chemotherapy is then given. The duration of chemotherapy depends on the drug itself.
Chemotherapy is also given for severe cases, advanced forms and relapses after surgery.
Adjuvant therapies
Cleansing with an enema with the addition of copper sulfate has a good effect.
Radio exposure. This method is suitable for influencing the tumor before and after surgery in order to reduce the tumor in volume and prevent the occurrence of metastases.
Radiation is used as the main method of therapy in selected cases. This is due to the fact that almost all parts of the large intestine (with the exception of the rectum) are quite mobile and can change position as a person changes body posture.
Diet therapy. There is no specific diet for patients with this type of disease. However, they should pay great attention to including a sufficient amount of fresh and steamed vegetables and fruits in their diet.
They not only saturate the body with useful substances, but are also easier to digest and help improve peristalsis processes in the intestines. Patients who have undergone resection (partial removal) of the intestine should remember that the food they consume should be light, not retained in the stomach, and not cause nausea and accumulation of gases in the intestines (flatulence). Another important aspect is maintaining water balance and diet.
Vitamin therapy. The intake of the required amount of vitamins into the body improves the patient’s general condition and helps maintain a certain balance in the functioning of organs and systems.
There are also traditional methods that are used in the treatment of adenocarcinoma of the large intestine. However, they are a kind of addition to the main treatment. And before using folk remedies, it is imperative to consult with your doctor.
Forecast
For a good prognosis, adenocarcinoma must be diagnosed in the early stages. If the patient already has metastases, he will live for about 4 months, which will also depend on the location of the tumor.
If the esophagus is affected, then when treated in the first and second stages of the disease, a person lives for five years or more. In the third and fourth degrees - death in 25% of cases.
If the liver is affected, the patient will live no more than three years.
Adencarcinoma is a type of cancer in which you need to immediately consult a specialist and carry out the necessary treatment depending on the type of disease, location and degree of damage to the organ.
Typology of the disease
Based on the data obtained during the diagnostic examination, a specialist can easily determine the extent and course of the disease. Based on this information, appropriate treatment will be prescribed. The disease is divided into the following types:
- poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. One of the varieties includes mucous adenocarcinoma, a characteristic feature of which is the release of large amounts of mucus;
- highly differentiated;
- moderately differentiated;
- undifferentiated. This type is characterized by an acute course and unfavorable outcome.