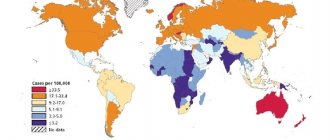
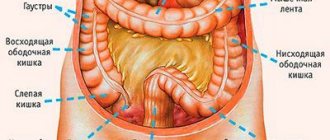
Colon cancer is a malignant tumor that most often forms in people aged 40-70 years. The disease is asymptomatic for a long time or manifests itself as intestinal dysfunction. For this reason, the tumor is more often detected at a late stage of the oncological process, when difficulties arise with performing radical surgery.
- For the diagnosis and treatment of colon tumors, all conditions have been created at the Yusupov Hospital:
- European level of room comfort;
- The latest expert-class diagnostic equipment with high resolution;
- High level of qualification of doctors;
- Application of international protocols and standards for the treatment of malignant neoplasms of the colon;
- Attentive attitude of medical staff to the wishes of patients and their relatives.
Patients requiring palliative care may be treated in hospice care. Severe cases of colon cancer are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council. Doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest qualification category take part in its work. Leading specialists in the field of oncology collectively develop patient management tactics.
Symptoms of colon disease
Signs of this disease:
- Aching, spasmodic pain occurs in the lower abdomen, as well as in the umbilical area.
- After painful bowel movements, relief comes.
- In the absence of inflammation, eating and the occurrence of pain are not related to each other.
- Constipation appears, gradually turning into a chronic form.
- Flatulence develops (most often after eating).
- There may be blood and mucus in the stool.
Diarrhea may also appear, alternating with constipation.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis (UC)
Several factors can provoke the development of the disease:
- heredity;
- presence of infection;
- autoimmune reactions;
- inflammatory processes.
Symptoms can be local (local) or general. The first include:
- feces mixed with mucus, blood, and sometimes pus;
- stool disorder;
- lower abdominal pain;
- flatulence.
Common symptoms include:
- increase in body temperature;
- weight loss;
- general weakness, loss of appetite;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- pain in muscles and joints.
Video about the disease with doctor’s recommendations:
Traditional therapy consists of using:
- Sulfasalazine. In the acute form, 1 g is prescribed 3–4 times a day. During the period of remission, take 0.5 - 1 g twice a day.
- Mesalazine. In case of exacerbation, 0.5-1 g is prescribed 3-4 times per day. In the remission stage - 0.5 g 2 times a day.
- Corticosteroids are used for severe UC. Prednisolone is used at a dose of 40-60 mg per day, the course of therapy is 2-4 weeks. Then the dosage of the drug is reduced to 5 mg per week.
Immunosuppressants are also used in some cases:
- Cyclosporine A. Prescribed for the acute form of the disease at 4 mg/1 kg of the patient’s body weight (intravenously).
- Azathioprine. Used orally at 2-3 mg/1 kg body weight.
In addition, the attending physician, as a rule, prescribes anti-inflammatory medications with an analgesic effect (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol). If you have UC, taking vitamins B and C is mandatory.
Crohn's disease
Possible factors provoking the development of this disease include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- autoimmune system disorders;
- unbalanced diet;
- presence of infection in the body;
- bad habits;
- regular psycho-emotional tension, stress.
Common symptoms include:
- malaise;
- weight loss;
- increase in body temperature.
We recommend watching a video about Crohn's disease:
Local symptoms:
- systematic diarrhea;
- pain in the abdomen, similar to pain from appendicitis;
- infiltration;
- perforation of the intestinal walls;
- bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction.
Extraintestinal disorders:
- joint pain, limited mobility;
- inflammation of the sacroiliac area;
- deterioration in the functionality of the visual organ;
- skin rashes.
Aminosalicylates are prescribed as therapy. For example, Mesalazine 3-4 g/day. or Sulfasalazine 4-6 g/day, dividing the dose into 4 doses. The dosage of medications is gradually reduced after the remission stage appears.
Diverticulosis of the colon
The main reasons for the formation of the disease:
- violation of the structure of the walls of the colon;
- dysfunction of blood vessels;
- weakening of muscle tissue.
In addition, there are factors that can provoke the development of the described pathologies:
- chronic intestinal inflammation;
- regular constipation/diarrhea;
- unbalanced diet;
- trauma/surgery;
- deficiency of useful compounds;
- natural wear and tear of muscles (in old age);
- insufficient consumption of plant fiber.
Among the signs of the development of the disease are:
- increased gas formation, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen;
- excessive salivation;
- intestinal dyspepsia;
- systematic stool disorder;
- formation of streaks of blood and/or mucus in the stool;
- feeling of nausea;
- lower abdominal pain
- fever;
- intestinal bleeding.
For uncomplicated diverticulosis, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- laxatives (Duphalac, Romphalac, Goodluck);
- antidiarrheal drugs (Silix, Loperamide, Lopedium);
- painkillers (Drotaverine, Spazmalgon, No-shpa);
- agents that stimulate gastrointestinal motility (Motilium, Domperidone);
- enzymes (Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin);
- broad-spectrum antibiotic drugs (Amoxicillin, Ceftriaxone, Ampicillin).
In some cases, surgical treatment is used.
Kinds
Macroscopically, two forms of malignant neoplasm of the colon are distinguished - exophytic and endophytic. The first form of cancer is characterized by tumor growth into the intestinal lumen. It can take the form of a node or polyp, most often found in the right half of the colon, and is shaped like a cauliflower. An endophytic tumor in most cases forms in the left half of the colon. It infiltrates the intestinal wall, gradually covers its entire circumference and causes circular narrowing. Ulcers often form on the tumor.
Morphologists distinguish the following histological types of malignant neoplasms of the colon:
- Adenocarcinoma;
- Mucosal cancer;
- Solid cancer.
Colon cancer metastasizes late. This allows oncological surgeons to perform radical surgical interventions even with large tumors. The tumor is involved early in the inflammatory process. It often transfers to the fiber that surrounds the intestines. Metastases can remain in regional lymph nodes for a long time. They are removed during surgery along with the mesentery.
Make an appointment
Colon polyps
There are several factors that can trigger the development of the disease:
- heredity;
- chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine system disorders;
- autoimmune diseases;
- presence of bad habits;
- frequent stress, emotional overstrain.
Polyps appear:
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- the formation of mucus and/or blood in the stool;
- intestinal discomfort;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- pain syndrome in the lower abdomen;
- intestinal obstruction.
In some cases, intestinal bleeding is present, which can result in anemia.
Polyps cannot be cured with the use of medications. Therapy for this pathology is carried out only by surgery.
In case of early diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is considered favorable. Relapses are possible, which usually occur a couple of years after surgery.
Diagnostic methods
Doctors at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of colon cancer based on an analysis of the clinical picture of the disease, physical examination data, endoscopic and radiological studies, and biopsy results. The following changes may occur in the blood test:
- Anemia (decreased number of red blood cells and hemoglobin);
- Hypoproteinemia (decreased protein concentration);
- Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate;
- Hypoprothrombinemia (decreased platelet count);
- Decreased hematocrit.
A laboratory test is used to determine the presence of occult blood in the stool. During irrigoscopy (x-ray examination of the large intestine with barium contrast), the location, size, extent and growth pattern of the tumor are determined. X-rays show characteristic signs of a malignant tumor of the colon:
- Narrowing (stenosis) of the intestinal lumen;
- Filling defect;
- Rigidity of the intestinal wall.
Colonoscopy (endoscopic examination) allows you to examine all parts of the colon and perform a biopsy. Sections of tissue from pathologically changed areas of the intestine are sent to a morphological laboratory to verify the histological type of cancer. Using colonoscopy, performed using the latest equipment, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital identify the initial stages of colon cancer that are inaccessible to other research methods.
To exclude the presence of liver metastases, radioisotope scanning is performed. Doctors at the oncology clinic take the results of the study into account when determining the stage of the tumor process and drawing up a plan for surgical intervention. Positron electron computed tomography (PET-CT) is performed if metastases are suspected. If using these diagnostic methods it is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis, oncologists perform exploratory laparotomy.
Before surgery, surgeons carry out a differential diagnosis of colon cancer with the following diseases:
- Tuberculosis;
- Crohn's disease;
- Actinomycosis.
If the tumor is located in the left half of the colon, amebiasis, diverticulitis, and ulcerative colitis are excluded. If the hepatic angle is affected by a malignant tumor, a differential diagnosis is made with a tumor of the liver or right kidney, calculous cholecystitis. If oncologists suspect cancer of the splenic flexure of the colon, they exclude a tumor and cyst of the spleen, tail of the pancreas or left kidney.
Hirschsprung's disease
This disease is congenital, occurs in utero, and is hereditary.
Main symptoms:
- constipation;
- feeling of nausea;
- abdominal pain;
- gagging;
- flatulence.
We recommend a video about congenital disease in children:
Conventional treatment cannot completely cure the patient. However, it can be used to prepare the patient for surgical therapy. To do this you need:
- stick to the diet menu;
- stimulate peristalsis with massage, therapeutic exercises;
- do enemas;
- use protein preparations, electrolyte solutions intravenously;
- take vitamins.
The prognosis for Hirschsprung's disease is relatively favorable if surgical treatment is performed before complications develop.
Recovery after surgery
The Ilyinskaya Hospital has implemented the concept of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS).
This set of measures is aimed at the fastest possible physical and psychological rehabilitation of the patient after even extensive surgical interventions, as well as social adaptation. The ideology is based on the results of many years of international clinical research, recognized and implemented in all developed countries. It includes: preoperative preparation - prehabilitation, a special technique for administering anesthesia during surgery in combination with minimally invasive operating techniques, early mobilization of the patient (you can sit up in bed, do breathing exercises, get to your feet soon after transfer to the ward), early alimony ( You can start eating and drinking soon after surgery). This helps to quickly restore intestinal function and avoid the development of complications from the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
All patients who have undergone surgery for colon cancer remain under the supervision of an oncologist and regularly undergo scheduled examinations to timely detect the progression of the disease and adjust the individual treatment plan.
Infectious colitis
The main cause of the disease is the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
Infectious colitis can also occur as a result of syphilis or tuberculosis. Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves in:
- increased body temperature;
- development of diarrhea with blood and mucus;
- general weakness;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area;
- the appearance of plaque on the tongue;
- drying of mucous membranes.
The mainstay of treatment is the use of antibiotics. The doctor also prescribes enzyme preparations and probiotics. It is necessary to monitor the water regime.
In case of timely detection of the disease and its treatment, the outcome is considered favorable. An unfavorable prognosis for infectious colitis occurs when the disease progresses to a severe form. In order to prevent the development of this pathology, it is necessary to regularly wash your hands and adhere to hygiene rules.
CAUSES OF PROPRESSION OF INTERNAL ORGANS (GIT)
This pathology, like many other diseases, can be congenital or acquired . The cause of chronic organ prolapse may be the already mentioned weakness of the ligamentous apparatus and muscles.
ᅠᅠ The reasons related to acquired omission include:
- Hard physical labor;
- Regular physical or strength exercises for which the body is not prepared;
- Metabolic disorders, which can result in various diseases;
- Overweight;
- Age (especially after forty);
- Consequences after childbirth.
This disease was once considered the province of the elderly, but over time, prolapse of one or more internal organs is increasingly found in middle-aged and even young people.
Colon dyskinesia
The causes of the disease have not yet been identified, but there are factors that can trigger its occurrence:
- systematic psycho-emotional tension, stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- unbalanced menu;
- drug abuse;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- individual intolerance to certain products;
- lack of vitamins;
- hormonal imbalance;
- presence of infection;
- sedentary/overactive lifestyle;
- endocrine disorders;
- gynecological diseases.
We recommend a video about irritable bowel syndrome:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jaiYO2zCkrI
Signs of the disease:
- stool disorder;
- flatulence;
- abdominal pain;
- nervousness, depression.
As a medical treatment, the doctor prescribes:
- Drugs that regulate gastrointestinal motility (Trimedat, Excedrin, Motilium).
- Antiemetic drugs (Cerucal).
- Antispasmodics (No-spa, Papaverine, Metacin).
The prognosis is considered favorable, but long-term remission can be achieved only in 10% of cases.
Treatment of pain in the intestines on the right and left lower abdomen
To determine the cause of severe pain in the intestines on the left and right side of the lower abdomen, the patient should visit a doctor. After the initial examination and consultation, the patient will be sent for testing. A general analysis of blood, urine and feces will show the internal indicators of the body and demonstrate the presence of any abnormalities in the systems of the human body.
For clearer results, the patient is referred for a bacteriological examination of stool, colonoscopy and endoscopic examination. After receiving the test results, the attending physician prescribes treatment for the patient. A medical expert prescribes medication, homeopathic or surgical intervention in advanced cases.
If necessary, to obtain information about the condition of the internal organs, the doctor refers the patient to undergo a computed tomography or ultrasound scan. These diagnostic tests are not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under sixteen years of age. Health care professionals do not recommend these procedures for certain groups of the population. The use of radiation and contrast fluid can negatively affect healthy organs.
To make an appointment for a consultation or examination at the private clinic “KDS Clinic”, leave a request on the website and managers will contact you as soon as possible.
Colon cancer (Colon cancer)
Provoking factors:
- heredity;
- the predominance of animal fats and refined foods in the diet;
- unbalanced diet;
- obesity;
- physical inactivity;
- chronic constipation;
- elderly age;
- atony, intestinal hypotension in older age;
- precancerous conditions;
- working activities in hazardous industries.
Signs:
- pain in the abdominal area;
- feeling of heaviness;
- rumbling;
- loss of appetite;
- alternating constipation with diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- belching;
- intestinal obstruction may occur;
- impurities of blood and mucus in the stool;
- deterioration of general condition.
The leading method of treating the disease is surgery. Radiation therapy is used as an auxiliary treatment. Chemotherapy is used in rare cases.
With timely detection and treatment of ROC, the prognosis is favorable.
REASONS FOR PROPRESSION OF INTERNAL ORGANS IN WOMEN
Almost half of women, to one degree or another, suffer from prolapse and prolapse of the uterus (prolapse) , which is almost always accompanied by prolapse of the vaginal walls, prolapse of the rectum, and bladder (with ensuing consequences that do not pose a threat to life, but greatly affect its quality, suppressing the moral state of a woman).
Moreover, there is no dependence on the number of vaginal births - everyone suffers, both those who have given birth and those who have not given birth, the elderly and teenagers. This happens due to the weakening of the muscles that support these organs, especially the uterus, which seems to hang on these muscles that support it. The uterus is suspended by ligaments in the center of the pelvis and can move freely in the pelvic cavity. Normally, the uterus is held in place not only by ligaments, but also by the pelvic floor muscles . When the ligaments and muscles weaken, the uterus prolapses . In severe cases, the uterus may come out. The structures of the pelvic floor are hormone dependent. Their strength depends on the presence of female sex hormones (estrogens) . During menopause, estrogens decrease and the strength of the pelvic floor structures decreases.
Often this prolapse leads to prolapse of the walls of the vagina and bladder , or, on the contrary, prolapse of the bladder leads to prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls. Our doctor will immediately determine, using simple tests during examination, what the cause is.
In such cases, official medicine recommends hormone replacement therapy, which supposedly strengthens the ligamentous apparatus, or surgical intervention is prescribed. However, this method has not undergone enough research and has a large list of side effects (harmful effects on other organs and the general health of a woman), so the specialists of the Health Palace use only drug-free methods of healing in their practice.
Prevention of diseases
In order to minimize the likelihood of colon diseases, it is recommended to eat foods rich in fiber, avoid consuming unhealthy fats, promptly eliminate signs of constipation, and be more attentive to your health.
If symptoms of intestinal dysfunction occur, you should consult a proctologist.
Upon reaching the age of 50, you should visit your doctor annually and undergo a colonoscopy (even if there are no complaints).
In addition to the main treatment, the patient must adhere to a dietary menu, which is the key to successful therapy and transition to a long-term stage of remission.
Therapeutic measures after surgery
After the operation, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, where doctors monitor vital functions (blood pressure, oxygen saturation, kidney function), and also provide the necessary therapy. If the postoperative period is favorable, the patient is transferred to a hospital ward, where he receives further treatment. The doctor selects the diet for the patient in the postoperative period individually, depending on the volume and nature of the intervention. The main task after surgery is early rehabilitation of the patient. Subsequent treatment tactics after discharge are determined based on the results of histological examination at the oncology consultation