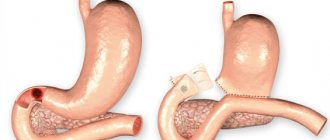
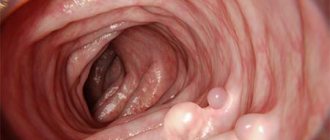
Polyps are benign tumors that grow into the lumen of hollow organs and are distinguished by a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Quite often, polyps affect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. The risk of their occurrence increases in older people, smokers, with type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, and also with a family history. Polyps are often detected accidentally, during endoscopic examination (gastroscopy and colonoscopy), performed on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist.
Polypectomy
Neoplasms carry the risk of becoming a malignant tumor and therefore must be removed. If a single polyp less than 0.5 cm in size is detected, expectant management can be used - such a polyp can be observed over time by performing an endoscopic examination at least once a year, which will prevent the development of complications. In all other cases, polypectomy is a necessary measure.
Polypectomy with endoscopic examination - 15,000 - 40,000 rubles.
5-15 minutes
(duration of procedure)
1-3 days
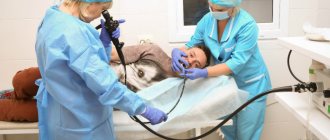
An operation to remove polyps from the stomach and intestines (polypectomy) is a fairly common surgical procedure. The procedure, at first glance, is simple and minimally invasive, because it is performed using endoscopic equipment, that is, without incisions.
However, despite the apparent simplicity of the manipulation, the removal of polyps has a number of important nuances on which the further prognosis of the disease depends. If patients tolerate this procedure quite easily and with a minimal recovery period, then the doctor is required to have extensive practical experience in performing diagnostic and surgical procedures. The type of endoscopic equipment used also matters.
If polyps are detected, endoscopists at the CELT clinic can perform a polypectomy during an endoscopic examination, provided that the size of the polyp does not exceed 10 mm. If the tumor turns out to be large, the operation is postponed and performed after additional examinations. If necessary, to decide on the extent of intervention, a biopsy of the lesion is first performed for histological examination.
Indications
- polypoid formation of the stomach or colon more than 5 mm;
- polypoid formation less than 5 mm, suspicious for malignancy.
Contraindications
- blood clotting disorder;
- acute inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract;
- acute infectious diseases;
- critical condition of the patient.
Symptoms
In the early stages, in most cases, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. It can only be detected by endoscopic examination. If the disease progresses, the following symptoms occur:
- pain after eating that is aching or pulling;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- blood during bowel movements;
- irregular and/or modified stools;
- vomit;
- smell from the mouth;
- abdominal pain radiating to the shoulder blades or lower back;
- fast saturation;
- decreased appetite;
- flatulence;
- general weakness.
Most of these symptoms are characteristic of gastritis and a number of other gastrointestinal diseases. Therefore, for diagnosis you need to contact a medical center; only a specialist can determine the disease and the degree of its development.
Main types of polyps
There are three main types of polyps:
- Adenomatous. If we rely on statistics, then this type of neoplasm is the most common and more often than others undergoes malignancy. Every second inhabitant of the planet over 60 years of age suffers from polyps in the stomach and intestines, the size of which usually exceeds 1 cm.
- Serrated. The likelihood of transformation into cancer directly depends on the size of these polyps and their location. So, the smaller the tumor size, the lower the risk of degeneration. Localization of a neoplasm in the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract increases the likelihood of malignancy, while its location in the lower parts of the colon rarely undergoes malignancy.
- Inflammatory. They are not polyps in the true sense of the word. They occur against the background of various inflammatory diseases (for example, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, etc.). Despite the low risk of transformation into cancer, this type of polyp creates favorable conditions for the growth of cancer cells.
Do I need to remove polyps in the uterus?
The opinion of experts is clear - remove them, since they are often the cause of infertility and can lead to various complications. In some cases, the final decision is made by the patient, who is informed of the possible consequences of refusing surgery. If the following indications are present, surgical intervention is mandatory:
- age after 40, premenopausal period, when hormonal changes occur in the body, provoking the active growth of tumors;
- if the size of the polyps is more than 10 mm, they interfere with conception, cause bleeding, and can develop into oncology;
- in the treatment of infertility - overgrown formations impair the movement of sperm through the tubes, and even in the case of fertilization lead to termination of pregnancy in the early stages;
- lack of effect from hormone therapy, which relieves the symptoms of the disease - bleeding, menstrual irregularities, pain, discharge mixed with pus;
- the presence of adenomatous forms.
The decision is made by the doctor after diagnosis. If the neoplasms are single, their size does not reach 10 mm, conservative treatment with the use of hormonal drugs is possible.
How is the operation performed?
One of the important factors determining the tactics of polypectomy is the size of the tumor:
- Polyps up to 0.5 cm. In this case, removal of the tumor can be carried out at the stage of diagnostic examination - fibrogastroscopy or colonoscopy.
- Polyps larger than 0.5 cm. The operation begins only after additional examination methods have been carried out, excluding the presence of contraindications. After polypectomy, provided that a tumor up to 3 cm in size is removed, the stay in the clinic ranges from several hours to 2-3 days. Active monitoring of the patient continues as long as the patient’s general condition requires.
At the end of the procedure, the removed material is always subjected to histological examination.
Surgery to remove endometrial polyp
Polyps are removed in several ways, the most used of which are hysteroscopy and curettage. Regardless of the technology of surgical manipulation, a tissue sample must be sent for histological examination for oncology. Other methods are also used:
- scraping;
- cryodestruction (carried out with liquid nitrogen);
- polypectomy;
- laser coagulation;
- diathermocoagulation.
Before determining the optimal technique, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis - examination, ultrasound, tests. The patient’s age, individual characteristics of the body, and areas of localization of tumors are also taken into account. The order of the procedure and the timing depend on the method of intervention.
Why choose CELT clinic?
- Medical personnel. The high level of qualifications and many years of experience of our specialists indicate that you can trust us with your health.
- Manufacturability. Advanced medical technology allows all diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be carried out at a very high level.
- Accuracy. You can be confident in the reliability of the results of histological examination of the collected material.
- Save time. The entire course of treatment, starting with a clinical examination, examination of the patient and ending with a series of therapeutic measures, including highly specialized care, takes a minimum amount of your precious time.
Removal of endometrial polyp with laser
Laser therapy is an effective technique that involves the use of laser beams of varying intensities. So, for small tumors, weaker rays are used. For large ones, over 10 mm, high-intensity rays are used. During the procedure, a hysteroscope with an LED and a mini camera is inserted into the vagina. Then the surgeon, guided by the image on the monitor, directs a laser at the affected area and burns out the polyp. The beam removes the tumor layer by layer without damaging other tissues, eliminating infection and completely removing the stem. There are no scars left after the procedure.
Doctors performing polypectomy – endoscopists:
Gerasimets Viktor Alexandrovich
Endoscopist
22 years of experience
Make an appointment
Danyushin Vladislav Mikhailovich
Endoscopist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 37 years
Make an appointment
Endometrial polyp curettage
Curettage or curettage is a popular technique that involves removing the top layer of endometrial cells. To do this, an inert gas or a special liquid is pumped into the uterus to improve visibility of the operated area. Then a hysteroscope equipped with a camera and illumination is inserted into the cavity vaginally, through which an enlarged image of the area affected by polyposis is displayed on the monitor screen. Having obtained a clear image, the surgeon scrapes off the endometrial mucosa with a curette. The procedure takes 20-40 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia. If no complications arise, the patient is discharged the next day. Contraindication to curettage is inflammatory processes in the uterus.
Watch the video
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Endoscopic polypectomy of the intestine and stomach
I had a gastroscopy at your center and was very worried about how everything would go, but it turned out that everything went quickly and painlessly.
I cannot describe in words how grateful I am to Vladislav Mikhailovich Danyushin. For his golden hands, professionalism, kindness of heart! Wonderful doctor! Low to you... Read full review Tatyana K
28.07.2021
On 02/01/2021 I was examined at the diagnostic and treatment department of CELT JSC. I would like to express my gratitude to the head of the department, Alexandra Ivanovna Malykhina, for her attentive and informal attitude towards me, as well as for the effective organization of work to clarify my diagnosis and prescription... Read full review
Alexander Sh
02.02.2021
Removal of endometrial polyp - hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopic removal is considered the most gentle, since it is carried out without violating the integrity of the tissue. Dilators are inserted into the vagina, allowing the surgeon access to the affected areas. Then, using a hysteroscope equipped with a light source and a video camera, an enlarged image of the polyp is displayed on the monitor. Guided by the video material, the doctor removes the tumors and cauterizes the areas where they were located.
The procedure lasts 20-40 minutes and is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the number of polyps.
A week before hysteroscopy, the patient should not douche, use suppositories, take medications (except those prescribed by the gynecologist), and sexual intercourse should be avoided for the last 3 days. The operation is scheduled for the 10-15th day of the menstrual cycle. The recovery period lasts 1-2 months. You can plan a pregnancy in six months.
Consequences of polyp removal
Since polypectomy is considered a minimally invasive, gentle operation, complications are rare. Usually after it there is bleeding that lasts up to 10 days, brown discharge, and leucorrhoea mixed with blood. If the discharge has an unpleasant odor or contains pus, you should immediately consult your doctor. After removal, the first few days the temperature may rise to 38 degrees, pain in the lower abdomen. There is also a change in the menstrual cycle. The first couple of months the cycle is not regular. Then it is restored. If menstruation has not returned, has become painful and lasts more than 7-8 days, this is a reason to consult your doctor.
Polypectomy is usually well tolerated and proceeds without complications in 90% of cases.
Recovery
After using minimally invasive polypectomy techniques, the recovery period is 2-3 months, which depends on the patient’s age, body condition, the nature of the tumors, their size, and quantity. To consolidate the effect and prevent relapses, the following types of therapy are practiced:
- Medication. For the first three days, No-Shpa (Drotaverine) is prescribed to eliminate pain and also prevent the accumulation of blood clots in the uterus. If necessary, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and/or antibiotics if there is a pathogenic microflora.
- Herbal medicine, taking vitamins, dietary supplements, diet, promoting a speedy recovery.
- Hormone therapy. Indicated if the occurrence of polyps is due to hormonal imbalance. The selection of drugs is carried out individually.
One of the treatment methods or all in combination can be used. Also, after the operation, you cannot have sex, lift weights (no more than 3 kg), play sports, go to the sauna, or take baths.