pain
gastrointestinal tract
stomach ulcer
stress
pancreatitis
The entire group of gastrointestinal diseases has a number of general and specific symptoms. In addition to the general clinical symptoms characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, symptoms such as abdominal and back pain . If this symptom occurs in combination with other signs of gastrointestinal abnormalities, then their relationship can be traced. Regardless of previously diagnosed or undiagnosed diseases of the digestive system, the appearance of back pain is a direct indication for seeking advice from a gastroenterologist.
Causes of stomach pain
Pain in the stomach is a sign of inflammatory, ulcerative or degenerative changes in internal organs, as well as irritation of nerve receptors. It can be acute or aching, bother the patient constantly, appear suddenly or at certain hours. In some cases, it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes the discomfort is associated with eating - the pain intensifies on an empty stomach or after eating.
Stomach pain can be divided into several categories:
- visceral - irritation of nerve receptors on the walls of the abdominal cavity and internal organs occurs;
- parietal - occurs when the peritoneum is irritated;
- inorganic pain (neurogenic, psychogenic and others not associated with damage to the digestive tract).
The causes and treatment of stomach pain are interrelated, so it is important to determine which pathology triggered its development. The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that in some diseases it radiates, that is, it is transmitted along the nerves from distant areas. This is why self-medication at home can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous.
Gastritis
Gastritis is one of the most common causes of stomach pain, inflammation of its mucous membrane. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. In the second case, it manifests itself only during periods of exacerbation, which may be due to irregular and unhealthy diet, taking certain groups of drugs, stress or other factors.
All gastritis is conventionally divided into microbial and non-microbial. A complete classification of this disease identifies several main types:
- type A - autoimmune, associated with the development of an allergic reaction to one’s own organs and tissues;
- type B - exogenous, occurs when the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is activated;
- type C - can be triggered by chemical irritation of the mucous membranes with drugs (NSAIDs), chemicals or bile;
- inflammation due to an increase or decrease in the concentration of hydrochloric acid;
- special forms of gastritis.
There are two more types of gastritis that require radically different treatment tactics. They can be distinguished by the results of laboratory tests of gastric contents:
- hyperacid - occurs with intense release of hydrochloric acid and increased acidity of gastric juice;
- hypoacid - accompanied by a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice.
Inflammatory processes can also be triggered by abnormalities in the structure of the stomach. Thus, when the pyloric sphincter is weak, the contents of the duodenum are thrown into the stomach, which does not occur normally, and causes pain. It is also necessary to take into account the nature of inflammation. It can be aseptic, purulent, fibrinous, hemorrhagic (with bleeding) or mixed.
Peptic ulcer
The appearance of an ulcer on the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum may be associated with a long-term chronic course of gastritis, as well as other diseases. Among other things, it can be triggered by weakness of blood vessels and disruption of blood flow in a certain area. Peptic ulcer disease occurs in a chronic form with periodic relapses. It manifests itself with a number of characteristic symptoms:
- hunger pains - discomfort in the stomach during long breaks between meals;
- night pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- digestive disorders, including flatulence or diarrhea;
- the appearance of blood impurities in the stool, that is, its coloration in a black tint.
The most dangerous condition is perforation of the ulcer. This condition is accompanied by severe pain in the stomach and deterioration in well-being, including loss of consciousness. If the contents of the stomach or duodenum enter the abdominal cavity, there remains a risk of purulent inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis) with all the manifestations of sepsis.
Hungry (night) stomach pain
Hunger pain in the stomach is usually called those that occur 5-6 hours after the last meal. It is during this period of time that the food bolus passes through the stomach and duodenum so that they remain completely empty. This can be easily prevented during the day (including by drinking water), which is why hunger pain is also called night pain. They often occur between 3 and 5 am.
The main cause of hunger pain in the stomach is irritation of the mucous membrane by the organ’s own contents. Here it constantly secretes gastric juice, which digests food into small components. However, it affects its own mucosa in a similar way. If it is initially damaged, it will react to irritation with acute pain.
The causes and treatment of nighttime stomach pain may vary. In most cases, this syndrome is caused by gastritis of various origins. However, it can also be caused by a more dangerous condition - peptic ulcer disease.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, which is closely related to the functions of the stomach and duodenum. Its main function is the production of pancreatic juice. It is released into the lumen of the small intestine and neutralizes the acidic contents that come from the stomach and contain hydrochloric acid. Pain with pancreatitis is caused by inflammatory processes and dysfunction of the organ - if pancreatic juice is produced in insufficient quantities, the mucous membranes of the digestive tract are irritated by acids.
Among the causes of pancreatitis are:
- disruption of the outflow of pancreatic juice and its accumulation in the organ cavity;
- non-compliance with the diet, consumption of large amounts of animal fats, alcohol and other unhealthy foods;
- hormonal factors;
- gastritis, hepatitis, cholecystitis.
The pain with pancreatitis is acute and spreads to the upper abdomen. It can be encircling in nature and located in the area of the left and right hypochondrium. Discomfort increases after eating or prolonged fasting.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder can also be one of the causes of pain in the stomach. This organ is a hollow sac in which bile accumulates. Then it enters the bile ducts into the lumen of the small intestine and participates in the digestion (emulsification) of fats. Violation of this process leads to pathologies of the digestive system, gastritis and duodenitis.
All cholecystitis can be divided into two groups:
- calculous - associated with the formation of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder, irritation of its walls and blockage of the bile ducts with stones;
- non-calculous - develops due to poor diet, injuries, or infection activity.
The work of the gallbladder, unlike the pancreas, is directly related to the digestive processes. Its sphincter relaxes when food enters the stomach so that bile can flow freely into the intestines. If a long period of time passes between meals, the liquid fills the bladder and causes its walls to stretch.
In digestive pathology, the composition of the food consumed is important. An abundance of animal fats, which contain excess cholesterol, provokes the formation of stones. They can be of different shapes and sizes, have smooth or sharp edges. Stones can clog the bile ducts and injure the mucous membrane of the biliary system. The pain with cholecystitis is acute, spreading to the area of the right hypochondrium, stomach and intestines. It is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, and increased gas formation.
Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
One of the main causes of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is the activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora. The main gastric infection is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which can remain in its cavity for a long time and cause irritation of its mucous membrane. It is part of the gastric microflora of most of the population, but its activation occurs only with a confluence of favorable factors. These include mutations and increased virulence of individual strains, decreased body resistance and irritation of the gastric mucosa with food or drugs.
The bacterium is a trigger for the development of a number of pathologies:
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- adenocarcinomas and lymphomas of the stomach.
The pain is localized in the epigastrium and mesogastrium and can be sharp, cutting or aching. The clinical picture is complemented by characteristic symptoms of diseases of the digestive tract: decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea. Infectious inflammation can also be triggered by other pathogens, including staphylococci or streptococci.
Neoplasms
Gastric tumors are a group of neoplasms that differ in origin, size and degree of danger to the patient. All of them can be divided into two groups: benign and malignant. The former are limited in size, do not grow into organ tissue and do not affect large vessels, and do not form metastases. The danger of benign tumors is that during the process of their growth they can become malignant, that is, become malignant.
Benign tumors include:
- polyps - rounded formations on a stalk that are easily removed surgically;
- leiomyomas - originate from the muscular layer of the organ wall;
- lipomas - from the submucosal layer;
- angiomas - vascular tumors;
- Neuromas - develop from nervous tissue.
Among the malignant neoplasms of the stomach are:
- adenocarcinomas - stomach cancer that originates from the epithelium;
- carcinoid - has a neuroendocrine origin, can secrete hormones;
- leiomyblastomas - develop from cells of epithelial and muscle tissue;
- malignant lymphomas and others.
All neoplasms are manifested by constant pain in the stomach area. There may be a decrease in appetite and a quick feeling of filling the stomach with food while eating. The patient's general condition worsens, accompanied by headaches and general intoxication. Small benign tumors may not appear for a long time and are only discovered then. when they reach significant sizes.
Other reasons
Painful sensations in the stomach can occur with more rare conditions, which must be taken into account during diagnosis. These include pathologies not only of the gastrointestinal tract, but also of other organs. So, pain can have the following causes:
- diaphragm spasm - discomfort increases with certain body positions;
- colitis (inflammation of the large intestine) - also manifests itself in the upper abdomen;
- appendicitis - pain can occur not only on the right, but also in any part of the abdominal cavity;
- coronary heart disease - pain radiates to the stomach;
- pathologies of blood vessels (thrombosis of intestinal vessels, dissection of the abdominal aorta and others).
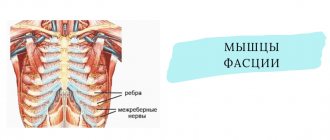
All these pathologies are manifested by chronic or acute pain in the stomach, which can spread to other areas. So, it can be encircling, that is, also covering the area of the left and right hypochondrium, or one-sided. Painful sensations that primarily arise in the stomach area and then spread to the back are often interrelated.
Why are girdling pains dangerous?
The danger of such sensations is due to the fact that they can be a sign of a serious illness and for this reason they should not be ignored.
In what cases may sensations indicate the development of pathological processes in the human body:
- if accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- provided that the sensations are acute and there is no way to eliminate them on your own;
- in the presence of pathologies in the functioning of the organs of the digestive system;
- if, in addition to unpleasant sensations, a person has other symptoms: vomiting, belching, heartburn.
Pain is dangerous because it can disrupt the usual rhythm of life, introducing its own adjustments, which is not always convenient for a person.
If unpleasant sensations appear with frightening frequency, occurring more often than 2-3 times a day, then you should consult a doctor for help.
Diagnostic methods
It is possible to understand the cause of stomach pain and determine the correct treatment tactics based on instrumental and laboratory studies. At the initial examination, the localization and nature of pain is determined by palpation, as well as the degree of its irradiation.
Next, a set of studies may be prescribed:
- Ultrasound - determines the condition of the organ wall;
- MRI, CT are more informative methods that are necessary if tumors are suspected;
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- urine and stool tests;
- probing of the stomach and duodenum with further examination of the contents (acidity is determined, microscopy and bacterial culture are performed).
Diagnosis begins with simpler methods that allow you to identify the most common stomach diseases. If necessary, additional studies are prescribed. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has all the conditions for conducting a comprehensive diagnosis of stomach pain.
Causes of pain in men
“It hurts in the lower abdomen, lower back and right side” - men often go to the doctor with such complaints. To understand what caused it, it is worth considering the cases in which such a symptom appears.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis
differs not only in that it pulls the lower back on the right and the stomach, but also in some other symptoms. For example, a man notes a burning sensation when visiting the toilet, as well as problems with erection. The cause of the disease is often stagnation of capillary blood, as well as the effect of bacteria on the body.
Bacterial infections
If unpleasant symptoms appear, when there is pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, the problem may lie in the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body. Bacteriological causes of pain are considered quite common. For example, stomach and back pain occur due to sexually transmitted diseases. In this case, a man may notice uncharacteristic discharge from the urethra, redness of the penis, impaired sexual function, etc.
Orchiepididymitis
It is an inflammation of the testicles, which can develop against the background of surgical interventions in the body, be a consequence of injuries or sexually transmitted diseases. In addition to abdominal and lower back pain, the man suffers from headaches, chills, nausea, and a fever.
Inguinal hernia
If the lower back hurts badly, and the pain radiates to the lower abdomen, and the pain itself is sharp and even unbearable, the cause may lie in an inguinal hernia. Sometimes hernia pain is even stronger than with appendicitis, and the patient has no choice but to call an ambulance.
Colitis
It is a pathology of the duodenum, or more precisely, an ulcer. The acute period of the disease lasts about a week, after which it becomes chronic, and the man constantly feels pain in the back and abdomen.
Treatment of stomach pain
To treat stomach pain, in most cases, taking medications is sufficient. Regardless of the diagnosis, the patient will have to follow a gentle diet. Eating is recommended every few hours in small portions. It is necessary to exclude all foods that can irritate the mucous membrane of the organ: fatty and sweet foods, alcohol and carbonated drinks, baked goods and sweets, sauces and spices.
Drug treatment may include several stages:
- antispasmodics and painkillers;
- sorbents;
- drugs to correct the acidity of gastric juice;
- antibiotics and others.
Surgical intervention is indicated for benign neoplasms that do not grow deep into the wall of the organ. Surgery may also be prescribed for gastric ulcers with the risk of perforation of its walls. Some structural anomalies of the organ also require surgical treatment if they interfere with the normal functioning of the digestive tract.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of stomach pain. The clinic has the opportunity to undergo a full examination, consult with specialists of a wide and narrow profile, and receive an appointment for treatment. Therapy is carried out under the supervision of doctors until complete recovery.
Do you need to go to the doctor?
A visit to a doctor is considered a necessity, since the lack of medical assistance in such a situation can lead to serious, undesirable consequences.
Conscious refusal of medical correction of a condition is fraught with the development of pathologies; this should not be forgotten. In addition, only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of pain.
Girdles, sharp or other pain in the abdomen may indicate various problems. They are not considered a key symptom when prescribing and conducting diagnostic procedures, but they complement the clinical picture well. If such unpleasant sensations appear, you should consult a doctor and go through a series of diagnostic procedures. This will help maintain health and avoid serious complications.
Prevention
Doctors at the 5th Hospital will not only select the optimal diagnostic and treatment option for each patient, but will also advise on how to prevent relapses.
Diet occupies a special place among measures to prevent intestinal and stomach diseases. It is important to learn to maintain balance in nutrition. You should not overeat; you should chew food carefully and slowly. Water and willow tea https://teahelp.ru/tea/herbal-tea/ivan-chaj/ should be consumed in sufficient quantities; coffee is not recommended in this case. At the same time, when choosing a diet, experienced doctors take into account all factors:
- functional state of the intestines, liver, pancreas
- secretory function of the stomach,
- intestinal motility,
- the presence of other concomitant diseases.
In addition to your diet, it is important to reconsider how you store and process food. Do not leave food open in the sun. Avoid damp food storage areas. Otherwise, they may begin to mold and rot. Avoid contact between raw foods and cooked foods.
Exercise therapy is also of great importance in the complex of preventive measures. Instructors-methodologists select their own loads and exercises for each patient.