Drug treatment of ulcerative colitis
When UC is initially detected, the symptoms are usually mild, and the doctor chooses conservative therapy. Prescribing various medications can give good results over a long period of time. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis with symptoms, the treatment of which does not involve surgery, can last for years. The goal of therapy in this case is to prevent the patient’s condition from worsening, prevent exacerbations and prolong remission.
In each specific case, the specialist decides how to treat UC based on the clinical picture. Traditionally, a certain combination of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics is prescribed in the required dosage. In advanced or complex cases of ulcerative colitis and exacerbations, treatment can be supplemented with hormonal medications. Corticosteroids, such as prednisolone, should be prescribed in courses, as continuous use is undesirable. For nonspecific ulcerative colitis, the diet should be gentle, excluding excessively spicy, salty, sour foods and eating regularly.
If long-term therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, aminosalicylates, does not bring a noticeable effect, when deciding how to treat UC, a gastroenterologist may prescribe immunomodulatory drugs. Among them, the most common are 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine.
Conservative therapy for UC disease can be carried out for many years. During periods of exacerbations and deterioration of the condition, the doses of medications taken are increased. In especially severe cases, for the fastest effect, the doctor, when choosing how to treat ulcerative colitis, prescribes intravenous administration of hormonal drugs.
Sometimes symptomatic treatment requires the use of other medications. Exacerbations of ulcerative colitis during pregnancy, as well as treatment of UC in children may require hospitalization. Staying in a hospital will allow for more careful monitoring of the condition and care for patients, monitoring proper nutrition for nonspecific ulcerative colitis, timely and clearly dosed medications.
Causes
The reasons why the pathological condition develops are still under study. This complicates the prevention of the disease, since it is impossible to eliminate risk factors without a clear understanding of them.
Experts suggest that the impetus for the development of Crohn's disease is given by :
- genetic failures, predisposition;
- bacteria, viruses;
- medications;
- autoimmune disorders;
- features of the structure and functioning of the intestines.
It is believed that the disease is formed as a result of the influence of a complex of preconditions that trigger an acute inflammatory process.
Surgical treatment of nonspecific ulcerative colitis
Sometimes, for nonspecific ulcerative colitis, surgery is the only possible treatment. The doctor resorts to this method only when conservative therapy is ineffective or the patient’s condition sharply worsens due to an exacerbation.
Coloproctectomy - removal of the colon, rectum and anus - an operation that allows you to radically cope with the disease. The disadvantage of such an intervention may be the subsequent need to use colostomy bags throughout life. There is another option, in which the feces are not immediately removed outside, but into an internal reservoir, from which the patient can empty it himself 3-4 times a day. Here you need to take into account that the container may leak, which will require another operation.
Symptoms and signs
The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on the severity of the pathology and its specific location. Often, a complex of signs allows one to suspect the development of Crohn’s disease. They are divided into intestinal and extraintestinal manifestations.
Intestinal manifestations of the gastrointestinal tract include:
- diarrhea with bloody impurities that does not stop for 5-6 weeks;
- chronic anal fissures;
- fever;
- anemia of unknown origin, weakness;
- pain, abdominal cramps;
- heaviness in the abdomen, bloating, nausea, vomiting;
- decreased appetite and weight loss.
Extraintestinal signs of pathology are most often expressed in lesions:
- skin (purulent pyoderma, erythema nodosum);
- eye (uveitis, iridocyclitis);
- mouth (arthropathy, aphotic stomatitis).
In children, Crohn's disease can also cause delays in overall development and puberty. Source: Clinical and laboratory features of Crohn's disease in children. Kalatina Yu.E., Sorokin D.V., Volosnikov D.K. Pediatric Bulletin of the Southern Urals No. 1, 2022. p. 66-71.
What is the range of possible surgical interventions?
The range of surgical interventions in case of ineffectiveness of drug treatment and diet for nonspecific ulcerative colitis includes several types of operations. In our clinic you can receive high-quality treatment, whatever the causes of UC and its consequences in a particular case. Doctors will choose the most appropriate type of intervention for each patient. One operation is enough to completely eliminate the disease.
Sometimes the doctor will consider removing the colon while preserving the rectum and anus. At the same time, holding the chair is maintained. The disadvantage of this method is that it maintains the risk of developing colitis and cancer in the remaining part of the rectum.
Diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of the pathology are similar to many other intestinal diseases. Therefore, it is quite difficult to diagnose it. To make a diagnosis, a pediatrician or gastroenterologist may prescribe the following specific studies:
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity with double contrast - to assess the width, lumen, structure of the intestine, and identify fistulas;
- irrigoscopy - to analyze the condition of the large intestine and detect narrowed areas;
- sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy - to visualize the intestinal mucosa;
- biopsy - for the purpose of laboratory examination of intestinal tissue from the pathological area.
Laboratory blood tests and stool tests are also required, which help to detect other causes of diarrhea. Source: Diagnosis of Crohn's disease in childhood. Doroshenko K.V., Tsupik I.S., Marukhno N.I. Pacific Medical Journal No. 4, 2016. p. 70-72.
If necessary, the doctor can also conduct additional diagnostics: ultrasound, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, etc.
Are there other surgical alternatives?
Today, a method has been adopted in world practice in which a reservoir is created from the small intestine, connected to the anus. Typically, in this case, it is necessary to form a temporary ileostomy, followed by its closure after a few months.
The reservoir, the so-called pouch, functions as a storage device to reduce the frequency of bowel movements. The use of this technique allows one to achieve physiological stool holding. In cases of complications in the form of inflammation of the reservoir, antibiotic therapy can be carried out, sometimes it is necessary to resort to removal and the creation of a permanent ileostomy.
Classification
Since a pathological focus can develop in any part of the digestive tract, the disease is primarily classified depending on the location of the inflammatory epicenter :
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- terminal ileum;
- the area of transition of the small intestine to the large intestine;
- small intestine (ileitis);
- rectum and colon (colitis);
- simultaneous lesions in the large and small intestine (ileocolitis);
- tongue, lips, oral cavity are the rarest localizations.
Depending on the degree of prevalence of the outbreak, two forms are distinguished:
- localized - the lesion occupies up to 30 centimeters;
- common - the length of the pathological area is over 100 centimeters.
Based on the characteristics of clinical manifestations, four forms of pathology are distinguished:
- inflammatory – without narrowed areas and fistulas in the intestine;
- stenotic – with areas of narrowing and intestinal obstruction;
- penetrating – with fistulas and fistulous tracts in the intestine;
- perianal - with fistulas, ulcers, cracks, abscesses in the anal area.
Depending on the nature of the course, Crohn's disease is of three types:
- acute – diagnosed when less than six months have passed from the onset of the disease;
- chronic continuous - established when periods of remission with appropriate treatment do not exceed six months;
- chronic relapsing - defined if the child has periods of remission exceeding six months.
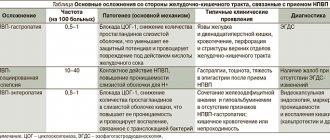
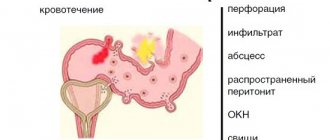
Possible complications of nonspecific ulcerative colitis
In complex cases of ulcerative colitis, various complications can develop, even threatening the patient’s life. These include intestinal ruptures, bleeding, severe infectious processes, accompanied by severe inflammation with high fever and general intoxication of the body. It is known that patients with UC have an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
If anti-inflammatory therapy does not have an effect, surgery is prescribed. Complications after surgery can include the occurrence of various infections - against the background of a general weakening of the body, progression of the disease in non-removed areas, or due to a rupture of the reservoir.
Medical Internet conferences
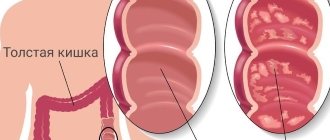
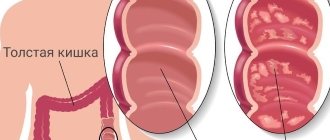
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic diffuse inflammation of the colon mucosa, initiated in the rectum and spreading proximally. Nonspecific ulcerative colitis, characterized by a progressive course and causing a number of complications, is a big social problem, as it disrupts the child’s lifestyle and leads to early disability. It can develop at any age, even in the first weeks of life.
Child S., 4 years old, is observed in the clinic with a diagnosis of Ulcerative colitis, total, severe recurrent course. The diagnosis was made at 2 years of age based on complaints of fever to febrile levels, abdominal pain, frequent, loose stools mixed with blood and mucus, and weight loss. Colonoscopy revealed bright hyperemia, swelling of the colon mucosa with fibrin deposits, and the absence of a vascular pattern. Cytological examination revealed pronounced lymphoid infiltration. A morphological study of a biopsy specimen of the colon mucosa revealed signs of exacerbation of colitis with sclerosis of the lamina propria and atrophy of the glands.
She received salofalk, and then prednisolone at the rate of 1 mg/kg body weight, and symptomatic therapy was carried out. During treatment, the patient’s condition stabilized and she was discharged 2 months after hospitalization. Subsequently, the child’s condition remained stable, which made it possible to begin a slow reduction in the dose of hormones and in October 2011. (17 months after the start of therapy), prednisolone was discontinued, treatment with salofalk was continued at a dose of 500 mg/day.
Relapse of the disease in February 2012. The therapy included budenofalk 3 mg/day, the dose of salofalk was increased to 1 g/day. During a control colonoscopy, the mucous membrane of the colon is inflamed in all parts, the vascular pattern is practically absent, the mucosa has small erosions, hemorrhages, contact bleeding, haustration is smoothed.
Due to the severity of the condition, since March 2012. Hormonal therapy was resumed again (prednisolone 2 mg/kg/day), the dose of salofalk was increased to 2 g/day. After which the manifestations of hemocolitis stopped. She was discharged in satisfactory condition with recommendations to continue the course of prescribed therapy.
Over the next period of time, the girl's condition remained stable. He continues to receive maintenance therapy: prednisolone 15 mg/day, salofalk 1.5 g/day.
Thus: UC occurs in children of all age groups; In recent years, there has been a tendency towards an increase in the frequency of manifestations of UC at an earlier age with an increase in the proportion of severe total forms.
Registration for surgery for ulcerative colitis (UC)
Treatment of UC in Moscow in our clinic is carried out in accordance with the latest standards. We try to perform operations while preserving the function of natural bowel movements and, if possible, avoiding subsequent use of hormonal and anti-inflammatory therapy. We have excellent results when performing total coloproctectomy with the formation of a reservoir from the small intestine and its anastomosis to the anus.
Our department was the first in Russia to accumulate significant experience in performing various types of surgery, both open and laparoscopic. After the intervention, the quality of life of our patients improves significantly. Watch an interview with our patient, who kindly agreed to talk about her experience and life before and after the operation.
If you have decided to consult for surgery in our clinic, make an initial appointment with a doctor by phone. You can also use the appointment form located in the lower right corner of the screen.