Diet for proctitis is an integral part of complex treatment. All products in digested form reach the inflamed rectum. The healing process depends on the strength of the irritating effect. Violation of a balanced diet, abuse of spicy seasonings, fried and smoked fatty meats, and alcohol are one of the causes of proctitis. Constipation and diarrhea, bloating largely depend on the foods consumed. Proctologists claim that if the restrictions and eating regimen are observed, after 2 weeks the patient’s condition improves significantly.
General rules
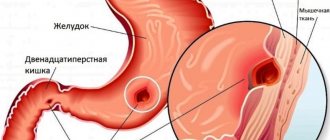
Proctitis is an inflammatory-dystrophic disease of the rectal mucosa. Most often it is a combined disease with other parts of the large intestine ( proctosigmoiditis - rectum/sigmoid colon, proctocolitis ).
Isolated inflammation of the rectum is much less common. There are acute (develops within 2-3 days with superficial damage to the mucous membrane) and chronic forms of proctitis. In turn, there are several forms of chronic proctitis: catarrhal-hemorrhagic, erosive (ulcerative), catarrhal-purulent, polyposis. The most common causes of proctitis are: infection (streptococcal, viruses, parasites), dietary errors, Crohn's disease / ulcerative colitis , hemorrhoids , chronic constipation , sexually transmitted diseases, food allergies, medications, rectal injuries, radiation therapy for intestinal cancer .
Acute proctitis is characterized by a sudden onset, a feeling of heaviness/burning in the rectum, pain radiating to the groin/perineum, tenesmus (false urges) due to constipation, and increased temperature. With ulcerative proctitis, there is an admixture of cloudy mucus/sometimes blood in the stool.
Chronic proctitis is characterized by alternating phases of exacerbation/remission. In the (remission) phase, the disease can be practically asymptomatic or with a feeling of discomfort, slight burning/itching/pain in the anal area, a feeling of incomplete bowel movement and the presence of impurities in the feces, and in the acute stage - with symptoms of acute proctitis. Often chronic colitis occurs with stool disturbances (constipation, less often with unstable stools with constipation changing to diarrhea). The stool is lumpy/dense, sometimes with mucus, in small portions.
Treatment of proctitis is predominantly conservative. Diet for inflammation of the rectum, along with drug therapy and hygienic procedures, is the most important component of complex treatment and is based on treatment Table No. 3 and 4 ( 4A , 4B ) depending on the type of functional disorder (constipation/diarrhea).
The fundamental principle of therapeutic nutrition is maximum sparing of the rectal mucosa, which is achieved by excluding any irritating foods from the diet. Food should contain a minimum amount of plant fiber, which increases irritation of the inflamed intestines and causes increased gas formation.
Hot/spicy/fried foods, smoked meat/fish, canned vegetable salads, legumes and pickles are removed from the daily diet. The consumption of fresh fruits and berries is also limited. Alcoholic/carbonated drinks are strictly prohibited. Freshly prepared juices, especially those with pulp, are also excluded, as are all sweets, ice cream and chocolate, bran, dried fruits, nuts, and seeds.
The basis of the diet consists of soups with vegetable/chicken broth, boiled porridge in water, semi-liquid dishes, soft-boiled chicken eggs, dishes of carefully chopped boiled/steamed meat, boiled fish, low-fat dairy products, cottage cheese and jelly. The only fruit you can eat is baked apples. It is not recommended to consume other fruits/berries/vegetables during the acute period. Bread - only stale white bread or crackers. The amount of free fluid is at least 1.5 l/day.
The diet for proctitis in remission is more expanded to include kefir and sour cream, potatoes, cabbage, carrots, strawberries, apples, plums, the consumption of which should be in moderation. When diarrhea occurs, the diet includes foods that slow down intestinal motility: pureed/slimy dishes (soups, mashed potatoes, pureed cereals, jelly, dishes made from double-rolled minced meat, jelly), pureed rice and products that have an astringent effect - dogwood decoctions , pears, lingonberries, bird cherries, blueberries, quinces, pomegranate peels, strong tea.
In treatment, it is extremely important to rinse the intestines with warm mineral alkaline water of Borjomi/Essentuki, which activates the motor function of the intestines/promotes the removal of mucus. For therapeutic purposes, after complete cleansing of the intestines, enemas with a warm infusion of chamomile are recommended, and from the second week of the disease, they are replaced with enemas from a collargol . Oil microenemas are given at night for 14 days. After a 10-day break, the course of treatment must be repeated.
In case of severe constipation, in the remission stage, nutrition is adjusted by introducing products that activate intestinal motor function and promote normal bowel movements - primarily containing non-coarse plant fiber: vegetables/berries/fruits, wholemeal bread, cereals, muesli, dried fruits ( figs, prunes). Also, it is necessary to increase the amount of free liquid consumed to 2 l/day through pumpkin/carrot, apricot, plum and peach juice, and mineral water. It is mandatory to take bifido-drugs.
Methods for diagnosing proctitis
Since the manifestations of chronic proctitis are irregular and quite easily tolerated, they, as a rule, do not cause much concern and do not prompt you to consult a doctor. Meanwhile, without proper treatment, the disease progresses. Inflammation can spread to other parts of the intestine, to the tissue surrounding the rectum (paraproctitis), leading to the formation of scars that narrow the intestinal lumen and contribute to constipation.
Therefore, as soon as it becomes clear that there are some problems with the anus, you should definitely see a proctologist.
The diagnosis of proctitis is established on the basis of a proctological examination, during which the doctor performs a digital rectal examination. To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental diagnostic methods are used: anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. A biopsy and laboratory tests are also performed.
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is carried out using special endoscopic equipment, which allows the doctor to examine the condition of the walls of the rectum over a significant extent - up to 30 cm. Sigmoidoscopy requires preliminary preparation, since the intestines must be cleared of feces.
Biopsy
A biopsy is performed during sigmoidoscopy. Tissue from the rectal mucosa is taken for examination. A biopsy is performed for differential diagnosis with tumor processes.
Coprogram
Stool tests are being carried out. A coprogram (general stool analysis) allows you to determine the type of proctitis, identify digestive disorders and detect the presence of blood in the stool. Bacteriological analysis of stool is used to identify the pathogen that caused the inflammation.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Authorized Products
Diet for proctitis includes:
- Yesterday's wheat bread, crackers.
- Soups made with low-fat chicken/fish broth with the addition of boiled cereals (buckwheat, semolina, rice), meatballs, pureed meat, egg dressing.
- Low-fat varieties of sea/river fish, steamed in pieces or boiled meat in the form of meatballs, to which you can add well-cooked white rice.
- Skinny red meat and poultry in the form of steamed cutlets, quenelles, meatballs.
- Soft-boiled eggs/in the form of a steam omelet, up to 2 eggs per day, butter for dishes.
- Puree porridge cooked in water (rice, oatmeal, buckwheat).
- Baked apple puree - without exacerbation, pureed raw vegetables/fruits.
- Mashed calcined cottage cheese in casseroles/in its natural form.
- Green tea, cocoa, rosehip infusions, fruit juices, blackcurrant, blueberry, bird cherry, pear and quince jelly.
For constipation, the diet is adjusted towards introducing into the diet:
- Appetizers in the form of salads from pureed fresh vegetables, vinaigrettes with the addition of vegetable oil.
- Products containing coarse fiber: vegetables/fruits, sauerkraut, wholemeal bread (cereal, bran, day-old rye).
- Soups (borscht, cabbage soup, cold soups (okroshka, beetroot soup) in low-fat meat/fish/vegetable broth).
- Semi-viscous porridge made from buckwheat.
- Lean beef, chicken (without skin), turkey, lean fish.
- Vegetable oils (corn, olive, sunflower).
- Side dishes - baked/boiled vegetables (carrots, beets, pumpkin) and raw vegetables, sour sauerkraut.
- Fruits that stimulate intestinal motility: prunes, melons, peaches, figs, apricots, plums, soaked dried fruits.
- Cottage cheese, fresh yogurt/kefir, cheeses.
- Weak coffee/tea with milk, cold fruit/vegetable juices.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| green beans | 2,8 | 0,4 | 8,4 | 47 |
Fruits | ||||
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| Cherry juice | 0,7 | 0,0 | 10,2 | 47 |
| Strawberry juice | 0,6 | 0,4 | 7,0 | 31 |
| tangerine juice | 0,8 | 0,3 | 8,1 | 36 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Apple juice | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 42 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Causes of intestinal inflammation after radiation therapy
The following mechanisms underlie radiation damage to the intestine:
- Damage to the intestinal epithelium that develops under the influence of ionizing radiation. This leads to its focal necrosis, desquamation (peeling) and atrophy.
- Development of nonspecific inflammation of the mucous membrane and submucosa. The tissues are infiltrated by neutrophils, hyperemia, swelling, and bleeding are observed.
- Due to trophic disorders (arterioles are damaged), the blood supply to the affected areas of the intestinal mucosa deteriorates, which further aggravates ischemia and necrosis. As a result, atrophic changes progress with the development of fibrosis of the submucosal layer.
- Against this background, pathogenic flora begins to join, which causes infectious complications, including sepsis.
The end result of long-term trophic disorders of the intestinal wall and necrosis is the formation of strictures (narrowing of the lumen), the formation of fistulous tracts, the formation of telangiectasias and the development of bleeding from them.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for proctitis in the acute stage of exacerbation/acute proctitis excludes:
- Rich broths, fatty fish/meat, mushrooms, animal fat, pickles and marinades, smoked meats, sausages, fast food products, semi-finished products.
- Products containing coarse fiber (vegetables, bread with seeds/rye/whole grain, bran).
- Barley/millet/pearl barley porridge, pasta and legumes.
- Pastries, fresh bread, sweets (jam, honey, candies), dried fruits.
- Whole milk/milk soups, cream, sour cream, fried and hard-boiled eggs.
- Kvass, coffee with milk, carbonated/alcoholic drinks.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsnip | 1,4 | 0,5 | 9,2 | 47 |
| parsley (root) | 1,5 | 0,6 | 10,1 | 49 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| dried fruits | 2,3 | 0,6 | 68,2 | 286 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| Wheat groats | 11,5 | 1,3 | 62,0 | 316 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| vysivkovy bread | 9,0 | 2,2 | 36,0 | 217 |
| Old Russian grain bread | 9,6 | 2,7 | 47,1 | 252 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| butter cookies | 10,4 | 5,2 | 76,8 | 458 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| seasonings | 7,0 | 1,9 | 26,0 | 149 |
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
Bird | ||||
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| grape juice | 0,3 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 54 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition for proctitis , according to the majority of patients, has a positive effect on the condition of the mucous membrane of the large intestine and rectum, including, since it includes only gentle products and excludes/limites all irritating factors.
- “... I went to the hospital about difficulty defecating, pain in the lower abdomen, and frequent passing of gas. During the examination, a diagnosis was made: acute proctosigmoiditis. They prescribed a strict diet with the exclusion of everything fatty, spicy, fried, and alcohol. I had to switch to light vegetable/chicken soups, boiled meat, boiled porridge, and from vegetables to boiled beets, pumpkin and carrots. I cook for myself separately; the slow cooker makes excellent dietary dishes. I also take a decoction of sage, chamomile, calendula, give enemas and suppositories”;
- “... The diagnosis is ulcerative proctosigmoiditis, the doctors said that my diet requires constant adherence to Diet No. 4. I quickly adapted to this diet, but I need to take food with me to work. Such nutrition for 1-2 months normalizes the intestines, relieves discomfort, bloating and diarrhea.”
Basic rules of nutrition for proctitis
Dietary requirements for damage to the large intestine are based on the characteristics of functional disorders (constipation or diarrhea), the depth and extent of inflammation. The more pronounced the changes in the mucous membrane of the rectal canal detected during sigmoidoscopy, the more strictly the diet will have to be selected and the longer the diet period.
The fewest restrictions are with the mild superficial (catarrhal) form of proctitis. Long-term adherence and gradual expansion of permitted dishes will be required in case of erosive and ulcerative disease. Sluggish inflammation in patients with malignant tumors in the post-radiation period is caused by suppression of the immune system, so it is important that the products that stimulate defense forces, vitamins are always present in the composition, and that the level of proteins and sweets that degenerate cells “love” is maintained at a reduced level.
The correct approach to choosing products for proctitis will ensure the maximum gentle effect on the mucous membrane. For this it is recommended:
- eat in small portions (no more than a glass) 5-6 times a day, control the possibility of overeating;
- to eliminate mechanical and chemical irritants, prepare dishes without seasonings, avoid hot sauces, pickles, pickled vegetables and fruits, canned food, replace frying with steam cooking, and boiling;
- compare the set of products for the menu with the functional state of the intestine;
- during an exacerbation and in acute proctitis, it is preferable to eat semi-liquid meals, use rubbing and crushing components to improve absorption.
In order not to disrupt your metabolism with food, the rules require:
- intake of sufficient quantities of components from food to support biochemical reactions in the body;
- When calculating your diet, stick to a sufficient amount of calories, proteins and fats; carbohydrates should not limit your energy intake;
- Avoid suppressing the growth of beneficial bacteria with excess protein foods.
Important! During the treatment of acute proctitis, you need to gradually switch to a normal diet; in the chronic form, you need to stick to the diet all your life.