There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Types of polyps Signs of polyposis Causes of development of neoplasms Prevention Surgical methods of treatment
A polyp is a neoplasm of a benign nature. It is located on the intestinal mucosa, has a thin or thick stalk and a seal at its upper end. Dimensions can vary from a few millimeters to 6 cm. The length of the leg can reach 2 cm. In 10-30% of cases, the tumor degenerates into a malignant one. The time frame varies: sometimes it takes several years, and sometimes much less. Polyps most often have a mushroom shape.
Reliable reasons for the appearance of formations have not been identified to date. Most often, the disease is detected due to hereditary predisposition, chronic colitis, low stomach acidity, and inflammation in the intestines.
Types of polyps
Depending on their location, tumors can be single, numerous, or group. Numerous polyps (diffuse polyposis) are damage to a large area of the mucous membrane. The shape and size of the formations are different. With group localization, polyps are located in a limited area of the intestine. Their size does not exceed 5 mm. Polyps are classified as villous, adenomatous or mixed.
Polyps in the large intestine
Colon polyps (colorectal) are benign neoplasms (growths) on the inner wall of the organ. Adenomatous polyps of the large intestine (adenomas) have the highest risk of degeneration into cancer; inflammatory, hyperplastic, and hamartomatous formations are also found. The last three species almost never regenerate.
Adenomatous formations are the most common pathology. They are rather hard, smooth, round, pedunculated polyps. Villous tumors are usually broad-based, have a spongy structure, and often bleed.
Fibrous polyps (consisting mostly of connective tissue) often form. They may fall out of the anus during defecation.
Pseudopolyps are also classified as a separate group. They are located on inflamed areas of the mucous membrane, are quite small, and bleed easily. They disappear after eliminating the cause of inflammation.
Reasons for appearance
Polyps in the intestines can be inherited.
The main reason is hereditary predisposition. Previously, a colonoscopy (a medical examination of the colon) was prescribed only if someone in the immediate family suffered from colon cancer.
It is a proven fact that any change in the development of mucosal cells depends on hereditary factors. Other causes of pathology:
- Poor nutrition. If the diet includes a large amount of animal fats, then this has a detrimental effect on the condition of the entire digestive tract. Fecal masses are formed due to fiber, which is absent in animal fats. Because of this, intestinal perilstatics decrease, the process of defecation becomes difficult, and regular constipation appears. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of meat and fatty dairy products, as well as white flour, smoked meat, margarine, soda water, and sugar. Stagnation of feces injures the delicate walls of the intestine, which leads to the appearance and localization of polyps.
- Inflammatory processes. Chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane leads to aging and death of epithelial cells. Instead, pathogenic growths grow. The main cause of inflammation is diseases of the abdominal cavity and digestive system. For example, dysentery, enteritis, typhoid fever, ulcerative colitis.
- Abdominal vascular pathology. Polyps develop against the background of varicose veins, atherosclerosis of the peritoneal aorta, thrombosis and ischemia.
- Cell aging. The main reason is age-related changes in the body. Cells undergo natural aging and, closer to 50 years, pathogenic growths develop, and the formation of the intestinal mucosa is disrupted. The aging process is accelerated by poor nutrition, alcohol consumption, smoking, and the environmental situation of the city.
Symptoms of polyposis
If the size of the polyp is several millimeters, then it is not felt at all, and the doctor can only detect it by chance. Large formations are mainly detected when patients complain of bleeding from the anus. This is due to the fact that growths that have reached several centimeters in diameter are prone to ulceration and can break through the intestinal wall.
Main symptoms:
- Bleeding.
- Presence of blood in stool.
- Mucous discharge (with or without inclusion of blood).
- Constipation.
- Diarrhea.
Polyps are quite difficult to identify, since their symptoms are similar to other gastrointestinal diseases.
A growth on the mucous membrane may have a thin stalk or a wide base. From an oncological point of view, villous neoplasms have the worst prognosis. They grow like a “carpet” and are reborn in 40% of cases.
The disease affects 5-15% of the total population and almost 50% of those over 50 years of age.
The most dangerous is multiple polyposis, which is hereditary in nature. In this case, in 80-100% of cases a malignant tumor is formed.
Endoscopic polypectomy:
Endoscopic polypectomy, used in our clinic, is a surgical procedure to remove polyps through a videogastroscope or videocolonoscope, followed by electrocoagulation of the base of the polyp to prevent bleeding. Endoscopic polypectomy has been called a “desired achievement of medicine ,” since its introduction into practice made it possible to achieve optimal treatment results without organ resection (removal) and without reducing the patient’s quality of life.
Surgical removal
Important! If polyps are detected, surgical intervention is necessary. You cannot self-medicate with folk remedies. Only a qualified surgeon can provide assistance.
SM-Clinic uses modern methods for treating polyps.
- Endoscopic polypectomy. An endoscope with a loop-shaped electrode is inserted into the anus. This electrode grasps and compresses the tumor stalk. Then, using electrocoagulation, the wound remaining from the polyp is cauterized. Large formations can be removed in parts.
- Laser technique. A directed laser beam is applied to the stalk of the polyp. Soft tissues evaporate layer by layer. The operation takes place with minimal trauma and does not entail complications.
General preparation for intestinal polypectomy
Colonoscopy with removal of tumors requires special preparation. It consists of maximal cleansing of the intestines. You also need to adjust your diet within 5 days. It includes easily digestible foods with low fiber content: rice, eggs, vegetables and fruits without seeds or peels, lean meat, fish. In 2 days they switch to soft dishes: fruit and vegetable purees, omelettes, pureed soups, soft and ripe fruits without peel.
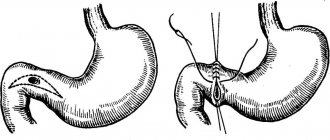
Removal of duodenal polyps
Polyps of the duodenum are extremely rare, and they are highly susceptible to degeneration into malignant tumors. The treatment strategy when they are detected is mandatory removal followed by histological examination of the removed tissues.
Before the procedure, differential diagnostics are carried out - optionally prescribed:
- radiography;
- endoscopic examination using a probe and a miniature video camera;
- Ultrasound;
- CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity.
Small polyps on a long stalk are removed during duodenoscopy - an endoscopic examination. Neoplasms are removed with microsurgical instruments, the sections are cauterized with a diathermocoagulator - a medical high-frequency current generator.
Relatively large polyps are removed during polypectomy surgery. The surgeon exposes the duodenum, dissects its walls and excises tumors. After tissue removal, their histological examination is carried out to determine whether they are benign or malignant.
Endoscopic colon polypectomy
Before removing colon polyps:
- conduct a physical examination;
- diagnostic colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy;
- They do a stool test for occult blood.
On the eve of the operation, a slag-free diet is prescribed and a cleansing enema is performed.
The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. The patient is asked to lie on his back or side. An endoscope is inserted through the anus and rectum into the colon. To open it, air is supplied.
Using a camera and a light source, the doctor visualizes the polyp. It is excised with microsurgical instruments or an electrocoagulator. After excision, the mucous membrane is cauterized to stop bleeding. The removed tissues are sent for histological examination.
Rectal polypectomy
The surgeon discovers polyps near the anus during a digital examination. The main method of identifying them in other localizations is hardware sigmoidoscopy. If, based on the results of preliminary diagnostics, a full-fledged intervention is indicated, the following is prescribed:
- laboratory blood and urine tests;
- ECG;
- fluorography;
- consultation with a therapist.
Additionally, they may prescribe intestinal colonoscopy, gastroscopy of the stomach, CT scan of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound of the heart and veins of the lower extremities.
If the polyps are located in the middle parts of the rectum - no further than 10-12 cm from the anus - endoscopic removal of the formation is performed using electrocoagulation under the control of a video camera. Microsurgical instruments are inserted through the anus. A passive lead electrode is attached to the patient's lower back. The active electrode in the form of a loop is placed over the polyp and tightened. After this, high frequency current is applied. The tissues are instantly charred and the vessels are sealed.
Relatively large polyps in the rectum - more than 2 cm - are removed through punctures in the abdominal wall during laparoscopic surgery. Polyps with a wide base are excised during a classic laparotomy with opening of the abdominal wall.
Symptoms
Polyps in the intestines can cause bleeding from the anus.
In many cases, tumors are discovered accidentally during a colonoscopy, and the symptoms of an intestinal polyp may not be pronounced.
- Bleeding from the anus. Patients often confuse this symptom with anal fissures, hemorrhoids and fistula. As a rule, bleeding is accompanied by a large amount of mucus.
- Regular constipation. Feces pass on their own, but rarely and painfully, or with the help of enemas or laxatives.
- Painful sensations. Large polyps cause cramping pain in the intestinal area (in some cases confused with flatulence). Painful sensations may also appear in the lower abdomen.
- Foreign body sensation. The feeling occurs in the rectum near the anus.
- Diarrhea. Frequent bowel movements with loose stools. Blood, pus, and serous discharge may be present.
- Damage. Constipation causes an inflammatory process where solid stool damages the intestinal walls. Anal fissures often appear, which must be treated with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs. If this is not done, purulent fistulas may form.
- Exhaustion. Polyps are soft tissue that grows due to nutrition. It enters through the circulatory system and lymphatic currents. The patient often experiences an increase in appetite, or, conversely, a decrease. Symptoms of anemia may be present: pale skin, circles under the eyes, dizziness, nausea, headaches. In some cases, anemia is a clinical symptom.
- Dropping out. If the tumor is located in the rectum, it may fall out during defecation, or block the passage of feces near the sphincter. This symptom is also accompanied by bleeding.
Treatment of polyps in the intestines
The only effective way to get rid of polyps is their surgical removal. In the vast majority of patients, this procedure (polypectomy) is performed during an examination of the colon. It is very quick and painless. Large polyps may require surgery. Whenever possible, doctors try to use techniques with minimal intervention – microinvasive laparoscopic surgery.
In very rare cases, when there are too many polyps, they are removed along with the affected area of the intestine. This is a complex operation that requires preparation and long recovery.
All removed tissues are sent for histological examination. Based on the structure of the tissue, a histologist can determine the type of polyp and identify the initial signs of malignancy. This information will allow the attending physician to determine the prognosis and schedule of preventive examinations.
In our center, consultations are conducted by an experienced gastroenterologist, a high-class specialist. Make an appointment by phone: 8 (49244) 9-32-49.
Advantages of the diagnostic and treatment procedure
Colonoscopy is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the condition and age of the patient. The procedure, as a rule, is well tolerated, so the patient’s performance is restored within a few days after it is performed.
The use of colonoscopy for therapeutic purposes is possible only when the tumors do not exceed 2 cm in size. Otherwise, laparoscopy is performed, which requires longer rehabilitation. When a large number of tumors accumulate in one area, intestinal resection becomes necessary. This method is quite traumatic and requires removal of the affected areas.
Our advantages:
If you need to have gastrointestinal polyps removed, feel free to contact our clinic. When performing an operation with us, you can be sure that:
- Highly qualified endoscopists with extensive experience in diagnostic and operative endoscopy will work with you
- The operation will be performed using modern expert-class digital equipment from Pentax.
- Our experienced anesthesiologists will ensure a restful sleep throughout the operation.
- The equipment will undergo complete automatic disinfection in a washing machine, which completely eliminates the “human factor” when processing the endoscope
- After the operation, you will be placed in a comfortable 2-3-bed room with a bathroom
- You can choose a convenient time for the operation: we work every day, seven days a week.