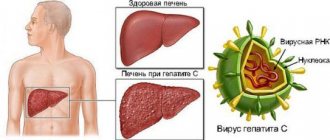
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease with a tendency to progress. The disease leads to the development of irreversible changes in the cells of the organ. As a result, normal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue, which makes normal functioning simply impossible. This affects the functioning of vital organs and systems of the body.
Damage and inflammation of liver cells leads to their complete death. Eighty percent of recorded cases of cirrhosis were caused by viral hepatitis or alcoholism. Parasitic diseases, taking certain medications, autoimmune processes, and more can also provoke the appearance of a terrible disease.
The disease develops quite slowly. The first signs may be completely absent. Over time, the following symptoms may appear: jaundice, itching, spider veins, weakness, decreased performance, weight loss due to loss of appetite. In this article we will talk in more detail about decompensated cirrhosis of the liver.
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
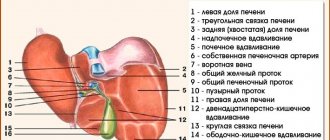
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic progressive liver disease characterized by restructuring of the liver tissue and vascular bed, a decrease in the number of functioning liver cells (hepatocytes), proliferation of connective tissue, the appearance of regeneration nodes and the subsequent development of liver failure and portal hypertension.
In economically developed countries, liver cirrhosis is one of the leading causes of death between the ages of 35 and 60 years.
up
How does cirrhosis manifest?
For a long time, liver cirrhosis is asymptomatic or with minimal atypical manifestations. Weakness, increased fatigue, decreased performance, irritability, tearfulness, touchiness, and a tendency to hysterical reactions appear.
Digestive disorders often occur: nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, intolerance to fatty foods and alcohol.
Characteristic signs of cirrhosis are heaviness and pain in the abdomen, mainly in the right hypochondrium, spider veins in the upper half of the body, redness of the palms, hemorrhages in the skin, bleeding of the mucous membranes. Complaints of itchy skin and joint pain are common.
Severe forms of the disease occur with severe impairment of liver function and life-threatening complications, primarily portal hypertension (increased pressure in the portal vein), leading to bleeding from the dilated veins of the esophagus, ascites, and hepatocellular failure.
up
What are the causes of liver cirrhosis?
The most common causes of liver cirrhosis are:
- chronic viral hepatitis B (and D),
- hepatitis C,
- chronic alcoholism (alcoholic liver disease),
- metabolic disorders,
of which the main one is metabolic syndrome accompanied by fatty liver disease - non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In addition, cirrhosis is caused by hereditary diseases: hemochromatosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, etc., as well as autoimmune liver diseases, including primary biliary cirrhosis and toxic liver damage from industrial poisons and drugs.
up
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
Liver assessment
The diagnosis in the early stages of liver cirrhosis is difficult to establish, since there are often no pronounced changes in the liver. First of all, an ultrasound examination of the liver (ultrasound diagnostics) is performed, which makes it possible to identify diffuse changes in the liver tissue and an increase in its size (although this does not always happen). It is advisable to carry out Dopplerography of the vessels of the abdominal cavity to determine the width of the lumen of the vessels and the speed of blood flow. This allows us to determine the presence of signs of portal hypertension.
Important for characterizing the structural and functional state of liver cells is a biochemical blood test (ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, protein fractions), as well as a clinical blood test and coagulogram - blood clotting.
To accurately diagnose the degree of fibrosis, modern non-invasive (replacing biopsy) examination methods are used: elastometry (elastography) of the liver using the Fibroscan, Fibrotes, FibroMax apparatus. Liver damage is characterized by degrees from 0 to 4; 0 – healthy liver, 4 – cirrhosis.
Determining the cause of liver cirrhosis
First of all, it is necessary to do tests for hepatitis B and C viruses, since viruses are the most common cause of cirrhosis, especially in combination with alcohol. If viruses are not identified, then the search for the cause consists of excluding hereditary liver diseases, autoimmune indicators, as well as alcoholic liver disease, NAFLD and toxic liver damage.
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
The severity of cirrhosis is determined by the Child-Pugh scale, taking into account the severity of clinical and laboratory data, the main of which are the content of bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin in the blood, as well as the severity of encephalopathy and ascites. There are active and inactive cirrhosis, compensated and decompensated. Decompensated cirrhosis is characterized by the development of portal hypertension, the appearance of ascites, and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding.
up
Diagnostic examination
Laboratory tests, biopsy, ultrasound, and laparoscopic examination will help to assess the patient’s condition. Using ultrasound diagnostics, a specialist can pay attention to the increased size of the liver, as well as the presence of structural changes. The organ has a dense structure with nodules.
Laparoscopy allows you to determine the type and degree of pathology, as well as the general condition of the affected organ. Using a biopsy, you can learn about structural changes in the liver at the cellular level.
In a general blood test in cirrhosis, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, and hemoglobin levels are decreased. With microscopy of urinary sediment, a specialist will be able to see salts, as well as an increased level of red blood cells. In a biochemical study, the level of bilirubin, AST, and ALT will be increased. Laboratory tests will help make a diagnosis.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis
Treatment of liver cirrhosis is carried out with the aim of stopping or slowing down the progression of the disease and improving the quality of life.
The treatment program includes: therapeutic regimen and nutrition, drug treatment, prevention and treatment of complications.
Treatment results and prognosis depend on the severity of the disease.
With compensated cirrhosis, the functional state of hepatocytes is preserved, there are no signs of portal hypertension and disturbances in the protein-synthetic function of the liver. Treatment of cirrhosis at this stage of the disease is determined by the cause of the disease, depending on which specific therapy is prescribed. In addition, it is necessary to limit mental and physical stress.
If the cause of cirrhosis is viral hepatitis B or hepatitis C, then antiviral therapy is prescribed, which, as research in recent years has shown, not only suppresses the activity of the virus, but also has an antifibrotic and anticirrhotic effect.
For alcoholic cirrhosis (alcoholic liver disease), hepatoprotectors are prescribed, which, subject to complete abstinence from alcohol, make it possible not only to stop the progression of cirrhosis, but also help reduce the degree of fibrosis.
In case of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFL), adherence to the diet and rules of nutrition in combination with drug treatment, including hormonal disorders that cause liver damage, gives good results. It is possible to reverse the development of fibrosis and restore the functional and structural state of the liver.
A patient with liver cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation and the development of complications requires dietary, medicinal, and in some cases endoscopic and surgical treatment.
Decompensated cirrhosis is characterized by the development of severe complications, the main of which is portal hypertension, i.e. persistent increase in pressure in the portal system. This is manifested by splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach and bleeding from dilated veins, accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity - ascites.
Various groups of drugs are used to treat portal hypertension: vasoconstrictors and vasodilators.
With the development of ascites, 50% of patients live for about 2 years, and only 25-50% of patients who do not respond to drug therapy survive 6 months. The goal of conservative therapy for ascites is to remove accumulated fluid from the body. For this purpose, a special salt-free diet and diuretics are prescribed.
In the terminal stage of liver cirrhosis, only a liver transplant can save the patient's life.
up
Possible complications
As the disease progresses, serious complications can occur, such as cancer, bleeding, fluid accumulation, and more. Let's talk about the most common processes that occur at the stage of decompensation.
Hepatic encephalopathy
Pathology leads to neuropsychic disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of changes in behavior and consciousness. With cirrhosis, the blood accumulates toxic substances that primarily affect parts of the brain. The person becomes inattentive and irritable, his sleep is disturbed, and drowsiness becomes permanent.
Gradually, the patient becomes lost in time, his speech is impaired, and his behavior becomes inadequate. Treatment includes infusion therapy. Hepatoprotectors help reduce the concentration of toxins in the circulatory system. Sometimes even gastric lavage is required. To reduce the absorption of decay products, antibacterial agents are used.
Brain damage is primarily associated with toxic substances entering the blood
Ascites
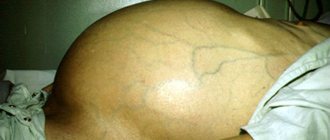
Due to the accumulation of fluid, the abdomen increases in size. In cirrhosis, deformed cells compress blood vessels, which leads to impaired blood supply. Fluid accumulation can be reported by measuring abdominal circumference daily. The umbilical ring is stretched and the navel turns outward. Veins are clearly visible on the skin of the abdomen.
Bed rest is recommended for patients. The amount of salt is sharply limited, and fluid intake is also reduced. Under the control of diuresis, diuretic drugs are prescribed. If there is no response to these drugs, a puncture of the abdominal cavity is performed.
Hepatic coma
The pathological process causes a decrease in the number of active cells. If, along with a violation of the functional activity of the liver, changes in metabolic processes occur, hepatic coma develops. It appears suddenly and lasts from 1 to 3 days.
Treatment is carried out in the intensive care unit, where vital functions must be constantly monitored. Patients are prescribed parenteral nutrition through the administration of medicinal solutions with nutrients. Detoxification therapy is carried out.
So, cirrhosis of the liver is a dangerous, progressive disease that can ultimately lead to death. Decompensation is the third stage of the disease, in which serious structural damage to the organ and severe clinical symptoms are observed.
The prognosis is generally unfavorable, which is why it is so important not to miss the first symptoms. Carefully following medical recommendations, adjusting your diet, giving up bad habits - all this will help prolong your life.
Dietary recommendations for liver cirrhosis
For cirrhosis, prepare meals without salt, reduce the amount of free liquid and introduce foods rich in potassium.
Nutritional balance
The main parts of food are proteins, fats, carbohydrates, water, minerals and vitamins, which must be strictly balanced. The ratio between proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be 1:1:4. Animal proteins should make up about 60% of the total protein. Of the total fat, 20-25% should be vegetable oils as a source of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The balance of carbohydrates is expressed in the ratio of starch, sugar, fiber and pectin. Sugars should be represented by fruits, berries, dairy products, and honey. It is extremely important to maintain a balance of vitamins and minerals, which must be supplied to the body daily in accordance with daily requirements.
Diet
This is the number of meals and the interval between them during the day. For healthy people 3-4 times a day at 4-5 hour intervals. For some diseases, such as obesity, it is necessary to eat 5-6 times a day
up
Prevention
As a preventive measure it is necessary:
- give up alcohol;
- eat healthy food, following the rules of proper nutrition;
- prevention and timely treatment of hepatitis;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- bile duct drainage;
- taking vitamins.
Following these recommendations will certainly help in the fight against the disease.