One of the invasive ways to study the condition of the patient’s body tissues is a biopsy. Carrying out a biopsy means that a section of the affected tissue is surgically removed from the person being examined, after which it is subjected to a thorough histological and microscopic analysis. The procedure requires varying degrees of surgical intervention and is a complex diagnostic method. However, there are situations when other, non-invasive and less dangerous research methods cannot provide the doctor with the complete information necessary to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. For example, a biopsy is the most accurate method for detecting pancreatic cancer, although its value is not limited to this.
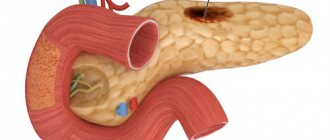
About the organ
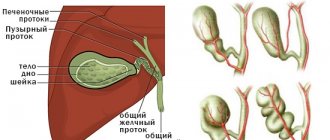
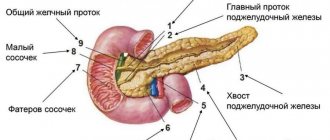
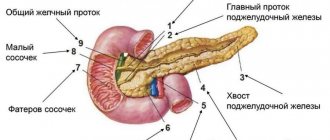
The pancreas is a small organ located behind the stomach and performs two very important roles:
- Digestive. It is she who produces digestive enzymes that promote the breakdown of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
- Endocrine. The function is no less important: it produces hormones involved in the metabolism of the human body - insulin, glucagon, gastrin and others.
Therefore, any pathology that arises and develops in an organ becomes a serious threat to human life.
Pancreatic oncology is a serious disease, it is characterized by the growth of a cancerous tumor from once native tissues. Various factors can contribute to the occurrence of the disease, including tobacco smoking, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, obesity, poor diet, hereditary factors, etc.
Types of oncology
The part of the organ where the cancer is localized is taken as the basis for classifying types of cancer:
- Head;
- Body;
- Tail of the pancreas.
Considering that a neoplasm can appear from different cells, they distinguish
- Adenocarcinoma. The most common form consists of cells that produce digestive enzymes;
- Insulinoma. Cells that produce insulin;
- Gastrinoma. Cells are a source of gastrin, etc.
Can an endoscopist make a diagnosis without histology?
No, it can only describe visual signs of changes in the mucous membrane, which is why the term gastropathy was introduced in 1984. Histological examination, in turn, is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. For example, the diagnosis of gastritis can only be established on the basis of a histological examination of mucosal samples by a morphologist. Even the most highly accurate endoscopic picture of the disease, according to medical standards, requires morphological confirmation. Only the result of the histological conclusion determines the presence of gastritis, its stage (acute or chronic) and its form (infectious, HP-associated, reflux gastritis, atrophic, lymphocytic, granulomatous, eosinophilic, hypertrophic).
Remember, only when the correct diagnosis is established can the correct treatment be prescribed.
Determining the form of gastritis gives the doctor information to make a definitive diagnosis, for example, to identify Crohn's disease of the upper gastrointestinal tract or a disorder in the ability to digest gluten (celiac disease). To assess the volume of the lesion, an accurate histological assessment of gastritis and gastropathy is required, which directly depends on the number and location of biopsies. According to the latest recommendations of the European Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, during gastroduodenoscopy, at least 4 biopsies should be taken from different parts of the stomach for a morphological assessment of gastritis.
How to understand that you are sick?
Although the tumor can occur for a long time without any symptoms, at later stages they clearly manifest themselves:
- Acute pain in the upper back or abdomen;
- Sudden weight loss;
- Jaundice;
- Vomit;
- Diarrhea;
- Weakness, hand tremors;
- Heartbeat faster than usual;
- Constant feeling of hunger;
- Sometimes fainting;
- Heartburn, increased stomach acidity, stomach ulcer that does not go away after treatment - with gastrinoma;
- Weight loss, constant thirst, frequent urination, the appearance of a red-brown rash on the skin, the tongue becomes smooth and acquires a bright orange color - with glucagonoma.
A biopsy of the pancreas is a very important and reliable diagnostic procedure, because the pancreas itself is a key organ of the digestive and endocrine systems. It, as noted above, secretes vital hormones and enzymes that are involved in the processes of digestion and metabolism.
Any failure or dysfunction is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Everyone understands well that it is much more effective and easier to treat a disease when it is detected as early as possible. Therefore, due to the patient’s symptoms of diabetes or pancreatitis, as well as his sudden weakness and weight loss, urgent diagnosis is necessary to detect cancer.
The task of a biopsy is not only to confirm/or refute the presence of a disease, but to differentiate the processes that occur in the organ of interest to the doctor. Pieces of material taken during the procedure for subsequent study in the laboratory help establish the true nature of the tumor.
Biopsy as a diagnostic method is very accurate and helps the doctor choose the right treatment tactics, however, biopsy can also be performed as an element of a comprehensive diagnosis, together with ultrasound, CT, MRI and other well-known techniques.
Why is a biopsy necessary for peptic ulcer disease when the diagnosis has already been established?
When an ulcer is localized in the stomach, we are never completely sure of its benignity, so in all cases it is recommended to perform multiple biopsies from the edges of the ulcerative defect, followed by histological examination to exclude the malignant nature of this lesion. When the ulcer is localized in the duodenum, a biopsy depends on the type of ulcer and is performed if rare diseases are suspected, such as neuroendocrine tumors and Crohn's disease. For patients with gastric ulcers, it is recommended that a control endoscopic examination be performed with repeated multiple biopsies taken at the end of the course of conservative treatment, since cancer cells may not be visible against the background of inflammation.
Indications and contraindications
The procedure is necessary for patients who:
- Pain in the pancreas is diagnosed;
- Jaundice;
- Biochemical blood parameters have changed;
- The levels of pancreatic tumor markers (CA-242, CA 19-9) increased.
Without a biopsy, one can only guess the nature of the tumors in the organ, but its true nature cannot be established.
Another significant role of the procedure is to confirm or refute a previously made diagnosis. It is the biopsy that is the “last resort” in the medical practice of making diagnoses.
Meanwhile, there are contraindications to performing a pancreatic biopsy:
- Poor blood clotting;
- Acute infection;
- General unsatisfactory condition of the patient.
Preparation
You need to prepare for the procedure in advance:
- In a few days you need to stop drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Balance your diet (here you need to adhere to a diet that will not be too aggressive for the pancreas, so forget about fatty, fried, smoked foods);
- For 3 days, remove from the diet foods that can lead to increased gas formation and flatulence (raw vegetables, legumes, fatty dairy products, black bread).
- Undergo a comprehensive examination (blood and urine tests, allergy tests, ultrasound, pregnancy test);
- The procedure is performed on an empty stomach, the last meal is a light dinner no earlier than 12 hours before the procedure.
Types of procedure
In modern medicine, several types of biopsy are used:
- Intraoperative;
- Laparoscopic;
- Percutaneous;
- Endoscopic.
Intraoperative differs from other topics; material for subsequent study is taken directly during the surgical operation. This is usually the tail part of the organ.
The method itself, used for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes, is dangerous and complex, since the consequences can be more rapid growth of cancer cells, the development of an inflammatory process or peritonitis.
The procedure can be carried out using the following methods:
Breast biopsy
- Straight. If the patient has a large superficial tumor in the upper or lower edge of the organ. The doctor makes an incision on the anterior abdominal wall and uses a needle or a special gun to collect material.
- Transduodenal. To examine the organ, the duodenum is used. To collect the material, a thin needle is used, which is connected to a 10 ml syringe with 4 ml of air.
Percutaneous biopsy is the least traumatic method. It is performed quite often using anesthesia. The needle is inserted through a miniature cut in the skin. For monitoring, a stationary ultrasound machine or tomograph is used.
Laparoscopic biopsy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure. It serves both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It is often used to detect abscesses, pancreatic cancer, serious pathologies of the biliary tract in patients, and in some other cases.
During the procedure, the doctor visually examines the patient's entire abdominal cavity and pancreas. This allows you to select the desired area for tissue sampling.
With an endoscopic biopsy, it is possible to take not a piece, but a whole column, which is sometimes very important. Using the duodenum, where the doctor inserts an endoscope, he uses a special needle under ultrasound control to collect tissue. This type of biopsy is quite safe, since the skin is not damaged, and severe complications rarely occur.
Another advantage of this method is that it is successfully used for minor tumors with difficult access.
We can say that each method given has its own advantages and disadvantages. Based on the practice of the integrative oncology clinic Onco.Rehab , we say: the doctor chooses which method of pancreatic biopsy will be optimal in this particular case, taking into account many factors.
Features of processing seized material
After the surgeon has collected the affected tissues, they must be sent to the laboratory for study. Tissues are transported in special sterile tubes. Before starting to study the biomaterial, diagnosticians process it and prepare it for research.
Selected tissues are treated with paraffin or frozen, after which they are cut into thin sheets - sections, using a microtome knife. The resulting sections are placed on rectangular sterile glasses and stained.
The material prepared in this way is studied under a light microscope. Using high-precision optics, the doctor can determine the nature of the pathology affecting the organ, its severity, and even the prognosis of its development.
If microscopic examination is not enough to make a diagnosis and identify a cancerous tumor, an immunohistological study of tissues is carried out. To do this, the sections are exposed to various antitumor sera. The appearance of yellowish granules in one of the preparations, visible under a microscope, indicates that the tumor is of precisely the nature against which the serum is directed in a particular section.
Electron microscopy magnifies organ cells up to 100 thousand times and allows one to examine the state of the organelles of pancreatic cells.
Recovery
- After the procedure, the patient needs to remain under the supervision of a doctor for some time, and only then will he be discharged.
- After the procedure, an eight-hour fast is indicated.
- You can only drink non-carbonated alkaline water.
- The patient is transferred to parenteral nutrition for 24-48 hours only if indicated.
- The patient must follow a therapeutic diet (diet 5p according to Pevzner) for at least a month.
- Take food 5-6 times a day in fractional portions, in mushy or ground form. The food should be warm.
- Cerucal and Sandostatin may be prescribed by your doctor.
- There are no complications - the patient is discharged the next day after the procedure
- For several days after discharge, semi-bed rest must be observed.
- Avoid physical activity for a month.
- Alcohol consumption is prohibited.
Biopsy in Turkey at Anadolu Medical Center
Biopsy abroad is performed by experienced professionals using the latest equipment. It is more accurate and faster. Each patient is provided with an individual approach.
Biopsy in Turkey in Anadolu is a reliable method for determining the type of tumor. Experienced staff ensure the absence of complications and a quick recovery period.
Depending on what kind of biopsy is performed, the cost of the examination also varies. What matters is the status of the chosen medical institution, the urgency of the procedure, and its complexity.
Details about how a biopsy is performed and prices for medical tests can be obtained from the consultants of the medical institution by phone or through the feedback form.
The material was prepared in agreement with medical doctors.
Complications
Often the culprits of complications are patients who take lightly both their health and recommendations for restoring the body after the procedure.
The most common complications are:
- Feverish symptoms;
- Chills;
- Dizziness;
- Weakness;
- Stomach ache;
- Nausea and vomiting.
Bleeding may occur due to possible damage to blood vessels, but this is extremely rare. And to minimize them, the partners of the Onco.Rehab clinic perform biopsy procedures under the control of ultrasound, CT, and other modern technologies.