Biopsy is a test that is widely used in medicine. This term itself comes from the Greek words “bio” - living and “opsis” - to study. In other words, a biopsy is a comprehensive study of a small fragment of living tissue, during which a variety of pathologies can be identified.
The liver is often the target of biopsy because this organ is vulnerable to various inflammatory and viral diseases. In addition, it is in the liver that metastases often appear in cancer of other organs. It is not always possible to recognize pathology using ultrasound or tomography, but examining a tissue sample obtained as a result of a biopsy helps to “shed light” on the essence of the disease, determine its etiology and choose the right treatment method.
Some patients who are not well-versed in liver biopsy are intimidated by the procedure. However, there is no need to fear that removing a fragment of liver tissue will negatively affect the health of the organ. The liver recovers very quickly after any manipulation. In addition, during a biopsy, 1/50,000 of the organ is removed. This is a negligible amount, and therefore the procedure will not have any negative consequences for the patient’s condition.
Indications
- with damage to small bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis, chronic drug-induced cholestasis)
- to detect infections: tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilis, cytomegalovirus infection, herpes, etc.
- before and after liver transplantation to assess possible complications
- before kidney transplant
- to make a diagnosis of fever of unknown origin
- to determine the causes of abnormalities in the results of liver function tests
- if you suspect genetically determined familial liver diseases
- with jaundice of unknown origin without enlargement of the bile ducts
2.How to prepare for a biopsy?
Tell your doctor:
- About a possible or confirmed pregnancy;
- If you are taking any medications;
- If you are allergic to any medications or latex;
- If you have recently had pneumonia;
- if you have or have had ascites;
- If you have problems with the circulatory system or are taking blood thinning medications.
It is recommended not to eat 10 hours before the liver biopsy. Immediately before the biopsy, you should empty your bladder.
Types of biopsy
Targeted fine-needle biopsy is the safest biopsy method. But it is not used to diagnose chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
A targeted biopsy with a medium-diameter needle is performed under the guidance of ultrasound, CT or angiography. This type of biopsy produces a higher percentage of positive results than others.
Menghini needle biopsy “in 1 second” is performed using a 1.4 mm needle with an oblique and slightly convex cut, equipped with a rod. The procedure does not require anesthesia; sometimes pain relief is performed after the examination.
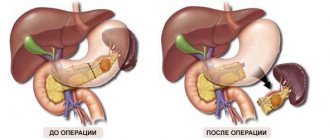
A laparoscopic biopsy is performed using a thin tube with a camera at the end (laparoscope), which transmits an image of the liver to a monitor. The doctor inserts a laparoscope through an incision in the wall of the abdominal cavity and, looking at the screen, removes fragments of liver tissue from specific areas. This type of biopsy is used when a specific tissue sample needs to be taken.
A transvenous biopsy is performed if the patient has problems with blood clotting or fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, that is, when other types of biopsy are contraindicated for him. During the test, the doctor inserts a thin tube with a biopsy needle (catheter) into a vein in the neck and advances it to the liver, where he collects a piece of tissue for examination.
Goals and possibilities of biopsy
Many liver diseases, including chronic hepatitis, cancer, etc., do not have pronounced symptoms in the early stages. They usually manifest themselves as mild malaise, fatigue and other nonspecific health problems. Blood tests such as blood biochemistry, liver tests, etc. can shed light on the condition of the liver; however, they do not make it possible to assess the degree of organ damage and the dynamics of the disease. In such cases, a biopsy is resorted to.
During the biopsy, a thin column of liver tissue is taken, which is essentially a histological section. By studying this section under a microscope, a pathologist can assess the condition of both the superficial and deep layers of the liver. During the study, the exact cellular composition of the organ is determined, along with normal hepatocytes, cancer cells, polyp fragments, fibrous formations, etc. can be detected.
Thus, biopsy is the most reliable research method at the moment. This procedure is a mandatory step in confirming serious liver pathologies.
For example, treatment of cancer involves taking toxic drugs and undergoing traumatic procedures (radiation therapy, etc.). You should only take such a risk if the presence of cancer cells is confirmed with 100% accuracy.
How to prepare
During preparation you must:
— tell your doctor about pregnancy, lung and heart diseases, allergies to medications, diabetes, and problems with blood clotting;
- inform the doctor about taking anticoagulants that thin the blood;
- a week before the procedure, you must stop taking aspirin, aspirin-containing and some anti-inflammatory drugs - you should consult your doctor about this in advance.
The following laboratory tests must be performed before a liver biopsy:
- general blood analysis
- general urine analysis
- blood clotting test
- HIV test
- hepatitis test
How to behave after the procedure
Doctors recommend bed rest for 24 hours after any type of biopsy. You should lie on your right side for at least two hours after the procedure. An ice pack may be placed on the biopsy site. Every two hours, patients have their blood pressure measured and their heart rate monitored. Eating is allowed no earlier than three hours after medical procedures.
As a rule, within a day after performing those types of biopsies that are considered minimally invasive, patients are discharged from the hospital. Doctors recommend refraining from physical activity for at least two days after the procedure. For a week after the biopsy, you should stop taking medications containing Aspirin, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition, thermal procedures are not permitted.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
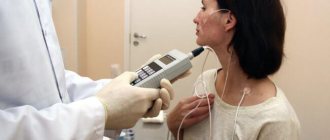
How is a biopsy performed?
In most cases, a liver biopsy is performed in a hospital or day hospital setting, since after the procedure the person must be under medical supervision for 4 hours.
The procedure itself lasts no more than 5 minutes.
- The patient lies on his back.
- The needle insertion site is disinfected and an anesthetic injection is given.
- The doctor makes a small incision and inserts a special needle through it, with which he removes a fragment of liver tissue for further histological examination.
After the procedure
- The patient may experience mild discomfort or mild pain in the shoulders or back. In this case, the doctor prescribes painkillers.
- Physical activity should be avoided for 24 hours.
- It is not recommended to drive for 8 hours.
- You should avoid taking blood thinning medications for a week.
If within 72 hours after a liver biopsy you have a fever, chills, nausea, weakness, difficulty breathing, acute pain in the liver, chest, shoulder, or abdomen, you should consult a doctor immediately.
How does the procedure work?
How is a puncture percutaneous biopsy performed in modern clinics? We will describe the procedure step by step, from preparation for liver biopsy to recovery after taking the material.
Preparation
Already a week before the procedure, you should begin preparing. How to prepare for a biopsy? Firstly, you should avoid taking blood thinning medications (such as aspirin, etc.) for 7 days before the intervention. This is to avoid bleeding during and after the tissue sample is taken.
The procedure should be carried out on an empty stomach. Usually it is done in the morning; You should not have breakfast on this day. Dinner the day before should be light; you should avoid brown bread, dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits (these foods stimulate gas formation, which can lead to bloating). The attending physician may advise you to perform a cleansing enema in the evening or in the morning before the intervention.
If you are taking medications, be sure to check with your doctor to see if you can take them on the day of your biopsy.
Material collection procedure
On the day of the operation, the patient undergoes a follow-up examination, including blood pressure measurement, a blood clotting test, a complete clinical blood test and an ultrasound of the liver. If there are no violations, proceed to the procedure.
First, the patient is asked to change into sterile surgical clothing and lie on his back on the examination table. Doctors often offer the patient a sedative so that he does not experience severe nervous tension during the intervention.
The skin on the patient's abdomen is disinfected, and the area in the projection of the liver is numbed with local anesthetics. The patient may experience some pain during the injection, but will feel quite fine after the biopsy. In other words, the pain of this procedure can be called moderate.
It takes a few minutes for the anesthesia to take effect. At this time, the patient is told how to breathe correctly during the collection of biomaterial. After this, the doctor inserts a special needle into the patient's right side, removing a small amount of liver tissue. The material is usually collected under ultrasound guidance. Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy allows you to accurately select the point for needle insertion. Thanks to this, the cut is more informative and eliminates the possibility of puncturing large blood vessels, the colon, etc.
A percutaneous needle biopsy takes only a few seconds and is performed under local anesthesia.
After taking the material
After the liver biomaterial is taken, it is sent to the laboratory for testing. The patient remains in a supine position for another 4 hours, during which it is forbidden to get out of bed, go to the toilet, eat, etc. All this time the patient is under medical supervision, since complications of the biopsy usually appear in the first 2-3 hours after the procedure.
Gradually, the effect of anesthesia wears off, so the patient may experience pain in the right side, shoulders, etc. If the pain is severe, the doctor will give an additional injection of pain medication.
results
To evaluate the results of a study in modern medicine, 2 methods are most often used:
The Metavir method is used if a biopsy is performed for hepatitis C. During the study, the stage and degree of inflammation is established - from 0 to 4 points. The stages of inflammation make it possible to draw a conclusion about the amount of fibrous tissue and its scarring. Scarring stages are also graded on a scale of 0 to 4.
The Knodel method is used to display the results of a biopsy for the presence of the degree of inflammation, necrosis of the liver lobes, the degree of scarring of the organ, etc.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Possible risks
A liver biopsy is considered a fairly safe procedure (which is why it is often performed on an outpatient basis rather than in a hospital). It is usually easily tolerated by patients and does not lead to any complications.
In approximately 0.2% of cases, bleeding occurs after tissue collection. As a rule, this complication occurs in the first 2-3 hours after the procedure. At this time, the patient is still in the clinic, so he is provided with immediate medical assistance.
Another possible consequence of the intervention is aching pain in the side, right shoulder or epigastrium (the area above the stomach). Pain occurs in approximately one in four patients undergoing a biopsy. To eliminate pain, the doctor will prescribe analgesics in the form of tablets. As practice shows, within 1-2 weeks the pain goes away completely.
After the procedure, the liver recovers very quickly. This is not surprising, because this organ has a very high reparative potential. You've probably heard that a healthy person can donate part of his liver for a transplant, and after some time it will fully recover. For a biopsy, only 1/50,000 of the liver’s mass is taken; this amount is insignificant for the general condition of this organ. That is why you should not worry that the procedure may have any consequences for the functional state of the liver.
Risks of Liver Biopsy
A liver biopsy is a generally safe procedure when performed by an experienced doctor. Here are the main risks associated with this diagnostic method:
- Pain and bruising at the site of tissue collection are the most common complication of liver biopsy. As a rule, in this case, the patient is simply given an anesthetic (paracetamol with codeine).
- Internal bleeding occurs in rare cases. This condition requires hospitalization.
- Infection in the bloodstream is also a rare complication of biopsy.
- Accidental damage to a neighboring organ (for example, the gallbladder) is possible.
If you have a transjugular (transvenous) liver biopsy, the following complications are possible (they are also quite rare):
- Hematoma on the neck at the site where the catheter was inserted into the vein
- Temporary problems with the facial nerves. In rare cases, a transjugular biopsy may damage nerves and affect the face and eyes (for example, short-term drooping of the eyelid)
- Temporary voice problems. You may become hoarse or lose your voice for a short time
- Lung puncture. If a needle accidentally punctures your lung, air will enter and cause a collapsed lung (pneumothorax).
How does rehabilitation work?
No rehabilitation is required. The procedure takes only a few minutes: under ultrasound control, a sample of liver tissue 1–3 cm long is taken using a special needle, which is then sent to the laboratory for examination. This does not cause any harm to the organ. After the biopsy, the patient remains under the supervision of medical personnel for about 2 more hours, and then he is sent home.
You can contact the hepatologist in the comments. Don't hesitate to ask!
Article published: 2019-08-07
This article was last updated: 08/07/2019
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try using search
doctor or administrator.
Read the dictionary of terms.
Expert author: Gastroenterologist-hepatologist Ekaterina Kashukh, gastroenterologist Daniela Purgina
Benefits of oncological
The biopsy is performed in comfortable conditions and with special care for the patient. You can fully trust our doctors - the specialists of the Sofia Oncology Center will make every effort to ensure that the procedure is quick, painless and worry-free.
Advantages of the Sofia Cancer Center:
- everything in one place for liver diagnostics, treatment and research: hospital, outpatient department and own laboratory;
- experienced doctors;
- one of the best equipment: biopsy is carried out using the latest and high-precision ultrasound machines, providing detailed information;
- 30 years of unique experience and impeccable reputation;
- individual support around the clinic;
- numerous certificates and awards, including JCI;
- plenty of parking spaces.
In what cases is it prescribed?
A biopsy is performed in cases where difficulties arise in making a diagnosis. For example, in case of viral hepatitis , a liver biopsy is performed to assess the histological index of activity and stage of the disease, the degree of chronicity of the process. There are certain criteria that make it possible to determine the severity of fibrosis in the liver using histological examination of the material obtained during biopsy. This allows you to determine further treatment tactics and prognosis for the patient. Biopsy is also used:
- when there are some neoplasms in the liver (for example, metastatic cancer, nodular hyperplasia, etc.) and their nature cannot be determined using ultrasound, CT or MRI;
- if the cause of liver cirrhosis is not clear;
- if there is hepatolienal syndrome of unknown etiology.
Make an appointment
The clinic is located in the Central Administrative District (CAO) of Moscow, next to several metro stations: Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya.
You can sign up for the cost of the study by phone or through the online form!