Any poisoning is always unpleasant, especially when it comes to children. At the first symptoms of poisoning, many parents begin to fuss and worry. But worrying won’t help here; the child needs to quickly receive specific medical assistance and then show it to a doctor. Do not panic if your child starts vomiting. This is a completely normal phenomenon, as the body tries to get rid of toxic substances that have entered it. If vomiting becomes indomitable, then you need to use antiemetic drugs for children that can stop the unpleasant urge.
Emergency care for poisoning
All adults should understand that prescribing anti-vomiting medications for children on their own is very dangerous. Before you start taking drugs from this drug group, you need to figure out why the child is vomiting. There are many reasons for this, the main ones can be identified as follows:
- food poisoning from stale food;
- infectious diseases of the digestive tract;
- malfunction of the pancreas;
- allergic reaction;
- unstable liver and kidney function;
- head injuries.
Also, vomiting in children can occur when overeating, when consuming fatty foods, and when motion sickness occurs. Vomiting can be indomitable or one-time.
Repeated profuse vomiting most often indicates poisoning. In this case, the baby needs help. To begin, thoroughly rinse the stomach with a large volume of slightly salted water. Allow the child to drink as much liquid as he can, and then press with his fingers on the root of the tongue. Such actions are performed until the waste water is clean. This helps remove the remains of undigested food and some of the pathogenic bacteria that provoked intoxication.
Only after the stomach has been thoroughly rinsed can anti-vomiting medicine be given to children, otherwise it will not be absorbed and will be released with vomit. For children under 1 year of age, the stomach is washed only in a hospital setting and under the watchful supervision of doctors.
For children under 3 years of age, gastric lavage at home is performed with great caution. The baby must be in an upright position and his well-being must be constantly monitored. At this age, body weight is small, so dehydration occurs quickly. If your health worsens, immediately call an ambulance or take the child on your own to the hospital.
Restoring water balance
In case of poisoning, the child suffers from severe vomiting and diarrhea, due to which a lot of fluid leaves the body and dehydration begins.
In between gagging, the child should be fed small portions, this will slightly restore the water balance. Pure still water, decoctions of raisins and dried apricots, as well as water with the addition of lemon juice and honey are suitable for drinking. You can use the pharmaceutical drug rehydron, but it has an unpleasant taste, so children take it with great reluctance.
Milk and dairy products, soda, coffee and strong tea should not be used for feeding children.
When should you start taking antiemetic drugs?
If the child’s vomiting does not stop for a long time, then they begin to give antiemetics for children. This can only be done after consultation with a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist. If the nearest medical facility is far away, you can call an ambulance, where a doctor can advise on the advisability of taking such drugs.
If you suspect rotavirus, you should not immediately try to stop vomiting. This is how the body fights pathogenic microorganisms that have penetrated it. If you immediately take anti-vomiting pills for children, the stomach will not have time to clear itself naturally, which means that the disease may not only drag on, but also cause serious complications.
Prevention is everything!
There is a misconception that if rotaviruses are transmitted through contaminated objects, then it is enough to observe the rules of personal hygiene to defeat them. This is partly true, but in the case of young children the rule does not work. Because the virus is highly contagious, it is also less affected by common hand sanitizers and soaps. Only solutions of alcohol, iodine and chlorine are effective against rotaviruses.
It is also generally accepted that it is enough to get sick once to acquire immunity for life. This idea is not entirely correct, since there are several types of rotaviruses. Therefore, there is a risk that each time the body encounters a different type of virus from the same group.
Today, a vaccine against rotaviruses has been developed - the live Rotatek vaccine for oral administration. It protects against the five most common types of rotaviruses in Russia. Immunity after vaccination lasts about five years.
Medicines that can be used for children
Pharmaceutical companies make many different anti-nausea and vomiting medications to treat children. Many of them have one active ingredient and differ only in name and price. In pediatric practice, doctors use relatively safe antiemetics.
In pharmacies you can find medicines from this group not only in tablets, but also in powder and solution for injection. All anti-vomiting drugs have many contraindications and side effects, so they should only be prescribed by a doctor.
Cerucal
The active ingredient of this drug is metoclopramide hydrochloride, which can be found in pharmacies in tablets under the same name. Moreover, it will cost an order of magnitude cheaper than cerucal. This drug is available in small tablets of 10 mg and a solution for injection, where 1 ml contains 5 mg of the active substance.
This medication helps suppress the activity of dopamine receptors, strengthens the muscles of the digestive organs and increases intestinal motor function. This drug is prescribed for persistent nausea and vomiting caused by various reasons. It can be given to children over 2 years old. The dosage for children from 2 to 14 years is calculated as follows - 0.1 mg per kilogram of body weight, while no more than 0.5 mg per kilogram should be used per day. The medicine is taken 30 minutes before meals. The therapeutic effect of the tablets begins 20 minutes after administration and lasts up to 6 hours.
Contraindications
Cerucal's instructions describe many contraindications that need to be taken into account, especially when prescribed to young children. These include the following diseases and conditions:
- individual intolerance to the components included in the medicine;
- lactose intolerance;
- glaucoma;
- stable low pressure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- suspicion of bleeding in the digestive organs;
- epilepsy.
For children under 4 years of age, Cerucal is prescribed with great caution. The dosage is calculated by the attending physician in accordance with body weight.
Side effects
This antiemetic has many side effects that can cause a lot of unpleasant minutes:
- Persistent migraine and dizziness.
- Unreasonable fatigue.
- Feeling of fear, increased irritability.
- Atypical drowsiness.
- Nervous tics are often observed in children.
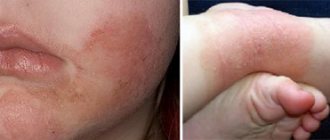
- Allergic reactions.
In addition, dry mouth and diarrhea are occasionally observed. If side effects occur, stop treatment with the drug and consult a doctor about adjusting therapy.
Motilium
The active substance of this drug is domperidone.
The medicine is available in tablets and suspensions. One tablet contains 10 mg of this substance, and syrup for oral use contains 1 mg per 1 ml. Medicines for vomiting in a child, such as motilium, are prescribed for impaired digestion, which is accompanied by congestion in the stomach. In addition, the medication will help with flatulence, heartburn, hiccups, stomach pain, vomiting after taking medications and in infants with excessive regurgitation.
For children, an antiemetic is prescribed in a dosage of 2.5 ml per 10 kg of body weight up to 3 times before meals, and also, if necessary, at night.
Contraindications
The drug is not recommended for use in a number of chronic diseases and certain conditions, these include:
- Malignant tumors of the pituitary gland.
- High levels of prolactin in the blood.
- Simultaneous use of certain antifungal and antibacterial drugs.
- Suspicion of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Intestinal obstruction of various etiologies.
- Body weight is less than 35 kg for the tablet form of the drug.
- Individual intolerance to individual components that are included in the medication.
- Pregnancy at all stages and breastfeeding.
Babies under 1 year of age are allowed to take the drug in the form of a suspension with great caution. Motilium treatment is prescribed only after weighing all the risks.
Side effects
Both tablets and suspension can cause various disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems:
- Severe pain occurs in the intestines.
- There may be constipation or diarrhea.
- Intense thirst that is very difficult to quench.
- Atypical drowsiness and persistent migraine.
- Increased excitability and nervousness.
- Allergic reactions, up to Quincke's edema.
- Disruptions in the endocrine system.
Most often, side effects occur in children due to disruption of the digestive tract and disappear immediately after discontinuation of the medication. If a child experiences serious health changes, then this is a reason to stop taking Motilium and consult a pediatrician.
But-spasm
The active substance of this drug is prifinium bromide. No-spasm is available in several dosage forms - coated tablets, injection solution, syrup and a special solution that is used in the treatment of children.
This medicine is prescribed for colic, nausea and vomiting. In complex therapy it is prescribed for the treatment of gastritis, colitis, enteritis and spasms of the muscles of the digestive organs in infants. No-spasm is often prescribed before diagnostic procedures on the digestive tract.
The dosage depends on the patient's age. Adults and children over 12 years of age are prescribed 30-60 mg up to three times a day. Children from 6 to 12 years old: 15-30 mg up to three times a day. Syrup is used to treat children under 6 years of age. Children under 3 months of age are given 1 ml of the drug every 6 hours. From 3 months to a year it is allowed to give 2 ml of medication every 6 hours. From one to two years, give a teaspoon every 8 hours. From 2 to 6 years old, give 2 teaspoons up to 3 times a day.
The drug is administered by injection very slowly, as blood pressure may drop sharply!
Contraindications
This medicine has many contraindications that may be an obstacle to its prescription. If, however, the medication is prescribed to such groups of patients, then in exceptional cases. Contraindications look like this:
- individual sensitivity to the components of the drug;
- for heart disease, when increased heart rate is dangerous;
- with hyperthermia;
- for intestinal diseases, which are characterized by obstruction;
- for older people, when intestinal motility is reduced;
- for eye diseases that are characterized by increased intraocular pressure;
- for liver and kidney diseases;
- for chronic diseases of the respiratory organs;
- for brain injuries, especially in children.
It is not recommended to prescribe the drug to children with severe neurological diseases, as well as diseases of a genetic nature.
Side effects
The drug no-spasm has few side effects. They all quickly disappear after the drug is completely discontinued or the therapeutic dose is reduced. Very rarely, patients complain of the following health changes:
- Feeling of dry mouth and extreme thirst.
- Pupil dilation.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Persistent constipation.
If any side effects occur, you must inform your doctor. If the child’s well-being worsens after taking the medication, then this is a reason to adjust the treatment.
Domperidone
It is used in tablets for children over 5 years of age, but is available in the form of suppositories. It is convenient to use suppositories for severe nausea and frequent bouts of vomiting. The dosage of the medicine should be determined by the doctor, taking into account the child’s age and weight.
Dietary supplement against vomiting
{banner_banstat9}
The anti-vomiting powder for children “Primadofilus”, which contains bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria, has proven itself well. This drug is prescribed to restore the functioning of the digestive tract. Indications for use are allergic reactions, dysbacteriosis and weak immunity. Doctors often prescribe this drug as a mild antiemetic that works only locally and does not have a detrimental effect on other organs and systems.
The only contraindications to the prescription is individual intolerance to the medication. Side effects include allergic reactions.
You should not start taking any medications, even harmless ones at first glance, without consulting a doctor. This is especially true for the treatment of young children.
Where can you get infected with rotavirus?
Anyone can become infected with rotavirus, regardless of gender and age. However, children aged 6 months to 2 years get sick more often than adults3. The source of rotavirus is people - patients with symptoms of infection or healthy virus carriers2,3,4, who usually do not have any complaints5.
Sick people and healthy virus carriers release viruses into the environment along with feces3,4. Then the pathogens get into the water, onto household items, hands and clothes and through them are transmitted to other people4. This means that rotavirus is transmitted to children by violating hygiene rules4, swimming in bodies of water3 or consuming contaminated water4 and food3. The airborne mechanism of transmission of rotavirus infection cannot be excluded3,4.
Not all children are equally susceptible to rotavirus infection3. Children are most often infected with rotavirus:
- aged 6-18 months3;
- those who are bottle-fed6;
- having concomitant diseases6;
- with weakened immunity6.
Up to contents
Diet after vomiting
It is not enough just to stop the child from vomiting; you need to make sure that the unpleasant urge does not arise again. This can be achieved by following a diet. The child’s meals in the first days of illness should be fractional and gentle. The diet includes only healthy and natural products. It is unacceptable to give your baby fried and smoked foods, as well as food that is richly flavored with spices.
You need to include protein-rich foods in your meals. These are lean meats - chicken, rabbit and veal. Dairy products – bifidokefir and low-fat cottage cheese. It is not recommended to give your child confectionery products, especially those made with yeast dough, as they will provoke fermentation and a new attack of vomiting. The child should receive carbohydrates from porridges - buckwheat, oatmeal and rice.
In the first days, you should not load your stomach with fresh fruits and vegetables. You can give baked apples with honey or well-ripe bananas. It is better to cook light soups from vegetables using a second broth. All food is prepared by steaming or in the oven; it is also allowed to boil foods.
After bouts of vomiting, a child should not be offered dishes made from cabbage and legumes. They cause severe bloating and are difficult to digest.
Rotavirus infection - “disease of dirty hands” or “intestinal flu”?
In fact, both names fully characterize the disease. Since viruses are mainly transmitted through unwashed children's hands, contaminated toys, food or water.
Once in the body, viruses rush into the small intestine, causing damage and rejection of its villi.
As a result, immature cells of the small intestine appear that do not produce enough digestive enzymes. Therefore, the digestion and absorption of nutrients is impaired. Thus, a cascade of complex processes is launched, leading to the release of water and salts into the intestinal lumen, which is manifested by loose stools and dehydration.
The source of rotavirus infection is a sick or clinically healthy carrier (without signs of disease). Isolation of the virus in feces begins on the second day of illness and then continues for two months even after all symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
How to prevent vomiting using traditional methods
{banner_banstat10}
If a child suffers from nausea and vomiting, then it is not necessary to start giving the baby medications. Tea with lemon balm or mint, as well as a delicious drink made from fresh lemon with honey, will help stop attacks of vomiting. These drinks are given in small doses, but often. In some cases, it is enough to drink strong sweet tea and lie down for a while.
Rice water with raisins gives good results. It relieves inflammation from the stomach and reduces its tension, due to this the urge to vomit gradually disappears.
Antiemetic drugs relieve the gag reflex well. But you cannot use them thoughtlessly, as there are many contraindications. Before the doctor arrives, the child is well hydrated to prevent dehydration. Only the doctor decides how appropriate it is to take antiemetic medications in a particular case.