- Symptoms of colon polyps
- Risk factors
- Diagnosis of neoplasms
- Treatment
- Popular questions
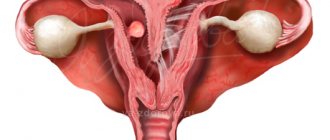
Colon polyps
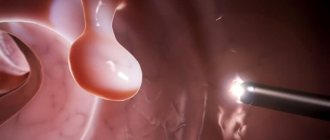
are benign formations, usually asymptomatic and most often found in patients complaining of discomfort, intestinal dysfunction, pain in the anus, pathological discharge from the anus, which also occurs in other diseases (hemorrhoids, paraproctitis , anal fissure, colitis, rectal cancer, etc.).
The prevalence of formations increases with age and ranges from 25 to 35% among the population over 50 years of age.
The clinical significance of this pathology is due to the fact that from 70 to 95% of colorectal cancer cases develop in the “polyps-cancer” sequence Source: Vladimirova A.A. The use of aquascopy in the diagnosis of colorectal polyps / A.A. Vladimirova [and others] // Bulletin of the All-Russian Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. - 2006. - No. 6 (52). — P. 32-35. .
Risk factors
Risk factors and mechanisms of colon polyps are being actively studied. Among the environmental factors, the nature of nutrition is significant, with a predominance of refined foods in the diet, which contribute to constipation and prolonged stasis of intestinal contents. Dysbacteriosis of the colon has some influence on the occurrence of polyps, reflecting a violation of local and decreased general immunity, contributing to changes in the differentiation and regeneration of mucosal cells. The role of concomitant diseases of the biliary system and impaired production of bile acids, which have a mutagenic effect on the mucous membrane, is also noted as a risk factor. Active chronic inflammation and mucosal dysplasia play a certain role in the occurrence of polyps.
What to do when a polyp is detected
If polyps are detected during colonoscopy and a histological examination reveals a hyperplastic polyp, which is a risk factor for colon cancer, follow-up and colonoscopy are performed every 3-5 years.
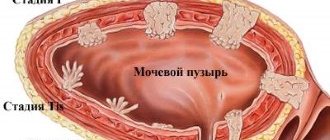
Depending on the size of the adenomatous polyp, histology, and type of polyp (pedunculated or broad-based), treatment tactics are selected. This may be endoscopic removal of a pedunculated polyp or surgical removal of a sessile polyp.
If a malignant polyp is suspected, it is removed. Colonoscopy is subsequently performed at 6 and 12 months. If histology is good, colonoscopy is performed after 2 and then after 3 years, then individually.
Diagnosis of intestinal tumors
Among non-invasive methods for diagnosing colon polyps, the stool occult blood test
. At the same time, the hemoccult test is characterized by a high percentage of false negative results and is not very informative in the presence of polyps less than 2 cm and when the formations are localized in the right half of the colon.
Quite common in the diagnosis of polyps is digital examination of the rectum.
. The method allows you to evaluate the shape and consistency. mobility, presence or absence of a polyp stalk. Low-lying polyps are always detected by digital examination. Small adenomatous polyps located above 5-6 cm from the anus are difficult to determine using the finger method.
Sigmoidoscopy is an important method in the diagnosis of villous tumors.
. This research method is more informative and makes it possible to detect most colon polyps, because more than 50% of them are localized in the rectum and sigmoid colon, i.e. within reach of the rectoscope.
Irrigoscopy
allows you to diagnose most polyps more than 1 cm in diameter; smaller formations can be detected much less frequently.
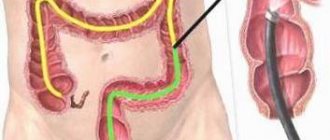
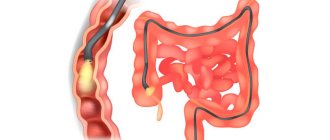
The most accurate and affordable method for detecting colon polyps is currently colonoscopy.
. During the procedure, the condition of the colon mucosa is visually assessed. Also during colonoscopy, it is possible to perform various therapeutic procedures: removal of benign tumors, stopping bleeding, removal of foreign bodies, recanalization of intestinal stenosis.
Virtual colonoscopy
allows you to obtain three-dimensional computer sections of the colon mucosa even with a small lumen diameter. The sensitivity of this method for diagnosing polyps larger than 1 cm is 90%; for polyps measuring 0.5-0.9 cm 80%; 67% when the size of the polyp does not exceed 5 mm. The disadvantages of the method are the rather expensive cost of the procedure and the impossibility of performing a biopsy of the formations.
For a targeted study of the condition of the rectum and colon and if a tumor lesion is suspected, special ultrasound
, which are associated with filling with air or diagnostic medium.
All types of modern diagnostic tests are available at the SM-Clinic. Currently, diagnosing polyps does not require much time and is carried out quickly and painlessly.
What is a colon polyp
A polyp is a protrusion of the intestinal mucosa into its lumen. The term "polyp" comes from the ancient Greek word "polypus", which means "many-legged", because. most polyps consist of many lobules. The histological structure of the polyp is very important. Depending on it, polyps that are precancerous (adenomatous polyps) and hyperplastic polyps that do not increase the risk of developing colon cancer are identified.
The incidence of adenomatous polyps increases with age and is 23-41% of cases in healthy people aged 50-82 years. If there were cases of colon cancer in the family, then in 60% of cases adenomas were detected during colonoscopy. In Europe and the USA, colon adenomas are found in 40% of people over 60 years of age. Studies have shown that colon adenomas (or villous adenomas) can develop into colon cancer within 5-10 years.
Recognize in time
To identify polyps, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. After examination by a coloproctologist, the following types of instrumental diagnostics may be prescribed:
- sigmoidoscopy (examination of a section of the intestine (up to 30 cm) using an endoscope);
- colonoscopy (comprehensive endoscopic examination of the intestines);
- irrigography (x-ray examination of the intestine using a contrast agent);
- biopsy of the polyp to clarify its histological structure and assess the risk of degeneration into cancer;
- and other studies (according to the testimony of a coloproctologist).
Modern diagnostic methods are available to all patients of the ON CLINIC medical center.
Effective treatment of polyps at ON CLINIC
Modern diagnostic equipment and gentle methods of surgical treatment allow coloproctologists of the Multidisciplinary Medical Center ON CLINIC to diagnose and effectively treat polyps of any size, multiple types (including villous adenomas).
Thanks to the introduction of a modern endosurgical treatment method (transanal endoscopic microsurgery), operations are performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient’s performance is restored in the shortest possible time.
After the operation, the patient is observed in a comfortable day hospital at ON CLINIC under the supervision of the attending physician. Control endoscopy is carried out every year, for preventive purposes - every three years.
Coloproctologists at ON CLINIC will help each patient prevent the development of a dangerous disease. And with the help of preventive studies, the disease can be recognized in time (including asymptomatic polyps), and highly effective treatment will be carried out in accordance with international standards.
ON CLINIC – modern standards of diagnosis and treatment!
Advantages of the author's methodology
- There is no need for open surgery or laparoscopy - more traumatic interventions.
- There is no need to remove the rectum or create an intestinal stoma on the anterior abdominal wall, which allows you to preserve the natural functions of the rectum and colon.
- The number of postoperative complications is practically eliminated.
- In patients with severe somatic pathologies or at the patient's request, it is possible to do without general anesthesia by performing the operation under general anesthesia.
- Rapid recovery after surgical treatment: the patient begins to walk and drink on the first day, liquid food is allowed on the second day, discharge is possible on the 2-3rd day. After surgical removal of polyps in the colon, a person is considered functional within 14 days.
As for the price for removing polyps in the colon, the cost of the operation consists of a number of factors, first of all we are talking about the volume of interventions and the presence of complications - then longer and more extensive treatment will be required. Therefore, timely seeking medical help, without waiting for complications to develop, is the best option.
I have personally performed more than 100 transanal operations to remove polyps in the large intestine of various locations, as well as over 300 laparoscopic interventions on the intestine; the accumulated experience is presented in the monograph “Minimally invasive surgery of the colon.” I also regularly conduct seminars on the treatment of intestinal tumors: both benign and malignant. I always strive, if possible, to carry out an organ-preserving intervention, because not only the health, but also the psychological state of the person who trusts my knowledge and experience depends on this.
Symptoms of the disease
Small tumor-like growths usually do not manifest themselves in any way and often become an accidental finding during examination and examination by a proctologist or endoscopist. Studies that help identify benign tumors are digital examination of the rectum, sigmoidoscopy, in some cases, irrigoscopy, and the most informative method is fibrocolonoscopy.
The patient may have a concomitant disease of the rectum or upper colon and will consult a doctor with this problem. For example, for hemorrhoids or anal fissure, colitis or chronic constipation. According to existing protocols, older people are sent for a colonoscopy for the purpose of a preventive examination, and already during the examination, an endoscopist can detect one or more asymptomatic polyps. This is why it is so important to undergo timely preventive examinations. Now in many clinics there are a lot of convenient options (for example, “one-day check-up”) for a full health assessment.
- If the tumor-like formation (polyp) is large, the following symptoms may appear: Mucus, bloody-mucous discharge;
- Cramping pain in the abdomen;
- Pain in the anus;
- Prolapse of a polyp into the anus;
- Diarrhea or constipation;
- Itching in the anal canal;
- Electrolyte disturbances - arrhythmia, convulsions, anemia with large villous tumors and significant loss of fluid through secretion by the glandular cells of the polyp.
How to treat?
Colon polyposis can only be cured by surgery (removal of the polyp). Conservative methods of treatment have not received a positive assessment and are dangerous because they delay the timing of proper treatment, delaying and aggravating the process, leading to complications.
Growths up to 0.5 cm in diameter, at the discretion of the physician, are removed or biopsied to determine their histological structure/risk. If the formation has reached 0.5 cm or more, it must definitely be removed. Polyps of 2 or 3 centimeters are already considered large.
How to recognize a polyp
In most cases the disease is asymptomatic, but some patients may experience certain symptoms, e.g.
- pain - aching, bursting, cramping, localized in the lower or lateral part of the abdomen; after defecation, the intensity of the manifestations weakens or disappears;
- digestive dysfunction - constipation alternates with diarrhea;
- mucus or blood in the stool - this sign is characteristic of villous polyps located in the lower intestines.
Large polyps can block the intestinal lumen, which causes intestinal obstruction. The patient experiences intense pain, nausea, vomiting, lack of stool and passing gas. With this development of events, the patient needs urgent help from a surgeon.
To determine the type of polyp, its location and indications for surgery, as well as select the correct surgical treatment tactics, you must send me a complete description of the colonoscopy, histology data, and, if possible, MSCT data of the cavity with contrast, by email to my personal email address, indicate your age and main complaints. Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.