Home » Intestinal adenoma » Tubular adenoma of the colon
What is tubular villous adenoma of the colon? This is a benign neoplasm that instantly affects the intestinal mucosa. The size of the neoplasms is 2 centimeters, after which growth stops. If the volume of adenoma grows rapidly, then the disease progresses and affects neighboring healthy organs. Tubular adenoma of the colon with dysplasia is considered the first stage of low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of the colon. The pathology turns into a malignant tumor if timely treatment is not provided.
When the first signs of adenoma appear, you need to contact a proctologist to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body and begin treatment. The private proctology clinic “Proctologist 81” employs highly qualified specialists who use modern treatment methods and new equipment that can diagnose the disease even at an early stage.
Reasons for the development of tubulovillous adenoma of the colon with dysplasia
There are certain reasons for the development of tubular-villous adenoma of the colon with dysplasia. Pathologies in all parts of the large intestine appear due to influences that provoke the growth of benign tumors. The reasons include the increased content of animal fats in food. A lack of plant fiber in the diet leads to gastrointestinal disorders. This problem is typical for areas with cold climates and undeveloped agriculture.
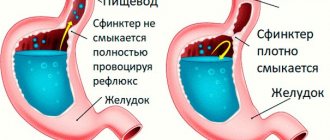
Tubular adenoma of the sigmoid colon is also inherited. People with a genetic predisposition are much more likely to develop pathology. The disease often becomes malignant. The cause of the formation is called chronic and acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, the appearance of hemorrhoids and others.
The patient's lifestyle and environment are of great importance. Factors such as exposure to radiation, alcohol abuse, and smoking negatively affect intestinal motility and the digestive tract. It is advised to exclude from the diet foods that cause fermentation, carbonated drinks, and baked goods.
Causes of adenomas in the intestines
Scientists have not yet figured out the exact etiological factor contributing to the development of intestinal adenomas. There are several theories about the occurrence of benign neoplasms. Most doctors believe that a combination of several factors plays a leading role in the occurrence of this disease. Based on this, there are several reasons for the appearance of tubular adenoma: Genetic predisposition. Heredity is of great importance in the occurrence of intestinal polyps. In some cases, tubular adenomas are detected in several family members. Nature of nutrition. It is believed that people whose diet contains a large amount of animal fats are prone to the appearance of both benign neoplasms and gastrointestinal cancer. In turn, the risk of developing these pathologies is reduced by consuming vegetables, herbs, and foods rich in fiber. Bad habits. Exposure to the body of various chemical agents and ionizing radiation. Stressful situations. Most often, tubular adenoma occurs in elderly people. Due to the fact that this group of people has an increased risk of developing intestinal cancer, polyps are subject to mandatory removal.
Adenomatous polyps
All types of polyps have their own signs that the patient notices. The following characteristics are distinguished:
- there are no inflammatory reactions;
- polyps are located in the final section of the large intestine;
- have the appearance of single polyps from the epithelium;
- have a smooth and even surface;
- the structure is considered dense;
- placed on a thin stalk that grows rapidly;
- redness and irritation appear on the mucous membrane;
- cracks form;
The characteristic of the formation is the size of the polyp. It is small and increases if left untreated. To diagnose tubular villous adenoma of the sigmoid colon, studies are carried out, including rectoscopy and irrigoscopy. The procedures allow us to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and diagnose the presence of tumors and cysts. Determination of the type of polyp is carried out without histological examination.
Tubular papillary adenoma of the colon and tubulovillous adenoma of the colon are similar in appearance, so you should contact a proctologist who can make a clear diagnosis for the patient.
Features of localization of adenomas
Adenomas can occur in different places.
Adenomas in the large intestine can occur in a variety of areas. Studies provide the following results on the frequency of localization of adenomatous polyps:
- 25% - rectum;
- 25% - sigmoid colon;
- 18% - descending colon;
- 13% - ascending colon;
- 11% - transverse colon;
- 7% are blind.
Symptoms of the tubulovillous variety of the disease
Depending on the histological structure, adenomas are divided into three groups. Among them:
- villous;
- tubular;
- mixed.
Tubulovillous adenoma of the colon is considered a malignant variant of the disease. Transformation into a tumor occurs in a matter of weeks. There are first, second and third degrees of three degrees of change in cell morphology.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with first-degree dysplasia is considered a precancerous condition. Becomes the basis for the appearance of a malignant tumor. The patient should pay attention to the symptoms, according to which the attending physician will determine the diagnosis. In the early stages, the size of the polyps is one centimeter, so there are no symptoms. An increase in the tumor leads to the appearance of the following signs:
- minor intraintestinal bleeding;
- inclusions of blood in the stool;
- the appearance of pus and mucus during bowel movements;
- impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea and constipation;
- vomiting and nausea;
- violation of the motor function of the digestive system;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- sensation of a foreign body in the anus;
- flatulence and bloating;
- itching and burning in the anus;
The patient feels severe discomfort in the abdominal area, which intensifies after eating. Possible lack of appetite. If left untreated, tubular adenoma with dysplasia moves to the second stage. The morphology and biochemical processes in the body change. The disease often becomes malignant, and a number of complications appear. Therefore, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Progression of the disease is observed.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the structure of the adenoma. At the initial stages of development, it is difficult to notice signs of a tumor. The neoplasm is detected at later stages. This usually happens when examining other diseases.
The first symptom appears when the growth size is 2 cm. Patients experience certain complaints. Each case is individual. Adenoma is characterized by:
- Pain during bowel movements.
- Burning in the anus area.
- Bloating and pain inside (if the transverse colon is affected).
- Release of blood.
- Feeling a foreign body in the intestines.
- Alternating constipation with diarrhea.
The small size of the adenoma does not cause any inconvenience. As the tumor grows, it shrinks the intestinal walls. As a result, obstruction develops. There is a high probability of progression of pathologies.
Diagnosis of the disease
The presence of tubular adenoma is extremely difficult to detect in the early stages. There are no symptoms, and the size of the tumor does not exceed a few millimeters. According to medical statistics, for many years the pathology occurs without clinical manifestations and does not cause discomfort to the patient.
For diagnosis, the patient visits a proctologist, who conducts an initial examination and learns about the medical history. Clinical and biochemical studies are being carried out. The patient takes a general blood, urine and stool test. It is mandatory to conduct a stool test for occult blood, which will determine the presence of disorders in the intestines. Tests such as irrigoscopy and colonoscopy are popular.
Irrigoscopy is considered an X-ray examination of the colon, which is performed using contrast fluid. For example, barium sulfate. The procedure reveals the contours of the mucous membrane in the affected area and suggests the nature of changes in the body. Diagnostic testing is not carried out for allergic diseases, pregnancy and the lactation period. Contrast agents are considered allergens.
Colonoscopy is most effective in identifying and diagnosing adenomas. Allows a medical expert to identify a formation on the mucous membrane and perform a biopsy for morphological examination of the affected tissue. During a colonoscopy, the surgeon can identify an existing polyp or coagulate it using a medical device.
The results of the examination are interpreted by a specialist who will clearly make a diagnosis and prescribe an effective course of treatment.
Rehabilitation
Recovery takes place under constant medical supervision. If endoscopic intervention was performed to cut off a benign polyp, the first control gastroscopy is done two weeks later. For cavity removal of adenomatous neoplasms - when the incision has completely healed. The basis of patient rehabilitation is diet. In the first month, the patient is allowed only liquid porridges and pureed soups. Then he is transferred to dietary table No. 1 for people with gastrointestinal diseases.
The basis of the diet of a patient with adenomatous benign neoplasms is:
- vegetable broth soups;
- meat, low-fat fish;
- dried white bread;
- soft-boiled eggs (steam omelet);
- porridge with milk or water;
- sweet berries, fruits;
- fermented milk products with a low fat content.
Dishes need to be boiled, baked, steamed. Boil vegetables and pasta well and grind in a blender.
The following sweet desserts are allowed:
- cookie;
- jam;
- berry, fruit mousses, purees;
- cottage cheese;
- dry biscuit;
- paste;
- baked pies;
- honey;
- marshmallows
You need to eat sweets little by little, 2-3 times a week. It is permissible to diversify the menu with light sour cream sauces, adding a small amount of dill and parsley.
Prohibited for patients with gastric adenoma:
- fatty meat, fish, lard;
- baking from yeast dough;
- legumes;
- marinades;
- cabbage;
- canned food;
- mayonnaise;
- fast food;
- pickles;
- semi-finished products;
- radish, radish;
- citrus;
- confectionery;
- hot, spicy sauces.
Tea and coffee are allowed to be drunk occasionally, weak, with the addition of milk. Carbonated and alcoholic drinks should be replaced with natural sweet juices (not packaged), fruit drinks, and rosehip decoction.
During the first time after surgery to cut off benign adenomatous polyps of the stomach, patients are prohibited from taking a hot bath, lifting weights, or playing sports. Any discomfort or pain in the area of the affected organ should be reported to your doctor immediately. Drug therapy is used only as recommended by a doctor. Self-administration of any medications can provoke recurrence of adenomatous neoplasms. If necessary, the patient will be prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of adenoma
There are two approaches to treating tubular adenoma:
- electrocoagulation;
- excision of the polyp;
Conservative treatment does not guarantee complete recovery of the patient. The risk of relapse and the appearance of a malignant neoplasm remains. In most cases, complete excision of the adenoma is performed. Resection or removal of a single polyp does not cause discomfort to the patient and reduces the risk of recurrent disease.
Before excision of the polyp, a histological examination is performed to help examine the removed sample. The specialist makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Thus, it is possible to detect the transition of a polyp to malignant growth. If several polyps are found, then resection is not performed. The large volume of the operation does not allow proceeding with excision. An equally effective procedure is carried out, namely electrocoagulation.
Nutrition for gastric adenoma
The diet for adenomatous polyps in the stomach is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, taking into account the background pathology (peptic ulcer, gastritis, etc.). To prevent the growth of adenomas and their recurrence after surgery, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- “Heavy”, fatty, spicy and any dishes that can injure the gastric mucosa or cause irritation are excluded from the menu. The same goes for drinks.
- The consumption of “junk” food, fast food, processed foods, etc. is minimized.
- You should not overeat, it is advisable to eat in small portions in compliance with the principles of rational nutrition.
Any error in diet can aggravate the course of the disease.
Stages of pathology development
The formation of an adenoma begins with a harmless polypoid formation. It can take 3–4 years to grow to a significant size, after which the cells may transform into cancer cells. In total, there are 3 stages of adenoma development:
- First. Due to the lobulated surface, the polypous formation is similar in appearance and size to a raspberry. There are no disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, since the diameter of the tumor is small.
- Second. The tumor grows to a diameter of 10 mm or more. At this stage, the patient experiences unpleasant symptoms in the form of problems with the digestive tract.
- Third. The diameter of the tumor exceeds 30 mm, the tumor begins to degenerate into cancer. Other organs may be affected: brain, lungs, liver. In severe cases, peritonitis develops.
Prevention of neoplasms
To prevent the development of intestinal diseases, it is important to eat properly. The diet should include fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables. Spicy and fatty foods are completely excluded, as they irritate the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. To prevent intestinal adenoma, you must adhere to several more rules:
- visit a doctor regularly;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- stop taking frequent painkillers;
- maintain normal weight;
- avoid hypothermia.