- Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: description of procedures, main differences
- Indications for sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Preparing for research
- Contraindications to sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: painful or not
- Other bowel examination techniques
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy are among the instrumental studies that allow you to examine and study the condition of the colon. Endoscopic diagnostics of the intestine can be performed as a separate manipulation or used as part of a comprehensive examination of the patient. How are sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy performed? Sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy - which is better? We'll talk about this in this article.
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: description of procedures, main differences
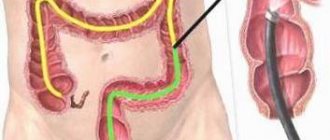
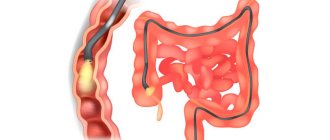
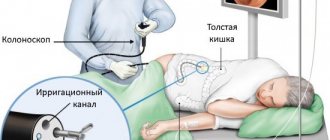
Sigmoidoscopy is a research method with which it is possible to examine the distal segment of the colon at a distance of 30 centimeters from the anus. This method was discussed in his article by V.P. Zemlyanoy, T.N. Trofimova, S.L. Nepomnyashchaya, T.V. Dementieva. The essence of the manipulation: a sigmoidoscope is inserted into the patient's rectum through the anus, and the doctor examines its walls, studies the vascular pattern, the nature of folding, the color, shine and elasticity of the mucous membrane, and evaluates the presence of pathologies and the tone of the intestine.
Colonoscopy is a highly informative instrumental research technique that allows you to examine the entire large intestine and the final section of the small intestine. Today, colonoscopy is considered the “gold standard” for diagnosing most intestinal diseases. The examination is performed using a colonoscope instrument. A flexible tube with a diameter of up to 8 mm is equipped with small video cameras, a powerful white light bulb, and a side channel through which additional manipulators are inserted if necessary. The cameras transmit an enlarged image to the monitor screen, which allows you to examine in detail the entire surface of the mucous membrane.
The main differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy:
- volumes of diagnostics (colonoscopy is considered to be a more informative method);
- possibilities of the procedure (during colonoscopy, a biopsy can be taken for further study of the material);
- carrying out manipulations with various instruments.
The main difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy is that colonoscopy can be used as a therapeutic procedure, since with the help of a colonoscope it is possible to excise various tumors, coagulate blood vessels and eliminate stenosis of the colon.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy (fibrocolonoscopy, colonofibroscopy) is a method of endoscopic diagnosis of diseases of the colon.
Colonoscopy is an important method for diagnosing colon diseases. It is performed using a special device - a colonoscope, of which there are currently quite a few different models.
In many countries, this study is performed by a coloproctologist; in Russia, it is performed by an endoscopist, which makes the use of colonoscopy even more informative. Colonoscopy, which has devices for photographing, performing biopsies and removing various pathological neoplasms, is a method for clarifying the diagnosis of diseases of the entire colon - from the cecum to the rectum. Every coloproctological patient should undergo a colonoscopy for rectal polyps and, even more so, for cancer of the distal colon detected during sigmoidoscopy. In these cases, it is necessary to examine the entire colon so as not to miss synchronous tumor or inflammatory changes located above the level reached by a rigid rectoscope or fibrosigmoidoscope. It should be borne in mind that irrigation and colonoscopy do not compete, but complement each other. Colonoscopy is indispensable for follow-up of patients after removal of polyps, after conservative treatment of ulcerative colitis, and especially for regular examinations of the colon in patients operated on for colon cancer.
Today, colonoscopy is the most informative method for early diagnosis of benign and malignant tumors of the colon, nonspecific ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, etc. and allows in 80-90% of cases to examine the entire colon. During a colonoscopy, the condition of the colon mucosa is visually assessed. During colonoscopy, it is also possible to perform various therapeutic procedures - removal of benign tumors, stopping bleeding, removal of foreign bodies, recanalization of intestinal stenosis, etc.
| Colon polyp | Colon diverticula | Colon cancer |
Indications for colonoscopy
The indication for a colonoscopy is suspicion of any disease of the colon.
Indications for colonoscopy are the widest. First of all, it should be performed if a tumor is suspected; in these cases, its resolution is significantly higher than irrigoscopy. Tumors and polyps of minimal size are detected. Colonoscopy is indicated for inflammatory diseases of the colon, especially ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is also used in emergency situations with intestinal bleeding, obstruction, and the presence of foreign bodies.
Sometimes an x-ray of the colon is performed before a colonoscopy.
Contraindications
The study is contraindicated in acute infectious diseases, peritonitis, as well as in the late stages of heart and pulmonary failure, severe disorders of the blood coagulation system. Colonoscopy should not be performed in patients with severe forms of ulcerative and ischemic colitis.
Technique
Colonoscopy is usually performed without anesthesia. For patients with severe pain in the anus, local anesthesia (dicaine ointment, xylocaingel) is indicated. In case of severe destructive processes in the small intestine or massive adhesions in the abdominal cavity, it is advisable to perform a colonoscopy under general anesthesia, which is mandatory for children under 10 years of age. The duration of the study strongly depends on the anatomical features of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract and his psycho-emotional status and under normal conditions does not exceed 30 minutes.
A colonoscopy is a fairly complex procedure, so try to help your doctor and nurse as much as possible by following their instructions. You will experience some discomfort during the test, but your doctor will do everything possible to reduce any discomfort. In many ways, following the instructions exactly makes it easier to endure the procedure.
You will have to remove all clothing from the waist down, including underwear. You will then be helped to lie on a couch or examination table on your left side, with your knees drawn up to your chest.
The colonoscope is inserted through the anus into the lumen of the rectum and gradually moves forward with a moderate supply of air to straighten the lumen of the intestine. During the examination, as directed by your doctor, you will be helped to turn onto your back or back onto your left side.
In some pathological conditions, to clarify the diagnosis, a microscopic examination of the changed areas of the mucous membrane is necessary, which the doctor takes with special forceps - a biopsy is performed, which extends the examination time by 1-2 minutes.
During a colonoscopy, you will have a feeling that your intestines are full of gases, causing you to have the urge to defecate. At the end of the study, the air introduced into the intestine is sucked out through the endoscope channel. Pain during this procedure is moderate because the intestine stretches when air is introduced into it. In addition, at the moment of overcoming the bends of the intestinal loops, intestinal displacement occurs. At this point, you will experience a short-term increase in pain.
How to behave after the study?
Immediately after the procedure, you can drink and eat. If the feeling of fullness of the abdomen with gases persists and the intestines are not emptied of remaining air naturally, you can take 8-10 tablets of finely crushed activated carbon, stirring it in 1/2 cup of warm boiled water. It is better to lie on your stomach for several hours after the examination.
Complications
Complications of colonoscopy, the most dangerous of which is bowel perforation, are very rare.
The success and informativeness of the study is determined mainly by the quality of preparation for the procedure, so pay the most serious attention to following the recommendations below. In order to examine the mucous membrane of the colon, it is necessary that there is no feces in its lumen.
Option #1
If you do not suffer from constipation, that is, the absence of independent stool for 3 days, then preparation for the study is as follows:
1. 2 days before the colonoscopy, you must switch to a special (slag-free) diet, excluding vegetables and fruits, potatoes, herbs, berries, mushrooms, legumes, and brown bread from your diet. Allowed: broth, semolina porridge, egg, boiled meat, boiled sausage, fish, cheese, butter, fermented milk products, except cottage cheese.
!!! On the eve of the colonoscopy and on the day of the examination, only liquid food is allowed - boiled water, broth, tea.
2. On the eve of the colonoscopy at 14-15 hours you need to take 30-40 grams of castor oil (2 tablespoons). For more comfortable use, the oil can be dissolved in half a glass of kefir.
Replacement of castor oil - aqueous solution of magnesium sulfate 30% - 150 ml at a time. Other laxatives (pursenide; bisacodyl 5 tablets - taken on the eve of a colonoscopy at 12.00 noon - stool usually appears after 6-8 hours) do not completely cleanse the colon, so they should be used in the preparation process if castor oil is intolerant. After independent bowel movements, you need to do 2 enemas of 1.5 liters of regular, room temperature water. Enemas are given at 20 and 21 hours.
3. On the morning of the colonoscopy (usually at 8 and 9 am), you need to do 1-2 more similar enemas, but always with “clean” water.
!!! There is no need to fast the night before and on the day of the test. You can drink broth, tea, mineral water, juice.
!!! During the days of preparation for a colonoscopy, you can take the medications you need, with the exception of iron supplements and activated carbon.
If you have a tendency to constipation, then to prepare for a colonoscopy you need to additionally follow several recommendations: 3-4 days before the study you need to switch to the special diet described above; At the same time, you need to take the laxatives you usually use every day. Further preparation does not differ from the above.
Option No. 2
Preparation for colonoscopy with the drug "Fortrans" (France)
The drug "Fortrans" is intended for preparing the gastrointestinal tract for diagnostic studies (including colonoscopy and irrigoscopy) as well as for surgical interventions on the intestines.
The required degree of cleansing of the large intestine is achieved:
- no cleansing enemas
- without additional laxative intake
- without long-term adherence to a slag-free diet
- without outside help
- no abdominal pain or excessive gas formation
The drug solution has a fruity taste. This type of preparation is ideal for patients with diseases of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
The action of the drug is based on the combination of a high molecular weight polymer with an isotonic solution of electrolytes, which prevent the absorption of water from the stomach and intestines. The solution promotes accelerated bowel emptying. The presence in the solution of electrolytes corresponding to the osmotic pressure of physiological solution replenishes the intestinal secretion of potassium, sodium, chlorine bicarbonate, and therefore there are no changes in the composition of body fluids.
There are two possible types of preparation with Fortrans:
A. One-stage preparation with Fortrans.
The day before (the day before the test), exclude vegetables, fruits, potatoes, berries, mushrooms, and greens from your diet.
On the day of colonoscopy, you can only drink sweet tea and boiled water.
On the day of colonoscopy, depending on your weight (up to 50 kg - 2 sachets, 50–80 kg - 3 sachets, over 80 kg - 4 sachets), the drug is diluted in water boiled at room temperature at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water, the required amount of solution Drink on the day of colonoscopy from 5-6 to 10 am in fractional portions (a glass every 15-20 minutes). The solution can be washed down with boiled water. The stool begins to pass 1.0-1.5 hours after starting to take the drug and stops 2-3 hours after taking the last dose of the drug.
On the day of the test, before the colonoscopy, you can drink a cup of sweet tea.
Colonoscopy may be performed no earlier than 4 hours after the last dose of the drug.
B. Two-stage preparation with the drug “Fortrans”.
Preparation is carried out both on the eve of the colonoscopy and on the day of the study.
On the eve of the colonoscopy, breakfast is allowed until 12 noon (semolina, yogurt, scrambled eggs, tea). After 12.00 clear broth, tea, and boiled water are allowed.
On the eve of the colonoscopy, depending on your weight (up to 50 kg - 1 sachet, 50-80 kg - 2 sachets, over 80 kg - 3 sachets), the drug is dissolved in water boiled at room temperature at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water. The required amount of solution is drunk from 17 to 20-21 hours in fractional portions (a glass every 15-20 minutes). The solution can be washed down with boiled water. The stool begins to pass 1.0-1.5 hours after starting to take the drug and stops 1-3 hours after taking the last dose of the drug.
On the day of colonoscopy, from 7 to 9 a.m., drink another 1 liter of solution at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water. After taking the last dose of the drug, stool stops after 1-2 hours. The solution can be washed down with boiled water. Colonoscopy may be performed no earlier than 4 hours after the last dose of the drug.
!!! During the days of preparation for a colonoscopy, you can take the medications you need, with the exception of iron supplements and activated carbon.
Emergency colonoscopy in patients with intestinal obstruction and bleeding can be performed without preparation. It is effective when using special endoscopes with a wide biopsy channel and active irrigation of the optics.
Option #3
Preparation for colonoscopy with Lavacol (Russia)
Description:
Powder of white or white with a yellowish or grayish tint. One packet of the drug is dissolved in 200 ml of water. The resulting solution is a colorless or slightly colored liquid, slight opalescence is allowed.
Indications for use:
Preparation for endoscopic or x-ray examination of the colon, as well as for surgical interventions that require the absence of contents in the intestine.
Contraindications:
Severe disturbances in the patient's general condition (including dehydration, heart failure), intestinal obstruction, toxic expansion of the colon, gastric stenosis, perforation of the stomach or intestines, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, impaired renal function.
Directions for use and dosage:
The contents of the package (14 g) are dissolved in 200 ml of water. Take 3 liters of solution (approximately 200 ml with an interval of 20 minutes) orally on an empty stomach 18-20 hours before examination or surgery. During and after the intake, only liquid food is consumed. Recommended hours for taking the drug are 14.00 - 19.00. After 10 pm, eating is not recommended.
Side effect:
In rare cases, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort are possible when taking the first doses of the drug.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies:
Without a doctor's prescription.
Release form:
Powder in bags of 14 g of combined film material. 15 bags, along with instructions for use, are placed in a cardboard pack.
Best before date:
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
- -Diagnostic methods in proctology
- -Diagnostic method anoscopy
- -Sigmoidoscopy (rectoscopy)
- -Digital examination of the rectum
- -Sphincterometry
- -Probe research
- -Test with dye
- -Biopsy
- -X-ray of the colon
- -Ultrasonography
Indications for sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
Main indications for sigmoidoscopy:
- chronic hemorrhoids;
- tumor pathological formations;
- chronic paraproctitis;
- prolonged constipation or diarrhea.
Manipulation is also performed before a full examination of the intestine.
Colonoscopy is prescribed for patients who have the following symptoms and conditions:
- blood in stool;
- systematic diarrhea;
- ulcerative colitis;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- abdominal pain;
- sudden weight loss;
- colon polyps.
This examination is mandatory for those patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer. According to the research conducted by Ya.S. Zimmerman, colorectal cancer currently ranks second (after lung cancer) among all cancer sites.
What does sigmoidoscopy diagnose?
Normally, the mucous membrane of the sigmoid colon is an intense pinkish color, with semicircular folds and pits. The mucous membrane of the rectum looks red, as it has a well-developed vascular network. The border between the rectum and the anal canal is purple. The lower part of the anal canal is gray-brown in color and extends into the skin of the perianal area, where the hair is located.
Sigmoidoscopy allows you to diagnose the following diseases:
- prostate adenoma in men, rectal endometriosis or retrocervical endometriosis in women;
- hemorrhoids, both external and internal;
- ulcerative colitis;
- chronic paraproctitis;
- rectal fissure;
- polyps of the rectum and sigmoid colon;
- enlarged anal papilla;
- malignant tumor of the intestine;
- anal fistulas;
- anal rectal abscess.
Preparing for research
Preparation for sigmoidoscopy is no different from preparation for colonoscopy. To examine the mucous membrane of the colon, before both procedures, you need to perform a special cleansing of the intestines and introduce temporary dietary restrictions: before starting the manipulation, you need to exclude vegetables, roughage and fruits from the diet for several days. Very often, proctologists advise sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy to be performed on an empty stomach.
Preparation for colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy includes:
- conducting cleansing enemas and microenemas (one enema is done on the evening before the diagnosis, the second on the day of the examination, several hours before the start of the manipulation);
- taking medications with a laxative effect.
Some patients who experience frequent constipation may combine laxative medications and cleansing enemas.
Vinikli nutrition - consult a doctor
To make an appointment for a consultation, call or fill out the return form:
(050) 301-99-26 (067) 446-11-79
Damn,
Your request has been successfully sent!
A call center specialist will contact you as soon as possible to clarify all the details.
Preparation before sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy should be especially thorough, as it affects the accuracy of the diagnostic results. The proportion of patients with poor bowel preparation is very high and, according to various sources, reaches 20-40%. This is stated in the monograph “Effective bowel preparation for colonoscopy,” published under the leadership of E.B. Avalueva, S.I. Sitkina, B.Kh. Samedova, E.I. Tkachenko and others.
Benefits of rectosigmoidoscopy
During the procedure, only a fragment of the colon is visualized: the rectum and part of the sigmoid. The length of the viewed area is up to 25 centimeters. Thanks to this, such an examination, unlike a colonoscopy, is carried out quickly, does not require anesthesia, and patients tolerate it well. The method does not involve radiation exposure, so it can be administered as often as necessary.
An endoscopic examination allows you to obtain complete information about the pathologies and condition of the mucosal tissues. At the same time, it allows you to combine diagnosis with treatment during one procedure.
Contraindications to sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
Contraindications to sigmoidoscopy:
- cardiovascular diseases;
- respiratory failure;
- vascular pathologies of the brain;
- severe inflammatory disorders: thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal vein, acute rectal fistula, anal fissure.
Colonoscopy is not prescribed for patients diagnosed with infectious diseases and blood diseases, heart or pulmonary failure, peritonitis, ulcerative or ischemic colitis.
Indications
Not only a proctologist, but also a coloproctologist, therapist, and gastroenterologist can prescribe an examination. Diagnostic rectosigmoidoscopy is indicated for patients who complain of:
- pain in the anus;
- anal fissures, hemorrhoids;
- sensation of a foreign body in the anal area;
- blood, purulent or mucus impurities in the stool;
- change in bowel movements – ribbon-like feces;
- prolonged constipation, which is sometimes replaced by loose stools.
Based on the results of the study, the doctor excludes the presence of neoplasms, foreign bodies or inflammation in the intestine and makes a diagnosis.
Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy: painful or not
All patients, without exception, are interested in the question: is it painful to do sigmoidoscopy? The correct preparatory stage before the study - diet, cleansing the colon with enemas and medications - allows you to avoid painful sensations during the procedure. The difference between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy at this stage is that in the first case, the examination is performed without anesthesia, since the instrument is inserted to a shallow depth, its duration is 10-15 minutes. As evidenced by numerous reviews of sigmoidoscopy, the likelihood of complications during this procedure is minimal.
Colonoscopy is a painful procedure, especially if there are cracks and damage in the anus, so special ointments and gels are used to relieve discomfort for local anesthesia. If there are certain indications, colonoscopy can be performed under general anesthesia or sedation. Discomfort during such an examination is caused by expansion of the intestinal walls to improve visualization. Pain may also appear as a consequence of inflammation. As a result, the procedure carries a risk of perforation or bleeding. These risks are eliminated by a comprehensive examination of the body before diagnosis and study of concomitant pathologies.
2.How is sigmoidoscopy performed?
During the rectoscopy, you will lie on your side on a special table. The doctor will first examine your anus manually. After this, he will insert a lubricated rectoscope into the anus. From time to time, your intestines will be inflated through the proctoscope. Special instruments can be inserted through the rectoscope to perform micro-operations or collect material.
The whole procedure takes from 5 to 15 minutes. Sometimes it takes a little longer when you need to collect material for analysis or remove polyps.
Visit our Proctology page
Details
Sigmoidoscopy is performed by a proctologist and takes 15-20 minutes. Examination with a sigmoidoscope is usually painless and is therefore performed without anesthesia. The patient is examined on the left side, if he is a man, and the prostate is examined at the same time. Before inserting the device into the anus, the rectum is palpated using the finger method.
The tube of the device is slowly inserted into the anal canal and carefully passed into the depths of the intestine 30-60 cm. If polyps are detected in this area during sigmoidoscopy, a biopsy of the tumors is immediately performed. During the examination, the doctor examines the mucous membranes of the intestines.
Among the unpleasant aspects of sigmoidoscopy is minor discomfort associated with the advancement of the endoscope tube during the examination. Sometimes some bleeding may occur after the examination.
Colonoscopy is prescribed when it is necessary to study the entire large intestine, which has a length of 120-150 cm. Such capabilities are available in a colonoscope - a special device that is similar in principle to a sigmoidoscope, but has a longer fiber optic cable.
Advancement of the endoscope during sigmoidoscopy is accompanied by the supply of air into the lumen of the intestine, which by the time of the examination should be completely free of feces. This explains the difference in preparation: cleansing before colonoscopy should be more thorough. The duration of the procedure is often determined by anatomical features, the presence of physiological bends and adhesions. In some cases, colonoscopy is performed under general anesthesia.
This procedure will allow the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment as soon as possible!
After the examination
The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization of the patient. When the doctor finishes the examination, the patient can rest for a few minutes on the couch and go home.
Since air is pumped into the intestines during the procedure, free passage of gases will occur over the next 24 hours. This should not be a cause for concern.
Bowel cleansing and insertion of a sigmoidoscope may cause irritation of the mucous membrane. Therefore, after the examination, doctors recommend following a gentle diet for 5-7 days. During this period, you should saturate your diet with dietary meat, dairy products, and eggs.
What is included in the equipment kit for rectoscopy?
A standard classic set of equipment for rectoscopy includes:
- set of tubes
- light guide
- illuminator
- pen
- blower bulb
- protective cover
- magnifying glass (optional)
- protective cover with tool channel (optional)
Read more about the main elements of the kit (the first 4 points of the list) below, but here I would like to immediately give a couple of comments about the “little things” (the last 4 points) so as not to return to them again.
A protective cover is a simple thing that protects the doctor from the troubles associated with poor preparation. The lid does not come into contact with the patient, so the need to treat it arises only in cases where it becomes dirty with intestinal contents. Accordingly, for one set of equipment for sigmoidoscopy it is enough to have two covers (the second is a spare one while the main one is being processed). You only need to remember that each manufacturer makes them for their own tubes (in the photo on the left, for example, there are two caps from two different manufacturers); as a rule, they do not fit third-party rectoscopes. Therefore, if there is a need to purchase several tubes, you definitely need to purchase them from the same manufacturer.
A blower bulb is also a very simple device necessary for inflating the intestine with air during rectoscopy, and any bulb fits kits from any manufacturer, both domestic and foreign. This is relevant when purchasing foreign sets, since pears from foreign manufacturers in our country cost surprising money for me, for example. Accordingly, you can save a lot by purchasing a domestic analogue.
A magnifying glass is the same protective cover, in which magnifying optics are used instead of ordinary glass, or an attachment with a magnifying glass on a regular cover. To be honest, in all 15 years of work I have never had a need to use it, moreover, I don’t really imagine in what cases it is impossible to do without it. If you want to save a little (this is only relevant when purchasing foreign kits, where such “little things” are not cheap), you definitely don’t have to order it.
The same can be said about the protective cover with a channel for tools - I have never used it in my life. It is assumed (understandably) that it is required when performing manipulations during rectoscopy. When you need to take a biopsy or remove a polyp, the standard lid is replaced with this device and manipulation is performed. But there is no objective need for this. The doctor understands whether the patient is well prepared before deciding to carry out additional manipulations, and with good preparation, the manipulation can be carried out by simply removing the protective cover (on an open rectoscope).
Additional tools necessary for carrying out therapeutic and diagnostic procedures during sigmoidoscopy:
- cotton holder
- biopsy forceps
- loop for electroexcision of rectal polyps
These tools will also be discussed below, but here I would like to talk only about the cotton holder (photo on the right). It is included in the recommended kits for rectoscopy, which are obsessively offered by most manufacturers (along with the same magnifying glass, for example). At the same time, I, for example, have never used it even once in my life. One tool is enough - biopsy forceps, with which you can do everything that a cotton holder is “needed” for.
Main differences between colonoscopy and rectoscopy
The main difference between rectosigmocolonoscopy and colonoscopy is the depth of examination.
A comparison of research methods is reflected in the table.
| Feature name | Colonoscopy | Sigmoidoscopy |
| Main areas of research | Whole large intestine | Rectum and terminal part of the sigmoid colon |
| Depth of examination | up to 150 cm | up to 35 cm |
| Devices used | Flexible fiberoptic probe equipped with an illuminated camera and forceps for collecting material (colonoscope) | Rigid hollow metal instrument, with a lighting device and an air supply system (rectoscope, sigmoidoscope) |
| Necessity of anesthesia | The procedure is painful and requires anesthesia. | Typically, no anesthesia is required. |
| Type of suspected pathologies | Probable location of the disease in the colon | Suspicion of lower intestinal disease |
| Time of the study | 15-30 minutes | 5-15 minutes |
Rectosigmoscopy in St. Petersburg
If you need to undergo an endoscopic examination of the lower intestinal fragment in St. Petersburg, contact the multidisciplinary one.
Our medical institution employs endoscopists with experience ranging from 6 to 22 years. Our specialists regularly improve their skills and participate in Russian and international conferences. Many years of experience allows our doctors to perform diagnostic and therapeutic rectosigmoidoscopy as efficiently and comfortably as possible for patients.
SM-Clinic is equipped with modern European endoscopes. Advanced equipment allows you to perform manipulations with minimal discomfort and obtain the necessary information for diagnosis and further treatment.
To make an appointment for an examination, a consultation with a doctor, or to find out the cost of services, please call. You can also fill out the feedback form on our website, and our administrators will contact you to clarify the details.