To study the gastrointestinal system, a wide range of different diagnostic techniques are used today. Therefore, if there is a need for an examination of the intestines, patients are concerned with the question of which diagnostic method is more informative, what is better - irrigoscopy or colonoscopy?
Despite the fact that both diagnostic methods are aimed at examining the large intestine and identifying pathological changes and inflammatory processes in it, they are fundamentally different from each other:
- Colonoscopy is performed using special endoscopic equipment - a colonoscope, equipped with powerful optics that provides the clearest picture possible when examining tissues and parts of the intestine.
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray examination method using a contrast agent that fills the large intestine immediately before the examination.
It is impossible to clearly determine which procedure is better. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. The doctor chooses the research method based on the purpose of its conduct, the stage of the disease, the presence of indications and other factors. Both methods have significant differences, but do not exclude them in any way; on the contrary, they complement each other.
What is this?
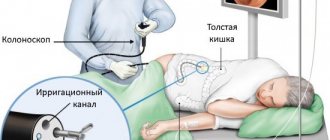
Irrigoscopy is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that can be used to examine the large intestine. It involves the use of a contrast agent and x-rays, which makes it possible to assess in real time the condition of the intestinal wall, its properties, relief, the nature of the warehouses, as well as determine the presence of foreign bodies or neoplasms. This manipulation is painless and is not accompanied by the risk of injury, and the radiation dose that the patient receives is less than during a CT scan.
Advantages and disadvantages of irrigoscopy
Irrigoscopy allows you to quickly and accurately diagnose the large intestine, including those sections into which endoscopic equipment cannot penetrate. Thanks to the contrast agent, which is evenly distributed throughout all parts of the intestine, the doctor receives a clear image in which large tumor formations and the anatomy of the intestine are clearly visible.
However, detecting an inflammatory process, a small polyp or a tumor at an early stage using irrigoscopy is difficult and often impossible.
Technique
The duration of the examination is 30-40 minutes
. Before it starts, an x-ray is taken of the organs in a supine position, after which:
- The patient lies on his side, raises his legs to his stomach and puts his arms behind his back.
- The X-ray contrast agent is barium sulfate: which is first diluted with water and heated.
- The endoscopist inserts it into the rectum through a tube (in rare cases, the contrast is given orally). For barium to spread throughout all intestinal sections, you must wait about 2 hours. For uniform distribution, the patient will need to remain in a motionless lying position.
- Air is pumped into the intestines, straightening the folds, and several photographs are taken.
- Air is removed through the equipped valve, and the endoscope is removed.
Using double contrast, it is possible to diagnose colon cancer with high accuracy.
Features of colonoscopy
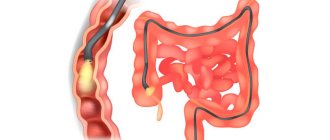
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination of the intestines using a probe, a method that guarantees the accuracy of information about the internal state of the rectum and colon. Despite the advantages, the procedure is dangerous; you should carefully choose a clinic and doctor.
Colonoscopy procedure
Indications and contraindications
Colonoscopy allows you to assess the general condition of the intestines and reveals a number of indications:
- inflammatory processes;
- the presence of polyps, neoplasms;
- violation of the integrity of the intestine (ulcer, erosion);
- bleeding and other discharge;
- disruption of the defecation process;
- decreased hemoglobin level;
- suspicion of cancer caused by the results of a blood test;
- monitoring changes in condition during treatment;
- prevention of cancer when a tumor has been detected and treated.
Colonoscopy is not recommended for severe diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory system, blood clotting disorders, severe forms of colitis, the presence of adhesions, and pregnancy. The possibility of carrying out the procedure is determined by the doctor.
Preparation period
You should start preparing in advance. For two or three days they adhere to a diet without fruits, vegetables, nuts, rye bread, and dairy products. Avoid carbonated drinks and coffee. The day before the examination, in the afternoon, do not eat heavy meals, only liquid soups. Eating is prohibited on the day of the colonoscopy. The intestines are removed from feces with an enema or special preparations, starting preparations the evening before the procedure.
Progress of the examination
The patient lies on his side, pressing his knees to his torso. The colonoscope is inserted through the anus, carefully moving along its length. Air is pumped into the intestine, straightening the folds. The image is transmitted to the computer from the camera at the end of the probe. The examination procedure takes up to half an hour; if surgical procedures are necessary, more time is required.
Colonoscopy is an invasive technique and the examination may be accompanied by pain. Sometimes pain relief is required. Local anesthesia may be used to make insertion of the colonoscope comfortable. If the intestine is damaged, the entire procedure may cause pain. In this case, the doctor will offer sedation or perform an examination under anesthesia. This procedure guarantees no pain. It costs more, but after waking up the patient will not remember the examination.
Before using anesthesia, make sure you are not allergic. It is necessary to notify your doctor about diabetes mellitus and the use of medications. Talk to your doctor before the procedure; the clinic may require HIV and hepatitis test results.
If examination of the colon is not required, rectoscopy is performed - diagnostics of the rectum. It is performed using a short endoscope, which is different from a colonoscopy. There is another type of examination of the rectum - sigmoidoscopy, which allows you to visually assess the condition of the area using an eyepiece.
Complications
Patients are often concerned about side effects from the procedure, but with proper preparation, good equipment, and the guidance of an experienced endoscopist, the risk is minimal. After a colonoscopy, the stomach is often swollen and heaviness is felt - activated charcoal tablets will help relieve this. After polyps are removed or tissue is collected, there may be a slight discharge in the stool. When the discharge is profuse, accompanied by nausea and pain, consult a doctor.
Differences from colonoscopy
Irrigoscopy or colonoscopy - which is better for the intestines? Before answering this question, it is necessary to highlight their main distinguishing features. This:
- Execution method
. Colonoscopy does not require the use of contrast or x-rays. Unlike competitive medical manipulation, it only uses a flexible probe with a camera. - Purpose
. Irrigoscopic examination is used exclusively for diagnostic purposes (except for intussusception in children), and during colonoscopy, polyps can be removed, bleeding can be stopped, or a biopsy can be taken.
Advantages and disadvantages of colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is the most informative method of examining the large intestine, allowing:
- identify even the most minor changes in tissues;
- detect malformations, tumors, fistulas and other pathological formations on the walls of the intestine;
- consider the condition of the peri-intestinal lymph nodes, identify changes in them, analyze the position of the intestine;
- carry out the necessary medical procedures (eliminate bleeding, remove polyps, etc.);
- take tissue for biopsy from a suspicious area.
Despite all the advantages of colonoscopy, there are a number of contraindications to its implementation - internal bleeding, Crohn's disease in the acute stage, obstruction and others.
What to expect after the procedure? Recovery
A doctor evaluates the results of a colonoscopy
You will be given time to lie down and rest until the effects of the sedative medications wear off. You can then go home, but you will need to ask someone to drive you as you may feel drowsy after taking the medicine. Also ask friends or family to stay with you for the first twelve hours after the procedure.
After the diagnosis, before you leave the hospital for home, the doctor may discuss the results of the examination and tests with you or schedule you another day for consultation. If biomaterial was collected or polyps were removed, the results will be sent to your doctor who gave the referral for the procedure.
Patient preparation
Before the patient is examined using an irrigoscopic device, he needs to prepare a little for this procedure. To do this, he must be on a special diet for about three days before the examination. This diet provides for the complete exclusion from the human diet of rye bread, potato and spicy dishes, the consumption of apples and mushrooms, legumes, chocolate products, and cabbage. During the diet, the patient is prohibited from consuming all types of gas-forming drinks.
The diet should not contain fresh herbs, raw vegetable and fruit dishes, as well as berries. The patient is recommended to eat more cereals during the diet, especially semolina, fermented milk products, soups, boiled meat or fish and eggs. Drink more tea, mineral water or juices.
Preparation for the procedure
Colonoscopy requires proper preparation
The diagnosis is carried out in a hospital outpatient department, lasts no more than an hour and is usually a one-day intervention. This means you will be tested and go home the same day.
During your consultation, your doctor will definitely tell you how to prepare for the procedure. It is very important that the bowel is completely empty during the diagnosis so that the doctor can see everything clearly.
To do this, the hospital will give you a strong laxative. It usually needs to be taken two days before the examination, but this issue should be clarified directly with the doctor or his nurse.
Because laxatives cause diarrhea, you should stay close to a restroom all day and drink plenty of clean fluids to stay hydrated. These types of liquids include water, lemonade, tea and coffee (without milk). You may experience some minor pain, but most of the time you won't. You may also be asked to:
- stop taking medications containing iron, as they can cause constipation, and during examination the intestines will appear dark, which will complicate the procedure;
- change your diet two days before the test - this condition depends on how much fiber you eat.
If you take medication for high blood pressure, for example, you can take it unless your doctor tells you not to. You may also be asked to stop taking medications that may cause constipation. In case you are taking blood thinning medications such as Warfarin, Aspirin or Clopidogrel etc., be sure to inform your doctor during your consultation so that you can be given instructions on how to take these tablets in preparation for the procedure.
If you have diabetes and are injecting insulin or taking medication for treatment, contact your doctor and tell them so they can put you at the front of the queue for the procedure. You will be told in detail when to give injections and at what time to take medications, as well as what you can eat before the examination.
During the consultation, the doctor will answer all your questions, discuss with you how the diagnosis is carried out, how to prepare for it, what to expect after it, tell you about all the painful sensations that you may experience, all the risks, alternatives, and about the pros and cons of the procedure.
What a virtual colonoscopy can show
Virtual colonoscopy is the same as computed tomography, but with a certain method of performing it, when the computer recreates an image of the colon in the form of a three-dimensional picture, similar to the image obtained with a colonoscope inserted inside. This procedure is non-invasive and is well tolerated by patients, who are more willing to undergo it than a classic colonoscopy.
Virtual colonoscopy allows a specialist to see on a computer monitor intestinal neoplasms with a diameter of more than 1 mm, erosions, inflammation and other changes, but with this method it is impossible to assess the color of the mucous membrane or take biopsy material. Therefore, virtual colonoscopy is indicated for patients with an already established diagnosis to determine the dynamics or rehabilitation control after surgery.
Factors determining choice
A careful study of the features of colonoscopy and irrigoscopy, existing diseases and consultation with a doctor will help you choose the optimal diagnostic method for a particular person and provide the necessary treatment.
Additional information on the topic of the article can be obtained from the video:
About risks, side effects and complications
As with any medical procedure, there are risks associated with a colonoscopy. For example, the intestines may not be properly cleaned, and the doctor will not be able to complete the examination. In this case, you will be asked to undergo a re-examination another time or choose a different diagnostic method. Intestinal rupture may also occur. It can be triggered by minor damage to the wall or insufflation of air.
If the gap is small and detected quickly, treatment will be based on fasting days and antibiotics, but if the gap is large, surgery may be required. In addition, bleeding may occur. This problem occurs in one in a thousand people undergoing the procedure. If you have had polyps removed, there is a 30-50% chance that bleeding may occur from the second to the seventh day after the examination. Most often, it goes away without your help.
Colonoscopy as a method of intestinal examination
Postpolypectomy syndrome also occurs. This is a syndrome in which, twelve hours after the procedure or later, the patient experiences stomach pain, high fever, and an increase in the number of white blood cells. The risk of such a problem occurring is extremely low.
To make the patient feel more comfortable during the procedure, he is administered sedative medications that cause the so-called twilight state.
Therefore, there is a small risk of respiratory and heart problems, as well as a reaction to the injection, nausea, vomiting and low blood pressure. It is very rare that an infection occurs during the procedure. This happens if the endoscope is not cleaned after a previous patient or is poorly sterilized.
You will be monitored by medical staff during and after the procedure, so you will get help right away if anything goes wrong.
Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy: what to choose
Irrigoscopy and colonoscopy have similar indications and contraindications, but the differences are obvious, for example, in the difference in equipment. The advantage of colonoscopy over non-invasive methods is that during the procedure it is possible to obtain data and remove tumors, polyps, take tissue for biopsy, and cauterize bleeding. A 100% accuracy level makes colonoscopy more informative and effective. Unlike irrigoscopy, colonoscopy provides information from the inside.
The main disadvantage of colonoscopy is the risk of damage to the intestinal walls by the probe and intestinal perforation. The contrast agent during irrigoscopy also causes a side effect. However, the doctor must compare the effectiveness; in each case, an individual type of examination is preferable.
Types of irrigoscopy
In proctology, two types of irrigoscopy are used:
- irrigoscopy with a simple contrast method, only a barium mixture is used - the procedure is indicated for elderly patients and weakened patients in the postoperative period, to determine intestinal motility,
- irrigoscopy with a double contrast method, using a barium suspension and air - used in most cases.
The first method, when tightly filling the intestine, allows you to obtain the clearest possible contours of the large intestine.
The second method allows you to identify tumors, polyps inside the intestinal lumen, detects ulcerative defects of the intestine, diverticula, and intestinal obstructions.
Often this study is complemented by other research methods (sigmoidoscopy, plain X-ray of the intestine).