A separate problem for medicine is the adhesive process in gynecology. Adhesions of the abdominal organs - in the uterus, on the ovaries and in the fallopian tubes - form and develop more often. In this case, the adhesive process can lead to serious problems with the reproductive system - pain, menstrual irregularities, miscarriage and infertility.
Our Avanta-Med clinic offers you high-quality diagnostics and non-invasive treatment of adhesions of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus and other organs in Novosibirsk. Our experienced gynecologists will conduct a high-quality examination and help you solve your health problems.
Reasons for the formation of adhesions
The main reason for the occurrence of adhesions is increased production of fibrin against the background of the inflammatory process. First, exudate appears in the pathological focus, the mucous membrane swells, and fluid accumulates in the fallopian tubes and other peritoneal organs. This leads to increased activity of fibroblasts, which begin to produce large amounts of fibrin. Its fibers polymerize under the influence of calcium ions, combine with the accumulated exudate and become insoluble. There is binding of the loose matrix and binding of all tissues that touch it.
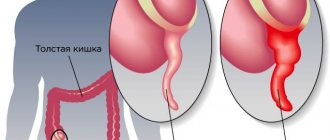
Prolonged inflammation leads to pathological changes. Epithelial tissue is replaced by nonfunctional scars. They can be localized in the abdominal cavity in the intestines, uterus, and ovaries. When adhesions appear in the tubes, their lumen closes, which leads to tubal infertility and requires contacting a gynecologist-surgeon who will remove scar tissue during laparoscopy.
Causes
Most often, synechiae occurs as a result of previous salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes). The timeliness and adequacy of the therapy reduces the risk of developing adhesions, but does not eliminate it 100%.
Much less often, the closure of the lumen of the fallopian tubes is caused by other reasons:
1. Fallopian tube endometriosis
: a hormonal pathology in which the endometrium of the uterus grows beyond the organ.
2. STD
(sexually transmitted diseases): genital herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, etc.
3. Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
: any inflammatory processes in the vagina, cervical canal, ovaries, uterus or lower intestines can provoke the growth of fallopian tube adhesions.
4. Surgical interventions
: complication after procedures such as abortion, cesarean section, uterine curettage, hysterosalpingography, etc.
Sometimes synechia develops against the background of long-term use of immunosuppressants or strong antibiotics, which cause activation of pathogenic microflora.
Complications
The danger is not the spikes themselves, but their consequences. Replacement of functional epithelium with scar tissue is the main cause of infertility.
Depending on the location and organs affected, complications may vary:
- Adhesions between adjacent organs in the pelvis lead to deformation of the organs and loss of their function. There will be pain, discomfort, and difficulty during sexual intercourse. Possible development of infertility, amenorrhea, complications of infectious diseases due to stagnation of secretions.
- Adhesions on the ovaries and fallopian tubes can lead to the development of infertility due to ovulation disorders and amenorrhea. Often, adhesions on the ovaries remain after cyst rupture in the absence of necessary therapy.
- Adhesions in the uterus will lead to disruption of the endometrium during menstruation, recurrent miscarriage and infertility.
The degree of complexity of the situation will depend on the location of the adhesion. For example, if scar tissue is located near the cervical canal, it will make it difficult for blood to flow during menstruation, which can lead to pain and inflammation of the uterus. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help avoid possible complications.
Diagnosis of adhesions in the uterus
With the help of modern diagnostic equipment, it is possible to discern even the most minimal changes and identify the development of synechiae at an early stage.
The following methods are used to diagnose adhesions:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis. To diagnose synechiae, it is best to carry out this study in the second phase of the cycle.
- Hysterosalpingography. X-ray diagnostic method using a contrast agent.
- Hysteroscopy. Used as a diagnostic operation.
- Pipelle biopsy. A vacuum sampling of the endometrium is performed for subsequent examination and identification of infectious causes of the disease.
- Lack of response to the use of hormonal drugs.
- No changes in hormonogram.
Ultrasound diagnosis of adhesions
Diagnosis by GHA method
Symptoms
Symptoms in the presence of adhesions in a woman are very different, however, several common signs can be identified:
- Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a constant, sometimes almost imperceptible, dull pain in the area of adhesion formation. It occurs due to tension and deformation of organs. In some cases, it can radiate to surrounding organs, the lower back and legs. The pain may intensify during sexual intercourse, physical exercise and prolonged exercise, hypothermia, and when the bladder is full.
- Impaired organ function - reduction or disappearance of menstruation, lack of ovulation, inability to become pregnant.
- In cases of formation of adhesions with intestinal loops - constipation, feeling of bloating, intestinal obstruction.
It is also worth noting that if a woman has adhesions, it is quite possible for her to experience increased pain during menstruation and ovulation. But it is worth considering that in half of the cases, adhesions do not cause any symptoms and are detected only during an ultrasound of the pelvic organs or a visual examination.
Diet for adhesive bowel disease
It is important to include foods enriched with calcium in the diet.
When treating intestinal adhesions, it is very important to follow certain nutritional recommendations so as not to worsen existing symptoms and help the body cope with the disease faster. It is necessary to eat food fractionally: in small quantities with a break of 3 to 5 hours. It is also important to drink enough liquid, preferably 2-2.5 liters of water per day.
Fatty, heavy foods and foods that cause gas should be avoided. It is not recommended to use:
- whole milk;
- hot sauces and seasonings;
- soy products;
- cabbage, radish, radish, corn;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- bananas;
- canned, pickled and smoked products.
It is recommended to include the following products in the diet:
- vegetable and low-fat broths made from dietary meat (rabbit, turkey, veal);
- fermented milk products enriched with calcium: kefir, cottage cheese;
- boiled or steamed fish, chicken and lean beef;
- dried fruits;
- natural unrefined oils.
It is advisable to eat foods that have been heat-treated (preferably steamed) to facilitate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. It is better not to eat hot and cold foods.
Diagnostics
To detect pelvic adhesions in women, use:
- Collection of general anamnesis and standard examination of the vagina;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
In rare cases, computed tomography may be used, which can allow visualization of adhesions in a place that is difficult to reach for other types of diagnostics. Doctors in our clinic conduct high-quality examinations. It is important for specialists to make the correct diagnosis and select the most effective treatment regimen.
How to reduce the risk of formation of adhesions on the fallopian tubes?
The main preventive measures are as follows:
- Prevention of inflammatory processes in the genital organs. To do this, it is recommended to avoid casual sex, use barrier methods of contraception (condom), monitor intimate hygiene and regularly visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations, because Many infections can remain asymptomatic for a long time.
- Reliable contraception to prevent unplanned pregnancy and associated abortions. Today, the most effective and recommended is hormonal protection. A gynecologist will help you choose the most optimal drug.
- If possible, conservative rather than surgical treatment of gynecological diseases. Any operation, even the most gentle laparoscopic one, leaves its mark. Taking into account the individual characteristics of collagen formation, there are categories of women who are distinguished by a pronounced adhesive process that developed after surgery.
For all questions of reproductive health, please contact the SM-Clinic clinic. Our staff includes qualified gynecologists, reproductive specialists and doctors of related specialties who work as a team to help you realize your dream of motherhood. The SM Clinic has introduced advanced diagnostic and treatment methods, incl. use of assisted reproduction methods.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of adhesions and elimination of the adhesive process is possible using conservative methods of therapy. These include:
- The use of physiotherapy is the impact of ultrasound, high-frequency current, magnetic waves on the commissure and the area where it is located. This allows you to slow down the process of proliferation of connective tissue.
- Drug treatment.
If adhesions are detected, surgical intervention by doctors is required. Surgical treatment will help solve this gynecological problem by eliminating already formed adhesions. The operation is a dissection of the commissure and is usually performed laparoscopically - through small punctures and under video control. If possible, the adhesive tissue is removed, and the attachment sites of the adhesions are cauterized using electrodes. Recovery after removal of scar tissue through laparoscopic access lasts several weeks. In the postoperative period, the woman is under the supervision of specialists.
How to treat adhesions?
Among the many causes of female infertility, ordinary adhesions occupy a special place. How to deal with them without harming your own health? An obstetrician-gynecologist consults.
“My lower abdomen often feels tight, and the doctor thinks that adhesions are to blame, although the ultrasound doesn’t show anything like that. How should I be treated?
Irina, Tula
Obstetrician-gynecologist consults
Adhesive disease, or, more simply, adhesions in the pelvis, occurs after frequent inflammation of the appendages, as well as due to untreated infections. Typically, women go to the doctor with complaints of constant aching or nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. Since these sensations are caused by anatomical disorders, the use of painkillers does not bring relief.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to see adhesions on ultrasound
. They can be suspected during a routine manual gynecological examination. When all possible causes of pain are rejected, a diagnosis of adhesive disease is made. There are several methods for treating adhesions.
Conservative treatment to prevent the occurrence of adhesions should be started in combination with anti-inflammatory treatment. It can also be effective at the initial stage of adhesive disease, when the pain is intermittent and not too intense. Aloe has a good healing effect. It is used as an injection of 2 milliliters every day. The course of treatment should consist of at least 10 injections. Along with aloe, you need to take folic acid, 1 capsule 3 times a day, and vitamin E, 2 capsules a day.
Now there are new effective drugs for the treatment of adhesive disease. Due to the content of special enzymes, they make adhesions more elastic and stretchable. This helps reduce pain. The course of treatment consists of 5-7 intravenous injections. But do not try to do this yourself - only a doctor can prescribe treatment.
A very effective method of treating chronic inflammation and the associated adhesive process is physiotherapy. It allows you to soften the adhesive structures, making them thinner and more extensible. This reduces, and in some cases completely stops, pain, improves the function of the intestines, which are often tightened by adhesions. The most effective physiotherapeutic methods include paraffin and ozokerite applications to the abdominal area. During the procedure, a paraffin or wax compress is applied to the lower abdomen, which warms up the adhesions, promoting their resorption. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. The course of treatment is 10 procedures. Courses can be repeated after 2-3 months.
Electrophoresis with zinc, magnesium and calcium has a good effect. In case of severe pain syndrome, novocaine is added to them. The procedures are alternated every day. If necessary, the course can be up to 20 sessions. A contraindication to any of the physiotherapeutic methods is active inflammation. You should not carry out the course during menstruation.
It must be remembered that physical therapy is not surgery.
, it cannot completely “dissolve” adhesions. Therefore, if symptoms remain after a full course, surgery to cut adhesions may be necessary.
The most unpleasant consequences of the adhesive process are obstruction of the pipes. You can find out whether your fallopian tubes are patent using hysterosalpingography. This is an X-ray examination of the uterus and tubes. In this case, a special substance is injected into the uterine cavity and how it is distributed in the tubes is observed. If they are impassable, the adhesions are separated using laparoscopy. If the tubes are in order, then physical therapy is prescribed to reduce pain and soften adhesions.
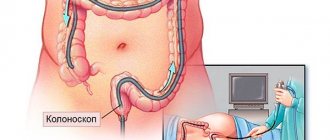
Laparoscopy
is a surgical intervention in which 3 small punctures are made in the abdominal wall, through which micro-instruments and an optical device are inserted into the abdominal cavity, to which a video camera is attached. The image is displayed on the screen, and with the help of manipulators, an operation is performed to separate the adhesions and restore the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Women with chronic inflammation of the appendages often suffer from so-called pelvic pain. For some, the adhesive process may be asymptomatic, but pregnancy does not occur. In this case, only diagnostic laparoscopy can help make the correct diagnosis and simultaneously dissect adhesions and check the patency of the fallopian tubes. If the end of the fallopian tube is “sealed” with adhesions, thanks to laparoscopic technology and instruments it is possible to perform a plastic surgery of the tube and restore its patency. The operation is performed within 30 - 40 minutes, the woman can be discharged after 1-2 days. After healing, there are practically no traces of the operation left.
You can make an appointment with a doctor about a week before the expected visit on any working day from 9:00 to 16:30. Registration is made by phone in Moscow or on the website, on the “Make an Appointment” page.