By the 36th week of pregnancy, the likelihood of labor beginning increases, so a woman is advised to prepare for the birth of her baby. At this time, you need to be especially careful about your mental and physical health.
Despite the fact that all the child’s organs and systems have already been formed, he still needs to gain weight, so his birth will be still premature. If your lower abdomen hurts severely at 36 weeks of pregnancy, you should consult a doctor to rule out the development of pathology.
What happens to the baby at 36 weeks of pregnancy?
At this time, the child practically does not let his finger out of his mouth, constantly sucking on it. In this way, he hones the sucking reflex and trains the muscles of his mouth, which in the future will allow him to take his mother’s breast without any problems. The baby's face is noticeably rounded, her cheeks become plumper.
The baby is formed and almost completely ready to be born. Now he weighs about 2.7 kg, and his height reaches 46 cm or more.
The bones of the fetus have become noticeably stronger, but the sutures of the skull do not heal, and the fontanelles, large cartilaginous areas, remain between them. This gives mobility for the easiest possible passage of the head through the birth canal. After the birth of a child, the fontanelles gradually ossify and overgrow.
At 36 weeks of pregnancy, the baby continues to move actively, although his movements are constrained, because there is very little space left in the uterus. At the same time, he had already taken his final position. Ideally, the child should be positioned head down. However, this does not always happen; sometimes the fetus may be in a breech or lateral presentation. It will no longer be possible to change its position, so doctors will consider the question of the method of delivery. There is no need to worry, because the child is in a breech or transverse position no more often than in 4% of cases. Moreover, with breech presentation, the possibility of natural childbirth remains.
The nervous, immune and endocrine systems continue to develop. The functioning of the heart and blood vessels is improved. The normal number of heart beats per minute should be 140. The baby’s heartbeat can be easily heard with a stethoscope.
Surfactant continues to accumulate in the lungs. Thanks to him, the baby will be able to breathe independently outside the mother's womb.
From this video you will learn how to prepare for the maternity hospital, what to take with you and what you need to consult with your doctor about:
33,34,35,36 weeks of pregnancy: what happens, development of pregnancy and fetus
- home
- Services and prices
- Services and prices
- About Us
- Doctors
- Schedule and appointments
- Reviews
- Doctor training
- Clinic addresses
- CIropedia
Week by week 33 - 36 weeks of pregnancy Elena Gevorkova Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
Week 33
BABY
At the 33rd week, the weight of the fetus is 1800-1900 g, and the body length is 43-44 cm. The amount of subcutaneous fat increases, due to which the folds and wrinkles on the baby’s body are smoothed out, and the skin turns pink. The vellus hairs covering the body of the fetus, called lanugo, become smaller, and the hair on the head darkens and thickens. The baby's skin is covered with a thin layer of cheese-like lubricant, the largest amount of which accumulates in the folds - axillary, cervical, inguinal - as well as on the back of the body and face. Lubricant is a viscous white mass; it is a secretion of the sebaceous glands mixed with skin flakes. Its function is to protect the baby’s skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
By this time, the fetal movements gradually change their usual character - they become more limited and less pronounced in amplitude due to insufficient space.
However, the strength of the movements increases, since by this time the muscular system of the fetus is already sufficiently strengthened. Sharp and strong fetal shocks can be sensitive to the internal organs of a pregnant woman. Depending on the position of the baby, the liver, stomach, bladder, ribs, etc. may “suffer.” By 33 weeks, fetal movements are already sufficiently coordinated. EXPECTANT MOTHER
The height of the uterine fundus from the level of the pubis at this stage is 34 cm. The volume of the abdomen is increased due to the weight of the child, placenta, and amniotic fluid. An increase in uterine pressure and strong fetal thrusts can cause some discomfort in the pregnant woman. Many movements previously available to the expectant mother, such as squats, become limited. Moderate physical activity - walking, fitness, etc. - requires frequent breaks.
A change in the center of gravity increases the load on the spine, which can manifest itself as pain in the lower back, sacrum, and pelvic region. The pressure of the uterus on the stomach can cause or worsen nausea, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness. An increase of almost 1 liter in the volume of circulating blood in a pregnant woman’s body increases the load on the kidneys, and the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder. All this can manifest itself as increased urination.
These ailments are usually associated with mechanical pressure of the uterus on surrounding organs; they are not symptoms of the disease and are temporary. And to relieve nausea, heartburn and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, frequent small meals are recommended.
Week 34
BABY
By this time, the weight of the fetus is approximately 2100 g, and the height is 45 cm. The appearance of the baby at this stage is practically indistinguishable from the appearance of a newborn - the body is proportional, the face is without wrinkles and folds. From this period, the cheeks are very pronounced, since, developing the sucking reflex, the fetus often sucks the thumb. This leads to the fact that the baby’s facial muscles, in particular the cheek muscles, are strengthened. The overall muscle mass of the fetus increases, and the bones become denser.
The baby’s internal organs are functioning intensively. During the day, he swallows multiple portions of amniotic fluid. Passing through the gastrointestinal tract, amniotic fluid stimulates the work of the muscle wall. The dense part of the amniotic fluid, which is a suspension of skin flakes, lubricant, vellus hair, is processed by liver and pancreatic enzymes, and the liquid part is intensively excreted by the fetal kidneys.
About 500 ml of amniotic fluid is processed in this way per day.
The production of bile continues, which accumulates in the gallbladder and, as the stomach fills with a suspension of amniotic fluid, enters the lumen of the small intestine. The functional development of the liver and pancreas during the prenatal period does not play a significant role, since the fetus lacks digestion; processes of production of bile and enzymes: lipase, which breaks down fats; trypsin, which breaks down proteins; amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates, etc. - are of a preparatory nature. FUTURE MOTHER
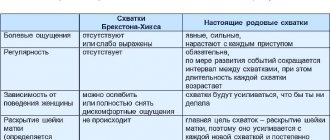
Most pregnant women begin to feel quite intensely false contractions at this stage. Strictly speaking, false or training contractions, also called Braxton-Hicks contractions, can appear after the 20th week of pregnancy: the longer the period, the more frequent and pronounced the contractions. They are episodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, lasting from a few seconds to 3-5 minutes. Braxton Hicks contractions are not pathological - they are a completely normal process in which the muscles of the uterus prepare for the difficult process of childbirth. This phenomenon is observed with varying degrees of intensity in almost all pregnant women.
Many first-time mothers are concerned about the difference between preparatory contractions and labor contractions.
Here are some differences:
- Contraction frequency. Training contractions do not become more frequent; the intervals between them may vary. Labor contractions are regular, the interval between them is reduced.
- Duration of contractions. Training contractions have different durations, from several seconds to minutes, their duration does not increase over time. Labor contractions tend to lengthen.
- Soreness. Preparatory contractions may not be accompanied by pain at all or may be quite noticeable, even to the point of feeling sharp pain. However, their intensity weakens over time and the pain goes away. Labor contractions are painful and constantly intensifying.
- Localization. Braxton-Hicks contractions can be felt in various places - in the lower part of the uterus, in the area of its fundus, along the side walls, and cover the entire abdomen. Labor contractions begin with a contraction of the lower abdomen, spreading to the front. Often during childbirth, pain in the lower back is felt, and the nature of the pain resembles menstrual pain.
- Connection with body position. Preparatory contractions may disappear after walking or, conversely, resting. Changing your body position can ease the tension in some muscles, which can also reduce the appearance of training contractions. Labor contractions may ease somewhat in a certain position - when bending forward, in a knee-elbow position, etc. - but their frequency and duration will still increase.
- Reaction to taking drugs. The use of antispasmodic drugs - NO-SHPA, BUSCOPANA, PAPAVERINE, etc., approved by the attending physician, can weaken or completely stop false contractions. The effect of antispasmodics on labor pains is minimal.
Any pain or discomfort should be reported to the gynecologist: this will help the expectant mother resolve doubts and cope with anxiety. A sense of security is the best companion of pregnancy.
Week 35
BABY
The body length of the fetus is 46-47 cm, weight - 2200-2300 g. These indicators can vary greatly in the last weeks of pregnancy.
The height and weight of the fetus largely depend on heredity and individual parameters. Starting from 35 weeks, the baby will gain 200-250 g weekly. The fetus occupies almost the entire uterine cavity, its back is rounded, its arms and legs are bent and brought towards the body. The layer of subcutaneous fat increases significantly, which significantly “rounds” the fetal body. Closing the eyelids and contracting the facial muscles changes the baby’s facial expression quite often. The skin of the body becomes pink, smooth, and the amount of cheese-like lubricant begins to decrease. Vellus hair covers certain small areas of the body - shoulders, back. Nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers. FUTURE MOTHER
The fundus of the uterus is 35 cm higher from the pubis, 15 cm from the navel. The uterus reaches such a size that it pushes aside the organs located below - the bladder, intestines, but also those located above the diaphragm, in particular the lungs. The growing uterus does not allow the lungs to expand, respiratory movements are limited, which is manifested by difficulty breathing. Almost all pregnant women, to one degree or another, experience a feeling of shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing, a desire to take a deep breath. As a rule, these sensations occur at 28 weeks and reach their peak at 35-36 weeks. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, the abdomen droops, which makes breathing much easier.
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is associated not only with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm, but also with the relaxing effect of hormones on the muscles of the bronchi and lungs. Most often it is provoked by physical activity - climbing stairs, long walks, etc. However, it is not uncommon for shortness of breath to occur at rest, especially when lying down. Both prolonged exposure to a horizontal position and excessive physical activity can contribute to increased shortness of breath. To alleviate her condition, the expectant mother needs to be rational about her daily routine - it is reasonable to alternate between rest and physical activity. It is important to monitor your posture, since slouching aggravates shortness of breath, reducing the already insufficient lung capacity. If shortness of breath is accompanied by blue lips or nails, sensations of pain behind the sternum, darkening before the eyes, nausea or vomiting, fainting, then you should urgently consult a doctor.
Week 36
BABY
The growth of the fetus by this time is approximately 47-48 cm, and the weight is about 2300-2500 g. The fetus enters a period of intensive preparation for childbirth. Each of the organs is already functionally mature enough to ensure the viability of the fetus. 36 weeks is the beginning of the preparatory journey, and the upcoming weeks of pregnancy are designed to finally shape the baby’s readiness for extrauterine life.
By 36 weeks, the fetus occupies its final position in the uterus. As a rule, this is a longitudinal position, occipital presentation - in this case, the fetus is positioned head down, facing the mother's back. This is the most comfortable position that ensures the greatest safety for the baby during childbirth. More rare is breech presentation, a condition in which the buttocks and legs of the fetus are located at the bottom of the uterus. This is a relative indication for operative delivery. The final decision on caesarean section or spontaneous childbirth is made by doctors in each case individually.
A change in the position of the fetus in the uterus is possible, but this does not happen often, since at this stage the fetus occupies almost all the free space in the uterus, which significantly limits its motor activity.
As a rule, if a change in the position of the fetus occurs, it is only from the pelvic to the head. The opposite cases - the transition of the baby from the head to the pelvic position - are practically impossible, since the fetal head is heavier than the buttocks and occupies a definitive longitudinal position, by analogy with a float in water, the heavy part of which always outweighs. FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the uterus is 36 cm, the volume of the abdomen is maximized, the bottom reaches the costal arches. At this stage, the pregnant woman’s body also begins its journey of preparation for the upcoming birth. Changes begin with hormonal changes: a woman’s level of special hormones – oxytocin and prostaglandins – increases slightly. These active substances play a vital role in the process of preparation for childbirth and directly during it. A slight increase in their level from 36-37 weeks of pregnancy leads to increased Braxton-Hicks contractions, increased frequency of urination and defecation, and the appearance of more abundant mucous discharge from the vagina.
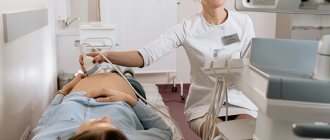
Is it necessary to do an ultrasound?
An ultrasound is usually not performed at 36 weeks of pregnancy. It is only necessary if the doctor needs to clarify any data. For example, to exclude the risk of the baby being entangled in the umbilical cord or to assess the degree of maturity and condition of the placenta.
When an ultrasound is nevertheless prescribed, the doctor necessarily measures the height and weight of the child, the volume of amniotic fluid, and assesses the readiness of the cervix for the upcoming birth.
If an ultrasound is not performed, then the woman will need to visit her gynecologist, donate blood and urine for a general analysis. At the appointment, the doctor will measure the abdominal circumference, the height of the uterine fundus, listen to the fetal heartbeat, weigh the woman and determine the level of blood pressure. These studies at 36 weeks of pregnancy are sufficient.
Possible problems
Breech presentation of the fetus at 36 weeks of gestation
Most often, the fetus takes its final position in the uterus by the 34th week of pregnancy. If we talk about the timing of the necessary measures for turning the fetus, then exercises can be done in the period from 29 to 34 weeks, and external turning in a hospital setting (the doctor acts on the fetus from the outside using his hands) - in 32-34 weeks. Even despite this period, the baby still has a chance to roll over if his size allows it. If this still does not happen, doctors will have to assess the degree of risks during childbirth naturally, and if necessary, a caesarean section will be prescribed.
Swelling at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Whether you had swelling before or not, by the end of pregnancy they will definitely appear. Therefore, their appearance and development must be clearly monitored, since this symptom may be a component of a phenomenon such as gestosis, or late toxicosis. To prevent swelling from increasing sharply, control the amount of fluid you drink during the day. A large amount of water in this case is not very good, but it is also not worth greatly reducing the volume of liquid consumed, so as not to cause dehydration. It is also recommended to reduce the amount of salt in the diet, because it contributes to fluid retention in the body.
Your legs are already under a lot of stress, and swelling will contribute to this even more. To ensure that your legs rest and the fluid stagnation in them does not increase, you need to find an opportunity to sit or lie down with your legs elevated during the day. To do this, you can place some kind of pillow under them or rest them on an overlying surface.
Nausea at 36 weeks of pregnancy
This condition can occur when a pregnant woman’s blood pressure increases. If this is not the first time you have felt sick, start monitoring changes in your blood pressure, and also contact your gynecologist. If swelling is added to the above symptoms, and protein is found in the urine, we can talk about the development of preeclampsia. This condition is a strict indication for hospitalization. In a hospital setting, the woman is provided with the necessary assistance, and if necessary, a caesarean section is performed.
Cold at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Due to a weakened immune system, a pregnant woman is more susceptible to colds, despite the fact that she tries with all her might to avoid them. If you suddenly feel weak, your temperature rises, your nose is stuffy, and your throat hurts, most likely you have a cold. Firstly, you should consult a doctor about treatment, because self-medication can lead to not very pleasant consequences. And secondly, you need to provide yourself with the opportunity to spend this time at home. It is believed that a cold goes away on its own within a week on average, but you can support your body by providing your body with a sufficient amount of warm tea or compote, which helps remove toxins. Also, symptomatic treatment of a runny nose and sore throat by washing and rinsing will speed up recovery. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, it can be “brought down” with a paracetamol tablet.
Diarrhea at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Diarrhea in the last stages of pregnancy can be caused by disturbances in the normal intestinal flora (dysbacteriosis), intestinal infections, exacerbations of gastrointestinal diseases, and even stress. It should be noted that this phenomenon in itself is not dangerous to the baby’s health. But if diarrhea continues long enough, it will lead to the development of dehydration, but this is dangerous for both the pregnant woman and her baby. That is why it is important to replenish fluid losses, and it is also necessary to adjust your diet. First, you need to avoid foods that irritate your intestines. These are spicy, smoked, salted and fried dishes. It is also worth reducing the fiber content in your diet for a while, because it also stimulates peristalsis. The food should be light, you can eat porridge, low-fat light soups, jelly. If your condition does not improve, consult your doctor.
What's happening to the stomach?
At this stage, the belly of most women reaches an impressive size. Many of them compare their belly with the bellies of other expectant mothers, and they may feel that it has not grown enough. Indeed, the abdomen may be small due to oligohydramnios or low fetal weight. However, if the doctor does not detect any pathologies, there is no need to worry. The belly may remain small due to the woman's body type.
Regardless of the size of the abdomen, by this time it most often begins to descend. The child presses his head against the pelvic floor, which may result in pain in the corresponding area. The drooping of the abdomen is a physiological process; it only indicates that childbirth is approaching. However, this does not mean that they have to start right now. After the belly has dropped, a woman can remain pregnant for another 1-2 weeks. At the same time, it will become easier for her to breathe, and digestive problems, including debilitating heartburn, will disappear.
The skin of the abdomen is now stretched, so it may itch. At the same time, stretch marks may appear. Getting rid of them in the future will be very problematic, so you need to take care of your skin in advance and regularly apply moisturizer to it.
Feel
The baby's movements are still very noticeable for the woman. Since the baby is already quite big, his stomach becomes cramped. But this does not mean that the child’s movements have become less intense. Sometimes they can even cause pain, especially when the baby kicks mom in the hypochondrium. A woman must be vigilant and monitor the baby’s movements. Normally, a child moves about 10 times a day.
Another leading feeling of a woman is the fear of the upcoming birth, this is especially true for those who give birth for the first time. The closer the date of the first meeting with the child, the more anxious your soul becomes. Therefore, by the 36th week of pregnancy, many women become more irritable, anxious and moody. Dealing with these feelings is difficult, but necessary. It makes no sense to dwell on your own fears, because it harms not only you, but also the child.
The last weeks of pregnancy can be regarded as the most difficult physiologically. It becomes difficult for the expectant mother to carry out her usual household chores, and sometimes even to walk. Therefore, you need to rest more, but you should not forget about physical activity.
It’s good if a woman manages to occupy herself with useful things. These include, for example, walking in the fresh air.
Thirty-sixth week of pregnancy
- If the child does not move for a sufficiently significant amount of time, this may be a negative signal, so you need to consult a doctor;
- If the child is too active in his movements, you need to try to change his position. If changing positions does not produce the desired results and you experience increased activity for several days, it is also recommended to consult a doctor.
How is mom feeling?
During this period of time, the stage of sleepless nights is formed.
In fact, the baby requires a greater amount of attention and is particularly active at night. Such activity provokes serious discomfort. When the child moves, pain occurs. My legs swell a lot and the constant discomfort in my back and lower back is driving me crazy. To eliminate negative manifestations, it is recommended to use prenatal gymnastics and light massage. To relieve tired feet, it is recommended to take not too hot foot baths.
If all the woman’s indicators are normal, then in this case there is no need to carry out additional research. For this period, planned studies can be prescribed, through which the position of the fetus and the condition of the mother’s birth canal are determined.
The last weeks of pregnancy always carry a certain risk of premature birth. If there is a serious drooping of the abdomen, then this is not a signal that the desired process will soon begin. It often happens that the child increases in size quite significantly, which provokes a drooping of the abdomen. You need to try to prepare everything in advance in order to quickly go to the hospital for childbirth. It is very important that during this period of time no stress or depressive conditions appear, significant physical activity should not be carried out, and nutrition must be strictly controlled. If serious fatigue occurs, you should immediately carry out the process of rest to eliminate the possibility of premature labor.
Edited: April 12, 2019
Author
Bulatova Lyubov Nikolaevna
About the author Sources Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, endocrinologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, specialist in the field of aesthetic gynecology
Outpatient care in the diagnosis and treatment of gynecological patients, including those with endocrine disorders; infertility; surgical treatment on an outpatient basis (polypectomy, RDV, biopsy, cryodestruction, radiosurgical treatment with the Surgitron device, mini-abortions); medical termination of pregnancy.
Conducting consultations on family planning with the selection of contraception; individual management of pregnancy. Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology; Fetal CTG. Aesthetic gynecology.
1. O. V. Berdnikova Pregnancy - week by week: A modern guide for expectant mothers
2. Olga Belokon “I’m pregnant, what should I do?”
3. Evgeny Komarovsky “365 tips for the first year of your child’s life”
4. Esther Gili “40 weeks to stop fearing motherhood and start looking forward to it”
5. William and Martha Sears "Waiting for Baby"
6. Fedor Katasonov “Pediatrics. A non-anxious approach to the child"
Reviewer
Ishchenko Irina Georgievna
About the reviewer Obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor, specialist in the field of aesthetic gynecology, candidate of medical sciences.
You know very well that a disease is easier to prevent than to cure. This statement becomes even more relevant in today's economic crisis!
I hope that in our clinic you will find your doctor - highly professional, sensitive and attentive to all your women's problems. Be healthy!
Weight
A woman's weight is constantly increasing. By this time, the increase may be 13 kg, which is the norm. Deviations up or down with a difference of 2 kg are not critical.
You should not worry about the weight you gain, as most of it will go away immediately after giving birth. After all, it consists mainly not of adipose tissue, but of the weight of the child, amniotic fluid, placenta, etc. Only the blood in the body of the expectant mother began to circulate per liter more.
It is also worth preparing for the fact that the weight will still increase, because a normal pregnancy can last up to 41-42 weeks. Therefore, it is important to continue to monitor your diet.
Pain at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Most women experience painful sensations of various localizations precisely in the last stages of pregnancy.
To understand when pain is a physiological phenomenon, and when medical attention is required, you need to try to determine its cause, among these:
- Shift in center of gravity due to enlarged abdomen. For this reason, back and lower back pain may occur. As a rule, they have a pulling nature and disappear completely after resting in a comfortable position.
- Preparing the body for childbirth and softening joints and ligaments. For this reason, pain may occur in the hip joints, in the pubic area, and in the lower abdomen. These pains are usually not too intense and only bother you intermittently.
- Pain in the anus is most often felt due to exacerbation of hemorrhoids. You should not endure such pain; you should definitely tell your doctor about your problem.
- Due to the increased tone of the uterus, nagging pain in the lower back may occur, and the stomach becomes as if it were made of stone. This can be dangerous, so be sure to consult a doctor.
- Sometimes women experience pain in their legs. They may be caused by swelling. A slight swelling that appears in the morning is normal. However, sometimes swelling increases sharply and does not go away for a long time. This may be a symptom of gestosis, a dangerous complication of pregnancy. In addition to edema, gestosis is characterized by such signs as the detection of protein in the urine and increased blood pressure. The doctor should immediately be aware of such disorders in the woman’s body.
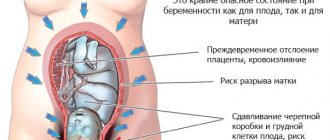
Acute abdomen during pregnancy
A woman at 36 weeks of pregnancy needs urgent medical attention if signs of an “acute abdomen” appear. With this condition, there is a delay in bowel movement from feces and gases, acute or cutting pain in the abdomen and involuntary tension of the peritoneum. Such signs indicate the development of surgical pathology.
During pregnancy, it is very difficult to recognize surgical pathology for several reasons:
- the location of the organs is changed;
- palpation is difficult or impossible;
- symptoms erased;
- decreased reactivity of the body;
- discomfort during pregnancy is similar to signs of diseases of the digestive system (nausea, bowel dysfunction, abdominal and back pain);
- difficulties in differentiating surgical from obstetric pathology.
- hormonal levels are changed.
That is why an examination of a pregnant woman should be carried out by a surgeon and an obstetrician-gynecologist, and the number of palpations of the abdomen should be as small as possible so as not to provoke increased uterine tone. The main complaint with an “acute abdomen” is pain.
When carrying a child, in addition to cesarean section, operations are performed in 0.2–2.2% of pregnancies
Based on their location, it can be assumed where the pathological process develops. Pain in the entire abdomen occurs with peritonitis due to bleeding, exudate, or the presence of intestinal contents in the abdominal cavity. Pain in the center at the very bottom of the abdomen is often caused by the tone of the uterus, and in the lower side by torsion or disruption of the integrity of the neoplasm.
Pain in the middle of the abdomen indicates intestinal pathology, and in the upper part it occurs when the functioning of the spleen, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and duodenum is disrupted. Most often diagnosed (in descending order) are acute appendicitis, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction, and pancreatitis.
Inflammation of the appendix
Appendicitis, in which pus has already begun to seep into the abdominal cavity, is diagnosed 2-3 times more often in pregnant women than in non-pregnant women. This is associated with a late diagnosis, since the woman does not consult a doctor immediately as soon as abdominal pain, nausea and lack of appetite appear, as she considers these to be signs of pregnancy.
Since the uterus forces the appendix to rise upward, moderate leukocytosis is normal for pregnancy, and palpating and listening to the abdominal cavity is difficult, this leads to a delay in diagnosis and appendectomy.
The greater the gestation, the less signs of peritoneal irritation appear. At the initial stage of the disease, temperature and pulse remain normal.
Nausea with appendicitis occurs in 70% of pregnant women, and vomiting in only half
The diagnosis can be made using diagnostic laparoscopy.
Gallbladder diseases
When carrying a child, the lithogenic properties of the secretion increase, in addition, bile stagnates due to impaired contraction of the bile ducts, and when the volume of the organ increases by 2 times, its ability to discharge bile decreases. All this leads to the formation of stones and inflammation.
With pathology, the pregnant woman is worried about nausea, vomiting, a slight increase in body temperature, pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, and lack of appetite. The attacks usually occur after eating and can last several minutes or hours. The gallbladder cannot be felt through the uterus. The diagnosis is made using ultrasound and laboratory testing.
Pancreatitis
The disease occurs as a result of autolysis of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is often a complication of cholecystitis. It can also be caused by an abnormality in the structure of the gland, infection, abdominal trauma, drug therapy, or alcoholism.
Predisposing factors are stagnation of bile due to the action of pregnancy hormones, increased amounts of enzymes and lipids in the blood, increased intra-abdominal pressure, spasm of the duct sphincter occurs with spasm of the uterine muscles, metabolic disorders.
The pathology causes the following symptoms:
- sharp or intensifying, girdling pain in the epigastric region;
- vomiting, nausea;
- prolonged slight increase in body temperature;
- tachycardia;
- peritoneal tension;
- Blood pressure changes depending on body position.
Pathology is detected during ultrasound. At the initial stage of the disease, conservative treatment is indicated, but if complications occur, surgical intervention is performed. If acute pancreatitis occurs after 36 weeks, then after the symptoms subside, early delivery is performed (in the absence of contraindications, delivery through the birth canal).
Discharge: norm and pathology
Discharge should normally be clear or milky white. They should not have an unpleasant odor. Sometimes mucus may be present in the discharge - this is a mucus plug that gradually comes out. Although it often goes away completely, and sometimes persists until childbirth.
If you find curdled clots in your discharge, you should consult a doctor. If symptoms such as swelling of the external genitalia and itching occur in parallel, this will indicate thrush. You should try to get rid of it before labor begins, so as not to infect the baby.
A sexually transmitted disease may be indicated by yellow or green discharge mixed with pus, foamy, and foul-smelling. Such discharge clearly indicates an infection that requires specific therapy.
Sometimes a woman discovers streams running down her legs. They may be clear or slightly yellowish. This is when your water breaks, indicating that labor is about to begin. In this case, you cannot hesitate to call an ambulance. Sometimes the water breaks in portions, which indicates thinning of the placenta. This situation should not be ignored. The woman should immediately see a gynecologist.
What dangers might await?
- The main danger in such late stages of pregnancy is gestosis.
- If a woman does not control her diet, significant weight gain is possible.
- Sometimes women notice that they have more hair on their body. This is a consequence of the activity of hormones in the body. After giving birth, everything should return to normal.
- Low water. If a woman's amniotic sac contains insufficient amniotic fluid, this can negatively affect the intensity of labor. In addition, there is an increased risk of adhesions forming inside the uterus, which can affect the baby and entangle the umbilical cord. Therefore, oligohydramnios should be detected in a timely manner.
False contractions: symptoms
False contractions are also called training contractions, or (after the doctor who first described them) Braxton-Hicks contractions. These are contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus, which do not lead to dilation of the cervix, and therefore to childbirth.
Some pregnant women don't feel them at all, but most experience contractions starting around the 20th week of pregnancy. In fact, false contractions also occur at earlier stages, the woman simply does not identify them. It should be noted that neither the presence nor absence of false contractions indicates any pathology during pregnancy.
False contractions do not give the most pleasant sensations. Many women sometimes do not even suspect how false contractions occur, because they feel them very weakly. Others are worried about how to distinguish contractions from false ones, because training contractions bring quite a lot of discomfort and frighten with their intensity.
The main signs of false contractions are their irregularity, short duration and relative painlessness. The difference between false contractions and real ones is that real contractions are so painful that they are difficult to confuse with anything else.
In order to remain calm and be able to turn the unpleasant sensations from training contractions to her advantage, a woman needs to know what false contractions look like. These are rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, training the main organ of a pregnant woman to contract so that during childbirth the cervix opens at the right moment. That is why false contractions are also called training contractions.
Many doctors also note that Braxton-Hicks contractions enrich the placenta with oxygen and nutrients, since during contraction blood flows to the fetus more actively.
So, false contractions have occurred, how to identify them? The muscles of the uterus are tense, you can feel or feel how it has hardened, it is not painful, but it can cause discomfort, the contraction lasts from several seconds to a minute.
Childbirth at 36 weeks of pregnancy
If labor begins at 36 weeks, it will be considered early or premature. As a rule, second and subsequent children are born at such periods. Therefore, if a woman begins having contractions that are not training (their intensity increases and the rest interval decreases), then she must go to the maternity hospital.
Chronic diseases of the genital tract, any acute infectious processes, fetal malformations, drinking alcohol and smoking during pregnancy can provoke childbirth at this stage. At risk are women under 18 years of age and over 40 years of age, as well as those mothers whose previous births were also premature.
Harbingers of imminent birth
No doctor can determine the exact date of birth.
However, you can understand that this day or hour is approaching by the following signs:
- The stomach dropped, the woman began to breathe easier, but at the same time the urge to urinate became more frequent;
- Training contractions began to occur more and more often;
- The woman’s weight stopped at the same level, or completely decreased by 1-2 kg;
- The mucus plug has come off;
- Frequent mood swings occur.
Early harbingers of labor can notify a woman of an approaching meeting with a baby better than any calculations.
From this video you will learn how to prepare for the maternity hospital, what to take with you and what you need to consult with your doctor about:
Why does my stomach hurt?
Abdominal pain during pregnancy occurs as a result of physiological processes. In the later weeks of pregnancy, women tend to exaggerate the intensity of pain because they are anticipating the upcoming birth, and any sensation that was not previously observed, be it a bowel disorder or tingling in the lower abdomen, is perceived as the onset of labor.
But not all future young mothers rush to consult an obstetrician, but wait for the appearance of regular contractions, the breaking of a plug or water, while being confident that pain, nausea or diarrhea is the beginning of the process and labor is about to begin.
That is why pregnant women turn to the doctor late when surgical pathology develops, and this leads to complications. To avoid unnecessary emotional experiences and prevent the development of complications, a woman should know in what cases she should immediately consult a doctor if she is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen at 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Natural causes
Many women periodically experience mild stomach pain during pregnancy. Discomfort occurs as the uterus enlarges and the ligamentous apparatus that supports it stretches.
Nagging pain is more intense in women who have undeveloped abdominal muscles
After the twentieth week of pregnancy, the baby begins to move, and the older he gets, the stronger his tremors are felt. The blow can sometimes fall on the organs, and a strong sharp pain is felt, which gradually subsides.
As the fetus enlarges, the nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back intensifies as the center of gravity shifts.
The uterus, enlarging, begins to put pressure on neighboring organs of the abdominal cavity, which leads to disruption of their function and deterioration of the digestive process. Hormones that prevent the tone of the uterus also have an effect on the rest of the smooth muscles. As a result, the peristalsis of the intestines and stomach is reduced, the bile ducts do not work as actively, which is why the secretion may stagnate.
Why do the muscles in the lower abdomen hurt during pregnancy?
Therefore, during pregnancy, stool disturbances often occur, pancreatitis and/or cholecystitis develop, stones form, heartburn and belching are tormented.
Against the background of a decrease in the body's immune defense and a deterioration in the movement of feces, the appendix may become inflamed. Appendicitis ranks first among surgical pathologies during pregnancy.
Food habits change during pregnancy, and women may eat large quantities of salty, heavy, fatty or incompatible foods. The enzymatic system cannot cope with incoming substances, hence indigestion, flatulence, and heaviness in the stomach.
By the 36th week of pregnancy, abdominal pain during training contractions can become much more noticeable. During such a false contraction, the walls of the uterus contract, but the cervix does not dilate and the waters do not break.
For some, training contractions are painful, the stomach seems to turn to stone, for others they cause slightly noticeable discomfort, but the contractions are irregular and short-lived, as a rule, they begin against a background of emotional stress. Often the pain goes away after changing body position or short rest.
At 36 weeks of gestation, the baby has already turned head down, so the stomach drops and no longer puts pressure on the diaphragm, which makes it easier to breathe and reduces heartburn. But the uterus puts more pressure on the bladder and intestines, which leads to frequent urination and difficulty bowel movements.
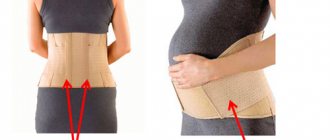
To reduce the load on the spine and pelvic bones, with the permission of a doctor, you can wear a bandage
In the later stages of pregnancy, the hormone relaxin is intensively produced, which is necessary to soften the connective tissue and ensure the divergence of the pelvic bones by 5–6 mm. When the bones move, a pulling or aching pain occurs in the pelvis, the intensity of which does not increase.
Normally, the pain disappears with proper rest. If the bones become too mobile, then they talk about symphysiopathy. With pathology, pain increases as pregnancy progresses and becomes even more noticeable when changing body position.
The hormone affects not only the ligamentous tissues of the pubic bones, but also others, for example, it softens the joints of the limbs, which is why the legs hurt in late pregnancy and the risk of dislocation increases even with minor external influence. Abdominal circumference reaches its maximum at 36 weeks of pregnancy. It is difficult for a pregnant woman to bend over, since the walls of the uterus rest against the ribs.
Obstetric pathologies causing pain
If the stomach becomes stone, this indicates that the uterus is tense and the birth process may begin. To reduce tone, you need to take a No-Shpa or Papaverine tablet, lie down and calm down. In such a situation, it is important to remain calm and breathe slowly so that the child does not develop a rapid heartbeat.
If your lower back hurts a lot, your lower abdomen is rocky, there are contractions and bleeding from the vagina, then you should urgently go to the maternity ward of the hospital. Obstetric pathologies may be indicated by uterine bleeding, breaking of water, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, leakage of amniotic fluid.
At 36 weeks of gestation, the mucous plug may gradually come off, preventing infection from entering the uterus. It is normal if the discharge is milky or almost transparent without inclusions. The mucus plug may come off in parts, revealing pink or brown streaks.
If the discharge is bloody, then this is a sign of the passage of the placenta or the onset of labor. When placental abruption occurs, in addition to discharge, abdominal pain, nausea, pallor, and dizziness are noted. If pathological discharge occurs (with a pungent odor, green, gray or yellow, cheesy or foamy), you should also urgently see a doctor, since this indicates an infection and if it is allowed to spread, it can spread to the fetal fluid.
If the microflora is disturbed, then burning and itching appears in the perineal area. With oligohydramnios, you can feel by touch how the baby is lying, where his arms or head are, the heartbeat can be heard clearly, and the baby’s movement is limited. With polyhydramnios, the opposite symptoms appear (the abdomen is greatly enlarged, fluid is felt under the hands, the child can hardly be felt, his heartbeat is muffled).
With polyhydramnios, due to excessive stretching of the uterine walls, the risk of premature birth is increased
When the integrity of the fetal bladder is damaged, amniotic fluid leaks. If this process has begun, then the birth must take place within the next 24 hours, otherwise the child will die due to hypoxia.
When the amniotic sac ruptures, fluid can come out immediately (and then the pathology is obvious), or it can leak periodically, and there is a feeling that this is urinary incontinence. Amniotic fluid is odorless and colorless, and its consistency is more like mucus than water. If amniotic fluid leaks, the abdomen decreases significantly in size.
Indications for caesarean section
About a third of all pregnancies end in caesarean section. In this case, the child does not pass through the birth canal naturally, but is removed from the uterus through an incision in the abdominal cavity. A cesarean section operation has clear indications for performing it and no doctor will do it just like that. Caesarean section can be planned or emergency.
When a caesarean section is necessary:
- The woman has a very narrow pelvis;
- The woman suffered injuries to the spine or pelvic bone;
- There is a tumor in the birth canal area;
- A complication such as placental abruption develops;
- There is a risk of uterine rupture or the threat of divergence of the old suture;
- A woman's uterus is underdeveloped;
- The fetus experiences hypoxia;
- The woman has diseases of the cardiovascular system, visual organs, and kidneys;
- The fruit is too large;
- The fetus occupies a transverse position in the abdomen.
If the doctor insists on a caesarean section, then you should not refuse. Remember that modern medicine allows this operation to be performed with minimal risks to the health of the woman and child.
Postpartum procedures with the baby:
Important Tips
- To reduce the severity of edema, it is necessary to control the amount of fluid you drink. This is especially true for evening time.
- It is useful to walk a lot in the fresh air. Thanks to this, the blood is enriched with oxygen, which reaches, among other things, the child.
- It is worth paying attention to your diet. It is important that the menu is balanced. The child especially needs calcium, vitamins and protein now. You should not get carried away with carbohydrate foods. The menu must include products such as whole grain bread, fresh vegetables and fruits. Under no circumstances should you go hungry.
- Don't forget about rest. Sleep should be of high quality and complete.
- Things for the hospital must be collected. The same rule applies to all necessary documents. The bag should be kept in a visible place.
- At such a late stage, a woman needs to be as careful as possible. You cannot make sudden movements, rush or rush. Even getting out of bed should be systematic and measured.
- You can't wear heels now. Shoes should be comfortable, with a slight instep.
- All a woman’s strength and thoughts should be directed towards preparing for the upcoming birth. This applies not only to arranging an apartment for the arrival of a small new resident, but also to maintaining one’s own health at normal levels.
How to relieve false contractions
You can try to reduce discomfort in several ways:
- drink clean water;
- take a more comfortable position;
- take a warm shower or ten-minute bath;
- take a walk in the fresh air;
- relax to the sounds of nature or meditative music;
- do breathing exercises.
False contractions before childbirth enable a woman to practice proper breathing during childbirth:
- frequent shallow breathing “like a dog” during a contraction to facilitate its passage. It is not recommended to breathe for more than 220 seconds to avoid dizziness from lack of oxygen;
- exhale slowly during the contraction and then take a deep breath of air, after the end of the contraction, repeat the deep exhalation and inhalation;
- slowly inhale through the nose and exhale sharply through the mouth.
You can practice other types of breathing that make contractions easier. We talk about them in this article.