In our clinic you can undergo an MRI of the abdominal organs with the issuance of a medical report. Based on the results of the MRI study, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and objectively assesses the condition of the patient examined in the clinic.
The need for non-invasive diagnostic methods has led to the development of technologies based on X-rays and the phenomenon of nuclear resonance. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging provide valuable information about the condition of the abdominal organs. The use of each of these methods has its own indications and contraindications.
When is a CT scan indicated?
On X-ray tomograms made using a computer, hollow organs are clearly visualized. Especially with the use of contrast agents. This is an excellent alternative to endoscopic examination of the stomach, intestines, and especially the gallbladder, which is unattainable with an endoscope.
CT scans clearly visualize the bones, which provides surgeons with guidance when surgery is to be performed. CT makes it possible to prepare based on the individual characteristics of the body, for example, to find out at what level the appendix of the cecum is located.
How to prepare for the examination
Before a CT scan of the stomach, you must follow a diet and follow a number of simple instructions. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. Therefore, before a CT scan of the stomach, it is recommended to take drugs that reduce gas formation, for example, activated carbon.
Diet
Intestinal motility and gases in the intestinal tract can distort CT scan data. Therefore, CT scans are done on an empty stomach or there is no point in the procedure. For best results, it is recommended to adhere to a certain diet.
For a couple of days, it is necessary to limit the proportion of foods in the diet that interfere with peristalsis. For example, peas, legumes, fermented milk products, black bread.
In what cases is magnetic resonance imaging indicated?
In turn, MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is ideal for imaging dense tissues rich in water. Hydrogen, which is most abundant in water, responds intensely to the fields created by the apparatus.
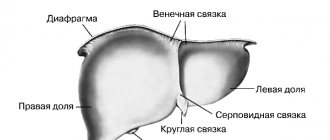
Sharp contrasts appear on the screen between areas with different water contents. The boundaries of the liver, pancreas, kidneys, and also small cavities inside massive structures are visible. MRI replaces ultrasound and is technically simpler. There is no need for a highly qualified specialist to examine the patient with ultrasound for a long time, choosing the best position of the emitter, and then correctly interpret the results.
Results of CT scan of the stomach
After images of the stomach and surrounding tissues are obtained, the radiologist will analyze them and draw up an expert opinion. If the doctor works directly in the clinic, this usually takes no more than two hours. Otherwise, the diagnostic results will be given only the next day.
In most medical institutions, the report is issued printed on paper, and a scanning protocol recorded on electronic media is also attached. Some diagnostic centers offer additional services: sending a report by email, free consultation with a doctor based on the results of the study.
Contraindications for X-ray examination
- The need to take repeated or regular photographs. Each shot gives radiation exposure to the abdominal area, which is not at all good for health.
- Pregnancy. While the fetus is in the mother's body, any radioactive exposure is contraindicated.
Contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging
- The presence of metal prostheses in the part of the body being examined.
- Excessive weight gain (severe obesity).
- Nervous and mental disorders, as a result of which the patient cannot remain motionless inside the device.
Comparison of methods and selection of the optimal one for the patient
In most cases, an MRI is preferable. We are talking about soft tissues filling the abdominal cavity, and it is obvious that in this situation CT is less informative. Even hollow internal formations, such as intestinal loops and bile ducts, are well contrasted on MRI using special contrast agents.
It is enough to look at images of internal organs taken using different methods to see a significant difference in the level of detail. Some abdominal structures are equally visible when appropriate contrast is used, with no major differences on CT or MRI. But others, in particular those located behind the peritoneum, are barely noticeable on CT.
However, CT scans are completed much faster. In urgent cases, a few minutes are enough to determine, for example, the location of a foreign body swallowed by a child. Metal or plastic will be clearly visible on a CT scan even without prior administration of contrast.
What does a CT scan of the stomach show?
Computed tomography is used in cases where previous examination methods were insufficiently informative (for example, ultrasound or endoscopy).
A CT scan of the stomach shows the condition of organs and tissues in case of injuries, before or after planned operations, helps to track the dynamics of the disease, identify anatomical anomalies, foreign bodies, and also detect neoplasms in the early stages of development.
When compiling a description of the study results, such indicators as the condition of the external and internal contours of the stomach, the thickness of its walls and their infiltration, the quality of the fat layer around it, the size of the lymph nodes, and the presence of polyps are taken into account.
The final diagnosis often depends on the results of a computed tomography scan, so it is better to entrust it to specialists from trusted clinics.
Patient preparation
When an MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity is performed, preparation for the examination is necessary. When contrasting, a contrast agent is injected inside or into the vessels. You should also prepare the digestive tract for examination of the abdominal cavity so that feces and excess volumes of gases do not interfere with the diagnosis of pathological changes.
When contacting medical centers, patients are explained in detail what diet to follow. Typically, in 2-3 days you should reduce the amount of food you eat and eat foods that do not lead to flatulence or constipation. The medical staff will provide you with a detailed plan for preparing for the MRI, and the same applies to CT.
How is a CT scan of the stomach performed?
Before starting the examination, you should remove all metal objects and jewelry that could negatively affect the scan result.
During the procedure, the patient must lie motionless on the table in the position indicated by the doctor (on his back, side). For the most accurate diagnosis, a polypositional study is performed, changing the position of the patient’s body 2-3 times. The results of the examination - detailed photographs and a description of the condition of organs and tissues - are received by the patient immediately after the procedure.
What is diagnosed by magnetic resonance?
Since the abdominal cavity is vast and consists of several sections, the tomograph reveals diseases of many systems: digestive, genitourinary, endocrine. Also, MRI can be useful in cases of damage to large vessels, although CT in this case is informative (with contrast).
A separate category of research is the use of a magnetic field to diagnose tumors. MRI effectively detects cancer of the stomach, liver, kidneys, and metastases of tumors with a primary source outside the abdominal cavity. Many tumor processes are extremely difficult or practically impossible to detect on CT, so it is obvious which diagnostic method should be used.
Indications for CT scanning of the stomach
- Inability to perform endoscopy.
- Monitoring the treatment of the disease and its dynamics.
- Suspicion of neoplasms, including polyps.
- Preventive examination (usually prescribed after 50 years).
- Suspicion of the presence of inflammatory processes or bleeding.
- Pain in the stomach or abdominal cavity of unknown etymology.
- Assessment of the consequences of organ injuries.
- Measuring the necessary indicators before and after surgical interventions.
How is magnetic resonance imaging performed?
The patient is placed on a retractable table of a huge device, the inside of which resembles a tank. Lie on your back so that the abdominal wall is on top. If a different position is indicated by the attending physician, the attendants fix the patient as prescribed. Then the table slides inside the device.
There is an emergency button on the wall, by pressing which the patient can urgently call for help. You should lie still while the MRI is taking place and you should not make any movements. The operator transmits instructions over the speakerphone. Sometimes you need to hold your breath, for a few seconds at most. This allows you to obtain clear tomograms that are not blurred by breathing movements.
When the diagnostic procedure is completed, the table moves out again, the patient stands up independently or is transferred to a stretcher (gurney). Everything is absolutely painless, there are no unpleasant sensations.
What happens after a CT scan?
If contrast was used during the procedure, the patient may be monitored for some time for any side effects or reactions to the contrast dye, such as itching, swelling, rash, or difficulty breathing.
If the patient notices pain, redness and/or swelling at the IV contrast site after returning home, they should report this to their doctor as this may indicate an infection or other complication.
If there are no reactions, the patient can resume normal diet and exercise.
What can be seen on a tomogram?
As in the case, complex computer processing of images obtained on MRI is performed. The result is a very clear picture of pathologies affecting the abdominal wall, intraperitoneal space and further body structures.
The doctor immediately sees which organs are affected and can clearly show it to the patient or relatives. The image from MRI is much clearer to non-specialists than CT, or, moreover, obtained from ultrasound.
Visualization helps to better justify the need for surgical intervention and obtain consent for surgical treatment. MRI images are transferred to the patient in digital form, say, as files recorded on a flash drive. Subsequently, they can be printed on a home printer and viewed on a computer screen.
In our clinic, MRIs are performed in strict accordance with standards, obtaining high-quality results that are easy to interpret for any specialist.
If there are contraindications, you can undergo a CT or ultrasound. An experienced doctor will examine you, identify indications and refer you to tests that will give the best results. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
CT scan of the stomach: what are the possibilities of this diagnosis?
What place does computed tomography of the stomach occupy in the general diagnostic series? What types of pathologies does it help identify?
These and other questions are answered by Lyubov Aleksandrovna Lazareva, a radiologist at Clinic Expert Kursk.
— Lyubov Alexandrovna, what is a CT scan of the stomach?
— This is a non-invasive, highly informative research method. It allows you to assess the condition of the stomach walls, identify gastric pathology, and, if necessary, clarify the diagnosis. This method also collects information before surgical treatment. Let me also note: in Kursk, CT scanning of the stomach is currently performed only in our clinic.
— Are CT and MSCT of the stomach the same study?
— Essentially, yes, since computed tomography of the stomach is performed only on a more modern, multislice computed tomograph (hence the abbreviation MSCT). The advantages of this device are that the patient experiences less radiation exposure during the examination, the procedure itself takes less time, the quality of the examination results is higher and the information content is higher. That is, in a nutshell, MSCT is the next step in the development of CT.
Read more about the computed tomography method in our article: When is CT irreplaceable?
— Is it true that the gold standard for examining the stomach is the endoscopic method - fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS)? And if so, why might the question arise whether to perform an FGDS or a CT scan of the stomach on a patient?
— Yes, that’s right: fibrogastroduodenoscopy is considered in medicine to be the optimal method for examining the stomach. However, some pathologies that are detected using FGDS require additional research, since the doctor does not always receive all the necessary information. This applies to diseases such as benign and malignant formations of the stomach. Also, MSCT of the stomach is performed when planning surgical intervention, since this method allows the doctor to assess the extent of spread of the pathological process beyond the stomach, the presence of distant metastases and damage to regional lymph nodes. FGDS does not provide such information.
On the other hand, in some cases, fibrogastroduodenoscopy may be prescribed after MSCT as an additional examination.
— In what cases and who can prescribe a CT scan of the stomach?
— A referral for a study can be issued by a therapist, gastroenterologist, surgeon and oncologist. This is done for the purpose of making a diagnosis if the patient has complaints relating to the gastrointestinal tract. Or, if a diagnosis has already been made, but additional information is required.
— I would immediately like to clarify the question about referral for a CT scan of the stomach: is it always necessary?
— It is advisable that the patient has a doctor’s referral and the results of other previously conducted studies (FGDS, X-ray).
— What does MSCT of the stomach show?
— CT scan (MSCT) of the stomach helps to identify pathologies such as inflammatory changes in the walls of the stomach, ulcerative lesions, developmental anomalies, benign and malignant formations, and the presence of distant metastases.
It is probably worth explaining here what is meant by distant metastases. Let's say a doctor is examining a primary malignant process in the stomach. When scanning, he sees nearby organs, in which he can detect metastases (for example, in the liver, lymph nodes).
Read materials on the topic:
How to and how NOT to treat gastritis How to protect the stomach from ulcers? Living in acid: what do we know about Helicobacter pylori
— How is a CT scan of the stomach done?
— Firstly, a CT scan of the stomach is always performed with contrast (otherwise the study will be uninformative, and serious pathology may be missed). Therefore, we first evaluate the patient’s kidney function; for this, a certain blood test is performed.
During the examination, the patient lies on his back. First, a CT scan is done while holding your breath without contrast (this is literally a few seconds), then a contrast agent is injected intravenously and a series of scans is performed. In total, the procedure takes no more than 20-30 minutes. But after the end of the study, we do not let the patient go for about half an hour, observe him, and make sure that there are no allergic reactions.
— Does the patient need any special preparation before undergoing a CT scan of the stomach?
- Yes. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. 10-15 minutes before the procedure, the patient drinks 500-750 milliliters of ordinary water, and immediately before the start of the study - another 250-500 milliliters.
— Are there any contraindications to CT scanning of the stomach?
- Yes. These are allergies to iodine and iodine-containing drugs, kidney failure. And one more thing: since there is no point in conducting a CT scan of the stomach without contrast (it is not informative), this study is also not performed on pregnant women or during lactation.
— Lyubov Alexandrovna, what could you say about the X-ray of the stomach? Is it currently in use? And if so, what is more informative - an X-ray or a CT scan of the stomach?
— X-ray examination of the stomach is a fairly common diagnostic method; it is mainly used in outpatient settings. It allows you to detect:
- hiatal hernia;
- ulcerative defects of the stomach wall;
- polyps;
- varicose veins of the esophagus, paragastric veins (including to assess the formation of porto-systemic anastomoses in portal hypertension syndrome);
- presence of tumor processes;
- narrowing of the gastric outlet.
With a fluoroscopic examination of the stomach, we can additionally assess the functional state of the organ.
In terms of the amount of information obtained about the condition of the walls of the stomach, the spread of the pathological process beyond its limits, and the condition of surrounding organs and structures, an X-ray examination of the stomach is inferior in its information content to computed tomography. But you shouldn’t completely exclude it; it has its rightful place in the diagnostic search.
In general, in practice, the diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and, in particular, the stomach itself most often begins with fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Then an x-ray may be prescribed and, to get as much information as possible, a computed tomography scan is performed. If the patient is unable to undergo FGDS, he may be immediately prescribed a CT scan of the stomach. In general, all these methods complement each other.
— And the last question: is it possible to do a CT scan of the stomach for children? Is this even necessary?
— The study is carried out strictly according to medical indications and the direction of the doctor.
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
If you need a CT scan of the stomach, you can sign up for the study here ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Where can I find the courage to make up my mind? Gastroscopy – WITHOUT fear! MRI of the stomach - an alternative to gastroscopy? How to check the small intestine? We talk about CT enterography. Virtual colonoscopy: an alternative or a diagnosis in itself?
For reference:
Lazareva Lyubov Alexandrovna
In 2007 she graduated from Kursk State Medical University (specialty in General Medicine).
In 2008 she completed an internship in the specialty “Therapy”, in 2011 - in the specialty “Radiology”.
In 2012, advanced training on the topic “Selected issues of MRI diagnostics.”
In 2015, advanced training in the specialty “Radiology”.
Since 2010, he has been working as a radiologist at Clinic Expert Kursk. Receives at the address: Kursk, st. Karl Liebknecht, no. 7.
Where to do a CT scan of the stomach in St. Petersburg and how much does it cost?
In clinics in St. Petersburg, the price for a CT scan of the stomach averages from 2,600 to 3,500 rubles. If contrast is performed, then an additional surcharge will be required for the iodine-containing drug used.
The cost largely depends on the type of device, the class of the medical facility, and the qualifications of the doctors working there. The price is also influenced by the offered promotions and discounts, and the possibility of performing the examination at night. If the question arises where to get a CT scan of the stomach at a low price, then it is best to look at our catalog of clinics in St. Petersburg with addresses and prices. You can fill out a feedback form on the website, the administrator will call you back and advise you on all questions regarding the upcoming examination.