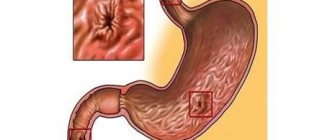
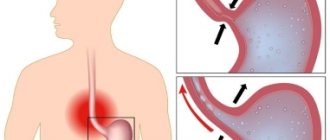
During the normal digestive process, bile is involved in the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates that accumulate in the intestines. After performing its function, bile enters the duodenum. There should be no bile in the stomach or esophagus. However, there are diseases in the process of which this scheme is disrupted and bile enters the stomach from the duodenum. There it mixes with gastric juice, after which bile refluxes into the esophagus.
Reasons why bile is thrown into the esophagus
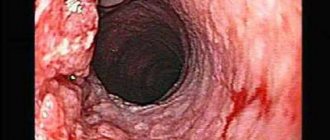
Bile reflux into the esophagus - unpleasant sensations
The entry of bile occurs in most cases from inflammatory diseases of the liver or gallbladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis). There may also be hydraulic reasons: disruption of the passage of bile flows, improper functioning of the sphincter, a kind of valve that is located between the stomach and duodenum.
With such deviations, bile refluxes into the esophagus. The possibility of the disease occurring due to poor diet and bad habits should not be ruled out. Experts have determined a list of the main reasons why bile is thrown into the esophagus:
- with excessively frequent consumption: carbonated drinks, strong tea, coffee
- from bad habits: alcohol, smoking, obesity caused by overeating
- with a hernia formed in the digestive tract, with cardiovascular diseases
- in the last months of pregnancy
- during bloating
- when eating quickly
The reflux of bile into the esophagus can be a single, rare occurrence - this should not happen regularly.
The process of bile formation
The gallbladder serves as a container that provides the duodenum with the necessary amount of secretion for processing food. The formation of bile is a constant process influenced by external and internal stimuli.
Features of the formation of liver secretions
- The duration of the undeveloped stage is from 3 to 12 minutes. At the end of the meal, the rate of production of this element increases. The formation of bile is determined by the acidity of the “filling” of the stomach, the period of its presence in this organ, as well as the production of hormones responsible for the activation of bile formation.
- The next stage is bile excretion. It takes from 3 to 6 hours. With the help of special fibers, the motility of the bladder and adjacent ducts is activated, stimulating the relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. Thanks to this, further movement of bile occurs.
- When the body is not busy processing food, bile enters the gallbladder and accumulates there until the next digestive cycle.
The process of bile formation is ongoing. The transition of secretion into the duodenum is discrete, only during the digestive process.
Symptoms to help make the correct diagnosis
Bile reflux into the esophagus - a reason to visit a doctor
Sometimes the disease we are considering occurs when there is an ulcer in the stomach or duodenum. These are serious diseases, the treatment of which involves a more extensive range of measures. With ulcers, bile reflux is a symptom, and not a separate type of disease.
Today, doctors can, based on general signs, make a verdict as accurately as possible and make the correct diagnosis. The main symptoms that determine the reflux of bile in the esophagus include:
- the mouth feels constantly dry
- frequent occurrence of heartburn
- a feeling of heaviness forms in the stomach area
- constant belching and bouts of vomiting
- the presence of a yellow coating on the surface of the tongue
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth
If several of these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Modern methods of diagnostic examination
As noted above, if symptoms of bile reflux into the esophagus recur regularly over the course of a week, you need to seek help from a medical specialist - a gastroenterologist. After the first visit to a specialist, a wide diagnostic examination is prescribed. The patient must undergo a set of tests: a general urine test, a clinical blood test.
In some cases, the doctor may require a biochemical blood test. Based on the examination results, the doctor decides on a treatment regimen. To undergo a diagnostic examination, the following methods are used:
What's the result?
It doesn’t matter which organ system is affected by the disease - it is easier to prevent the disease than to treat the consequences later. You should not give up preventive measures at the risk of your health. The main principle of maintaining health is that everything should be in moderation, and gastrointestinal health is no exception. If signs of illness are detected, it is recommended to go to the hospital for diagnosis. Banal dysfunction and properties of bile secretion become signals of a serious systemic disease (gastrointestinal diseases, bleeding disorders in the liver).
Therapy scheme
The reflux of bile into the esophagus cannot be ignored!
There is no point in ignoring such a problem as the reflux of bile into the esophagus. In addition to the fact that a person experiences discomfort, this disease can also become a springboard for the development of other diseases. Considering these facts, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis, identify the causes and decide on a treatment regimen. In modern realities, treatment can be carried out either conservatively or through surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This type of treatment involves the complete neutralization of bile, as an irritant to the mucous organs. The following medications may be prescribed for this:
- Maalox
- Domperidone
- Papaverine
- Metoclopramide
- Drotaverine
The purpose of a particular drug, as well as the dosage, is determined exclusively by a medical specialist.
Surgical intervention
Considering that the reflux of bile into the esophagus can occur due to a hernia or tumor that compresses the duodenum, the doctor may decide on surgical intervention. During the operation, the cause that contributes to the reflux of bile is surgically removed. The decision for surgical intervention is made by the endocrinologist based on the diagnostic examinations and tests performed.
Possible complications
Ignoring such changes in the digestive tract as the entry of bile into the stomach and esophagus, there is a high probability of complications and the emergence of dangerous diseases, among which should be highlighted:
- gastritis - the formation of an inflammatory process on the surface of the stomach due to the long-term negative effects of bile acids, which are themselves aggressive
- gastroesophageal disease - damage to the walls of the esophagus
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition in which the squamous epithelium of the esophagus becomes columnar
To avoid such pathologies, it is necessary to lead a correct lifestyle and regularly monitor your diet and diet.
Functions of bile
Bile is a liquid secreted by the liver, necessary for digesting food in the intestines. It enters this organ through the biliary tract.
Anatomically, bile belongs to the liver. However, before being sent to the intestines, it accumulates in the gallbladder. Hippocrates at one time noted the enormous role that this organ plays in the life of the body. In some teachings, it is considered the starting point from which health-improving activities should begin. The purpose of the gallbladder is to solve the following tasks:
- Providing the duodenum with the necessary amount of secretion.
- Making a significant contribution to metabolic processes.
- Formation of fluid that is part of the joint membranes.
In standard mode, this element penetrates the gallbladder and starts the digestion of products entering through the esophagus. However, in some situations, bile “goes astray” and goes directly into the stomach. Experts do not classify a failure in the food processing mechanism as an independent disease. The pathological process is considered a symptom of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
In the human body, this fluid is responsible for the following tasks:
- leveling the organic element pepsin, which is part of the gastric juice;
- revival of peristalsis;
- assistance in the production of micelles;
- preventing bacteria and proteins from sticking together;
- formation of feces;
- activation of the synthesis of intestinal hormones and mucus;
- fat emulsification;
- intestinal antiseptic.
However, the leading function of bile is to stimulate the transition of the digestive process from the stomach to the intestines.
The composition of this liquid is quite diverse, and any changes in the balance of components can lead to illnesses, including the formation of gallstones.
Reinforcement of therapy - proper nutrition
Proper nutrition - prevention of gastrointestinal diseases
To consolidate the positive effect after treatment, the patient must carefully monitor his diet and lifestyle. In other words, to prevent a recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to follow a diet, eat small meals (eating small portions throughout the day - 5-7 times a day) and give up bad habits. Excessively spicy and fatty foods must be completely excluded from the diet.
You should also avoid fried and smoked foods. Today, there are a lot of recipes for delicious and healthy food that is steamed or boiled. Nutritionists have developed dozens of diets that can prevent the reflux of bile into the esophagus.
Diagnosis and treatment
Despite many progressive research methods, accurate anamnesis and a thorough examination of the abdominal cavity are considered to be the leading methods for detecting bile in the stomach.
For these purposes, the following methods are used:
- liver function tests;
- magnetic resonance cholangiography to detect stones;
- duodenal intubation;
- Ultrasound;
- cholescintigraphy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Every year the diagnostic potential increases, and specialists are given the opportunity to promptly identify pathology.
Table 2. Treatment regimen
| Name | Characteristic |
| Non-selective blockers | Relieves muscle tension. |
| Myotropic antispasmodics | Restores the flow of bile. |
| Antispasmodics | Normalizes pressure in the gallbladder. |
| Choleretics | Improves motor functions of the bladder. |
The primary measure for this pathology is the prescription of drugs whose action is aimed at improving the motor processes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Table 3. Drugs for improving the motor processes of the gastrointestinal tract
| A drug | Description |
| Motilium | Stimulates peristalsis. Has an excellent antiemetic effect. |
| Itomed | Accelerates the movement of food throughout all parts of the digestive tract. |
| Cerucal | Keeps the gastrointestinal tract in good shape. |
Motilium is given great importance in therapy. This remedy has the ability to accelerate the excretion of feces, improves peristalsis and the functioning of the gallbladder, which is useful for the body when there is excess bile. The medication is available in several variations, including a suspension, convenient for treating young children.
Dealing with abnormal bile flow should be done in a comprehensive manner. An important factor is the use of products whose action is aimed at regulating acidity levels.
Table 4. Means for regulating acidity levels
| A drug | Additional properties |
| Phosphalugel | Neutralizes the effect of acid, envelops the walls of the stomach, protecting against irritation. |
| Maalox | It has carminative and choleretic properties. |
| Gastal | Strengthens the regenerative processes occurring in the gastric mucosa. |
The use of proton pump inhibitors is very important in therapy. Medicines can reduce the pathological activity of cells and reduce the production of hydrochloric acid. This has a positive effect on sphincter motility, which prevents bile reflux. For this purpose, the following means are used.
Table 5. Proton pump inhibitors
| A drug | Description |
| Dexilant | Reduces the secretion of gastric glands. Has an antiulcer effect. |
| Lansoprazole | Blocks the formation of hydrochloric acid at the final stage. |
| Nexium | An antiulcer agent that reduces the production of hydrochloric acid. |
Therapeutic diet
Compliance with therapeutic nutrition plays a huge role in preventing bile reflux. It significantly alleviates the unpleasant manifestations of diseases accompanied by the penetration of secretions into the stomach.
The principle of nutritional therapy is fractional nutrition. Food should be taken in small portions 5 times a day. The daily diet should be eliminated from the following components:
- fried, fatty and salty foods;
- smoked meats;
- hot spices;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
It is advisable to reduce the amount of consumption of vegetable oils and broths cooked using fatty meats.
To optimize the activity of the intestines and gallbladder, patients need to introduce the following products into their diet:
- bran;
- dried apricots;
- bell pepper;
- pears;
- carrot;
- prunes;
- honey;
- zucchini;
- pumpkin;
- watermelon
We should not forget that the presence of secretions in the stomach is considered a symptom, not a disease. Therapy should be focused on eliminating the factors that caused bile reflux. If it is not possible to completely stop annoying symptoms, treatment is used aimed at changing the patient’s lifestyle in a positive direction and reducing the clinical manifestations of the disease.