An acute attack of pancreatitis is accompanied by a significant deterioration in well-being; the patient experiences severe pain, up to loss of consciousness. It is impossible to cope with such a situation at home. The patient needs to be hospitalized.
Lack of adequate treatment leads to inability to work, resulting in disability, and in the worst case, death. Treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital has its own characteristics; it helps restore the functionality of the pancreas.
In which department are they treated with pancreatitis? It all depends on the clinical picture. Sometimes the patient is hospitalized in the intensive care unit, where conservative therapy is carried out. In some cases, the patient must be admitted to the surgical department if surgery is necessary.
Let's figure out when hospitalization is needed for pancreatitis, and how is treatment carried out in an inpatient setting?
Causes
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines.
- Abdominal injuries.
- The presence of worms and the toxins they secrete.
- Incorrect treatment with medications.
- Overweight.
There are several types of pancreas problems.
- Reactive pancreatitis. The cause of this disease is considered to be a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. During an exacerbation, intense pain appears under the left rib.
- Acute pancreatitis. Severe pain appears after certain factors: drinking alcoholic beverages the day before, spicy, fried or salty foods. And also after poisoning with preservatives or spoiled products. The patient's condition deteriorates very quickly. It is in this form that the symptoms of pancreatitis in a woman after 30 years of age are diagnosed. The pancreas must be treated for problems that are just beginning.
- Chronic pancreatitis. If a person repeatedly avoids treatment for pancreatitis, then gradually he leads his body to chronic manifestations of pancreatitis.
What patients with chronic pancreatitis need to pay attention to:
- try to follow a diet; remember that any deviation from the diet threatens you with a new exacerbation, and that healthy food can also be tasty;
- try to eliminate from your life all factors that provoke the development of chronic pancreatitis;
- Don’t be afraid of the need for long-term treatment and the fact that you need to take medicine every time you sit down at the table; By taking enzyme preparations, you help the body better absorb food and relieve additional stress on the pancreas;
- do not neglect treatment and closely monitor your health; This attitude will allow you to easily control the disease and prevent the development of its complications.
Share this page:
The most common questions that interest patients
- How long does it take to treat the pancreas? The duration of treatment directly depends on the form of the disease, duration and presence of complications. It is impossible to completely restore the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis, so constant maintenance therapy for the organ is recommended.
- How long does an exacerbation of pancreatitis last? The acute form is characterized by the occurrence of a sharp exacerbation, which lasts on average from two to seven days.
- What is the best way to treat an exacerbation of the pancreas: secrets of therapy
- Chronic biliary-dependent pancreatitis: symptoms, treatment and characteristics of the disease
- Features of pancreatitis in men: main symptoms, causes and methods of treatment
- What is pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment features in adults
Causes of exacerbation
The main cause of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis is alcohol abuse.
Other causes of exacerbation of the disease:
- Mechanical abdominal injuries.
- Complications after surgical operations.
- Diets that involve a minimum of protein.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Infectious diseases of the body.
- Excessive consumption of fatty and fried foods.
- Hereditary factors.
- High stress on the nervous system, frequent stress.
- Senile age (lack of enzymes in the body).
- Taking toxic medications.
- Smoking, especially if you are overweight.
- Chronic diseases of the liver, duodenum and gall bladder.
During an exacerbation, the activity of pancreatic enzymes sharply increases, the pancreatic tissue is irritated under their influence, swelling occurs, compression of the large pancreatic duct occurs, the blood supply to the gland worsens - the clinical picture resembles acute pancreatitis and, in fact, is not much different from it.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pancreatitis
The pancreas is a relatively small organ, but it performs a number of vital functions for the body. For example, the production of enzymes for the breakdown of products. When the gland malfunctions, enzymes remain in its ducts, thereby disrupting its functioning. What symptoms can occur with inflammation of the pancreas?
- Fever. It indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. Indicators can be very high. It is necessary to treat not only the symptoms, but also the organ itself.
- The pressure can become either very high or very low. With the intensive development of the disease, the patient notices a sharp change in pressure figures.
- Nausea, belching, dry mouth, hiccups are all symptoms that indicate problems with the pancreas. If you only eliminate the symptoms, the treatment may be delayed.
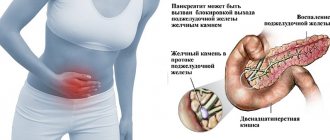
- Painful sensations. This is the very first symptom that occurs. The pain can be acute, constant, and sometimes changes to dull. They can be so intense that they even cause painful shock. Pain with pancreatitis is considered stronger than even with a heart attack. With partial inflammation of the pancreas, pain appears under the right or left rib, and with complete inflammation - around the waist. In case of severe pain, it is recommended to consult a doctor, and he will choose how to treat chronic pancreatitis.
- Vomiting with bile. A person cannot eat anything at this time. Fasting during an exacerbation period leads to faster recovery of the body.
- Change in complexion. The skin becomes pale at first, and then a gray, earthy hue. Facial features become more and more pointed.
- Sticky sweat.
- Shortness of breath associated with vomiting.
- You may first notice the presence of a yellow coating on the tongue.
- Constipation or diarrhea treatment at home. A sudden change in stool with an unpleasant odor and particles of food that has not been digested. Acute pancreatitis and loose stools are characterized by foamy discharge. But another situation is also possible. This is constipation, which is accompanied by bloating. The stomach becomes hard.
- Change in skin color. For example, the lower back and area around the navel may take on a bluish, sometimes marbled tint. The lower abdomen and groin area become greenish-blue.
- Manifestations of obstructive jaundice. Due to the increase in the size of the pancreas, compression of the gallbladder occurs and yellowing of the skin and sclera occurs.
If symptoms are detected, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, since pancreatitis causes very severe pain, and this can be fatal. Treatment for acute pancreatitis on your own is also not recommended.
Classification
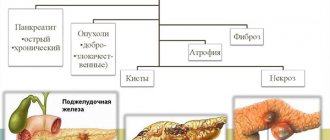
There are acute, chronic and reactive pancreatitis.
The following types are characteristic of acute pancreatitis: edematous form of acute pancreatitis, hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis, fatty pancreatic necrosis. For chronic pancreatitis, pseudocystic form, fibrous form, pseudotumorous pancreatitis are possible.
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by inflammation of the pancreatic tissue and its breakdown (necrosis), followed by atrophy, fibrosis, or calcification of the organ. Acute pancreatitis can manifest itself as acute inflammation of a part or the entire organ, or the breakdown of gland tissue with suppuration, hemorrhage or the formation of abscesses.
Chronic pancreatitis is a slowly progressive inflammation of the pancreas, accompanied by disturbances in its functions, periods of exacerbation followed by remissions. The outcome of the disease is similar to the outcome of acute pancreatitis (fibrosis, calcification, atrophy).
Reactive pancreatitis is an attack of acute pancreatitis against the background of exacerbation of diseases of the stomach, duodenum, gallbladder or liver.
Acute and chronic pancreatitis also differ in form.
Acute pancreatitis is an acute inflammatory-necrotic lesion of the pancreas. For acute pancreatitis, the main etiological factors are diseases of the biliary tract, alcoholism, trauma, vascular pathology (atherosclerosis, thrombosis, embolism) leading to pancreatic ischemia, infectious diseases of the duodenum, allergies, toxins, parasitic diseases, such as opisthorchiasis, medications. The pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis is based on the activation of proteolytic enzymes (mainly trypsin) not in the intestinal lumen, but in the pancreas itself with the development of its self-digestion.
Period of obvious damage to the pancreas
- High temperature up to 38 degrees.
- Diarrhea for a long time. Porridge-like stools, with inclusions of undigested food.
- Sudden weight loss that is not associated with changes in the quality and quantity of food.
- Sleep disturbance. You can't sleep. Insomnia.
- Food toxicosis.
- Constant feeling of hunger, especially in the morning.
- Reaction to salty mineral water.
- Bloating after eating.
- Pain in the left hypochondrium.
- Thirst in the morning and after eating.
- Frequent urination after eating.
Naturally, having such symptoms of the disease, I turned to a therapist. In general, I should have gone to an endocrinologist, but I didn’t know about that. I told her how my pancreas hurt. Passed blood and urine tests. So, in blood tests there was increased diastase, and in urine tests there was amylase of about 2000 E when the norm was 600 E.
Currently, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are a common pathology. With complaints of pain in the right hypochondrium, heaviness in the epigastric region or discomfort after eating, people are increasingly turning to the doctor. Such symptoms are caused by a large number of factors and diseases, which also include pancreatic pathologies.
- Strong pain. It occurs in the left side of the abdomen, and after a while it spreads to the entire abdomen.
- Nausea and even vomiting.
- Blood pressure becomes disorganized.
- Understanding of reality is disrupted.
- A state of shock may occur.
These symptoms are too severe to treat at home. Therefore, in case of acute pancreatitis, you should urgently call an ambulance. An experienced surgeon must examine the patient and be sure to admit him to the hospital for further treatment and observation. It is unlikely that it will be possible to avoid surgery on the pancreas in the acute form of the disease.
Here the signs are as follows:
- The pain becomes not as obvious as in the first case.
- In this case, dyspeptic syndrome predominates: heartburn, belching, nausea, bloating.
- Maldigestion syndrome occurs. This is when there is a disruption in the digestion of food to those particles that would be absorbed.
- Malabsorption syndrome occurs. In this case, the absorption mechanism in the small intestine is completely disrupted.
The following symptoms are typical for maldigestion and malabsorption:
- foul, profuse stool;
- weight loss;
- vision decreases in the evening;
- bleeding gums appear;
- Conjunctivitis, stomatitis, and skin itching may occur;
- anemia develops;
- due to the fact that calcium absorption is impaired, there are cramps and pain in the bones;
- neuropsychic agitation;
- the appearance of cold sweat;
- trembling in the body;
- dry skin;
- there is a feeling of constant thirst.
It is necessary to treat chronic pancreatitis to avoid surgery on the pancreas. Therapy must be adequate and reasonable. Only after passing all the necessary tests, as well as consultation with a doctor, therapy can be prescribed. Now let’s look at what kind of diagnostics a sick person should undergo in order for the picture of the disease to become clearer.
Forms of acute pancreatitis
There are mild (edematous) and severe (necrotic) forms of the disease. With edematous pancreatitis, the gland is enlarged 2-3 times, saturated with serous fluid and tense. The necrotic form, or hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis, is characterized by hemorrhages, the gland is partially or completely necrotic.
The symptom of acute pancreatitis is severe pain. In the most severe form - pancreatic necrosis, which entails shock with a sharp drop in blood pressure, pallor, and cold sweat. The edematous form of pancreatitis is often accompanied by severe pain; less often the pain is moderate or insignificant. The pain is localized deep in the epigastric region. Often patients note its encircling nature, irradiation into the back and both hypochondriums. Acute pancreatitis is characterized by profuse, repeated vomiting, first of food, then of mucus and bile. Characterized by a serious condition, fever, pallor of the skin, erythematous blisters may appear due to necrosis of subcutaneous fat. Characteristic is bloating caused by reflex intestinal paresis.
To make a diagnosis, a urine test for diastasis and electrocardiography are prescribed. It is most difficult to distinguish acute pancreatitis from acute cholecystitis; these diseases often occur together.
In case of acute pancreatitis, the patient is immediately hospitalized in the surgical department and is under constant medical supervision, since pancreatitis can take a severe course. We guarantee inpatient treatment in a leading clinic in Moscow, and in our center you get a unique opportunity for further outpatient treatment and observation by your attending physician.
Standards of care in hospital
In case of exacerbation of the disease, the following types of assistance can be provided in a hospital:
- resuscitation measures (for complications that threaten the patient’s life);
- surgical intervention (in case of extensive necrosis (death of cells) of the organ or blockage of the pancreatic ducts);
- intensive drug therapy;
- physiotherapy (during the recovery period);
- constant monitoring by specialists of the patient’s condition.
If a person exhibits symptoms of an attack of pancreatitis, the first step is to call an ambulance. While doctors are getting to the patient, it is important to quickly provide first aid. To do this, follow these steps:
- Place the patient on a sofa or bed.
- Apply a heating pad filled with cold water or a wet cloth to the painful area. It is strictly forbidden to heat the abdominal area.
- Open a window indoors. Ventilate it.
When the doctor arrives at the site, he will carry out the necessary procedures based on the presented clinical picture. Most often, Papaverine is administered during attacks of pain. Next, the patient is admitted to the hospital, but hospitalization cannot be refused.
At the first attacks of pain in the abdominal area, you must call a doctor or go to the hospital. A delay of even a few hours can seriously affect the patient’s condition and cause complications. In addition, acute pancreatitis without proper treatment can quickly develop into chronic pancreatitis.
The first step when pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms of pancreatitis appears is to call an ambulance at home. While waiting for the doctor, you will need to complete the following steps:
- Place the patient on a bed or sofa in a comfortable position.
- Apply a heating pad or a bottle filled with cold water and ice to the painful area.
- Ventilate the room.
- Have an empty basin or other container ready in case of excessive vomiting.
It is not recommended to take painkillers, soda solution or any medications on your own during an attack. You should also not drink any liquid, not even water.
Hospitalization
If emergency doctors suggest hospitalization during an attack of illness, it is highly not recommended to refuse, since pancreatitis cannot be cured at home, and a trip to the doctor may be delayed. As soon as the patient enters the medical facility, he undergoes a medical examination consisting of the following procedures:
- measuring body pressure and temperature;
- initial examination and palpation of painful areas;
- examination of blood tests (for the level of leukocytes and enzymes);
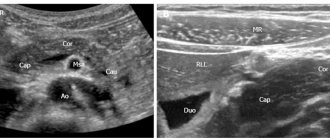
- Ultrasound examination;
- laparoscopy (in some cases).
Other procedures and consultations with doctors in other fields may also be necessary to identify the causes and intensity of inflammatory processes. Only after a comprehensive diagnosis is therapy prescribed, and the patient is placed in a ward for long-term observation.
How long does it take to treat pancreatitis after hospitalization? In case of exacerbation, infusion treatment is usually required, after which the patient is discharged to continue therapy at home. As soon as the patient is admitted to the hospital, his blood pressure is measured and he is sent for an initial examination to the doctor. Next, it is necessary to carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- blood test to determine leukocytes and enzymes;
- laparoscopy;
- ultrasound examination.
After carrying out all the necessary procedures, the doctor evaluates the pancreas and the patient’s condition and identifies the form of pancreatitis. Based on the data obtained, a method and treatment plan are selected and medications are selected. Treatment for moderate severity is carried out in the intensive care unit; for severe pain and intoxication, resuscitation may be required.
Forms of chronic pancreatitis
- Latent or asymptomatic - for a long time, patients do not feel any changes in their well-being.
- Painful - manifested by constant pain in the upper abdomen, intensifying during an exacerbation to severe pain.
- Chronic recurrent - without exacerbation there are no complaints, with relapse - characteristic pain.
- Pseudotumor is a very rare form in which the head of the pancreas is affected and its size increases due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue.
Chronic pancreatitis is a chronic periodically exacerbating inflammatory process leading to progressive irreversible anatomical and functional damage to the pancreas. Factors that provoke chronic pancreatitis include alcohol abuse, diseases of the biliary tract, stomach and duodenum, exposure to chemicals and medications (hypothiazide, corticosteroids), hyperlipidemia, hypercalcemia, hereditary predisposition, protein deficiency.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of ultrasound data, scatological examination, computed tomography, and the results of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Treatment for severe exacerbation of the disease is carried out as for acute pancreatitis. For mild exacerbation, outpatient treatment is indicated.
What tests are needed to make a diagnosis?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YkefLGAvbKg
In addition to the above-described methods for recognizing the disease, the doctor gives directions for the following tests:
- General blood analysis. Its results show signs of inflammation and possible anemia.
- Donating blood to determine blood sugar levels. Such an analysis is necessary to find out whether the patient has diabetes.
- General urine analysis. Shows possible kidney diseases.
- Electrocardiogram and echocardiography exclude heart disease.
After passing the above tests, the picture will become clearly visible, and the diagnosis of “pancreatitis of the pancreas” will be made or not.
Diagnostics
After determining the symptoms and etiology of the disease, the specialist doctor prescribes tests. Usually this:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- fecal biochemistry;
- saliva tests to determine amylase levels.
An accurate diagnosis may require additional abdominal tests, such as a CT scan, MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or endoscopy.
What to do in case of an acute attack of pancreatitis?
Most often, patients with edematous or necrotizing forms of pancreatitis are admitted to the hospital. The main goal of doctors in this case is to remove the patient from a dangerous condition and restore the functioning of the pancreas (as far as possible). During therapy for chronic pancreatitis, the patient's condition stabilizes and the symptoms stop.
The main objectives of the treatment of pancreatitis in a hospital setting:
- Relieving stress and providing rest for the organ. As a rule, fasting is prescribed for this for three to four days. In severe cases, catheters are installed to remove remaining stomach contents, and blockers are administered.
- Relieving swelling. Coolers are applied to the painful area of the abdomen, and diuretics are administered intravenously.
- Elimination of pain syndrome. Antispasmodics, analgesics and narcotic medications (in difficult cases) for intravenous administration are used.
- Suppression of enzyme production. Thanks to anti-enzyme drugs, restoration of gland tissue occurs faster and more efficiently.
After the fasting stage, a therapeutic diet is also prescribed to relieve stress and normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. How long it should last is determined by the doctor.
What to do in case of exacerbation?
First of all, you need to call an ambulance. If symptoms of pancreatitis appear, first aid for an exacerbation includes the following steps:
- complete exclusion of food and liquid intake;
- maintaining rest, you need to lie in bed on your back; if you are vomiting, you can take a position lying on your side with your knees pressed to your stomach;
- using an ice pack as a cold compress on the abdominal area.
After delivery to the hospital, the patient will be examined, and based on the results obtained, the doctor will choose the most effective therapeutic tactics. It is prohibited to self-prescribe pills and administer medications during exacerbation of pancreatitis.
If the exacerbation of a chronic process is limited to nausea after eating, the appearance of diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, you still need to consult a specialist to avoid complications. After the examination, the doctor will decide where it is necessary to undergo treatment - inpatient or outpatient.
Contraindications to self-medication
Naturally, the treatment of pancreatitis (choosing a method with appropriate medications) is prescribed by a doctor. The symptoms of the pathology are varied and may be similar to other diseases. Therefore, it is categorically unacceptable to treat pancreatitis on your own. You cannot tolerate paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, apply heat and rinse the stomach. You just need to seek medical help in a timely manner.
It is possible to quickly stop the course (or exacerbation) of the disease if it is detected just after it has begun.
Drug treatment
Treatment of pancreatitis during an exacerbation should begin immediately and always under the supervision of a specialist. Only a gastroenterologist can prescribe the correct treatment aimed at quickly relieving the exacerbation of the disease and preventing possible complications.
First of all, drug treatment is used:
- Vitamin therapy: fat-soluble A, E, K, D and B vitamins.
- Pancreatic enzymes: Pancreatin, Creon, Panzinorm with lipase at least 10 thousand.
- Drugs aimed at reducing the secretory function of the gland: Esomeprazole, Octreotide, Pantoprazole, Omeprazole.
- Drugs that relieve concomitant pain syndrome. These are antispasmodics: Drotaverine, Mebeverine, Spazmalgon, No-shpa. And also non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Tramadol, Ketoprofen.
It is worth noting that drug treatment of patients is individual. Only a doctor should select medications after carefully studying the symptoms of the disease. You cannot give injections or take pills without consulting a specialist. This can lead to serious consequences.
The hospital prescribes this treatment
- To reduce swelling, diuretics are prescribed. They help reduce enzymes in the blood, as well as the spread of toxins throughout the body. These may be medications added to an IV or taken separately in tablets.
- Drugs that are used intravenously: contrical reopolyglucin, saline solution.
- Omeprazole - tablets or quamatel - droppers.
- Tablets to reduce spasms.
- If the disease is advanced and has entered the purulent stage, then antibiotics are prescribed.
- In acute conditions - enzyme inhibitors.
- Treatment in hospital Medicines to relieve pain or stop vomiting.
- To maintain the body during dehydration caused by vomiting or diarrhea, it is necessary to take vitamins.
- The first days the patient does not eat and drinks only warm still water. In case of prolonged pancreatitis, when the patient has been fasting for several weeks, the doctor prescribes parenteral nutrition.
- Only when the functioning of the pancreas has significantly improved is one allowed to eat something. First it is yogurt, then cottage cheese, and after a few days he may be on a special diet.
- A state of complete rest. This will help reduce blood circulation to all organs, including the pancreas.
- It is necessary to treat pancreatitis not until the symptoms are eliminated, but until this problem is solved once and for all.
In acute pancreatitis, the pain is so severe that it must be relieved with the help of narcotic analgesics.
There are cases in which it is necessary to remove the affected area of the pancreas through surgery. Additionally, the abdominal cavity is washed.
When the acute period has passed, the patient is recommended diet No. 5. It consists of fractional meals - up to 8 times a day. Everything should be pureed, boiled or steamed. Food should be warm, but not hot or cold. You should not eat fried, smoked or salted foods; products, in copious quantities. But you should not take diet as the main treatment. You should also avoid drinking alcohol while you are undergoing treatment.
Acceptable products include: rye crackers soaked in water; porridge cooked in water, pureed zucchini, pumpkin, carrots, potatoes; puddings, jelly. Nothing else is allowed to be eaten. It is unacceptable to drink alcoholic beverages even in small doses.
Surgical intervention
Treatment of pancreatitis using surgical methods is used in advanced stages of inflammation with complications. Thus, the indications for the operation are:
- decomposition of organ tissue, pancreatic necrosis (including infected);
- the presence of abscesses;
- pancreas cancer;
- presence of cysts and pseudocysts;
- lipofibromatosis and benign neoplasms;
- enzymatic peritonitis;
- combination of pancreatitis and cholecystitis.
Depending on the extent and type of lesion, different forms of surgery may be used. Thus, the practice of complete or partial removal of the organ and laparoscopy with the use of drainage are used.
The operation is complicated by the fragility of the pancreas, which can cause bleeding during the procedure. In addition, the proximity of the gland to other organs increases the risk of accidental damage.
With a favorable outcome, complete or partial restoration of pancreatic function is possible after the rehabilitation period. Otherwise, complications are likely:
- development of peritonitis, accumulation of purulent fluid;
- exacerbation of pathologies associated with the work of the pancreas;
- blockage of the bile ducts;
- slow tissue healing, lack of positive dynamics.
In order to increase the likelihood of recovery, you must strictly follow the instructions of your doctor. Typically, postoperative therapy includes:
- peace and complete rest of the patient;
- taking restorative medications and antibiotics;
- preventive drug therapy;
- therapeutic diet.
After surgery, periodic medical examinations are also required to record the results of treatment and recovery.
How many people stay in hospitals with pancreatitis if surgery is necessary? This form of treatment can take varying amounts of time, depending on the scale of the problem.
Treatment of pancreatitis with surgery may be prescribed when complications are diagnosed. It is indicated for jaundice, lack of benefit from medications, and detection of formations in the pancreas on ultrasound.
In this case, time will be needed not only for preparation and actual surgical intervention, but also for the rehabilitation period. Thus, the patient spends about a week in the hospital after it and spends another 1.5-2 months in home treatment.
He is prescribed a special diet, drug therapy, physical exercise, and a daily routine plan is drawn up. It is necessary to be admitted to the hospital again at the first signs of complications.
Nutritional treatment of chronic pancreatitis is as follows:
In the first days of exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, it is recommended to completely abstain from food and drink only alkaline mineral waters (Borjomi, etc.) - this will help neutralize the acidity of the stomach and reduce the production of digestive juice in the pancreas.
After 2–3 days, boiled dishes, porridges, small amounts of lean meat, and boiled fish are introduced into the patients’ diet. Throughout the entire period of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of raw vegetables, fruits, whole milk and other foods that cause bloating. During periods of remission of chronic pancreatitis, in order to prevent new exacerbations, patients are advised to avoid drinking alcohol, fatty, spicy, sour or highly salty foods.
Elimination of pain in chronic pancreatitis is achieved by prescribing painkillers and antispasmodics (no-spa, papaverine, baralgin, analgin, diclofenac, etc.).
Establishing digestion and compensating for pancreatic enzyme insufficiency is one of the most important stages in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. For this purpose, patients are prescribed enzyme preparations (Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin). To increase the effectiveness of enzyme preparations, it is important to follow several rules for their use:
- correctly determine the dose of enzymes; for most patients, an adequate dose (in lipase equivalent) is 20,000 - 25,000; Usually, this dose of enzymes is contained in 1-2 tablets (medicine capsules);
- You need to take the medicine with every meal;
- take the medicine with the last portion of food, drinking a glass of alkaline mineral water; alkaline environment will protect enzymes from stomach acidity and maintain their activity;
- a course of treatment with enzyme preparations usually lasts 2–3 months, after which you need to reduce the dose of the medicine (to half) and continue treatment for another 1–2 months.
Currently, antacids (medicines that reduce stomach acidity) are used to increase the effectiveness of enzyme therapy and reduce the inflammatory process in the pancreas. Among them, the greatest preference is given to H2 receptor blockers (Ranitidine) and proton pump blockers (Omeprazole, Lanzoprazole). The dose of these drugs and the duration of treatment are determined by the attending physician.
Nutrition and medications
The use of medications and diet at the same time will help relieve the symptoms of chronic pancreatitis and eliminate the acute form of the disease. The list of required medications includes:
- painkillers and antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Baralgin, Drotaverine, Atropine, Platyfillin);
- means for reducing acidity and the action of digestive juices (Almagel, Phosphalugel);
- medications that replenish enzyme deficiency (Festal, Pancreatin, Mezim).
Salt solutions are used to restore water balance, and diuretics are used to eliminate edema. If there are signs of secondary development of cholangitis, antibiotics are also prescribed (Ampiox, Cefspan). Vitamin therapy is important.
In order to speed up the process of treatment and recovery, as well as prevent relapse of pancreatitis, it is important to follow a diet. The diet allows the consumption of the following products:
- porridges and cereal soups;
- side dishes of vegetables (stewed and fresh);
- vegetable broths and soups;
- light meat and fish products;
- dry white bread;
- light fermented milk products;
- non-acidic fruits.
It is prohibited to use:
- fried;
- smoked;
- semi-finished products;
- fast food;
- fatty meat and fish products;
- sweets, fresh baked goods and confectionery products;
- sour vegetables and fruits.
Rules for preparing and eating food:
- cook only with water, steam, bake in the oven without oil;
- Before cooking, remove rough skin (applies to vegetables), peel and excess fat (applies to fish and meat);
- eat fractionally, in portions of one hundred to two hundred grams;
- avoid prolonged fasting and overeating.
The last meal should occur no later than two hours before bedtime. Dinner should be as light as possible. It is permissible to be treated with traditional methods only with the permission of a doctor.
List of recommended products
The main condition for a disease such as pancreatitis of the pancreas is diet. This is the main principle of treatment. What is the essence of the diet? Use only those foods and dishes that will not irritate the mucous membrane of the pancreas. The following products can and should be used by people suffering from this type of inflammation.
- Wheat bread is stale, yesterday's bread.
- Soup made with recycled chicken or beef broth.
- Meat: chicken, veal, turkey. Method of preparation: boil, bake in the oven. The meat should not contain any seasonings.
- Fish, steamed, boiled or baked in the oven.
- Dairy products with a small percentage of fat.
- Boiled vegetables. If you want it raw, then only in grated form.
- Various types of pasta.
- Cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal).
- Baked fruits (meaning apples and pears).
- Jelly.
- Compotes, jelly, weak tea.
- Primary meat or fish broths. That is, fatty, high-calorie.
- Millet should not be consumed from cereals.
- Fatty meats, fish, poultry.
- Among vegetables, radishes, radishes, cabbage, sorrel and spinach are taboo.
- Fresh bread or any sweet products.
- Various types of sausages, canned food.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Ice cream.
- Strong tea, coffee.
Consumption of the above products will lead to a negative outcome, which is called “inflammation of the pancreas” (pancreatitis, simply put). In order not to play roulette with your health, remember the foods that you should not eat if you have this disease. After all, following a diet is already 60% of the positive outcome of the disease.
Diet for chronic pancreatitis
The diet for this disease is very unpleasant - it excludes all tasty foods. For example, chocolate, coffee, mushrooms, shish kebab, fried foods, smoked meats. Vegetables and fruits are boiled or baked, and then turned into pulp using a blender or meat grinder.
You need to eat several times a day. One meal should fit in a glass. But you should not allow yourself to feel hungry, so meals should be repeated at least once every three hours.
If the patient does not violate the diet, then painful sensations may not bother him. You need to know how to relieve pain if you don’t eat properly.
- Doctors prescribe drugs to relieve pain - Drotaverine, No-shpa. But if the pain does not stop within 24 hours, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
- Drugs to eliminate spasms in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medicines with a diuretic effect to reduce swelling.
Buckwheat diet for pancreatitis There is also an effective method for treating the pancreas.
Day one, two and three. Boil buckwheat powder in whey for 3 minutes. You need to take a tablespoon every hour. You don't need to eat anything else on this day.
Days four and five. Replace whey with low-calorie milk. You can eat this porridge as much as you like. Time is also not important. The main rule is that a person cannot starve.
Day six. Porridge with whey is consumed in the morning and evening, and during the day you can eat your favorite food.
Using these recipes you can treat the pancreas. But it is easier to do prevention than to treat.
Ambulatory treatment
As soon as the patient’s main symptoms are eliminated and the risks are reduced to the minimum possible, the patient is discharged and prescribed outpatient treatment and observation. During this period, the patient is entitled to complete rest, taking supportive, restorative and relapse-preventing medications, and diet.
In addition, the patient must periodically undergo medical examinations by the attending physician in the clinic to check for possible deterioration, as well as to record the state of health and well-being.
Chronic pancreatitis and home remedies
Folk remedies You can turn to home recipes only when the doctor has examined the patient and eliminated the need to stay in the hospital. Treat with home remedies.
Herbal decoctions. Take corn silk, dandelion root, violet, anise, celandine, knotweed. Take 2 tablespoons of herbs and pour them with a liter of hot, but not boiled, water. It is necessary to cool the broth. Take several times a day before meals. Drink the drink for two weeks, then take a break until the next exacerbation.
Dandelion. In the spring, you need to dig up the dandelion root, wash it and chop it finely. Pour boiled water, but it is advisable to observe the body’s reaction in the first three days in order to determine the dose. You need to take it for 2 months. For prevention, it is necessary to repeat twice a year: in spring and autumn.
Mint tea with honey. This remedy is absolutely simple, but has a large number of medicinal properties. Mint will help clear the gallbladder more quickly and improve the functioning of the pancreas. Honey contains 26 microelements from the periodic table, which are necessary for the functioning of the whole organism, in particular the gastrointestinal tract. You can drink mint tea in unlimited quantities and use this remedy for treatment or prevention.
Buckwheat with whey. This is ideal for the prevention of chronic pancreatitis, treatment with folk remedies. Pre-prepare the buckwheat - rinse and dry. Grind it using a blender. Separately, bring the whey to a boil.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before treating chronic pancreatitis, the doctor prescribes urine and blood tests and an ultrasound examination of the pancreas.
A blood test for pancreatitis shows an increase in ESR and a decrease in the amount of proteins. When analyzing urine, alpha-amylase is detected during the acute period of the disease, bilirubin is observed in the presence of obstructive jaundice. Ultrasound visualizes deformation of the gland, a change in the edge, or the development of nodules (cysts).
Stool analysis also evaluates the functioning of the pancreas.
In addition to the fact that the pain occurs in the left side in the hypochondrium, it can radiate to the area of the heart or peritoneum, and become encircling in nature. At the same time, he feels nauseous and vomits. There are particles of undigested food and a greasy sheen in the stool. The patient's weight decreases sharply.