One of the most important organs in the human body, which is actively involved in the process of digestion and more, is the pancreas. Most people are mistaken in thinking that all the most important processes (enzyme production, etc.) occur in the stomach. Of course, everything is interconnected for a person, and if at least one component part of the chain becomes temporarily inoperative or performs its functions poorly, this will affect everything. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the work of the pancreas, since without it a normal and healthy human existence is impossible.
What is important to know about the human pancreas
| Length | 14-22 cm |
| Width | 3-9 cm |
| Thickness | 2-3 cm |
| Weight | 70-80 gr |
| Structure | body, head, tail |
| Pancreatic hormones | • Insulin – reduces the concentration of sugar in the blood; • Glucagon – breaks down glycogen, increases blood glucose levels; • Somatostatin – inhibits the release of insulin and glucagon. |
| Digestive enzymes | • Alpha amylase - breaks down carbohydrates • Lipase - breaks down fats • Phospholipase A • Carbxylesterase • Trypsin - breaks down proteins • Chymotrypsin • Elastase • Carboxypeptidase A and B |
What does the human pancreas look like and work?
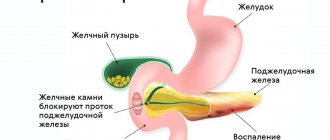
The pancreas consists of three sections:
- The head is the widest part of the organ, deflected downwards. A duct emerges from it, through which pancreatic juice enters the duodenum.
- The body is located across and slightly to the left of the spine.
- The tail is the narrowest and longest part of the organ.
The pancreas is a mixed secretion gland, that is, its main task is:
- Produce pancreatic juice , which contains digestive enzymes that break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the duodenum.
- Produce hormones in the blood that regulate protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
Why can a person’s pancreas hurt?
There are several diseases of the pancreas that are accompanied by painful sensations. This is often due to a disruption in the production of enzymes that break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates. In case of pathology of endocrine function (diabetes, cystic fibrosis and others), pain is not observed, since changes occur at the hormonal level.
Pancreatitis
This term refers to a group of diseases and syndromes characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. There are acute and chronic pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by:
- acute pain (also called pancreatic colic) in the upper abdomen, which often has a girdling character. A distinctive feature is that the pain increases after eating, but breathing and coughing do not affect it.
- nausea and vomiting , which does not bring relief. In the vomit, recently eaten food is first visible, and then mucus and bile. Even a sip of water can trigger vomiting.
- increased irritability, tearfulness, tremor of the upper extremities;
- increased body temperature;
- changes in the skin: increased humidity, pallor, jaundice.
Human liver
To understand how the liver works, drink 6 glasses of juice in a minute and name its composition
The cause of this condition may be a disease of the biliary tract or excessive alcohol consumption. These factors are the cause of the disease in 80% of cases.
Chronic pancreatitis develops when the organ itself is damaged (autoimmune, toxic damage) or due to disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems (usually the gastrointestinal tract). In 70% of cases, the cause is excessive alcohol consumption. An equally important factor is genetic predisposition.
There are three periods of chronic pancreatitis:
- Primary – up to 10 years. It alternates between periods of exacerbation and remission. The main symptom during an exacerbation is pain of varying intensity, nausea, sometimes vomiting, flatulence, and diarrhea.
- The second period (more than 10 years), it is characterized by disturbances in the functioning of both the stomach and intestines. It manifests itself as pain (usually dull, aching) in the upper abdomen and navel, constipation, and heaviness in the stomach.
- Complicated variant - can occur at any stage. It changes the intensity of pain, its nature and duration.
Pancreatic necrosis
Pancreatic necrosis is a form of pancreatitis in which many gland cells die simultaneously.
There are several types of this disease:
- unspecified;
- aseptic – the cause is often blunt trauma to the abdomen;
- fatty (enzymatic) - can be observed in acute pancreatitis, when enzymes affect surrounding tissues.
Symptoms of pancreatic necrosis are almost the same as those of acute pancreatitis:
- pain;
- nausea or vomiting;
- pain on palpation;
- the appearance of jaundice;
- flatulence;
- hyperglycemia.
Pancreatic stones
A rather rare disease, the cause of which no one still knows. It is believed that the problem is a violation of metabolic processes, which lead to an increased calcium content in pancreatic juice and, as a consequence, the formation of stones. With an absolutely healthy gland, such processes are not observed. There are predisposing factors:
- chronic pancreatitis;
- poor nutrition.
Most often, even in the presence of large stones, the disease is asymptomatic. However, there are such manifestations:
- cutting pain like colic in the upper abdomen;
- increased body temperature;
- vomiting or nausea;
- increased salivation.
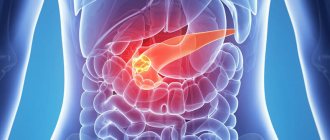
Pancreas cancer
Pancreatic cancer ranks 6th among other cancers. In 50% of cases, the tumor affects the head of the gland. The disease has four stages of development, and is most often detected when chemotherapy and surgery are impossible.
Main symptoms:
- Pain – occurs in 70% of cases and is associated with tumor growth into neighboring tissues and organs. Often the condition worsens in the evening and after drinking alcohol or fatty foods. When a tumor grows into the spine, pain is observed in the supine position.
- Jaundice is a fairly common symptom and is also observed in 70% of patients. Yellow discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes is associated with compression of the common bile duct, which disrupts the normal outflow of bile.
- Itchy skin – appears after jaundice and is associated with excessive concentration of bile acids in the blood.
- Unreasonable weight loss is the cause of intoxication and blockage of the ducts.
- Decreased appetite is constantly present. There may be an aversion to fatty or smoked foods.
- Increased body temperature, constipation.
Acute stomach
What condition do doctors call acute abdomen and why is it dangerous?
The appearance of digestive problems
We have found that digestive problems can occur due to a lack of enzymes. There are two main mechanisms by which the body lacks pancreatic enzymes. In the first option, the problem with the production of enzymes lies in the pancreas itself, i.e. the organ itself is not functioning properly.
Impairment of the pancreas can be a congenital problem or acquired, for example, after surgical interventions. As a rule, such a mechanism underlies serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), the symptoms of which will sooner or later lead to an appointment with a doctor8.
In the second option, the conditions under which enzymes can work correctly are violated. This is possible as a result of changes in the acidity of the intestinal environment, for example, due to inflammation or a change in the standard ambient temperature (36-37 ° C). The inflammatory process in the intestines can occur under various conditions: intestinal infections, allergic reactions (food allergies, atopic dermatitis).
How is the human pancreas treated?
Diet therapy
Basic principles of diet during exacerbation of pancreatic diseases:
- the first couple of days you are hungry;
- 1-1.5 liters of liquid (water, weak tea, rosehip decoction) in the absence of a gag reflex;
- eating thermally processed food 5-6 times a day (steamed, stewed, boiled) with an animal protein content of about 30%;
- products should be as gentle as possible (nothing hard, hot, or spicy).
Principles of diet during remission:
- in the diet the amount of animal protein should be 60%;
- reduced amount of fats and their complete exclusion from the diet in their pure form;
- easily digestible carbohydrates – about 350 grams per day;
- restriction in the use of table salt;
- the energy value of the diet should be at least 2500 kcal per day;
- Avoid sudden changes in diet.
Analgesics and antispasmodics
This group of drugs includes baralgin, analgin, paracetamol, no-shpa and others. Their main task is to relieve a painful attack and dilate the ducts, which helps pancreatic juice enter the duodenum. They are used only during the period of exacerbation of the disease. It is important not to use NSAIDs often enough, as this puts additional stress on the liver.
H2 blockers and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Prescribed to reduce secretion of the stomach and pancreas. PPIs also reduce the toxic effects of the immune system’s own cells on pancreatic cells, which further protects the organ.
The most effective drugs in this group: Nolpaza, Nexium, Pariet, Ultop, Omez.
Enzyme therapy
Particularly relevant in the presence of enzyme deficiency. Additional use of enzyme therapy helps get rid of diarrhea, flatulence, pain and heaviness in the abdomen. All enzymes are taken with meals 3-4 times a day. The most popular enzyme preparations are Mezim, Creon.
show more
Somatostatin drugs
This treatment method, according to clinical recommendations, is a method of questionable effectiveness. Drugs in this group are prescribed for the prevention of severe and complicated forms of pancreatitis.
Radiation therapy
Performed when a malignant tumor is confirmed. It can be either symptomatic, radical or palliative. Depending on the stage of the disease, radiation therapy can be carried out independently, or in combination with chemotherapy or subsequent surgery.
Duodenitis
Inflammation of the duodenum is called duodenitis. Let's study its 5 symptoms
Surgical intervention
It is a radical method of treatment. Most often performed in the case of pancreatic malignancy. The volume of the operation depends on the localization of the process and its prevalence.
Diagnostic methods. Screening
Usually, if symptoms appear, this indicates that the tumor has already grown beyond the pancreas. It is often at this stage that the patient is diagnosed. Currently, there are no recommended screening tests that would help diagnose the disease in its early asymptomatic stages.
Usually, first of all, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the abdominal organs to the patient, as the fastest, most accessible, safe and non-invasive diagnostic method. More informative studies are CT and MRI, they help to identify a pancreatic tumor and find out whether the cancer has spread to neighboring organs and regional lymph nodes.
Cholangiopancreatography is used to assess the condition of the bile ducts. To do this, a radiopaque substance is injected into the ducts endoscopically, through the duodenum, or with a needle through the skin, after which radiographs are taken.
PET scanning helps detect metastases. During the procedure, a safe radioactive substance is injected into the body, which accumulates in cancer cells and makes them visible in special photographs.
The most accurate method for diagnosing pancreatic head cancer is a biopsy. Tumor tissue for cytological and histological examination can be obtained in different ways:
- Using a needle through the skin, under CT or ultrasound guidance.
- During laparoscopy.
- During endoscopic ultrasound: a test in which an ultrasound probe is placed at the end of an endoscope inserted into the duodenum.
- During cholangiopancreatography.
How to keep your pancreas healthy at home
10 rules that will keep your pancreas healthy.
- Do not abuse alcoholic beverages.
- Use minimal amounts of sugar.
- Give preference to fresh vegetables and fruits.
- All products must undergo heat treatment.
- Dairy products should not be very fatty.
- Avoid baked goods. It is better to give preference to crackers and products made from wholemeal flour.
- Strong tea and coffee - in doses.
- The meat should be lean and cooked using the right amount of oil.
- The energy value of the diet should be approximately equal to daily expenditure (avoid overeating).
- If you violate the diet (fatty foods, smoked foods), use enzyme preparations with meals.
Risk factors
A normal cell becomes cancerous when certain mutations occur in it. It is often impossible to say exactly what caused the changes in DNA, so the causes of cancer of the head of the pancreas are unknown. Scientists only know about risk factors - various external influences and conditions of the body that increase the likelihood of disease:
- Bad habits: smoking (increases the risk by about 20%), alcohol.
- Low physical activity and excess body weight.
- A diet high in red and processed meats, low in fruits and vegetables.
- Family history (close relatives who have been diagnosed with cancer of the head of the pancreas), certain genetic defects and hereditary syndromes.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Stomach diseases: Helicobacter pylori infection, peptic ulcer.
- Viral hepatitis.
- There is evidence that the risks are increased by diseases of the teeth and gums.
Popular questions and answers
We discussed important issues related to the pancreas with general practitioner Tatyana Pomerantseva .
Which doctor treats a person's pancreas?
Initially, you need to contact a therapist to undergo general tests and examinations that will show which organ functions are affected. If there is a violation of the exocrine system (responsible for digestive enzymes), a referral to a gastroenterologist is necessary. In case of endocrine pathology, contact an endocrinologist.
What are the first signs of problems with the human pancreas?
Since the pancreas is a complex organ, the symptoms for each pathology are quite specific. Let us list the main signs by which one can suspect a disease of this organ: • pain in the upper abdomen (often encircling in nature); • nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief; • heaviness in the stomach after eating fatty foods; • suspected diabetes mellitus).
Maintaining digestion and treating enzyme deficiencies
If you have problems with digestion, enzyme preparations (more often called drugs to improve digestion) can help, the main task of which is to compensate for the lack of the body’s own enzymes. It’s not for nothing that this therapy is called “enzyme replacement”. It is critical that the enzyme preparation “mimics” the physiological process as closely as possible.
Today, there are various drugs to improve digestion. How to navigate the variety of means and make the right choice?
An effective enzyme preparation must meet the following criteria5,6:
- have an optimal particle size
- do not break down in the stomach
- quickly activate in the intestines
The drug Creon® meets all these requirements.
To learn more
1) Today, pancreatin minimicrospheres, which are contained only in the drug Creon®5,7, are recognized as the optimal particles. The invention of minimicrospheres was the result of many years of work to improve the effectiveness of enzyme preparations, which left far behind drugs in the form of tablets and capsules with other types of particles inside: pellets, mini-tablets, etc. In addition, Creon® minimicrospheres are produced using patented technology, which prevents other manufacturers from reproducing the same release form.
2) Creon® minimicrospheres are enclosed in a capsule that protects them from the destructive effects of the stomach. But that is not all. Each particle is covered with an acid-resistant coating in order to “reach” the intestines, where its work is necessary, completely intact. At the same time, some other encapsulated drugs can lose up to 30% of their activity6.
3) Creon® begins to work within 15 minutes after entering the intestines, improving digestion and thereby eliminating heaviness and discomfort after eating6.
Creon® has several dosages, including 10,000 IU of lipase - the minimum required dose of lipase to improve digestion in case of dietary errors, eating heavy foods and overeating. To obtain the effect, Creon®10000, like any enzyme preparation, must be taken with every meal - during breakfast, lunch and dinner.