gastritis
dysbacteriosis
dysbiosis
Helicobacter pylori
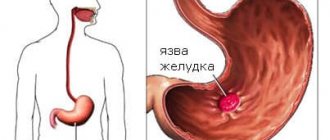
Helicobacter pylori infection in 80% of cases is the main cause of gastritis and gastric ulcers. An effective method for identifying this pathogenic bacterium is the 13 ST - urease test. In order not to get a false result from a breath test for Helicobacter , it is important to prepare for the test in advance. The main advantages of the urease test include painlessness, safety and accuracy.
Indications for the study
The appearance of individual symptoms or their combination is a direct indication for performing a breath test for Helicobacter Pylori. These symptoms include:
- emerging stool disorders in the form of chronic constipation or diarrhea;
- recurring heartburn;
- belching with a sour taste;
- discomfort and pain in the epigastric region, increasing after eating or at night (so-called hunger pains);
- nausea and vomiting;
- partial or complete loss of appetite;
- difficulty swallowing food.
As a rule, with chronic gastritis or gastric ulcer, the listed symptoms appear in combination.
Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori DNA
Helicobacter pylori, H. pylori DNA, quality
— determination of Helicobacter pylori DNA in feces using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with real-time detection.
The PCR method
allows you to identify the desired section of genetic material in a biological material and detect single molecules of microorganism DNA that are not detected by other methods. The principle of the method is based on a multiple increase in the number of copies of DNA sections specific to a given pathogen.
Using PCR analysis, it is possible to diagnose infection in the acute period and identify cases of carriage.
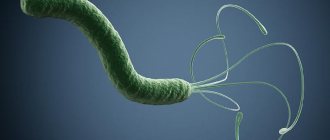
Helicobacter pylori
is a spiral-shaped bacterium that infects the stomach and duodenum. This pathogen can lead to various lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, the development of gastric and duodenal ulcers, and chronic gastritis.
Helicobacter is sensitive to high temperatures, but persists for a long time in a humid environment. The bacterium itself does not cause ulcers. It leads to stimulation of the formation of hydrochloric acid and disrupts the protection against the effects of acid on the gastric mucosa, leading to the development of an inflammatory process.
PCR is characterized by very high sensitivity (93–95%), which is an advantage when analyzing stool. Unlike bacteriological culture, this test can detect both spiral and coccal (non-culturable) forms of H. pylori. Due to the fact that the reaction reveals the DNA of the microorganism, the test is not used for differential diagnosis of a current infection or an infection in history - the test result will be positive for some time after the complete eradication of H. pylori, which is due to the identification of fragments of destroyed DNA of the microorganism.
It should be taken into account that the formation of stomach ulcers and the development of gastritis is associated with colonization of the gastric mucosa by toxigenic strains of bacteria. Infection with non-toxigenic strains leads to the development of these diseases in a small number of cases.
Diagnosis of helicobacteriosis in children
Diagnosis of helicobacteriosis in children presents certain difficulties. This is due to the child’s failure to perform the breathing maneuver when using the urease breath test, as well as the need for anesthesia when using invasive methods. Stool testing using RT-PCR is a good alternative to these methods and therefore can be successfully used in pediatric practice.
Indications:
- for the diagnosis of diseases caused by H. pylori: atrophic or antral gastritis;
- ulcers of the stomach and duodenum.
Preparation
To obtain a reliable result, the analysis should be carried out 14–21 days after the last dose of antibacterial drugs.
It is preferable to take a sample in the first 72 hours from the onset of the disease.
Feces are collected in a disposable container with a screw cap in a volume of no more than 1/3 of the container's volume. The feces must be freshly collected. The material is delivered to the medical office within 4–6 hours from the moment the analysis is collected.
The referral form must indicate the diagnosis and date of onset of the disease, information about taking antibiotics. When taking material, sterility must be observed.
Conditions that must be observed:
- freezing is not allowed;
- Long-term storage is not allowed (more than 5–6 hours);
- no transport media other than those specified are suitable;
- A container that is not tightly closed is not allowed;
- Biomaterial collected the day before cannot be examined.
Interpretation of results
The answer is given in a qualitative format: “detected” or “not detected”.
Reference values: not found.
"Detected":
- current H. pylori infection;
- History of H. pylori infection.
"Not detected":
- absence of H. pylori infection;
- incorrect collection of biomaterial for research.
What can influence the result?
- The presence of blood, bile, excess inorganic salts and other components in the stool sample can lead to a false negative result.
- Treatment with tetracycline, penicillin (aminopenicillins), macrolides (clarithromycin, azithromycin) and metronidazole may lead to a false negative result.
Progress of the procedure
The duration of the breath test for Helicobacter pylori is no more than 15 minutes. The test itself is divided into 2 stages:
The patient takes a comfortable position and fixes a special tube in the oral cavity, thereby preventing contact of the tube with the tongue.
Next, the patient is asked to take a urea solution. After entering the gastrointestinal tract, gas is formed under the influence of the urea solution. Together with the exhaled air, using a special device, the gas level is assessed and compared with the initial values.
Research results
After performing a urease test for Helicobacter pylori, each patient receives a conclusion indicating a positive or negative result. A positive result is indicated by the presence of IgA antibodies. In some cases, the results of diagnosing Helicobacter may be uncertain, so the test should be repeated after 14 days. The level of Helicobacter pylori contamination in the gastrointestinal tract is determined as a percentage and has the following form :
- Less than 1% is normal;
- No more than 3.5% - light degree of contamination;
- From 3.5 to 6.4% - moderate infection with Helicobacter pylori;
- From 6.5 to 9.4% - pronounced contamination of the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract with Helicobacter pylori.
If the percentage corresponds to indicators of more than 9.5%, then the person needs urgent treatment, as this indicates a severe degree of infection. The final interpretation of the test cannot be performed independently, since this must be done by a gastroenterologist.
Helicobacter: find to neutralize
A blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori is carried out if there are complaints of pain or discomfort in the abdomen, as well as for prevention if family members and loved ones have diseases of the stomach and duodenum. Laboratory tests for Helicobacter pylori are also performed to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- polyneuropathy, dementia);
- patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system (atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack);
- as part of a preventive examination, especially for people over 45 years of age who smoke.
To determine the presence of Helicobacter, an analysis of the content of immunoglobulins in the blood (IgG, IgM and IgA antibodies) is performed. These antibodies are produced by the body's immune system in response to infection. A positive test result indicates infection of the body. The results of the obtained tests will help the doctor correctly prescribe a set of treatment measures for you and thereby prevent the development of complications.
Sinevo performs a set of tests “Diagnostics of Helicobacter pylori ”, which includes blood tests for IgA, IgG and IgM antibodies to Helicobacter pylori.
The complex “Diagnostics of stomach diseases ” includes the following blood tests:
- Helicobacter pylori,
- IgG antibodies; total bilirubin;
- direct bilirubin;
- aspartate aminotransferase (AST);
- alanine aminotransferase (ALT);
- alkaline phosphatase (ALP);
- albumen; gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT);
- alpha amylase;
- serum iron;
- glucose;
- Complete blood count (CBC) + ESR.
The Diagnosis of Stomach Diseases complex is suitable for early diagnosis of H. pylori-associated chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers. The test results will be informative for determining the risk of peptic ulcers and stomach cancer.
In what cases are these tests prescribed:
- patients with complaints of pain and discomfort in the stomach;
- close relatives of patients with stomach and duodenal ulcers, stomach cancer;
- patients with diseases of the nervous system (depression, polyneuropathy, dementia);
- patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system (atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack);
- as part of a preventive examination, especially for people over 45 years of age who smoke.
Where to get tested for Helicobacter pylori
You can get tested for Helicobacter in Sinevo without an appointment, on a first come, first serve basis, in accordance with the schedule for collecting material in Minsk, Baranovichi, Bobruisk, Borisov, Brest, Vitebsk, Gantsevichi, Gomel, Grodno, Zhlobin, Lida, Mogilev, Mozyr, Molodechno , Novogrudok, Novopolotsk, Orsha, Pinsk, Polotsk, Rechitsa, Svetlogorsk, Slutsk, Smorgon, Soligorsk.
Preparing for the test
Obtaining a reliable and most informative result of a breath test for Pylori helps by following simple but effective rules. These include:
- 3 days before the test, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol and any alcohol-containing drinks and foods.
- Stop using antibiotics for one month.
- 1 hour before the test, it is permissible to drink no more than 10 ml of water.
- 6 hours before the test, it is strictly forbidden to eat, smoke or chew chewing gum.
- 1-2 hours before the test, you should thoroughly brush your teeth and use mouthwash.
In addition, 5 days before a breath test for Helicobacter, it is strictly forbidden to take antacids and anti-inflammatory medications. For 3 days, you should exclude from your diet foods that stimulate gas formation in the intestines (legumes, white cabbage, fresh baked goods, confectionery and foods with a high sugar content).
How to take the test correctly?
Carrying out the procedure for examining stool for the presence of pathogenic bacteria requires following certain rules. If preparation for analysis or collection of biological material is done incorrectly, the test results may show a false result. Feces have a certain shelf life. If the material is delivered to the laboratory late, the testing may also become unreliable.
Stages of collecting stool for analysis.
Preparing for the test
Preparatory measures for stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori include recommendations for following a certain diet, as well as adjustments in drug therapy (if any). If it is not possible to temporarily stop taking the prescribed medications, then this nuance must be reported to the doctor.
Substances contained in antibiotics and other categories of medications may cause incorrect interpretation of study data.
Recommendations:
Medical disposable containers for collecting stool for analysis. A few days before the procedure, you should stop taking laxatives or antacids;- within a month before the test, the patient should not take antibacterial drugs;
- You should not eat foods containing coarse fiber (beets, cabbage, radishes, radishes) for several days;
- for three days before the procedure, strong tea, coffee, hot spices and seasonings, red or orange vegetables and fruits are excluded from the diet);
- It is recommended to prepare dishes within three days before analysis only by cooking, stewing or steaming;
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages for several days.
Preparing containers
A sterile container for collecting biological material can be purchased at a pharmacy. When purchasing such a jar, the presence of contamination is excluded. As an alternative, you can use other container options (for example, baby food containers). An important nuance is their sterility. Containers must be as clean as possible from any type of contamination.
Collection of material
It is prohibited to collect feces from a diaper or toilet. The ideal option is to collect biological material from a pot or from a plastic bag. The container for storing feces should be one third full. The filled direction must be attached to the container.
How and for how long can the material be stored?
The container with stool is delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible. If it is not possible to quickly send material for analysis, you can use two storage options. In the first case, the feces are frozen once. In the second, they are stored for no more than two days at a temperature no higher than 4 degrees.
Other ways to detect Helicobacter pylori infection
In addition to the 13 CT-urease test, there are alternative methods for diagnosing Helicobacter pylori in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. The preferred diagnostic method is selected individually by the attending physician. Alternatives to a breath test include:
- Endoscopic techniques. We are talking about performing esophagogastroduodenoscopy. This method allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum by inserting an endoscope tube. Using this method, it is possible to detect erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane, as well as take a biopsy for histological examination.
- Laboratory analysis of stool. This method is also informative, but in order to avoid errors, 1 week before collecting biomaterial, it is necessary to avoid taking antibiotics. The analysis also allows you to identify signs of dysbiosis.
- Laboratory analysis of venous blood. The purpose of this study is to search for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori.
Who is recommended to have a stool test tested for Helicobacter?
Helicobacter pylori is present in the body for a long time without symptoms. Signs of disturbances in the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract appear only when bacteria are active. One of the main provoking factors is decreased immunity.
If a patient has certain diseases or individual symptoms, the test procedure for helicobacteriosis becomes mandatory.
Indications for analysis:
- carrying out antibacterial therapy (to monitor treatment results);
- erosions and ulcers of the duodenum or stomach;
- symptoms of dysfunction of the digestive tract (regular constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, pain in various locations);
- genetic predisposition to diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori (malignant tumors of the digestive organs, chronic pathologies of the digestive tract);
- progressive atrophy of the mucous membranes of the stomach;
- regular pain in the stomach after eating food;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- a sharp decrease in body weight in combination with other symptoms of abnormalities in the functional state of the digestive tract;
- presence of blood in vomit or feces;
- identified neoplasms and polyps in the digestive system;
- esophageal ulcer or gastroesophageal reflux.
We recommend watching the video: