Stomach flu
- this is not one, but a whole group of viral diseases, in which symptoms are pronounced, similar to intestinal pathologies, in particular gastroenteritis. The disease received its name due to the similarity of clinical signs with regular flu, namely:
- outbreaks during autumn and winter;
- rapid infection occurs, up to epidemics;
- catarrhal lesions are observed in the oropharynx;
- the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets (one of the methods);
- the disease lasts on average 7 days.
Those at risk are more likely to get sick
The group most susceptible to intestinal flu infection is young children under 3 years of age.
, about 50% of all intestinal problems are associated with this disease. It is worth noting that when breastfeeding, the baby is protected by the mother’s immunity, and the incidence of diseases during this period is extremely low. If the child is weaned, then in such cases infection is registered already from 3 months of age. After an illness, the child gains immune experience and the risk of further infections is reduced.
Older people get sick much less often; on average, this is every 4th case of intestinal infection.
Also included in the risk group is
people with weakened immune systems:
- in the presence of transplanted organs;
- cancer patients;
- for chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- HIV patients;
- pregnant women.
Diagnostics
The results of the following studies help a pediatrician or therapist make an accurate diagnosis:
- a blood test showing an increase in the level of leukocytes;
- stool analysis, where there is an increase in leukocytes, starch grains, as well as undigested muscle fibers;
- serological blood test;
- positive results of infection of cell cultures with viral particles of the patient’s stool;
- PCR method that examines blood and stool samples.
Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude a bacterial infection; the viral nature of the disease is confirmed by positive results of serological examination and bacterial culture.
Causes of intestinal flu
As mentioned above, the cause of this disease is viruses that have the ability to carry out their life activities in the epithelial cells of the small intestine.
Adenoviruses
They have increased resistance and survival, as a rule, they affect the upper respiratory tract, are accompanied by conjunctivitis, and the epithelium of the small intestine is also affected. This virus is especially dangerous for children under 2 years of age; adults, as a rule, have acquired immunity. The method of transmission is airborne, fecal, through contact with household items, food, water. Disinfection methods are ineffective; ultraviolet light is used to destroy viruses, or when heated to more than 60 degrees.
Rotaviruses
It selectively affects the upper respiratory tract and epithelial cells of the small intestine; during an exacerbation, it circulates in the blood and affects liver cells. Standard disinfection methods are not effective; the virus is very resistant and only dies when boiled. Remains viable on surfaces (eg fruit, door handles, towels) for up to 14 days.
Noroviruses (Norwalk)
It got its name from the city in the USA Norwalk, where an epidemic of “stomach flu” accompanied by vomiting was recorded. There is very little data about this virus, it is also very stable and has strong survivability, does not respond to standard disinfection methods, and dies at high temperatures. The disease spreads through water, food, contact household items, and seafood.
There are also Toroviruses and Astroviruses, but they are extremely rare.
Symptoms of rotavirus
The disease manifests itself 2–3 days after infection. Typical symptoms include:
- Pain in the stomach and intestines, rumbling in the abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting (especially common on the first day of illness and in severe cases of the disease)
- Diarrhea (it can last 3–5 days, and repeat every hour or a little less often up to 15 times a day)
- Constant urge to defecate
- Heaviness in the stomach and loss of appetite
- General weakness
- White coating on the tongue and swelling of the larynx
- Increase in temperature to 37–37.5 * C (appear more often with severe manifestations of the disease)
- The infection may be accompanied by damage to the upper respiratory tract - rhinitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx and tonsils.
How does stomach flu spread?
The disease spreads through infected people, through airborne droplets, and through feces
.
In other words, the virus spreads through contact objects, poorly processed foods, and neglect of personal hygiene. Intestinal flu spreads especially quickly in kindergartens, shared toys, tables, chairs, door handles, bed linen, pots.
I would especially like to note infection through bottled drinking water. There is evidence of large epidemics of intestinal flu that spread in this way. The fact is that these viruses can remain viable in water for months.
Prevention of rotavirus
Nonspecific prevention includes a set of sanitary and hygienic measures (regular hand washing, using only boiled drinking water, room ventilation, wet cleaning). Another important point is the timely isolation of a sick person who exhibits signs of acute respiratory viral infection and intestinal infection.
Gastroenterologists advise taking prebiotics and probiotics as a preventive measure. Probiotics, called “friendly bacteria,” are live microorganisms that aid digestion and improve protection against possible infections. Natural probiotics are found in fermented milk products: organic yogurt and cheeses, miso soup, sourdough bread, and sauerkraut. There are also probiotic supplements that come in capsules or drinks.
How does intestinal flu develop?
Viruses that cause disease enter the human body through the oral cavity, food, water, saliva, and dirty hands.
. They are not afraid of the acidic environment of the stomach; they easily overcome it and enter the intestines.
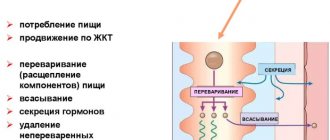
The main task of the intestines is to extract nutrients from food by breaking it down into its component parts using enzymes.
The entire surface of the intestinal walls is dotted with special villi, and these, in turn, are covered with epithelial cells - enterocytes. Intestinal influenza viruses, like parasites, penetrate these cells and begin to actively multiply, while the activity of the cell itself stops. Having reached critical filling, the cell literally explodes and mass infection of all surrounding cells occurs, the process repeats. As a result, first of all, the absorption of carbohydrates is disrupted; they begin to accumulate, creating a “plug” in the intestines. The body begins to supply liquid to dilute the resulting congestion, because of this, irritation of the intestinal walls occurs and reflex peristalsis is triggered, in simple words, diarrhea and diarrhea begin.
As a result of the overflow of the duodenum, food from the stomach cannot move normally, contractions of the walls begin and food comes out in the form of vomiting.
The immune system reacts to what is happening with the emergency production of specific antibodies, and the source of infection begins to decrease. Virus particles come out in the stool and begin a new round of infection.
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first appointment, the therapist listens to the patient’s complaints, studies the medical history, conducts a visual examination and palpation of the abdomen, measures body temperature and blood pressure.
To differentiate viral gastroenteritis from bacterial and determine the severity of the condition, laboratory diagnostics are performed, which may include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- examination of stool and vomit.
If necessary, the therapist refers the patient for consultation with a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist.
How does intestinal flu proceed, symptoms, signs
As has already become clear, this is essentially a group of diseases caused by various viruses, and the symptoms, as well as the course, are slightly different. On average, 7-10 days pass from the time of infection to the first manifestations. However, an infected person begins to infect others even before the first signs and symptoms of intestinal flu begin; this occurs towards the end of the incubation period.
As a rule, the onset of the disease is marked by a sharp rise in temperature of 38-40 degrees, diarrhea and vomiting. Less often, the patient begins to feel a loss of strength, a reluctance to eat, a headache, and may have a slight fever, but the next day, diarrhea and vomiting will definitely occur.
As a result of loose stools, the body rapidly loses fluid, dehydration occurs, this is very dangerous, especially for small children.
The gag reflex, as a companion to the disease, is also very dangerous, because it causes vomiting from everything, even from water. In such cases, hospitalization is necessary.
There may be nasal congestion and sore throat, especially when swallowing.
Temperature and fever last for 2 to 4 days; if this period increases, then most likely there is additional bacterial damage to the microflora.
Treatment
methods for intestinal flu in adults and children are the same. They rely on fluid replacement and proper nutrition to prevent dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, and malnutrition. Pharmacotherapy is also used for intestinal flu.
Bowel treatment can be done at home in the absence of symptoms requiring hospitalization. These include a fever greater than 38.5°C, blood in the stool, vomiting that prevents oral fluid intake, and symptoms of severe dehydration. In children, this is loss of consciousness, weakness, sunken and dry eyes, crying without tears, dry mouth and tongue, weight loss.
How to hydrate your body
To irrigate the body during intestinal flu, special medications are recommended that can be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription. Based on them, a liquid of optimal composition is prepared. If there is no access to a pharmaceutical drug, the patient can be given other lightly salted liquids, such as water, liquid tea, carrots or soup.
You need to drink a lot of liquid. Contrary to popular belief, Coca-Cola is not recommended for stomach flu because sugary carbonated drinks can make diarrhea worse. For the same reason, you should not drink fruit juice. It is worth knowing that cool liquids taken in small sips are better tolerated by patients.
How to prepare rehydration liquid
If it is impossible to use a pharmaceutical drug, you can prepare the irrigation fluid yourself. You will need the following ingredients:
- teaspoon of table salt;
- a teaspoon of baking soda;
- 0.5 cups of orange juice or 2 bananas;
- 4 teaspoons sugar.
All ingredients must be mixed and filled with boiled water to 750 ml.
What can you eat?
It is now believed that people without significant symptoms of dehydration can be fed as before the disease. This applies to both adults and children. The rule also applies to children who are breastfed or formula-fed. The latter need to be fed more often (every 3 hours). During intestinal flu, you should not starve patients or take long breaks from eating!
Diet
Both children and adults during stomach flu should avoid foods with a lot of sugar, fatty foods and foods cooked with fat. You can eat the traditionally recommended carrots, rice porridge or applesauce. However, they do not affect the duration of the disease, although they slightly improve stool consistency.
Drugs
Considering that the most important thing is to replenish fluids and continue nutrition, a child with intestinal flu can be given a probiotic with a proven effect or smecta. There is no justification for using activated carbon or tannins.
Medicines containing loperamide can only be taken by adults!
Questions and answers
How is rotavirus infection transmitted?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is fecal-oral, where the causative agent of the disease enters the environment along with the feces of the carrier or patient, and then on dirty hands into the body of a healthy person. Household items, food, dirty water - all this can become a source of infection.
What can you eat if you have rotavirus infection?
Recommendations for a patient with rotavirus infection include dietary table No. 46 with restrictions on the amount of carbohydrates and dairy dishes, as well as an increase in the amount of protein foods. This diet plan is aimed at restoring the body’s immune system and stabilizing the digestive system that has been hit by the virus.
How long does rotavirus infection last?
The duration of the disease depends on the state of health of the person and his immune system. It may take 10-15 days from the moment of infection to complete recovery, where the first 6-7 days are an acute period with a whole bunch of unpleasant symptoms. The incubation period lasts from several hours to five days, after which the infection immediately makes itself felt with a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.