Useful articles / August 8, 2019
People are accustomed to blaming unhealthy food and stress for the occurrence of gastritis and ulcers, although in fact most problems with the gastrointestinal tract are due to the insidious bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped parasitic bacterium that can penetrate the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. It produces toxins that affect the mucous membrane of these organs and cause pathological changes. The peculiarity of Helicobacter pylori is that the aggressive acidic gastric environment is a very comfortable habitat for it. And, if most bacteria die in such an aggressive environment, then Helicobacter adapts well to it. According to statistics, more than 80% of the Russian population is infected with this bacteria.
To accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment for gastrointestinal problems, the patient must be tested for the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body . What laboratory diagnostic methods exist today and how accurate are they?
Detailed description of the study
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that affects the gastric mucosa due to its resistance to acidic environments.
It is assumed that infection with this infection occurs at an early age and is transmitted to children from parents or in preschool institutions. The most likely route of infection is considered to be the fecal-oral route of infection when living with an infected person in the same house, as well as during a long stay in a large group.
In addition, the oral route of transmission of infection through saliva and kissing has been recorded. There have been suggestions about the possibility of Helicobacter pylori infection during fibrogastroscopy - an examination through an endoscope that has been insufficiently treated with disinfectants.
After penetration into the stomach, Helicobacter pylori colonizes its mucous membrane, causing gastritis of the antrum of the stomach. The bacterium is protected from exposure to an aggressive acidic environment by producing alkali (ammonia) and some other substances that damage the gastric mucosa.
In response to Helicobacter pylori entering the body, the immune system produces antibodies. Initially, antibodies of class A and M are formed, they are soon replaced by immunoglobulins of class G. In most cases, the body is not able to completely defeat this infection, which predetermines the preservation of a high level of class G antibodies to it.
When combined with other unfavorable conditions, such as stress, poor diet, and infection with this bacterium, it leads to the formation of erosions and stomach ulcers. The following symptoms are noted:
1. pain in the upper abdomen (on an empty stomach);
2. nausea;
3. belching air;
Some people are asymptomatic when infected with Helicobacter pylori. Long-term damage to the gastric mucosa by this bacterium leads to the development of atrophy and decreased acid production. The risk of developing stomach cancer and lymphoma increases. A particularly high risk of developing cancer is observed in those whose relatives suffered from it.
Determining the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the body is important for early diagnosis of gastric pathology. Class G antibodies are produced several weeks after infection and are detected throughout life in the presence of bacteria in the body.
This test is relevant, in combination with other antibodies (IgA, IgM), as a primary diagnosis of this infection, but is not recommended for assessing the effectiveness of treatment, because IgG may persist for a long time even after successful therapeutic measures.
How is the Helicobacter test interpreted?
If the research is qualitative, then there can be only two results - “positive” or “negative”. If a quantitative method is used, the analysis standards will depend on the specific laboratory, and only a doctor can interpret them.
How can you become infected with Helicobacter pylori?
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is called an intrafamilial infection and it occurs in 80% of the Russian population. The main modes of transmission: fecal-oral, oral-oral, household. This could be kissing, sharing utensils, eating insufficiently clean vegetables and fruits, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules... Most often, infection occurs in childhood through household contact. If, for example, parents have the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in their bodies, then it is passed on to their children. Another question is in what period of a person’s life it will manifest itself. Do not forget that most diseases of the upper digestive tract occur precisely because of this bacterium. Gastroenterologists warn that 100% of people with Helicobacter develop gastritis over time. Therefore, it is important to detect it and undergo treatment on time.
References
- Ivashkin V.T., Maev I.V., Abdulganieva D.I., Alekseenko S.A., Ivashkina N.Yu., Korochanskaya N.V., Mammaev S.N., Poluektova E.A., Trukhmanov A. S., Uspensky Yu.P., Tsukanov V.V., Shifrin O.S., Zolnikova O.Yu., Ivashkin K.V., Lapina T.L., Maslennikov R.V., Ulyanin A.I. . Practical recommendations of the Scientific Community for Promoting the Clinical Study of the Human Microbiome (NSOM) and the Russian Gastroenterological Association (RGA) on the use of probiotics for the treatment and prevention of gastroenterological diseases in adults. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2020
- GuevaraB, CogdillAG. Helicobacter pylori: A Review of Current Diagnosticand ManagementStrategies. DigDisSci. 2020
- Choi IJ, Kim CG, Lee JY. Family History of Gastric Cancer and Helicobacter pylori Treatment. N Engl J Med. 2020
Symptoms of infection
The test for Helicobacter pylori is carried out in cases where signs of gastrointestinal diseases appear:
- nausea (in combination with other symptoms);
- pain in the esophagus or stomach;
- heartburn;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- blood in stool or during vomiting;
- weight loss;
- poor appetite.
However, Helicobacter pylori is not considered dangerous in all cases.
If the above symptoms do not bother you, and the test shows the presence of this bacterium, then it does not pose a threat to health.
Preparation
An analysis for Helicobacter pylori involves the detection of specific antibodies in the blood serum, which are produced by the immune system when the pathogenic organism enters a person. These antibodies can be detected in the laboratory using simple chemical reactions. When detecting uninvited guests, the doctor must take into account that a sufficient amount of time must pass for the development of immune agents. That is, the formation of antibodies requires at least 7–10 days. It is this interval that is necessary for the appearance of an immune response to the pathogen.
The most accurate data can be obtained with the help of special preparation for analysis. It includes the following activities:
- a few days before the study, it is important to give up alcoholic beverages;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, you should avoid heavy physical activity and intense sports;
- Before the procedure you should not eat food, you are only allowed to drink water:
- collection of biological material is carried out in the morning;
- The study is carried out before the person starts taking any medications. If the patient is already undergoing therapy with certain medications, this must be reported when donating blood.
Accurate results can be obtained with proper preparation.
If the preparation rules are violated, a false positive response is possible. An incorrect result also often occurs in cases where the patient has undergone treatment, but antibodies are still present in the blood.
Important! A false negative analysis is observed if too little time has passed after the body has been damaged and the immune system has not had time to develop antibodies.
Indications for the procedure
Heartburn as a symptom of Helicobacter disease.
Despite the fact that Helicobacter pylori often parasitizes the human body, its presence does not always lead to pathological disorders.
A large number of people do not experience symptoms when this bacterium appears. If certain symptoms appear, a person should consult a gastroenterologist, who, after a preliminary examination, will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Like other diagnostic techniques, ELISA analysis has its pros and cons.
Advantages:
- high efficiency (about 95%);
- the ability to detect antibodies to the pathogen in the early stages of disease development;
- assessment of the dynamics of pathology and the effectiveness of drug therapy;
- safety and possibility of multiple use;
- availability.
Enzyme immunoassay has its advantages and disadvantages
Despite the large number of advantages, there are also disadvantages. Among them are:
- inability to detect infection from the first days of infection;
- the analysis shows the presence of antibodies, but not the bacterium itself;
- when Helicobacter pylori enters the body for the first time, the response is false negative;
- a false positive result occurs after the disease has been cured for some time.
An important aspect in conducting ELISA is the level of qualifications of laboratory staff and the equipment used. It is believed that the most accurate results can be obtained in private clinics, which have modern and expensive microscopes and other research equipment in their arsenal. Such an analysis will cost more than in a public hospital, but its results will be more accurate.
What can affect the result
Certain circumstances may affect the accuracy of the analysis. For example, in older patients, the body's immune response is slower, so it takes longer to produce antibodies. The same applies to people with very weakened immune systems, especially children who are often ill, as well as patients with various systemic pathologies.
Another group of patients who often experience a false-negative response are patients undergoing therapy with immunosuppressants. All these features must be taken into account by the doctor when interpreting the results and making a diagnosis.
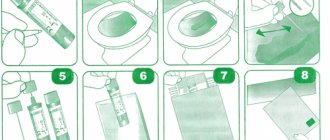
Express test for detecting Helicobacter pylori in the blood
A visit to a laboratory or other medical facility for testing to detect Helicobacter pylori is not required. You can purchase the test at a pharmacy. Doing it at home is not at all difficult.
The test allows you to detect antibodies to Helicobacter pylori in whole blood.
The tests most often include:
- Indicator tablet, which is packaged in an individual vacuum bag.
- Reagent for diluting the obtained blood sample.
- Pipette for adding blood to the tablet.
- Scarifier suitable for single use.
- Antiseptic wipe.
- Instructions for use.
If the test was stored in the refrigerator, then it must be kept at room temperature for 20 minutes before use. Then the test is removed from the packaging and laid out on a dry, clean and flat surface. The indicator window should be located at the top.
Hands should be washed with soap, after which the package with a disposable antiseptic wipe should be opened and the finger from which the blood will be drawn is treated with it.
The next step is to open the scarifier. With its help, a small puncture is made on the tip of the finger to allow blood to flow out.
Blood is drawn into a pipette. One drop of liquid is enough to perform the test. It is introduced into the round window located on the express test tablet. After the blood is in the indicator, 2 drops of the reagent are added to it. Leave the test for 15 minutes, after which you can evaluate the result.
A line appears in the test area of the tablet. If there is only one line, then the person is not infected with Helicobacter pylori. If there are two lines, then the result can be considered positive. Thus, the total testing time does not exceed 20 minutes.
How to donate blood
To donate blood, a person must receive a referral from the attending physician and appear at the clinic at the appointed time. Biological material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a vein on an outpatient basis. Immediately after this, the patient can go home.
Blood for Helicobacter is donated from a vein
Blood and stool tests
20–30 days before stool examinations, you should stop taking antibiotics, and three days before, you should stop using coloring products. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach. One day before, you need to eliminate fatty foods from your diet.
The results of stool tests are released the next day. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test is just as quick, but a Western blot test, which requires more time and more complex equipment, can take up to six days.
A stool test only shows the presence or absence of infection. Blood tests provide more accurate results and reveal the presence or possibility of developing peptic ulcers.
Preparing for analysis
To obtain objective indicators, you need to carefully prepare for testing for Helicobacter pylori.
Necessary preparations:
- Complete smoking cessation the day before the test. Nicotine negatively affects the gastric mucosa, distorting test results.
- Complete abstinence from alcohol. The reason is the same.
- Prohibition on drinking tea and coffee, which negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Temporary restriction on food intake for 8 hours before analysis.
Since blood for Helicobacter testing is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, you can take some food and water with you to the clinic.
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori
The endoscopic examination method is considered the most accurate test. A biopsy of the gastrointestinal tract reveals not only the presence or absence of bacteria, but also determines the stage of the disease, and also allows you to immediately find out whether the organs are affected or not.
This study is carried out using a gastroscope (a long tube inserted into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth and equipped with a camera and a device for taking a tissue sample). In addition to taking biomaterial for biopsy, the gastroenterologist visually examines the condition of the walls of the duodenum and stomach.
Two hours before the biopsy, you should not smoke or drink, and your last meal should be 12 hours before.
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori can be performed under anesthesia. The procedure lasts about twenty minutes. The doctor will determine the ulcer, if any, during the examination, and the patient will receive the test results the next day.
Our clinic has the opportunity to conduct FGDS with Helicobacter pylori and other studies.