basic information
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that disrupts the digestive system.
Helicobacter pylori is considered an enemy of the human digestive system. Helicobacter is a pathogenic bacterium that parasitizes the duodenum and stomach.
When a bacterium appears in the human body, it produces a large amount of toxins that damage the mucous membranes of organs.
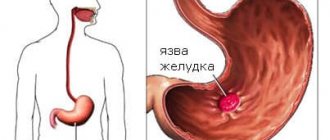
Against the background of its influence, the appearance of diseases such as ulcers, gastritis, etc. is observed.
Infection with the bacterium occurs when personal hygiene rules are not observed. If a person eats unwashed fruits and vegetables, this can lead to the appearance of Helicobacter pylori. If a person experiences a failure of the protective reaction or experiences a stressful situation, this leads to the appearance of symptoms of the disease. In most cases, patients experience belching, nausea, vomiting, and a burning sensation.
To ensure rational treatment of the disease, patients need to be correctly diagnosed. In most cases, a stool test is prescribed to diagnose the disease. This procedure is completely painless, which allows it to be used for various categories of patients. With its help, you can determine the presence of bacteria, even if it is in insignificant concentrations.
Helicobacter pylori is a rather dangerous bacterium. That is why it is necessary to identify it in a timely manner, which will ensure the effectiveness of treatment.
References
- Peptic ulcer disease. Clinical recommendations. Russian Gastroenterological Association, 2022. - 37 p.
- Kasper, D., Fauci, A., Hauseret, S. Harrison`s Principles of Internal Medicine 19/E (Vol.1). Dennis Kasper, Anthony Fauci, Stephen Hauseret all. McGraw-Hill Education, 2015.
- Ivashkin, V.T., Maev, I.V., Lapina, T.L. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in adults. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology, 2018. - T. 28(1). — P. 55-70.
- Antsilevich, L.M., Yagudina, L.A. Practical application of enzyme immunoassay in the diagnosis of diseases. PM, 2014. - No. 3(79).
Indications for the procedure
Heartburn as a symptom of Helicobacter disease.
Despite the fact that Helicobacter pylori often parasitizes the human body, its presence does not always lead to pathological disorders.
A large number of people do not experience symptoms when this bacterium appears. If certain symptoms appear, a person should consult a gastroenterologist, who, after a preliminary examination, will prescribe appropriate treatment.
When is a stool test for Helicobacter prescribed?
The main indications for analysis are patient complaints about:
- acute pain in the stomach after eating;
- involuntary belching;
- continuous heartburn;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- bloating;
- diarrhea or constipation that lasts more than three days;
- sudden weight loss;
- discharge of blood in vomit and feces.
Not all symptoms may indicate the development of an infection in the body, but in any case it is necessary to undergo a laboratory examination. Based on the results, the doctor will be able to definitively confirm or exclude the presence of such microorganisms.
The doctor may also prescribe a stool test to determine Helicobacter for those patients who have a genetic predisposition to chronic ulcers, gastritis, and stomach cancer.
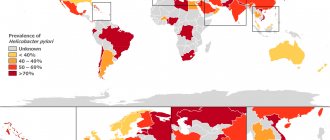
In almost all cases, infection occurs from relatives or in crowded places (schools, kindergartens).
Features of the analysis
A stool test will help detect Helicobacter pylori.
The most convenient and painless method for diagnosing Helicobacter is stool analysis. In this case, the polymerase chain reaction is studied.
This research method is used for children, seriously ill and elderly people.
Bacterial analysis allows you to most accurately determine the presence of a microorganism even in that case. If the active forms of bacteria change, and their concentration in feces decreases.
To obtain reliable results, the patient must collect the material correctly. A stool test should be performed only after a month has passed after completing a course of antibiotic therapy. Three days before collecting the material, it is recommended to exclude foods that have a coloring pigment from the diet.
Also, you should not eat foods that contain large amounts of coarse fiber. Doctors prohibit taking medications that enhance intestinal motility.
What is Helicobacter?
The name Helicobacter pylori translates as “spiral pyloric.” It is tied to the characteristic shape of the bacterium, localization in the pyloric region (the border zone of the stomach with the duodenum). The microorganism has flagella that help it move even in thick mucus.
Helicobacter is able to withstand the acidic environment of gastric juice. For life support, it uses the energy of hydrogen molecules produced by intestinal bacteria.
The bacterium synthesizes about 20 enzymes
The most famous Helicobacter enzymes:
- oxidase,
- urease,
- catalase.
The characteristics of the microorganism include:
- the difficulty of isolating by culture, since Helicobacter does not grow on conventional nutrient media;
- a long period of absence of symptoms indicating infection;
- the ability in a “dangerous” situation to transform into a spherical shape and be covered with a protective film.
The aggressiveness of the bacterium is the main cause of the atrophic form of chronic gastritis with further transition to peptic ulcers and cancer.
It is impossible to detect a spiral shape in feces, since the intestinal environment is unfavorable for the existence of Helicobacter. There is no necessary acidity, little oxygen, and strong destructive enzymes of bile and pancreas. Therefore, the coccal form of the bacterium is found in the stool.
Results
- there are several ways to determine Helicobacter in stool using a laboratory method;
- each analysis option has its own advantages and disadvantages;
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take several tests of different types;
- feces for analysis are collected taking into account a number of rules;
- a few days before the procedure, coarse fiber, fried, fatty foods, hot spices and seasonings, alcohol and any orange or red fruits are excluded from the diet;
- the container for feces must be sterile (pharmacy containers are the best option).
Video on the topic: Why is the Helicobacter pylori bacterium dangerous?
Test for intestinal dysbiosis
A study that allows you to assess the ratio of normal intestinal microflora and opportunistic microorganisms, as well as the presence of pathogenic bacteria. The study also reveals the sensitivity of pathogenic microbes to antibiotics and bacteriophages. Preparation for the analysis, in addition to following general recommendations, is not required, however, it should be noted that the accuracy of the result may be influenced by antibacterial therapy. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct research before taking antibiotics.
How to evaluate test results?
Decoding the research results is the job of a specialist doctor. You should not resort to independent interpretation or use the services of friends. The assessment is carried out based on a set of characteristics. PCR gives the following result:
- negative, if the Helicobacter genotype has not been isolated, is found normally;
- positive if the patient is at the height of the disease or has a history of infection.
During bacteriological examination:
- a zero number of bacteria was detected or Helicobacter is absent;
- if the number of microorganisms is greater than zero, helibacteriosis is confirmed;
- the sign S means sensitivity to the declared antibiotic;
- R - indicates resistance (resistance) to the drug;
- I - moderate sensitivity.
Stool culture allows us to give not only qualitative, but also quantitative characteristics of Helicobacter pylori infection. To do this, the degree of bacterial growth is taken into account:
- 1st degree - weak growth is observed on a liquid medium, on solid samples - no growth;
- 2nd degree - grows up to 10 colonies;
- 3rd degree - the number of grown colonies reaches 100;
- Grade 4 - the prevalence and activity of the pathogen is very active, more than 100 colonies grow.
The last two degrees are considered the most reliable sources of information about the participation of Helicobacter in pathological changes in the stomach.
Testing is carried out using enzyme immunoassay with standard sera
Immunological tests show a negative result if the pathogen antigen is not detected, positive - in the presence of helicobacteriosis. The reliability of immunological and cultural methods is significantly inferior to PCR; their implementation requires a massive prevalence of the pathogen in feces.
How to properly collect feces
To avoid unreasonable deviations in the results of the analysis and to make the study more informative, you should also follow the rules for collecting stool. There are only a few of them and they are simple:
- Only freshly excreted feces are collected for research;
- the sample is transported only in a plastic disposable container;
- Urine and menstrual blood are not allowed to enter the material.
Collection technique:
Before collecting stool, first urinate in the toilet and flush. Next, collect the stool by natural defecation into a toilet or bedpan. Then the feces are spooned into a clean, disposable container with a screw cap in an amount of no more than ⅓ of the container's volume. Close the container with a lid and deliver the stool to the laboratory as soon as possible.
Following these simple recommendations significantly increases the chances of obtaining reliable information.
Deviation from the instructions for collecting biomaterial may lead to erroneous research results.
Immunological research methods
The essence of the immunological analysis is the identification of antibody + antigen complexes in which the foreign agent is Helicobacter. More common use is for blood testing. But in fact, indirect signs of the presence of the antigen can be confirmed by the presence in stool, saliva, urine, and in pregnant women in the amniotic fluid.
The methods use ready-made “tagged” antibodies. When they treat the patient's stool containing antigens (remnants of Helicobacter), a compound reaction occurs with standard antibodies. The duration of the study is one day. A stool test for Helicobacter antigen is prescribed if the patient has any symptoms of digestive disorders.
The most common option is primary screening of the population (examination of all applicants or certain groups) who do not have specific complaints. It is not used in Russia due to the lack of a sufficient number of immunological tests in clinic laboratories.