The urease test helps determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which causes gastrointestinal diseases. Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that infects the walls of the stomach and duodenum. The proliferation of Helicobacter provokes the development of gastritis, ulcers, and gastroduodenitis.
When Helicobacter pylori enters the stomach, due to its spiral shape, it attaches to the walls of the stomach and begins to secrete an enzyme - urease. Urease disrupts the acid-base balance in the stomach, the concentration of ammonia increases, and this leads to an increase in the level of hydrochloric acid. In addition, the level of the hormone gastrin and the enzyme pepsin increases. Helicobacter Pylori begins to secrete lipase, mucinase, protease, they in turn destroy the upper layer of the gastric mucosa, and gastrin and pepsin corrode the walls of the stomach. In these places, inflammation begins, turning into erosion and then into an ulcer.
For Helicobacter, unlike other bacteria, the stomach is an excellent environment for life. Urease, produced by bacteria, can break down urea. It is due to this function that the urease test is based. It helps to identify the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body.
The essence of the method
The test is based on the ability of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium to produce the enzyme urease, which breaks down urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. Helpil systems are disposable discs impregnated with chemical reagents: urea and acid indicator. Tissue samples obtained during endoscopic examination are placed on the dry surface of the disc. In the presence of bacteria, urea decomposes within 3 minutes, and the resulting carbon dioxide turns the indicator blue.
The 13C-urease breath test for the determination of Helicobacter pylori is a laboratory diagnostic technique for infection caused by Helicobacter pylori, based on the analysis of a special reagent in exhaled air samples, the content of which changes under the influence of the urease enzyme secreted by the bacterium.
Synonyms Russian
Breath test with 13C-labeled urea, 13C-UDT.
English synonyms
The urea breath test (UBT).
Units
‰ (ppm).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Exhaled air.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 72 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 6 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- The study is carried out no earlier than 6 weeks after the end of the last dose of antibiotics (for any reason) and bismuth preparations.
- Two weeks before the study, you must stop (in consultation with your doctor) taking proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole) and type 2 histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine, nizatidine, roxatidine).
- The study is carried out no less than 24 hours after fibrogastroscopy (FGDS) or before it is performed.
General information about the study
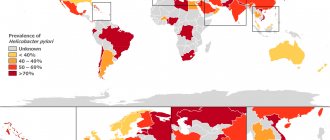
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative bacterium that is found in various areas of the human stomach and duodenum. Helicobacter pylori infection in the world is quite high (according to some data, at least 50% of the world's population), but in most carriers the infection is asymptomatic. The microorganism was isolated in 1983 by Australian scientists Robin Warren and Barry Marshall, who proved its role in the development of recurrent stomach ulcers and chronic gastritis. Later, data appeared on the influence of Helicobacter pylori on the development of stomach tumors and MALT lymphomas (lymphomas from lymphoid tissue of the gastric mucosa).
Helicobacter pylori is able to survive in the aggressive acidic environment of the stomach, including due to the intensive production of a special enzyme - urease. Urease breaks down urea to form ammonia, which neutralizes the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice and thus ensures that the acidity level (pH) is comfortable for the bacterium.
Among the diagnostic methods for determining Helicobacter pylori infection, the urease breath test has recently been increasingly used. This is a non-invasive study (that is, without fibrogastroscopy and biopsy of the gastric mucosa), based on the ability of bacteria to secrete urease. The main reagent in this test is 13C-urea, in which the 12C carbon atom is replaced by a 13C isotope. If Helicobacter pylori is present in the stomach, the urease produced by the bacterium breaks down the 13C-urea that entered the stomach with the test solution into ammonia and 13C-carbon dioxide, which is then absorbed into the blood, enters the lungs and is excreted with exhaled air.
Immediately before the test, the patient needs to drink 200 ml of orange or grapefruit juice to slow down gastric emptying. After 5-10 minutes, a control air sample is taken - the patient exhales into a special sealed bag, which is then closed and labeled accordingly. To ensure the accuracy of the test, it is especially important to exhale the last (alveolar) part of the air. Then the patient is given to drink 50 ml of a urea solution labeled with the 13C carbon isotope. This solution is tasteless and odorless; taking it is not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations. The solution is prepared immediately before administration; it must be drunk within five minutes after preparation. Adults drink the entire prepared solution (50 ml), and children from 5 to 12 years old drink half. Then you should be in a calm state for half an hour so that the results of the study are not affected by carbon dioxide released during physical activity. After 30 minutes, a second air sample is taken, the bag with which is also hermetically sealed and labeled. Air samples are then analyzed using an infrared spectrometer to determine the 13C/12C isotope ratio. If the patient is infected with Helicobacter pylori, then an increased amount of 13CO2 will appear in the second air sample compared to its content in the first (control) sample.
What is the research used for?
- To determine Helicobacter pylori infection in diseases of the stomach and duodenum, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of anti-Helicobacter therapy.
When is the study scheduled?
- Primary non-invasive diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in diseases of the stomach and duodenum;
- monitoring the effectiveness of eradication (anti-Helicobacter) therapy;
- the presence of acid-related and Helicobacter pylori-associated diseases in the family (among those living together);
- in case of refusal of fibrogastroscopy or impossibility of performing it;
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0 - 3 ‰.
The result of a urease breath test indicates the difference between the isotope ratio determined for the patient and the standard isotope ratio, measured in thousandths - ppm:
- negative urease activity – values less than 4 ‰ – correspond to the absence of urease activity and, therefore, the absence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach;
- positive urease activity - values of 4‰ or more - is characteristic of helicobacteriosis and, as a rule, is accompanied by clinical manifestations of gastritis, duodenitis, esophagitis.
At subthreshold values from 3‰ to 4‰, asymptomatic carriage of Helicobacter pylori is possible, which may require repeating the urease breath test or other tests for helicobacteriosis, taking into account a combination of clinical factors.
Main features of the testing methodology
Helicobacter can cause stomach or duodenal ulcers.
The Helicobacter group refers to bactericidal microorganisms located in the mucous membrane of the human stomach. Visually, these microorganisms look like small spirals.
These bacteria are often located on microscopic villi of the epithelium located on the inside of organs involved in the digestive system.
It is these bacteria that are considered the main causative agents of disorders such as stomach or duodenal ulcers.
Thanks to the information obtained by scientists as a result of testing the microorganisms Helicobacter pylori, it is possible to confidently determine the specific diagnosis of a patient. In addition, a pre-established diagnosis makes it possible to prescribe a course of treatment that will be particularly effective in the initial stages of the disease.
The testing methodology used is considered one of the most accurate and in demand in the field of modern medicine by specialists from various private industries. You should also familiarize yourself in detail with the characteristics of this type of bacteria:
- Bacteria are in most cases located in the lower part of the digestive system;
- When a bacterium interacts with air, it instantly dies;
- Diseases resulting from exposure to these bacteria are transmitted through saliva or other types of mucus;
- When this bacterium enters the human body, the process of moving to the stomach area immediately begins.
As you know, the stomach contains hydrochloric acid, which cannot cause any harm to bacteria such as Helicobacter. Under such conditions, the bacterium is able to penetrate deep into the structure of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs without any obstacles. Such exposure leads to disorganization of the digestive system in general and indigestion in particular.
Instructions
Dear comrade!
Here are a number of questions that will help you determine some of the properties of your personality. There can be no “right” or “wrong” answers here. People are different, and everyone can express their opinion. When answering a question, you must choose one of the answers - the one that most closely matches your views, your opinion about yourself. You need to answer as follows: put a clear cross in the appropriate box on the answer form. The left cell corresponds to the answer “A”, the middle one to the answer “B”, the right one to “C”.
DO NOT WRITE ANYTHING ON THE QUESTIONNAIRE ITSELF!
If something is not clear to you, ask a psychologist.
When answering questions, adhere to the following 4 rules:
- You don't need to spend a lot of time thinking about your answers. Give the answer that comes to mind first. True, sometimes the questions will not be formulated in as much detail as you would like. In this case, when answering, try to imagine the average, most common situation for you, which corresponds to the meaning of the question, and choose an answer based on this. You need to answer as accurately as possible, but not too slowly, approximately 3-4 questions per minute. Then it will take you about an hour to fill out the entire questionnaire.
- Try not to resort too often to intermediate answers like “I don’t know”, “something in between”, “sometimes”, “when how” and others, try to choose extreme, more definite answers.
- Be sure to answer all the questions in a row, without leaving anything out. Perhaps some questions will not seem very suitable to you, but even then try to find the best answer, the most accurate. Some questions may seem personal to you, but you can be sure that the answers will not be disclosed and will be used only for scientific purposes.
- Answer sincerely and honestly! Do not try to make a good impression with your answers, they must correspond to reality. We hope that you will answer without being guided by anyone, expressing only your opinion. In this case:
- You will be able to get to know yourself better.
- You will help us a lot in our work.
If everything is clear, then turn the page and get to work.
Preparatory procedures
It is necessary to stop taking medications before testing for Helicobacter.
In order to ensure the most accurate test results, certain preparation measures will have to be taken.
To avoid any violations, it is advisable to drink only drinking water before the procedures.
It is advisable to stop using antibiotics and other drugs a few weeks before the tests, the list of which includes:
- Ranitidine;
- Nolpaza;
- Nexium;
- Kvamatel;
- Paries.
The components of the above drugs can have a significant impact on the results of the patient’s examination and the accuracy of the diagnosis. The use of the following anti-inflammatory drugs is also not recommended:
How is eradication therapy tolerated?
From my own experience, as well as from the publications of other specialists, I can say – in different ways. There are patients who, when they come for a follow-up examination after eradication, say: “They were more frightening! There were no symptoms." But the most common complaints from patients are:
- bitterness in the mouth (in 95% of cases);
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- bloating;
- increased rumbling in the stomach;
- the appearance of heaviness or pain in the solar plexus area;
- acne on the face and body;
- various types of allergic reactions;
- candidal vaginitis (thrush) in women.
Some side effects can be avoided by carrying out preliminary prevention. For example, our patients and I first carry out a course of therapy aimed at eliminating the symptoms of exacerbation of gastritis or peptic ulcer, and after their severity has decreased, we begin eradication therapy. In order to prevent the development or progression of disorders of the liver and/or biliary tract, before starting eradication therapy, it is preferable to examine them: take tests, and, if necessary, perform an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Bloating, increased gas formation, acne on the face, vaginal discharge - all this is a consequence of dysbiosis. Therefore, in parallel with eradication therapy, I always prescribe drugs containing lacto- and bifidobacteria (in women, including vaginally).
Carrying out the test
Before testing for Helicobacter, you need to refrain from eating food.
The patient is almost always advised to fast before testing.
Before the procedures, each patient is given a specially prepared solution, which includes urea.
When the patient takes the solution, you need to insert a mouthpiece into his mouth, through which he needs to breathe for about nine minutes. Breathing should be as normal as possible.
In this way, the digital device can accurately determine the components contained in exhaled carbon dioxide. All results of the examination will be displayed on the monitor.
What is the cause of the development of ulcers and stomach cancer in HP?
The mechanism of formation of a cancerous tumor (carcinogenesis) and ulcerative defect (ulcerogenesis) is quite complex. To describe it in a nutshell, the main cause of the disease is the waste products of the HP bacterium - urease and ammonia. The first substance activates the inflammatory process in the mucous-submucosal layer of the stomach, thereby leading to the development of a defect. And ammonia promotes the development of atrophy (thinning) of the gastric mucosa, accelerated cell division, and, as a result, the development of tumors.