An ulcer is painful, disgusting and dangerous. In the recent past, doctors could not find the root cause of this pathology. They blamed it on stress, poor nutrition and treated it almost blindly experimentally.
At the end of the 19th century, German scientists discovered a spiral-shaped bacterium that lived in the stomach and duodenum. It was given the name Helicobacter pylori. In 1981, the connection between this microorganism and the appearance of ulcers in the stomach and intestines was scientifically proven, for which in 2005 the discoverers of the medical significance of the bacterium, Robin Warren and Barry Marshall, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine.
What kind of bacteria is this? How to destroy a pathogenic microorganism and cure erosion of the gastric mucosa once and for all? How to treat Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pylori: general information about the microorganism and route of infection
Helicobacter colonizes areas of the mucous membrane.
Helicobacter is a spiral-shaped gram-negative microorganism. Its dimensions are only 3 microns. This is the only microorganism capable of surviving and multiplying in the acidic environment of gastric juice.
Under favorable conditions, Helicobacter colonizes areas of the mucous membrane. The negative effect on the stomach occurs due to the complex properties of this microorganism:
- The presence of flagella allows for rapid movement in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Adhesion to stomach cells. This creates inflammation and the body's immune response.
- Produces enzymes that break down urea into ammonia. This neutralizes the hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, and the bacterium receives an environment favorable for development. Ammonia additionally burns the mucous membranes. This causes an inflammatory process.
- The microorganism produces and releases exotoxins that destroy mucosal cells.
Scientists have proven that Helicobacter strains in patients with ulcers are more aggressive than in patients with gastritis and other inflammatory processes in the stomach or intestines.
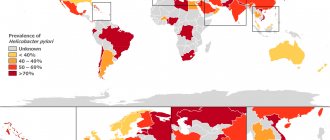
Infection with this microorganism occurs asymptomatically in 70% of cases. Doctors call possible routes of infection oral-fecal or oral-oral - through kissing, sharing utensils, in canteens and cafes, during medical procedures.
Helicobacter: diagnostic measures
To diagnose Helicobacter, you need to undergo tests.
Diagnostic procedures begin with interviewing and examining the patient. Then special studies are carried out to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis. Tests for Helicobacter pylori:
- Non-invasive procedures - blood for specific antibodies, breath test, stool and saliva analysis
- Invasive techniques - endoscopy with collection of material for histological examination
- To determine the microorganism in biological media, PCR analysis is carried out.
- For breath tests, the patient takes a solution of urea with labeled carbon atoms. The microorganism breaks down urea, and the labeled atoms are found in the air exhaled by a person. Additionally, an analysis is carried out to determine the concentration of ammonia in exhaled air.
The most accurate results are provided only by invasive examination methods.
"Gold standard" of diagnostics
First, to choose a treatment strategy, you need to make a correct diagnosis. There are many methods - from endoscopic to small, tablet-sized video cameras. The patient tries to choose the most comfortable option for himself and his wallet; there are certainly few daredevils who are ready to voluntarily undergo gastroscopy. A comfortable and painless method with sedation is not financially accessible to everyone; now such a complex costs about 10 thousand rubles. It is painless and informative, but even among wealthy patients there are many who are “afraid of anesthesia.”
Long courses of treatment with NSAID drugs
There are 2 methods of treating Helicobacter pylori infection.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively. According to the WHO methodology, any drug regimen must meet the following criteria:
- Efficiency and speed
- Safety for the patient
- Convenience – use long-acting drugs, short course of treatment
- Interchangeability - any drug must be interchangeable with a complete analogue or generic
Currently, 2 methods have been adopted for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. It is not recommended to use them simultaneously. If 1 scheme does not give a positive result, then the second one is used and vice versa. This prevents Helicobacter from developing immunity to drugs. Treatment regimens:
- Three-component method - 2 antibacterial drugs and 1 agent to reduce the acidity of gastric juice
- Four-component method - 2 antibacterial drugs, 1 - to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid, 1 - bismuth compounds
There is a 3rd treatment regimen for combating the microorganism. It is used when the first 2 did not have the desired effect. In this case, they speak of a resistant Helicobacter strain.
In this case, a preliminary endoscopic examination is carried out with the collection of material for a biopsy. In the laboratory, drugs for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori are individually selected. And only after that the doctor develops an individual course.
Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin, a 14-member macrolide, is a derivative of erythromycin with a similar spectrum of activity and indications for use. However, unlike erythromycin, it is more acid resistant and has a longer half-life. The results of studies showing that the triple eradication therapy regimen for Helicobacter pylori using clarithromycin gives a positive result in 90% of cases, led to the widespread use of the antibiotic.
In this regard, an increase in the prevalence of clarithromycin-resistant strains of H. pylori has been recorded in recent years. There is no evidence that increasing the dose of clarithromycin will overcome the problem of antibiotic resistance to the drug.
Antibacterial drugs
Macmiror destroys the parasite's genetic material.
The choice of antibacterial drugs that can cope with Helicobacter is small. This is "Trichopol" or "Metronidazole", or "Makmiror".
Trichopolum and Metronidazole are complete analogues. The main active ingredient of the drug, metronidazole, penetrates the microorganism and breaks down, releasing toxic substances.
They destroy the parasite's genetic material. The main active ingredient of Macmiror is nifuratel. It simultaneously inhibits the growth of bacteria and prevents the proliferation of microorganisms.
The peculiarity of this drug is that nifuratel does not reduce the patient’s overall immunity, but, on the contrary, improves the body’s defenses. Macmiror is a second-line drug. It is prescribed if treatment with metronidazole does not give the expected result. This medicine is used in the treatment of peptic ulcers in children.
Bismuth preparations and proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of Helicobacter
De-nol is a bismuth-based medicine.
A bismuth-based drug, De-nol, was used even before the discovery of the pathogenic microorganism. It has an enveloping effect, forming a film on the gastric mucosa.
It protects the walls from the aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid. After the discovery of Helicobacter, it turned out that bismuth subcitrate has an inhibitory effect on the bacterium. It is able to penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membrane, where the pathogen likes to settle.
Proton pump inhibitors - Omez, Omeprazole, Pariet - block areas of the mucosa responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid. This promotes the healing of erosions, reduces the acidity of gastric juice and allows the antibiotic molecules to be preserved in an acidic environment.
What kind of bacteria is this?
Helicobacter pylori - translated from Latin - is a spiral-shaped bacterium that lives in the pylorus. And indeed the microscopic bacterium looks like a spiral surrounded by hairs. With the help of these hairs - flagella, it quickly moves through the internal organs to its place of permanent residence - the pylorus - the lower tier of the stomach and the initial section of the intestine - the duodenal bulb. The Helicobacter bacterium has refuted the myth that hydrochloric acid in the stomach kills all microbes. On the contrary, the little predator feels at home in destructive acid, thanks to the enzyme urease, which breaks down hydrochloric acid.
How does Helicobacter affect the stomach? Destroys parietal (parietal) cells of the mucous (inner) lining of the stomach, releasing toxic products - toxins. Protective blood cells - neutrophils, lymphocytes and others - pursue the pest, trying to destroy both it and the altered parietal cells - inflammation occurs. The amount of protective mucus in the area where the bacterium resides is noticeably reduced, and hydrochloric acid rapidly affects the altered area, exacerbating the constant inflammation of the mucous membrane. This is manifested by pain in the stomach “in the pit of the stomach,” heartburn, belching, coating on the tongue, bad breath, constant nausea, that is, symptoms of chronic gastritis. Chronic long-term inflammation of the gastric mucosa leads to changes in its cells, including the development of stomach cancer.
How does Helicobacter enter the body? Since Helicobacter lives in the stomach, infection is possible when the bacteria enters the human body through the mouth. This is the habit of taking food or dishes with unwashed hands, and the desire to try food on someone else’s plate or take a bite from an apple or a friend’s sandwich when offered to try - this is how children often become infected. In addition, you can become infected by sharing utensils or through kissing, which is why Helicobacter is often found among members of the same family.
So why now go to a cafe with your own dishes? Fortunately, Helicobacter is not a resistant bacterium and washing dishes in the dishwasher is enough to destroy them. Good restaurants and cafes are of course equipped with such machines, and you can visit them without the risk of infection.
Helicobacter pylori. How to do without antibiotics?
There is no effective treatment regimen for diseases associated with Helicobacter without the use of antibiotics. Only in some cases, without symptoms of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract and with a low contamination of bacteria, is it possible to remove Helicobacter pylori from the body.
All treatment regimens place a serious strain on the body. If carriage is detected without signs of inflammation, it is recommended to use more gentle methods.
Traditional medicine and Helicobacter
Traditional medicine recipes should not be used without consulting a doctor.
What does traditional medicine offer for the treatment of Helicobacter? Recipes are often contradictory:
- Raw chicken eggs. It is recommended to drink 1 raw egg before breakfast. This should normalize the normal microflora of the stomach.
- St. John's wort, calendula and yarrow are mixed in equal proportions. Make a decoction - 250 ml of water per 5 g of mixture. Take the infusion 0.5 cups 3 times a day for a month.
- It is recommended to consume 1 teaspoon of rosehip syrup per month.
- Flaxseed decoction. For 1 tablespoon of seed you will need 1 glass of water. Simmer over low heat for 20 minutes. Strain the broth and take 1 tablespoon before each meal.
The use of traditional medicine recipes should only be started after consulting a gastroenterologist. Otherwise, within a month of treatment you risk getting a perforated ulcer with all the ensuing consequences.
Diet for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection
Modern techniques allow you to be cured in a matter of weeks.
There is no specialized nutrition to combat Helicobacter. During treatment, you should adhere to the diet recommended for patients with gastritis, ulcers and other diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Food should be light, pureed and not irritate the mucous membranes. Heavy, spicy, fried and fatty foods are prohibited.
An ulcer is a dangerous disease. The cause of this pathology has now been identified. Helicobacter pylori should be treated under the guidance of a gastroenterologist. Modern techniques make it possible to get rid of this microorganism in a matter of weeks.
Endoscopy
It is considered the most reliable and “reference” method for diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection. There is a rapid mucosal biopsy test, where the presence of bacteria is determined on the spot. And there is a histological examination. A biopsy specimen must be taken from different parts of the gastric mucosa. This is an in-line, but very reliable method that allows you to determine the nature of the biopsy cells: whether there are tumor processes or inflammation in the tissue; what is the nature of mucous secretion? It also allows you to determine whether it is atrophic or ordinary gastritis.
There is some skepticism regarding revolutionary methods such as capsule endoscopy. This is a popular and comfortable method, but a capsule with a microvideo camera, passing through the gastrointestinal tract, may not show all its departments. In difficult cases, it can get stuck in hernias, protrusions, and diverticula. Or maybe you won’t even notice them. It is also not possible to take a biopsy specimen for examination using this capsule.