The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that can live and multiply not only in the stomach of an adult, but also of a child. This microorganism is quite insidious, since after penetration into the gastrointestinal tract, it does not reveal itself in any way. The asymptomatic existence of the bacterium can continue until a person develops a disease of the digestive system, the mildest of which is gastritis. In the inactive stage, bacteria can exist for a long period of time.
Diseases that can be caused by Helicobacter pylori:
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- Gastritis.
- Gastroduodenitis.
Children are most often diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori by the age of five. There can be several ways of infection. Part of the source of infection is the mother or another adult from the child’s immediate environment. Infection can occur when a mother eats from the same dish with her child or licks his spoon and then feeds it to the baby.
First signs
When Helicobacter pylori is activated in a child’s body, the first symptoms of the disease appear, which include:
- Frequent belching during which an unpleasant odor is clearly felt.
- Heartburn that occurs from time to time.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Darkening of stool.
- The appearance of a white coating on the tongue.
- Painful sensations in the abdomen.
- Unstable stool, in which diarrhea can be replaced by constipation.
If an adult ignores these symptoms in a child, the disease will progress, leading to the development of severe complications. Also, the first sign of Helicobacter pylori infection in children may be an allergic reaction in the form of urticaria. If you donate blood, it is possible to detect iron deficiency anemia.
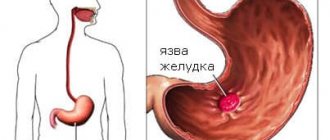
Treatment of peptic ulcer
— What are the main methods of treating peptic ulcers in children?
— Treatment includes antibacterial (against Helicobacter pylori infection) and antisecretory therapy (reducing acid formation). The doctor selects the medication regimen individually. As a rule, triple therapy is used: two antibiotics and an antisecretory drug. The treatment regimen is 7-14 days, after 4-6 weeks - mandatory endoscopic monitoring.
Previously, a strict and long-term diet was also prescribed. Now the recommendations are simpler: eat regularly and limit irritating foods during the acute period of illness: pickles, marinades, hot spices, rich broths, fatty and fried foods, smoking/alcohol (for teenagers).
— Does the degree of infection with Helicobacter pylori infection, which is indicated by plus signs in tests, matter whether it is treated or not?
— Previously, this was left to the discretion of the doctor. Currently, according to modern requirements, Helicobacter pylori is recognized as a clearly pathogenic microorganism and, if detected, requires unambiguous treatment.
Main symptoms
When Helicobacter pylori in a child exists in the body for a long time, this will lead to the following symptoms:
- Child's mental retardation.
- Constant fatigue and malaise.
- Rapid pulse.
- Increased moodiness.
- Dry mouth.
- Hair loss.
- Delayed physical development.
Rapid weight loss can also be a sign of Helicobacter pylori infection. This bacterium is very dangerous to the child’s health, so treatment should be started immediately after it is detected. The longer Helicobacter pylori exists in the body, the more difficult it will be to get rid of it. It triggers adaptive mechanisms that allow it to remain viable even under the influence of drugs.
Very often, a person does not even suspect that he is a carrier of the infection, since there are no specific symptoms that would be characteristic of Helicobacter pylori.
Why should a child take a breath test for Helicobacter?
The study allows for early diagnosis of a group of serious diseases that can be caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. If the pathology has already been diagnosed and treatment has been prescribed, the test makes it possible to assess the effectiveness of this treatment and, if necessary, correctly correct it. Bacteria of this type can live in the body for a long time without manifesting themselves in any way until they receive an impetus for rapid development and damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, and therefore this study is recommended for all children to identify individual risks, especially if the child has a hereditary predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases.
Routes of infection
Helicobacter pylori enters the child's body through the fecal-oral route. Children's hygiene skills are not fully developed, so it is not difficult for them to become infected.
Possible routes of infection of a child with Helicobacter pylori:
- Through contaminated water.
- Through contaminated food, for example, by eating unwashed fruits or berries.
- Through expired food.
- If hygiene measures are not observed.
The weaker a child's gastrointestinal tract, the higher the likelihood of developing an infection. The state of the digestive system is negatively affected by eating fast food and the absence of liquid dishes on the menu.
It is extremely rare that infection occurs iatrogenically, when non-sterile instruments are used in the clinic during diagnosis.
The risk of infection of the child from other family members is high. If at least one person is a carrier of Helicobacter pylori, then the risk of transmitting the bacteria to people living with him in the same apartment is equal to 95%.
A child can be infected not only at home, but also at school or kindergarten. It is enough to not wash your hands once after a walk for harmful bacteria to enter the body. Moreover, at a young age, children put everything in their mouths, from toys to their fingers. Be sure to teach your child to wash their hands after visiting the restroom.
Preparation for UDT
The accuracy of the results obtained largely depends on proper preparation for the procedure. Pediatric gastroenterologists at the SM-Doctor clinic suggest adhering to the following recommendations:
- For 2 weeks before the test, the child should not receive antibiotics or other drugs that can change gastric secretions.
- The study is carried out on an empty stomach, at least 6, and preferably 14 hours after the last meal. Dinner should be easily digestible. You can give your child something to drink in the morning, but no later than 1 hour before the procedure.
- On the morning of the test, he must brush his teeth with or without a neutral toothpaste.
- On the day of the study, chewing gum is not allowed.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of a child becoming infected with Helicobacter pylori appear, you should consult a specialist. First you need to visit a pediatrician. If suspicions are confirmed, then it is necessary to undergo treatment under the supervision of a pediatric gastroenterologist.
A preliminary diagnosis can be made even based on the mother’s complaints and on the basis of an examination of the child. Antibodies to Helicobacter pylori can be detected in the blood and stool. Therefore, it will be necessary to submit these materials for research.
Using an endoscope, the doctor examines the gastric mucosa and assesses the degree of damage. During the study, it is possible to take a biopsy of the coolant, which is subjected to laboratory tests and Helicobacter pylori is detected in it.
Non-invasive methods include a breath test, when a conclusion about the presence of bacteria in a child’s body is made based on a study of exhaled air. Children are recommended to undergo a breathing “Helic test”, during which the child will need to drink a solution of urea. This substance does not pose any threat to the baby’s health, so the study is absolutely safe.
Modern medicine also has molecular methods for detecting Helicobacter pylori. To carry it out, dental plaque is taken from the subject.
To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is required.
Advantages of conducting a breath test for Helicobacter at SM-Doctor
In our clinic, consultations are conducted by highly qualified pediatric doctors with solid experience in diagnostic practice and competent interpretation of the results obtained.
The test performed is completely painless and safe, while its high information content allows you to avoid invasive endoscopic procedures, which are difficult for children to tolerate.
The medical laboratory is equipped with the most modern high-precision diagnostic equipment. In particular, the study of exhaled air samples is carried out using an infrared spectrometer IRIS made in Germany.
Our clinic has created the most comfortable conditions for young patients and their parents, eliminating physical inconvenience and psychological stress.
How is Helicobacter pylori treated in children?
Self-treatment of Helicobacter pylori in children is unacceptable; therapy should be carried out by a doctor. Antibacterial drugs are used to remove bacteria from the body. Moreover, a combination of at least two antibiotics is necessary. At the same time, they must be non-toxic to the child’s body. Be sure to prescribe medications that are aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice.
Most experts do not recommend that children take proton pump inhibitor drugs, as they negatively affect the overall development of the child. Preference is given to H2-histamine blockers. Antibiotics should be selected in such a way that they are detrimental to a given bacterium. Otherwise, the microorganism will develop resistance to them and will not respond to the therapy.
There are specially designed regimens for treating children from Helicobacter pylori. Thus, it is prohibited to take drugs from different drug groups at the same time. A certain period of time must pass between them. Some medications are taken once a day, and some are taken 2 times a day.
Taking antibiotics is always associated with the risk of developing dysbiosis. The fact is that antibacterial drugs are destructive not only for harmful, but also for beneficial bacteria living in the child’s gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, you cannot extend the treatment period on your own.
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor; on average, the course is 7 days, although, at the discretion of the specialist, it can be extended to 15 days. Doctors do not consider folk remedies even as auxiliary ones, since they will not have any effect.
Drug therapy has several goals, including:
- Reducing the risk of developing stomach cancer.
- Reducing the risk of internal gastric bleeding.
- Preventing the formation of stomach ulcers.
- Prevention of iron deficiency anemia.
You should be prepared for the fact that the therapy will have a number of side effects. After all, drugs for getting rid of Helicobacter pylori cannot be considered absolutely safe.
Read more: Helicobacter pylori eradication: which drug to choose?
Undesirable symptoms during treatment include:
- Stool disorders.
- Metallic taste in mouth.
- Abdominal pain.
- Constipation.
If a child complains of one or more symptoms, then he must be shown to a doctor. It is possible that the doctor will recommend some other medications. Although negative manifestations from the digestive system are not always associated with taking medications. It cannot be ruled out that they are manifestations of the disease itself.
Features of the first treatment option
Omeprazole is a medicine for the treatment of Helicobacter in children.
At the first stage of the fight against Helicobacter pylori, only drug therapy is used.
There are several treatment options, which allows you to choose the most suitable option depending on the individual characteristics of the baby’s body.
The first treatment option requires the use of proton pump inhibitors. The dosage of traditional medicines should be standard. Most often, young patients are prescribed: