An inguinal hernia is the protrusion of internal organs covered by peritoneum through the inguinal canal.
Causes
The causes of inguinal hernias can be divided into two groups:
- predisposing factors - gender, age, body type, anatomical weakness of the walls of the inguinal canal, etc.;
- producing - conditions that contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure: heavy physical labor, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to a slowdown in bowel movements, etc.
Lipoma of the spermatic cord, which occurs in 32.4-72.5% of healthy individuals, is also a risk factor for the occurrence of inguinal hernia. As the size of the lipoma increases, the inguinal ring stretches, the lipoma puts pressure on the lower edges of the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles, which contributes to an increase in the height of the inguinal space.
In women, a common cause of hernia development is pregnancy.
A hernia appeared in the groin. What to do?
You or your relative, father, husband, friend, colleague or just a loved one has an inguinal hernia. It always appears at the wrong time and unexpectedly for its new owner, sometimes on both sides at once (bilateral). The process of herniation begins. The scenario and first signs of the appearance of a hernia vary. Anything can happen against the background of complete well-being and good general condition. Unpleasant pulling sensations in the lower abdomen appear and disturb, or after strong physical activity (static tension, heavy lifting, repairs, sports) a sharp pain occurs in the groin. Unpleasant sensations and pain may subside and go away on their own, but then a characteristic tumor-like hernial formation (bulging, bulging) of an oval or round shape is discovered in the groin area.
Consultation with a surgeon, candidate of medical sciences
Make an initial appointment in Moscow by phone
An inguinal hernia comes in different sizes (from a pea or larger) and can enlarge with coughing, sneezing, straining and physical activity. Pain, discomfort and discomfort are usually periodic. The hernia is mobile, reducible, and over time, it can begin to descend into the scrotum, turning from just inguinal to inguinal-scrotal. In addition to pain and discomfort, there are often dysuric phenomena (impaired urination - frequent, difficult or involuntary, urinary retention, pain and discomfort in the urethra). Periodic chronic constipation and/or bloating may be a concern. If your close relatives (father, grandfather, great-grandfather and others) had a similar pathology, then the likelihood of it happening to you and your children is very high. The process, location and age at which the formation appears in the groin may be similar. The symptoms are often the same.
A hernia has appeared. It would seem that there is nothing wrong and you can continue to live with her. Especially if it is small in size and practically does not bother you. Yes, there is some discomfort, there are inconveniences, but it seems that you can put up with it. In this situation, some choose the “ostrich” tactic and try to avoid the problem and not pay attention to it. Others enter a mode of observation and watchful waiting. You know, indeed, you can live like this for some time, but you need to take into account that the hernia carrier’s quality of life will suffer and decrease. Taking this factor into account, you need to decide what to do next.
If nothing is done, the hernial protrusion, as a rule, gradually increases in size and becomes more and more disturbing. More and more new symptoms appear that make it difficult to live peacefully. The discomfort is growing. But most importantly, there is always a danger of complications (strangulation, coprostasis and others). An inguinal hernia is like a “bomb” in your pocket, which can suddenly explode at any moment (both day and night) (complicated - pinched). And then she will have to be operated on as an emergency, which means that the likelihood of postoperative complications increases many times over, even after a well-performed surgical intervention. Hernioplasty (surgery) in such a situation will be less reliable, and the likelihood of relapse is very high.
When an injury occurs, it will be a great success if there is a good hospital and a qualified surgeon nearby. And if not? What if you are far from home? Business trip? On a rest? Fishing? Abroad? In such a situation, everything is left to chance. You are taking a risk... The consequences can be unpredictable and sometimes disastrous. The hernia limits freedom of movement. You need to constantly remember it. Among other things, the condition of a person with a hernia negatively affects not only him, but also affects his family, relatives and friends. A man can quietly plunge into prolonged depression and frustration. It's no secret that behind the outer brutal shell, imperturbable character and iron will often hide fears that are not voiced even to oneself. The stronger sex can solve the most difficult problems, be a stone wall for their loved ones and friends, stand to death, but men also need help and support. Often, hernia carriers do not want to talk about their problems and show their weaknesses. Sometimes the mere mention of a visit to the doctor or the need for surgery puts you into a stupor. It seems that it is easier to die than to solve this problem.
No matter how difficult and scary it may be, it is necessary to face this problem head on. And here only really close people whom a man trusts can help. These are usually parents, wives, children or friends. We need to walk this path together, step by step. The path from the appearance of a hernia to surgery and successful rehabilitation. To make the right decisions, you need to find answers to the many questions that arise with your family and friends.
What is an inguinal hernia? How does she look? What are its reasons? Why did it appear specifically for me? What health risks does an inguinal hernia pose? Who is treating? Where to contact? How to cure a hernia? Is it possible not to contact a surgeon? Is it possible to do without surgical treatment (not undergo surgery)? Is it possible to cure a hernia with folk, home or alternative remedies? Is it dangerous not to have surgery? If I have surgery, where can I do it? Where is the best place to do this operation? How long does the operation take? Does it hurt? What anesthesia or anesthesia is used to perform the operation? What surgical procedures are used to remove an inguinal hernia? What is the best operation to do? Open cavity or laparoscopic? What are the differences between surgical interventions for inguinal hernia? Is it possible to cut out hernias from both sides at once? What is needed before surgery? What examinations are needed? How much does surgery to remove an inguinal hernia cost? Cost of surgery (hernia repair)? What are the complications? What to do if there is a complication? What kind of rehabilitation is necessary after surgery? For how long is sick leave issued? What to do? And many, many other very diverse questions...
No one prepares to answer these questions from childhood, and many will not even need it in life. But if you are faced with such a problem, then you cannot do without collecting information. You should not complain about fate, rely on miracles or traditional healers. You need to learn as much as possible and immediately and consistently act. If you go to any forum on inguinal hernias, to the questions and answers section or frequently asked questions (FAQ, Q&A), and type reviews in search engines, you will see a lot of different opinions and advice. Sometimes they can be contradictory or even mutually exclusive. In order to act, you need information and knowledge from different sources. Read, analyze, think, ask and make decisions, only for you. We will try to help you, tell you in detail about inguinal hernias in men and answer your questions...
Complication of scrotal hernia - strangulation
The most dangerous condition is when the hernia in the scrotum is strangulated. In this case, the part of the intestine that prolapses into the hole in the abdominal wall is compressed, preventing the intestine from returning to the abdominal cavity. Contents in this area cannot move further, resulting in a blockage.
The intestine itself is limited in blood supply and soon, due to ischemia, necrosis develops in this area. It is not difficult to detect pathology. The hernia, which was still soft, becomes hard and painful. The skin becomes red and hot. After a few hours, bloating, sharp abdominal pain, nausea, and sometimes vomiting appear.
Definition
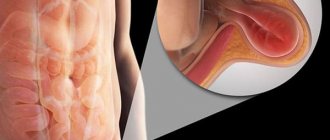
An inguinal hernia
is a pathological formation that should not exist normally. This is a tumor-like protrusion of a round or oval shape in the groin area (lower abdomen) on the right, left, or on both sides at once. An uncomplicated hernia is best detected in an upright position (standing) and can disappear (reduced) in a horizontal position (lying down).
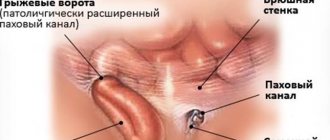
An inguinal hernia consists of the following elements:
- hernial orifice
(the place where the hernia emerges is weak spots or holes in the anterior abdominal wall in the groin area, inguinal rings)
- hernial sac
(a section of the peritoneum that exits through the hernial orifice along with the contents - the abdominal organs)
- hernial contents
(what is inside the hernia and hernial sac - omentum, intestine, bladder, etc.)
Causes and predisposing factors
No one is immune from an inguinal hernia. This problem can occur in any man. If you have it, then this is not bad luck, not someone’s fault or someone’s machinations, but in most cases a coincidence of circumstances. The mechanism of formation of a hernia in the groin is simple. The protrusion (hernial sac with contents) exits through the hernial orifice under the skin and subcutaneous tissue or descends into the scrotum. The main causes of hernia are predisposing and main producing factors.
Predisposing factors
, significantly increase the likelihood of a hernial protrusion.
First of all
Of these factors, heredity and genetic predisposition influence hernia formation. They determine the anatomical features of the body, which lead to the appearance of a pathological formation in the groin:
- Congenital weak walls and connective tissues of the inguinal canal
- Expanded, enlarged inguinal rings
- Asthenic body type
Secondly
The appearance of a hernia can be affected by age and age-related changes:
- Decreased tone of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall (abdomen) and groin area
- Thinning of the connective tissue in the area of the inguinal rings
Less common
the following predisposing factors:
- Abdominal injuries, especially in the groin area
- Muscle atrophy due to prolonged absence of physical activity
- The likelihood of a hernia is high if you are obese or malnourished.
Main producing factor
this is tension (straining) of the abdomen (heavy and excessive physical activity, heavy lifting, work as a loader, professional sports, constipation, vomiting, coughing, sneezing and others). It leads to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which in turn is a direct trigger for hernia formation.
Signs of pathology
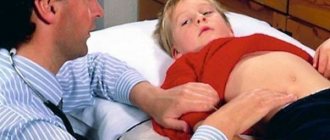
The main sign of the development of a hernia in the groin is a visually noticeable protrusion in this area. After performing strength exercises, jumping, and overexertion, the protrusion becomes even more obvious. If you take a lying position, the hernial bulge disappears. Ignoring the problem leads to the size of the hernia increasing several times.
A right-sided direct inguinal hernia in the early stages does not lead to intense pain. But if the patient is subjected to significant physical stress, then the pain syndrome can become unbearable. When walking, the bulge can cause discomfort to a person.
In most cases, the patient is able to independently recognize the disease by palpating the bulge. When palpating a hernia in the early stages, there should be no pain.
Forms of inguinal hernia
The disease has several forms, despite one localization. What forms of pathology are there:
- Congenital - in this case, the hernial bulge appears from the inguinal canals that are not completely overgrown after the testicles descend into the scrotum.
- Acquired - appears after intense exercise, jumping, coughing, sneezing, etc.
- Direct - appears through the hole in the groin, located in its upper part. This type of pathology occurs in 30% of cases in male patients after forty years.
- Oblique - a pathological bulge in this case enters the upper opening of the canal in the groin and exits through the lower one. If compression of the spermatic cords occurs, then infertility may occur.
- Internal hernia (canal type) - enters the inguinal canal, located in the upper part and is recognized only after tension of the peritoneal muscles.
Based on which side of the groin the hernial bulge is located, a right-sided and a left-sided hernia are distinguished. There is also a combined type of pathology - bilateral.
Treatment of inguinal hernia
Conservative
Conservative treatment (without surgery) cannot radically solve the problem and is only possible in some exceptional cases:
- If severe general condition, concomitant diseases or serious contraindications do not allow elective surgery. Surgical intervention in such cases is performed only for emergency, life-saving indications in case of life-threatening complications (strangulation, etc.).
- If for objective reasons you have not yet decided to undergo or are postponing surgical intervention.
For a reducible, uncomplicated inguinal hernia, it is possible to temporarily wear a unilateral or bilateral bandage (special support device). It does not relieve the hernia patient from the problem and has only a palliative, alleviating effect. The bandage is necessary to maintain the hernia in a reduced state so that it does not interfere, does not actively progress, and to prevent strangulation. Wearing this device is contraindicated for irreducible inguinal hernias, funiculoceles and hydroceles. In rare cases, in case of irreducible and very large hernia formations, when surgery and wearing a bandage is impossible, special, individual suspending bandages - suspensors - are recommended.
Other conservative treatment methods (physiotherapy, herbal medicine, folk and home remedies, special physical exercises) also do not help to radically get rid of the hernia and the need for surgery. There is no convincing evidence of their effectiveness. You shouldn't rely on them.
Surgical
You should definitely contact a surgeon.
Treatment of inguinal hernia is only surgical. It is impossible to correct a hernial formation so that it no longer comes out without surgery. It is imperative to close or eliminate the hernial gate (defect - weak point), through which the hernia comes out under the influence of intra-abdominal pressure. Without this, the problem cannot be solved. Timely planned surgery (hernia removal, hernia repair, plastic surgery) is the most reasonable and complete solution to the problem. A more effective method has not yet been invented. The sooner you do it, the better, the smaller the volume of intervention will be and the significantly lower the likelihood of complications. You can save more time and quality of life for yourself, your family, friends and loved ones. An uncomplicated inguinal hernia in a man is an indication for elective treatment, while a complicated (strangulated) one is an indication for emergency surgical treatment. The operation can be performed at almost any age if there are no contraindications.
Contraindications to elective surgery:
- severe somatic and concomitant pathology (severe acute diseases)
- severe exacerbations of chronic diseases
- acute and chronic infectious processes
- acute period of heart attack or stroke
- severe renal, cardiac, respiratory or liver failure
- decompensated diabetes mellitus
- fever of any origin (increased body temperature)
- disorders in the blood coagulation system (high probability of bleeding)
- very old age
- exhaustion, cachexia
Main options
planned surgical treatment of inguinal hernia:
- Open tension-free hernioplasty using the Lichtenstein method (Lichtenstein hernioplasty, Lichtenstein Tension-Free Mesh Repair)
- Laparoscopic hernia repair.
They are the “gold standard” of treatment and the operations of choice, primarily due to the emergence of new, modern materials (synthetic mesh) and technological progress (video laparoscopy). Modern progressive techniques in the vast majority of cases have replaced older types of hernial orifice plastic surgery with their own, local tissues with tension (according to Bassini, Postemsky, Shouldice, Yanov, etc.).
Operation in Liechtenstein
Open hernioplasty with Lichtenstein mesh
(open installation of a synthetic mesh implant) is the most modern, popular and widespread method of eliminating inguinal hernias.
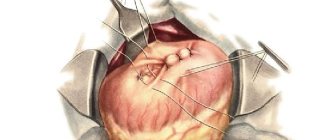
Surgery is performed under local, spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in the groin area, releases the hernial sac, and plunges the hernial contents back into the abdomen. Then the sac is excised, the inguinal canal is strengthened and the hernial orifice is eliminated by sewing in a synthetic, non-absorbable polypropylene mesh (Ethicon, Kovidien, Bard or others). It is non-toxic, hypoallergenic, elastic, durable and reliable. The mesh is fixed between the layers of the abdominal wall in the projection of the hernial orifice and after the operation grows with connective tissue, reliably strengthening the defect - a weak point in the groin area. The implant is imperceptible, does not restrict movement, does not create discomfort, lasts throughout life, does not collapse or dissolve within the tissues. The Lichtenstein technique is simple, effective and reliable. Plastic surgery of the hernia orifice without tissue tension with minimal trauma significantly reduces the likelihood of hernia recurrence (0-2%).
Planned herniotomy according to Liechtenstein. Removal of an inguinal hernia through an incision (conventional access) on the anterior abdominal wall with mesh repair.
Cost from 25,000 rubles.
Scrotal hernia: treatment
A scrotal hernia, unlike, for example, an umbilical hernia, does not reduce or heal on its own, so surgery is necessary.
- In children, operations are performed when the child is one year old.
- A man should consult a urologist if he notices the above symptoms immediately. The operation must be done within the time frame specified by the doctor, without delay.
The traditional method of surgical treatment of hernias, including scrotal hernia, is hernioplasty using the Bassini method (using your own abdominal wall tissue). The recovery period lasts from 4 to 12 weeks.
Bassini hernioplasty carries a risk of recurrence of the hernia, so it is recommended to perform the Lichtenstein procedure, during which the doctor protects the operated area with a polypropylene mesh. After such an operation, the risk of hernia recurrence is significantly reduced. The recovery period is also shorter, lasting 1-3 weeks.
Endoprosthesis for hernioplasty
Invasive treatment also uses laparoscopic techniques, in which special guides are placed in the groin through which surgical instruments are inserted. Using mini instruments, the operation is performed and a protective mesh is sewn in.
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic hernioplasty
for inguinal hernia is similar to other video-laparoscopic minimally invasive interventions.
It is performed under anesthesia (general anesthesia) using three small incisions (punctures) 0.5 - 1.0 cm. First, access is made to the navel area, through which a trocar is inserted. The abdomen is inflated with gas (pneumoperitoneum), so that the surgeon can easily see the abdominal cavity from the inside and perform manipulations there. A laparoscope equipped with a camera and a light source is then inserted through the trocar. A video camera from the inside transmits an image of the abdominal cavity and organs to the monitor. This makes it possible to see the hernia defect and perform plastic surgery. Instruments for manipulation and reconstruction are inserted through other small incisions in the lower abdomen. The mesh (implant) is placed over the hernial orifice inside the abdominal cavity and fixed to strengthen the abdominal wall and eliminate the defect. Closing the hernial orifice from the inside makes the repair more reliable. Laparoscopic operations are most effective for recurrent and bilateral inguinal hernias. They allow you to achieve an optimal cosmetic effect. Planned operation - laparoscopic hernia repair. Removal of an inguinal hernia through small, invisible incisions - punctures. Cost from 45,000 rubles.
The difference between laparoscopic hernia removal and open one:
- Laparoscopic hernia treatment is more expensive due to the higher cost of technical equipment and preparation for surgery. This is compensated by the quality of plastic surgery and the postoperative period
- Laparoscopy of an inguinal hernia is performed using several small incisions and does not require one large incision (good cosmetic result).
- Hernias on both sides (bilateral) can be removed through the same approaches without the need for additional incisions
- The recovery period after surgery is significantly reduced
- Minimal risk of wound complications, hematomas, seromas
- Daily activities are not limited
- Pain syndrome is less pronounced
- Minimal risk of relapse
- The patient can be discharged on the day of surgery or the next day
Preparing for planned surgery
Before carrying out a planned intervention, an examination by a surgeon and examination are required. This is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and make sure that you really have an inguinal hernia. Formations in the groin are different and there are many other diseases that may be similar to an inguinal hernia (femoral hernia, lipoma of the groin area, lymphadenitis, hydrocele - hydrocele of the testicular membranes, varicocele and others) and which need to be distinguished (differentiated). Treatment tactics for other pathologies are different. Examination and examination are necessary to exclude contraindications to surgical treatment. Before surgery, physical activity (heavy lifting) should be limited and overeating should be avoided. Chronic foci of infection must be sanitized (cured). If cough or constipation is present, appropriate treatment should be given. A few weeks before surgery, it is mandatory to stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
List of tests and examinations before planned surgery:
- Tests: complete blood count (CBC, finger prick), blood sugar, complete urine test (UCA), biochemical blood test (AST, ALT, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, urea, creatinine, total protein), blood test (for HIV , hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis), blood type, Rh factor
- ECG
- Fluorography (or chest x-ray)
Detection and treatment of inguinal hernia in men at the A.N. medical center. Begma
Our medical center provides detailed diagnosis and treatment of inguinal hernia using modern technologies. Clinic specialists carefully study all the details of the pathology and determine the most appropriate treatment method in each individual case.
If you have been diagnosed with an inguinal hernia on the right, do not hesitate with adequate therapy. After all, ignoring the problem can lead to infringement with all the ensuing circumstances, even the most fatal ones. The surgical intervention will be carried out at a high professional level, as carefully and painlessly as possible. You are guaranteed high-quality, qualified post-operative care and rehabilitation.
Leading clinic specialists with many years of experience in the field of surgery are waiting for you to conduct diagnostic procedures, make a diagnosis and carry out competent treatment. You should not expose your life to unjustified danger by putting up with the discomfort that this disease brings - it is necessary to solve problems in a timely manner, without waiting for them to worsen.
Complications
The main complications of an inguinal hernia are strangulation, coprostasis, irreducibility, and inflammation. Neoplasms and foreign bodies are less common.
- Infringement
the most common, severe and dangerous complication. This is a sudden, usually after loading or straining, compression of the contents of the hernia (organs released into the hernial sac) in the hernial orifice at the level of the neck of the hernial sac. With this complication, pain most often occurs in the area of the formation, which quickly increases in intensity. The hernia increases in size and acquires a bluish-purple color. In the strangulated organ, circulatory and lymph circulation disturbances occur. Necrosis (death) of the compressed contents of the hernial sac develops. Perforation (perforation) may occur, in which intestinal masses come out, which leads to a more serious complication - peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). The danger and risk to life increases. What to do? In such a situation, hospitalization and immediate, emergency (urgent) surgical treatment are necessary.
- Coprostasis
(stagnation of feces) develops in cases where the contents of the hernial sac are the large intestine due to a disorder of intestinal motor function. The occurrence of such a complication is facilitated by the irreducibility of the hernia, large meals and a sedentary lifestyle. Coprostasis is manifested by intractable constipation, abdominal pain and nausea, and less commonly, vomiting. It can lead to fecal strangulation of the hernia. What to do? It is necessary to empty the colon of its contents (enema). Hospitalization. Surgeon's observation.
- Inflammation
hernia develops when the cavity of the hernial sac becomes infected. This is possible with acute inflammation of the appendix (appendicitis) or Meckel's diverticulum (diverticulitis), if they are the contents of a hernia. At the same time, the general condition of the hernia carrier suffers, body temperature rises, chills occur, vomiting, stool retention and difficulty passing gases appear. The size of the hernia increases, the skin over it turns red. What to do? Hospitalization. Surgical treatment. Surgeon's observation.
- Irreversibility
(the hernia ceases to be reduced) occurs as a result of the development in the hernial sac of internal organs adhesions between themselves and the peritoneum, which is caused by chronic trauma to the hernial contents. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Planned surgical treatment.
- Rare complications
(hernia damage, hernia neoplasms, hernia foreign bodies). What to do? Hospitalization. Surgeon's observation. Surgical treatment.
What complications can occur during inguinal hernia surgery?
- Complications during anesthesia or pain relief (anaphylactic shock, cardiovascular disorders)
- Nerve damage
- Damage to other elements of the spermatic cord
- Damage to the vessels that pass through the spermatic cord
- Damage to the femoral vessels
Highly qualified surgeons make it possible to reliably remove hernias and perform plastic surgery with minimal risk of complications during and after operations. The complication rate is very low.
What are the postoperative complications?
- Complications after anesthesia and general anesthesia
- Hernia recurrence
- Wound infection, inflammation and suppuration of a postoperative wound, mesh infection
- Postoperative hematoma
- Prolonged pain syndrome (painful scars)
- Deep vein thrombosis of the legs
- Dehiscence (cutting) of seams, m.b. eventration
- Hydrocele of the testicle
- Seroma
Complications after anesthesia and anesthesia
After surgery, you may experience nausea, vomiting, urinary retention, sore throat, and headache. More serious problems include heart attack, stroke, pneumonia, blood clots in the deep veins of the lower extremities, thromboembolism, anaphylactic shock and allergic reaction. A complete examination before surgery, a thorough interview with the patient, high-quality preparation and early activation allow you to avoid many problems during general and local anesthesia. During general anesthesia, the professionalism of the anesthesiologist is very important. He must foresee all possible factors that may affect the result and assess the surgical and anesthetic risks. The general condition of the patient, concomitant complaints and diseases in the anamnesis are very important.
Relapse (the appearance of a hernia again in the same place after surgery)
Recurrence is the most common complication of an inguinal hernia, which occurs much less frequently when using a synthetic mesh and when the patient strictly follows all the doctor’s recommendations after surgery. Especially those related to heavy lifting and physical activity. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Planned surgical treatment.
Postoperative hematomas (in the area of the postoperative wound)
Bleeding at the surgical site may cause severe swelling and blue discoloration of the skin around the incision (hematoma). Sometimes this leads to the need to reopen the wound for revision and stop bleeding. Bleeding is a rare complication and occurs in less than 2% of patients. Some surgeons consider surgery in a one-day hospital unsafe and recommend that the patient remain under observation for at least a few days before discharge to exclude such complications. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Timely revision of the postoperative wound.
Wound infection (inflammation and suppuration of a postoperative wound, infection of the mesh)
Most often, wound infection occurs in older people and people who undergo surgery for complicated hernias (strangulated, etc.). You should be alarmed if there is fever (increased body temperature) after surgery. If against this background redness, swelling and pain appear in the area of the postoperative wound and discharge from the incision, then in most cases this is evidence of the development of a wound infection. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Postoperative wound infection requires antibiotics, dressings, and sometimes revision and sanitation of the wound.
Painful post-operative scars
Sometimes after surgery, sharp, stabbing pains appear in the area of the postoperative scar or near it after healing. The pain should go away over time. What to do? If the pain persists for a long time, it may be necessary to inject special medications into the area of the postoperative scar.
Seroma
Accumulation of serous fluid in the subcutaneous tissue after surgery. This is due to tissue trauma and damage to lymphatic vessels. Unpleasant sensations appear in the area of the wound, the temperature may rise, and by touch you can determine in the area of the postoperative wound, as a rule, a painless or slightly painful formation. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Ultrasound-guided puncture of the lesion or wound revision with drainage.
Hydrocele of the testicle
Hydrocele (hydrocele) is a complication in which fluid accumulates between the membranes of the testicle, which leads to enlargement of the scrotum. More often it happens on one side. What to do? Surgeon's observation. Surgical treatment.
Progressive minimally invasive techniques have made surgery to remove an inguinal hernia and subsequent plastic surgery more reliable and safe. Complications and negative results after such interventions are rare.
What are the consequences of ignoring the problem?
Incarceration (strangulation of the inguinal hernia) is the most dangerous and very common complication of the pathology. The acute period manifests itself in the form of pain in the groin and abdomen, pain in the hernial bulge, vomiting, weakness, chills, constipation, and the inability to straighten the formation. The symptoms are influenced by which organs are pinched in the hernial sac. If it is the colon, then the pain will be more pronounced. When the omentum is pinched, the pain is not so intense, and vomiting may be completely absent.
If the contents of the hernial bulge become infected and become inflamed, then the patient may develop a fever. The skin covering the hernia turns red and becomes hot to the touch. In this case, emergency hospitalization followed by surgery is necessary. If urgent measures are not taken in case of infringement, then necrosis (necrosis) of the organs present in the bulge occurs.
During an emergency operation to treat an inguinal hernia after cutting the hernial growth, the doctor carefully examines the pinched organs, identifying dead areas. These tissues are removed first, and the ring in which the pinching occurred is dissected. After this, the operational process proceeds as usual.
Rehabilitation after surgery for inguinal hernia removal
After surgical intervention in the early postoperative period, the man is in the hospital under the supervision of medical personnel. It is very important to follow the established regime and diet. On the first day after surgery, you should lie down and avoid physical activity to reduce the risk of postoperative complications. Any increase in intra-abdominal pressure is harmful. It is not recommended to eat foods that stimulate peristalsis and gas formation (fruits, sweets, yoghurts and lactic acid products). This needs to be monitored. The postoperative period after modern (minimally invasive) interventions, in most cases, proceeds without complications. A few days after the operation, he was discharged home. Discharge on the day of hernia repair and repair is not always safe and justified. As a rule, it is due to economic benefits for the hospital and for the patient. Meanwhile, transportation home on the day of surgery can be quite difficult and painful. During transportation and the first days at home, self-monitoring and observation of relatives is very important so as not to miss possible complications. It is necessary to monitor the general condition, body temperature, condition of the postoperative wound, appetite, stool and urination. Postoperative wounds usually heal by primary intention. Stitches can be removed on 8-9-10 days. Usually, after discharge you have to remain on sick leave for up to 10 days. Then the sheet closes and you can start working. Depending on the method of surgical intervention, it is recommended to limit physical activity to 4–6 months. After laparoscopic hernia removal, the postoperative and rehabilitation (recovery) periods are easier and more favorable. A month after such an operation, as a rule, you can lead your usual lifestyle.